Abstract
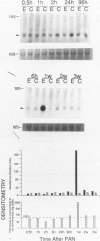
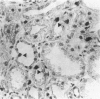
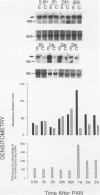
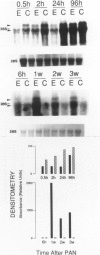
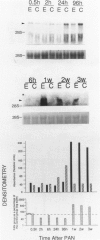
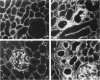
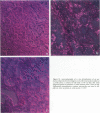
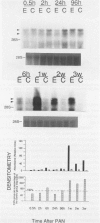
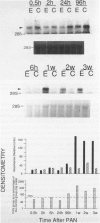
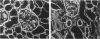
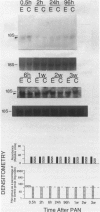
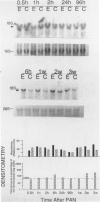
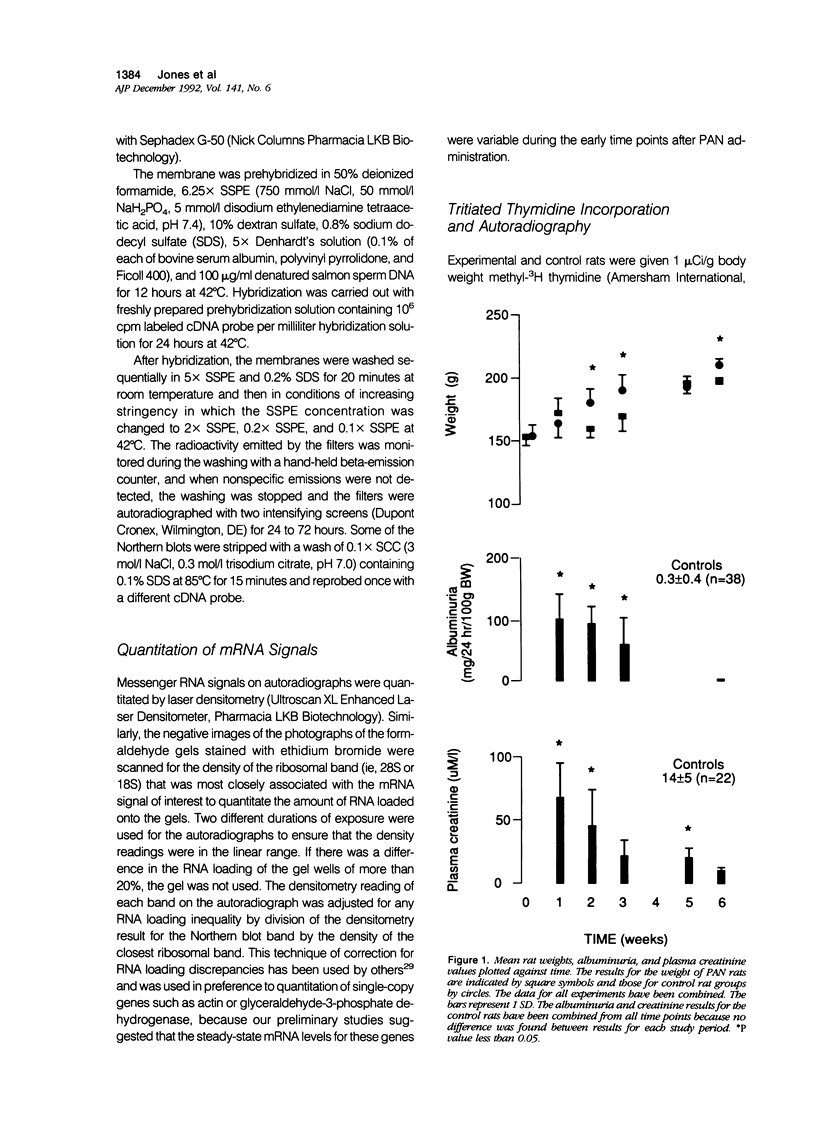
