Abstract
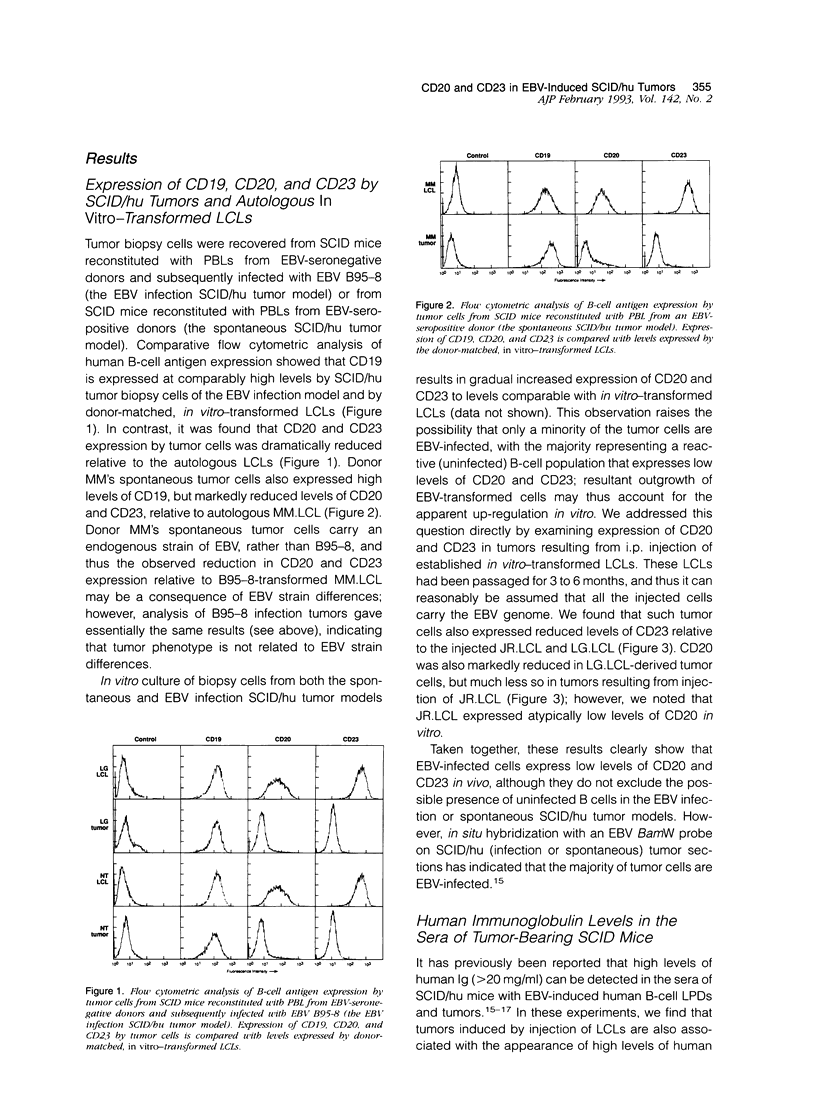
Intraperitoneal injection of immunodeficient C.B.-17/scid (SCID) mice with human peripheral blood leukocytes from Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-seropositive donors or with peripheral blood leukocytes from EBV-seronegative donors followed by an injection of EBV results in the development of human B-cell tumors. EBV-induced oligoclonal SCID/hu tumors closely resemble the EBV-associated lymphoproliferative disorders that are complications in immunosuppressed transplant patients. Previous reports have indicated that SCID/hu tumor cells are phenotypically similar to in vitro-transformed lymphoblastoid cell lines (LCL), which express high levels of mature B-cell lineage/activation antigens (CD19, CD20, CD21, CD23, CD30, CD39). In this study, however, flow cytometric (FACS) analysis showed that expression of CD20 and CD23 by SCID/hu tumor cells was markedly reduced relative to CD20 and CD23 expression by donor-matched, in vitro-transformed LCL. Injection of LCL into SCID mice also produced tumors in which CD20 and CD23 expression was greatly reduced relative to levels expressed by the injected LCL. In addition, tumorigenesis following LCL injection was associated with the production of high levels of human Ig in the sera of SCID mice. Our data thus indicate that EBV-driven tumorigenesis in vivo is associated with significant changes in B-cell phenotype relative to EBV-infected B cells transformed in vitro.
