Abstract
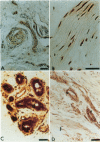
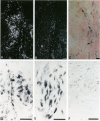
Lesions excised from nine patients undergoing surgery for Dupuytren's contracture (DC) and three normal fascia were examined for the presence of the angiogenic protein basic fibroblast growth factor (basic FGF). Endothelial cell proliferation assays established basic FGF-like activity in extracts of DC. Western blotting confirmed the presence of an 18,000-dalton protein which was localized in the lesions by immunohistochemical staining. All of the cells implicated in the progression of the disease (endothelial cells, fibroblasts, and myofibroblasts) contain the growth factor. Endothelial cells within the narrowed or occluded vessels, as well as fibroblasts surrounding these vessels, stained intensely positive. In situ hybridization using an antisense probe for human basic FGF and its receptor's (FGFR-1) mRNA established the major difference between normal and DC tissues: their levels are significantly higher than in the normal tissues. Thus the cells in DC also express both basic FGF and FGFR-1, suggesting a potential autocrine/paracrine role for basic FGF in the pathogenesis of DC. This finding is thus the first description of a nontumoral proliferative disease that can be directly associated with increased basic FGF mRNA. The possibility that therapies can be developed on the basis that basic FGF and its receptor are expressed in DC is discussed.
Full text
PDF










Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Azzarone B., Failly-Crepin C., Daya-Grosjean L., Chaponnier C., Gabbiani G. Abnormal behavior of cultured fibroblasts from nodule and nonaffected aponeurosis of Dupuytren's disease. J Cell Physiol. 1983 Dec;117(3):353–361. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041170310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bailey A. J., Sims T. J., Gabbiani G., Bazin S., LeLous M. Collagen of Dupuytren's disease. Clin Sci Mol Med. 1977 Nov;53(5):499–502. doi: 10.1042/cs0530499. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baird A., Culler F., Jones K. L., Guillemin R. Angiogenic factor in human ocular fluid. Lancet. 1985 Sep 7;2(8454):563–563. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)90512-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baird A., Esch F., Gospodarowicz D., Guillemin R. Retina- and eye-derived endothelial cell growth factors: partial molecular characterization and identity with acidic and basic fibroblast growth factors. Biochemistry. 1985 Dec 31;24(27):7855–7860. doi: 10.1021/bi00348a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baird A., Esch F., Mormède P., Ueno N., Ling N., Böhlen P., Ying S. Y., Wehrenberg W. B., Guillemin R. Molecular characterization of fibroblast growth factor: distribution and biological activities in various tissues. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1986;42:143–205. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-571142-5.50008-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baird A., Schubert D., Ling N., Guillemin R. Receptor- and heparin-binding domains of basic fibroblast growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(7):2324–2328. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.7.2324. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baird A., Walicke P. A. Fibroblast growth factors. Br Med Bull. 1989 Apr;45(2):438–452. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a072333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess W. H., Maciag T. The heparin-binding (fibroblast) growth factor family of proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:575–606. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.003043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crabb J. W., Armes L. G., Johnson C. M., McKeehan W. L. Characterization of multiple forms of prostatropin (prostate epithelial cell growth factor) from bovine brain. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 May 14;136(3):1155–1161. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)90455-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delli Bovi P., Curatola A. M., Kern F. G., Greco A., Ittmann M., Basilico C. An oncogene isolated by transfection of Kaposi's sarcoma DNA encodes a growth factor that is a member of the FGF family. Cell. 1987 Aug 28;50(5):729–737. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90331-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon M., Deed R., Acland P., Moore R., Whyte A., Peters G., Dickson C. Detection and characterization of the fibroblast growth factor-related oncoprotein INT-2. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;9(11):4896–4902. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.11.4896. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckenstein F. P., Shipley G. D., Nishi R. Acidic and basic fibroblast growth factors in the nervous system: distribution and differential alteration of levels after injury of central versus peripheral nerve. J Neurosci. 1991 Feb;11(2):412–419. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.11-02-00412.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emoto N., Gonzalez A. M., Walicke P. A., Wada E., Simmons D. M., Shimasaki S., Baird A. Basic fibroblast growth factor (FGF) in the central nervous system: identification of specific loci of basic FGF expression in the rat brain. Growth Factors. 1989;2(1):21–29. doi: 10.3109/08977198909069078. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esch F., Baird A., Ling N., Ueno N., Hill F., Denoroy L., Klepper R., Gospodarowicz D., Böhlen P., Guillemin R. Primary structure of bovine pituitary basic fibroblast growth factor (FGF) and comparison with the amino-terminal sequence of bovine brain acidic FGF. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(19):6507–6511. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.19.6507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finch P. W., Rubin J. S., Miki T., Ron D., Aaronson S. A. Human KGF is FGF-related with properties of a paracrine effector of epithelial cell growth. Science. 1989 Aug 18;245(4919):752–755. doi: 10.1126/science.2475908. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finklestein S. P., Apostolides P. J., Caday C. G., Prosser J., Philips M. F., Klagsbrun M. Increased basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF) immunoreactivity at the site of focal brain wounds. Brain Res. 1988 Sep 20;460(2):253–259. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(88)90370-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Florkiewicz R. Z., Sommer A. Human basic fibroblast growth factor gene encodes four polypeptides: three initiate translation from non-AUG codons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jun;86(11):3978–3981. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.11.3978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frautschy S. A., Walicke P. A., Baird A. Localization of basic fibroblast growth factor and its mRNA after CNS injury. Brain Res. 1991 Jul 12;553(2):291–299. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(91)90837-l. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabbiani G., Majno G. Dupuytren's contracture: fibroblast contraction? An ultrastructural study. Am J Pathol. 