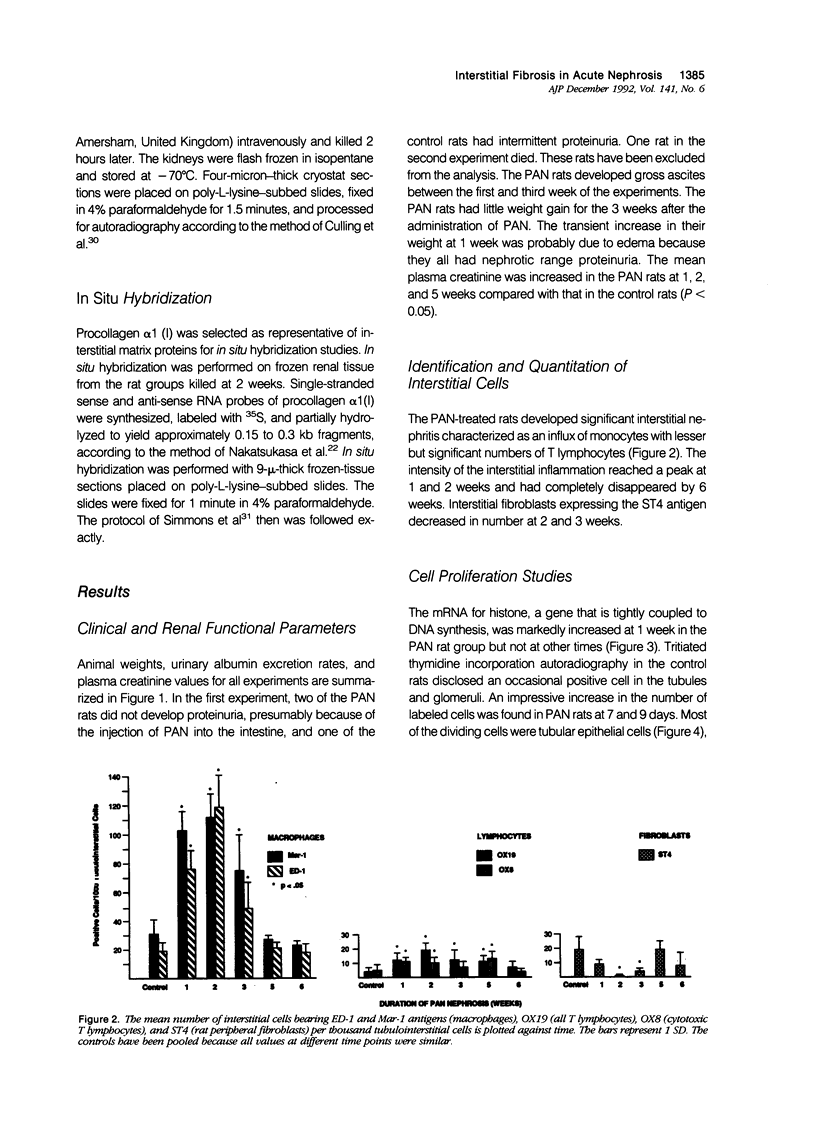
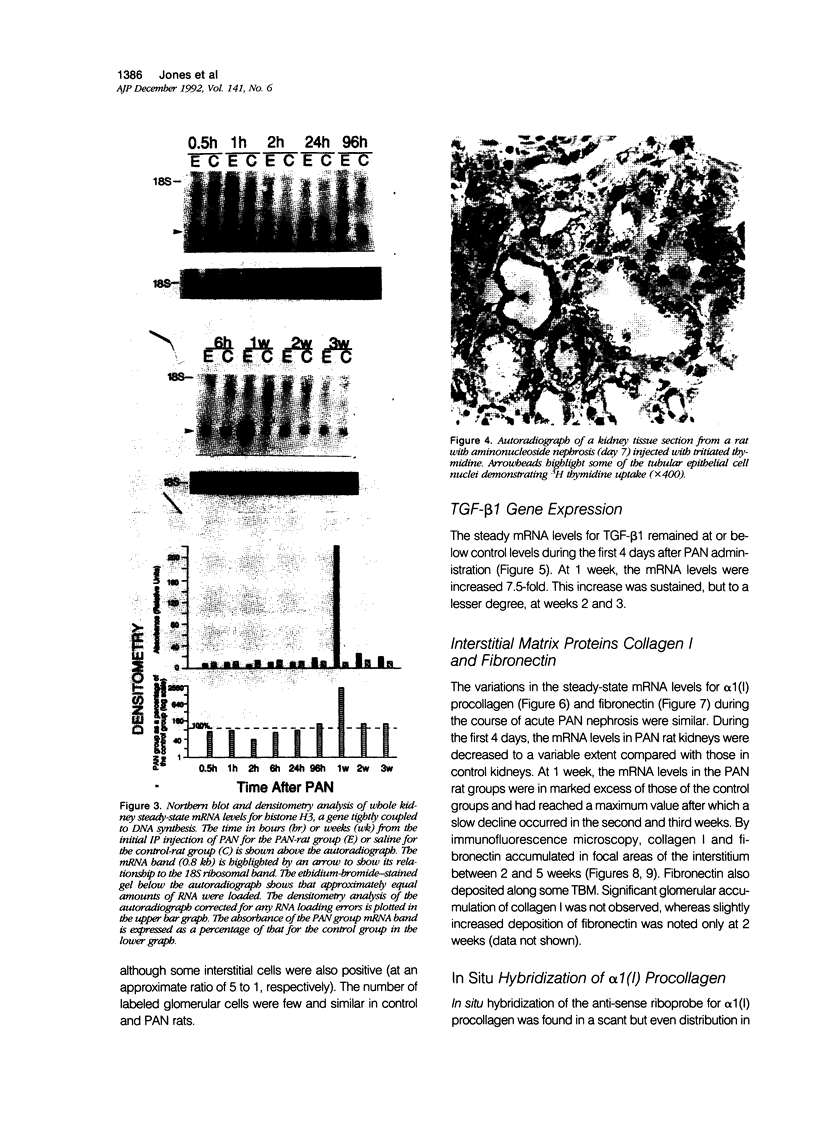
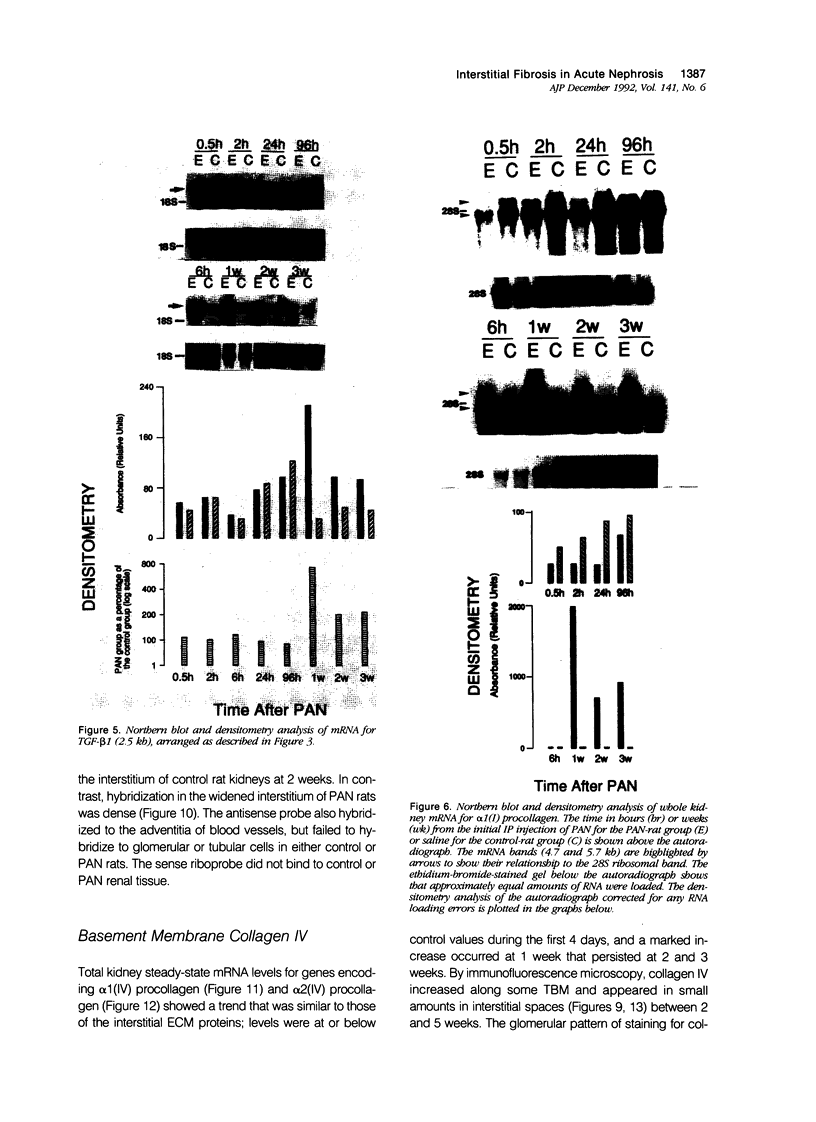
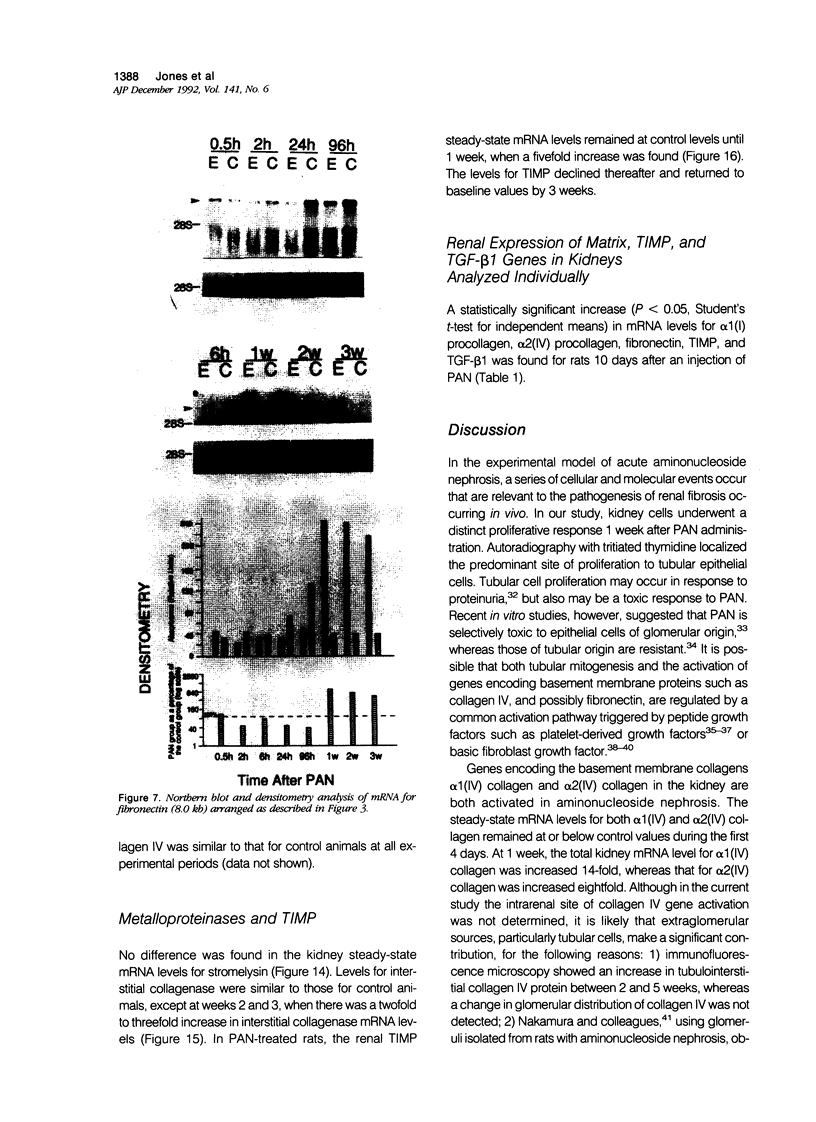