Full text
PDF

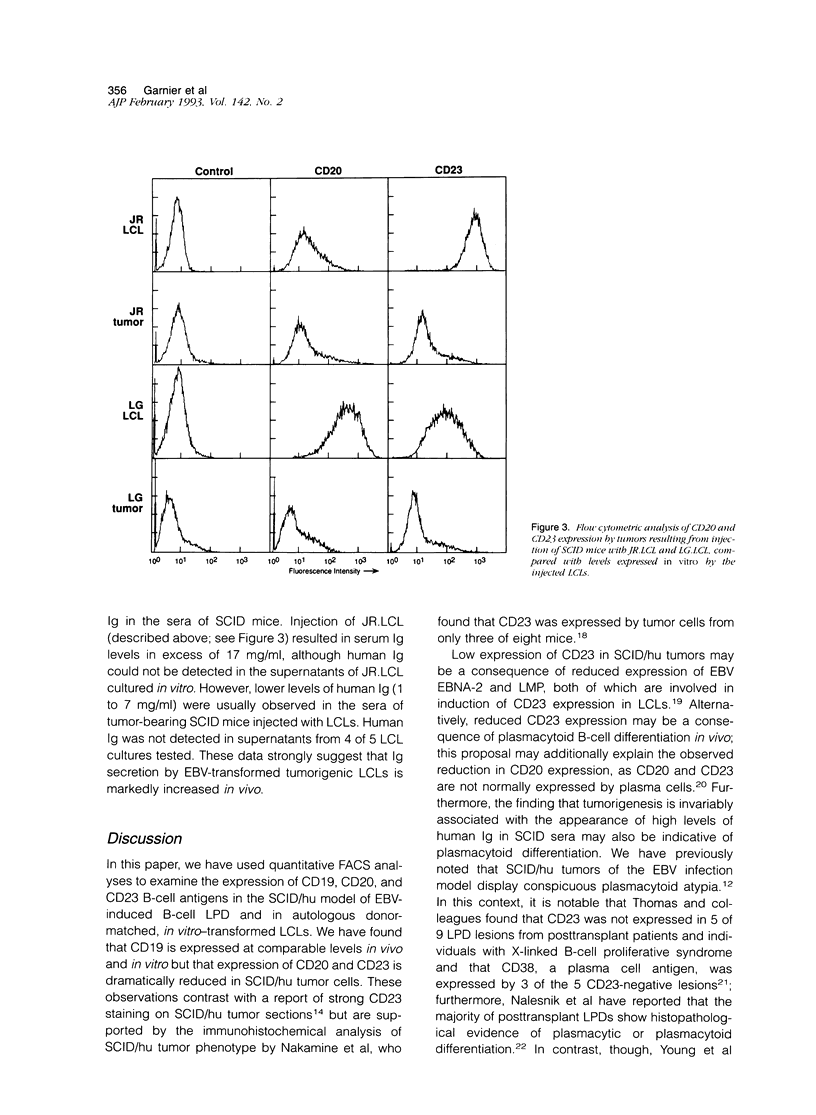


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Billaud M., Calender A., Seigneurin J. M., Lenoir G. M. LFA-1, LFA-3, and ICAM-1 expression in Burkitt's lymphoma. Lancet. 1987 Dec 5;2(8571):1327–1328. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)91214-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cannon M. J., Pisa P., Fox R. I., Cooper N. R. Epstein-Barr virus induces aggressive lymphoproliferative disorders of human B cell origin in SCID/hu chimeric mice. J Clin Invest. 1990 Apr;85(4):1333–1337. doi: 10.1172/JCI114573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregory C. D., Murray R. J., Edwards C. F., Rickinson A. B. Downregulation of cell adhesion molecules LFA-3 and ICAM-1 in Epstein-Barr virus-positive Burkitt's lymphoma underlies tumor cell escape from virus-specific T cell surveillance. J Exp Med. 1988 Jun 1;167(6):1811–1824. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.6.1811. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregory C. D., Tursz T., Edwards C. F., Tetaud C., Talbot M., Caillou B., Rickinson A. B., Lipinski M. Identification of a subset of normal B cells with a Burkitt's lymphoma (BL)-like phenotype. J Immunol. 1987 Jul 1;139(1):313–318. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton-Dutoit S. J., Pallesen G., Franzmann M. B., Karkov J., Black F., Skinhøj P., Pedersen C. AIDS-related lymphoma. Histopathology, immunophenotype, and association with Epstein-Barr virus as demonstrated by in situ nucleic acid hybridization. Am J Pathol. 1991 Jan;138(1):149–163. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanto D. W., Frizzera G., Gajl-Peczalska K. J., Simmons R. L. Epstein-Barr virus, immunodeficiency, and B cell lymphoproliferation. Transplantation. 1985 May;39(5):461–472. doi: 10.1097/00007890-198505000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karp J. E., Broder S. Acquired immunodeficiency syndrome and non-Hodgkin's lymphomas. Cancer Res. 1991 Sep 15;51(18):4743–4756. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore M. D., Cannon M. J., Sewall A., Finlayson M., Okimoto M., Nemerow G. R. Inhibition of Epstein-Barr virus infection in vitro and in vivo by soluble CR2 (CD21) containing two short consensus repeats. J Virol. 1991 Jul;65(7):3559–3565. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.7.3559-3565.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosier D. E., Gulizia R. J., Baird S. M., Wilson D. B. Transfer of a functional human immune system to mice with severe combined immunodeficiency. Nature. 1988 Sep 15;335(6187):256–259. doi: 10.1038/335256a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamine H., Okano M., Taguchi Y., Pirruccello S. J., Davis J. R., Beisel K. W., Kleveland K., Sanger W. G., Fordyce R. R., Purtilo D. T. Hematopathologic features of Epstein-Barr virus-induced human B-lymphoproliferation in mice with severe combined immunodeficiency. A model of lymphoproliferative diseases in immunocompromised patients. Lab Invest. 1991 Oct;65(4):389–399. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nalesnik M. A., Jaffe R., Starzl T. E., Demetris A. J., Porter K., Burnham J. A., Makowka L., Ho M., Locker J. The pathology of posttransplant lymphoproliferative disorders occurring in the setting of cyclosporine A-prednisone immunosuppression. Am J Pathol. 