1972 Jan;66(1):131–146. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez A. M., Buscaglia M., Ong M., Baird A. Distribution of basic fibroblast growth factor in the 18-day rat fetus: localization in the basement membranes of diverse tissues. J Cell Biol. 1990 Mar;110(3):753–765. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.3.753. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gospodarowicz D., Baird A., Cheng J., Lui G. M., Esch F., Bohlen P. Isolation of fibroblast growth factor from bovine adrenal gland: physicochemical and biological characterization. Endocrinology. 1986 Jan;118(1):82–90. doi: 10.1210/endo-118-1-82. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gospodarowicz D., Neufeld G., Schweigerer L. Fibroblast growth factor. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1986 Aug;46(3):187–204. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(86)90001-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hueston J. T., Hurley J. V., Whittingham S. The contracting fibroblast as a clue to Dupuytren's contracture. Hand. 1976 Feb;8(1):10–12. doi: 10.1016/0072-968x(76)90052-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isacchi A., Bergonzoni L., Sarmientos P. Complete sequence of a human receptor for acidic and basic fibroblast growth factors. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Apr 11;18(7):1906–1906. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.7.1906. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jennings A. M., Milner P. C., Ward J. D. Hand abnormalities are associated with the complications of diabetes in type 2 diabetes. Diabet Med. 1989 Jan-Feb;6(1):43–47. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-5491.1989.tb01137.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kischer C. W., Pindur J., Madden J., Shetlar M. R., Shetlar C. L. Characterization of implants from Dupuytren's contracture tissue into the nude (athymic) mouse. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1989 Mar;190(3):268–274. doi: 10.3181/00379727-190-42859. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kischer C. W., Speer D. P. Microvascular changes in Dupuytren's contracture. J Hand Surg Am. 1984 Jan;9A(1):58–62. doi: 10.1016/s0363-5023(84)80185-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krieg P. A., Melton D. A. In vitro RNA synthesis with SP6 RNA polymerase. Methods Enzymol. 1987;155:397–415. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)55027-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lappi D. A., Maher P. A., Martineau D., Baird A. The basic fibroblast growth factor-saporin mitotoxin acts through the basic fibroblast growth factor receptor. J Cell Physiol. 1991 Apr;147(1):17–26. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041470104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lappi D. A., Martineau D., Baird A. Biological and chemical characterization of basic FGF-saporin mitotoxin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Apr 28;160(2):917–923. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)92522-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindner V., Reidy M. A. Proliferation of smooth muscle cells after vascular injury is inhibited by an antibody against basic fibroblast growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 1;88(9):3739–3743. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.9.3739. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACCALLUM P., HUESTON J. T. The pathology of Dupuytren's contracture. Aust N Z J Surg. 1962 May;31:241–253. doi: 10.1111/j.1445-2197.1962.tb03271.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marics I., Adelaide J., Raybaud F., Mattei M. G., Coulier F., Planche J., de Lapeyriere O., Birnbaum D. Characterization of the HST-related FGF.6 gene, a new member of the fibroblast growth factor gene family. Oncogene. 1989 Mar;4(3):335–340. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mignatti P., Tsuboi R., Robbins E., Rifkin D. B. In vitro angiogenesis on the human amniotic membrane: requirement for basic fibroblast growth factor-induced proteinases. J Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;108(2):671–682. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.2.671. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montesano R., Vassalli J. D., Baird A., Guillemin R., Orci L. Basic fibroblast growth factor induces angiogenesis in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(19):7297–7301. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.19.7297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murrell G. A., Hueston J. T. Aetiology of Dupuytren's contracture. Aust N Z J Surg. 1990 Apr;60(4):247–252. doi: 10.1111/j.1445-2197.1990.tb07362.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reilly T. M., Taylor D. S., Herblin W. F., Thoolen M. J., Chiu A. T., Watson D. W., Timmermans P. B. Monoclonal antibodies directed against basic fibroblast growth factor which inhibit its biological activity in vitro and in vivo. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Oct 31;164(2):736–743. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)91521-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruffino C., Berton A., Bonanni F., Maiolino L., Ortino O. Elevata frequenza dell'associazione diabete mellito-malattia di Dupuytren. Minerva Med. 1989 Apr;80(4):371–375. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sano H., Forough R., Maier J. A., Case J. P., Jackson A., Engleka K., Maciag T., Wilder R. L. Detection of high levels of heparin binding growth factor-1 (acidic fibroblast growth factor) in inflammatory arthritic joints. J Cell Biol. 1990 Apr;110(4):1417–1426. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.4.1417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schubert D., Ling N., Baird A. Multiple influences of a heparin-binding growth factor on neuronal development. J Cell Biol. 1987 Mar;104(3):635–643. doi: 10.1083/jcb.104.3.635. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shum D. T., McFarlane R. M. Histogenesis of Dupuytren's disease: an immunohistochemical study of 30 cases. J Hand Surg Am. 1988 Jan;13(1):61–67. doi: 10.1016/0363-5023(88)90202-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson J. A., Haudenschild C. C., Anderson K. D., DiPietro J. M., Anderson W. F., Maciag T. Heparin-binding growth factor 1 induces the formation of organoid neovascular structures in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(20):7928–7932. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.20.7928. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar] [Retracted]
- Vande Berg J. S., Gelberman R. H., Rudolph R., Johnson D., Sicurello P. Dupuytren's disease: comparative growth dynamics and morphology between cultured myofibroblasts (nodule) and fibroblasts (cord). J Orthop Res. 1984;2(3):247–256. doi: 10.1002/jor.1100020305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhan X., Bates B., Hu X. G., Goldfarb M. The human FGF-5 oncogene encodes a novel protein related to fibroblast growth factors. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Aug;8(8):3487–3495. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.8.3487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]