1988 Oct;133(1):173–192. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nalesnik M. A. Lymphoproliferative disease in organ transplant recipients. Springer Semin Immunopathol. 1991;13(2):199–216. doi: 10.1007/BF00201469. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okano M., Taguchi Y., Nakamine H., Pirruccello S. J., Davis J. R., Beisel K. W., Kleveland K. L., Sanger W. G., Fordyce R. R., Purtilo D. T. Characterization of Epstein-Barr virus-induced lymphoproliferation derived from human peripheral blood mononuclear cells transferred to severe combined immunodeficient mice. Am J Pathol. 1990 Sep;137(3):517–522. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pisa P., Cannon M. J., Pisa E. K., Cooper N. R., Fox R. I. Epstein-Barr virus induced lymphoproliferative tumors in severe combined immunodeficient mice are oligoclonal. Blood. 1992 Jan 1;79(1):173–179. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Randhawa P. S., Yousem S. A., Paradis I. L., Dauber J. A., Griffith B. P., Locker J. The clinical spectrum, pathology, and clonal analysis of Epstein-Barr virus-associated lymphoproliferative disorders in heart-lung transplant recipients. Am J Clin Pathol. 1989 Aug;92(2):177–185. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/92.2.177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rooney C. M., Gregory C. D., Rowe M., Finerty S., Edwards C., Rupani H., Rickinson A. B. Endemic Burkitt's lymphoma: phenotypic analysis of tumor biopsy cells and of derived tumor cell lines. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1986 Sep;77(3):681–687. doi: 10.1093/jnci/77.3.681. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe M., Young L. S., Crocker J., Stokes H., Henderson S., Rickinson A. B. Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-associated lymphoproliferative disease in the SCID mouse model: implications for the pathogenesis of EBV-positive lymphomas in man. J Exp Med. 1991 Jan 1;173(1):147–158. doi: 10.1084/jem.173.1.147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas J. A., Hotchin N. A., Allday M. J., Amlot P., Rose M., Yacoub M., Crawford D. H. Immunohistology of Epstein-Barr virus-associated antigens in B cell disorders from immunocompromised individuals. Transplantation. 1990 May;49(5):944–953. doi: 10.1097/00007890-199005000-00022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uckun F. M. Regulation of human B-cell ontogeny. Blood. 1990 Nov 15;76(10):1908–1923. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang F., Gregory C., Sample C., Rowe M., Liebowitz D., Murray R., Rickinson A., Kieff E. Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein (LMP1) and nuclear proteins 2 and 3C are effectors of phenotypic changes in B lymphocytes: EBNA-2 and LMP1 cooperatively induce CD23. J Virol. 1990 May;64(5):2309–2318. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.5.2309-2318.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young L., Alfieri C., Hennessy K., Evans H., O'Hara C., Anderson K. C., Ritz J., Shapiro R. S., Rickinson A., Kieff E. Expression of Epstein-Barr virus transformation-associated genes in tissues of patients with EBV lymphoproliferative disease. N Engl J Med. 1989 Oct 19;321(16):1080–1085. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198910193211604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