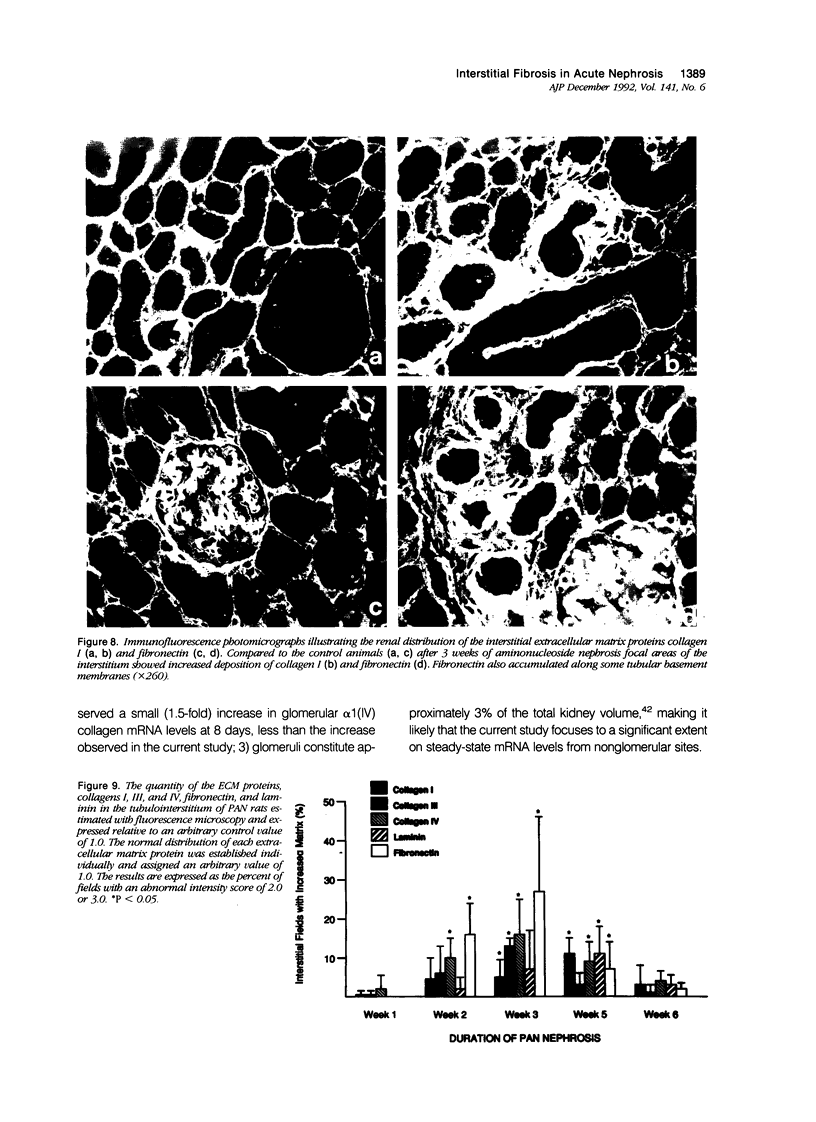
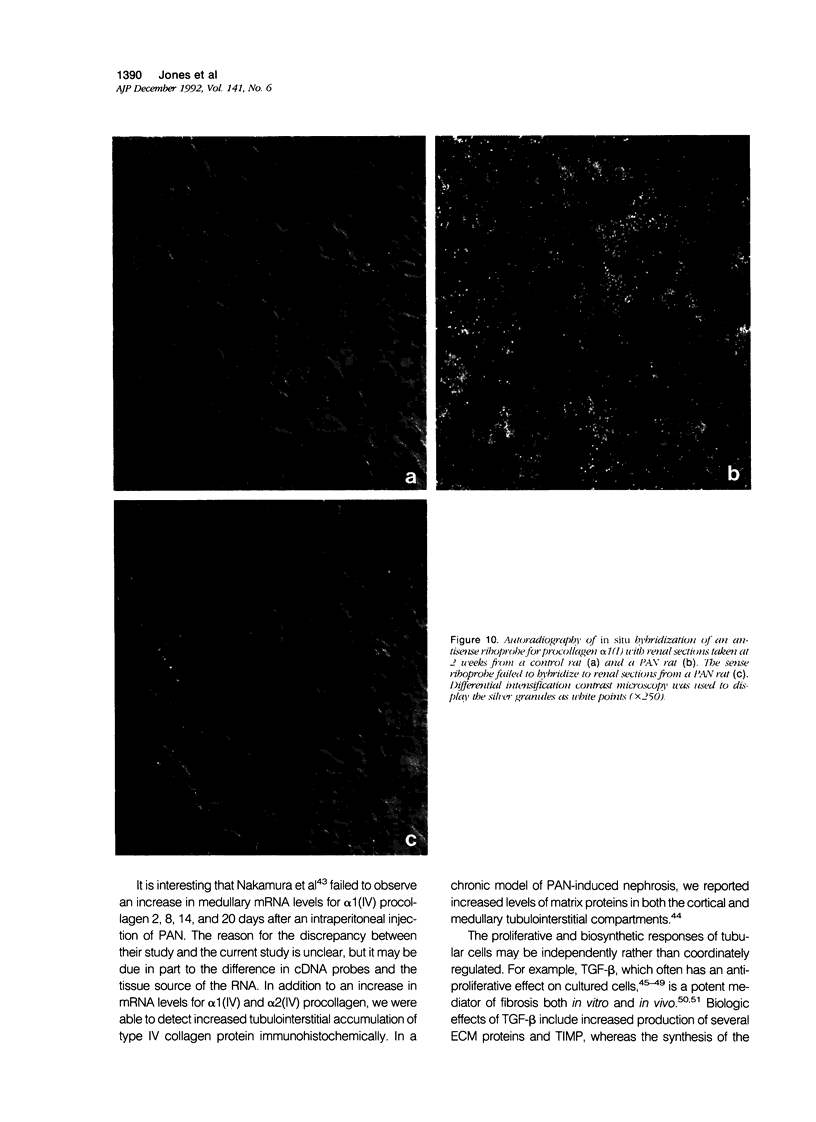
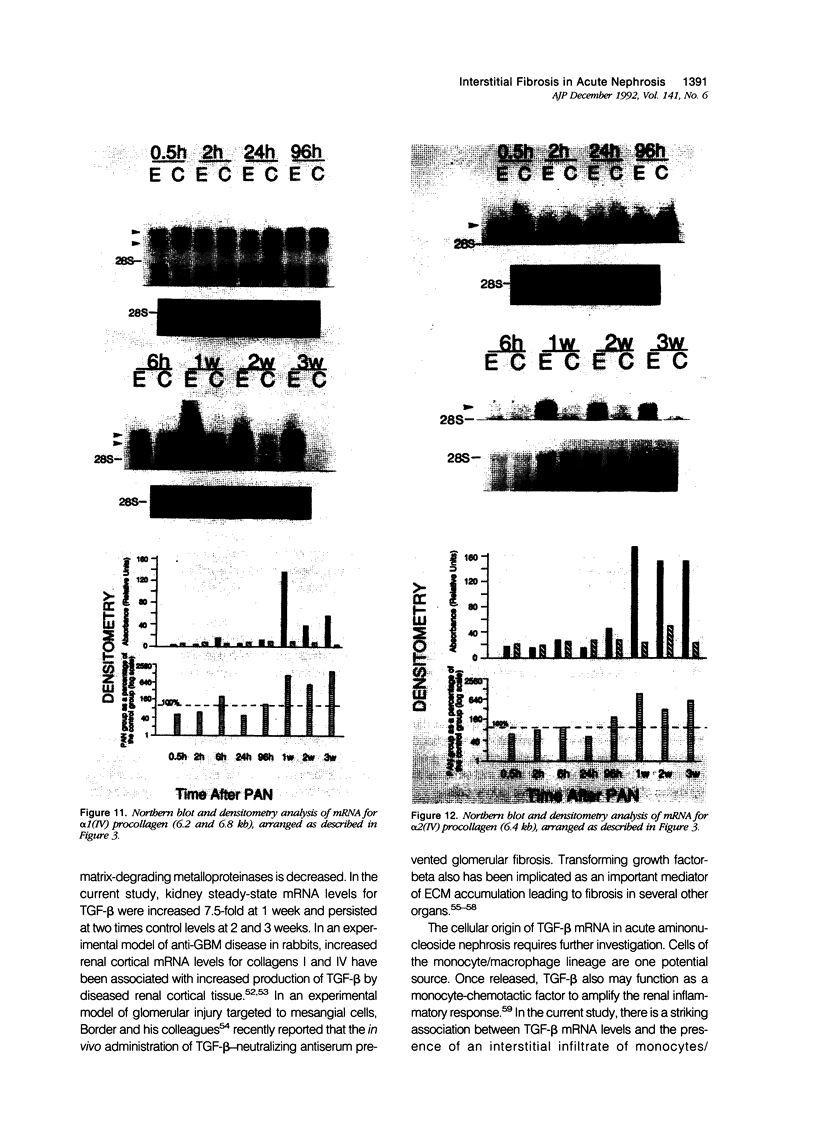
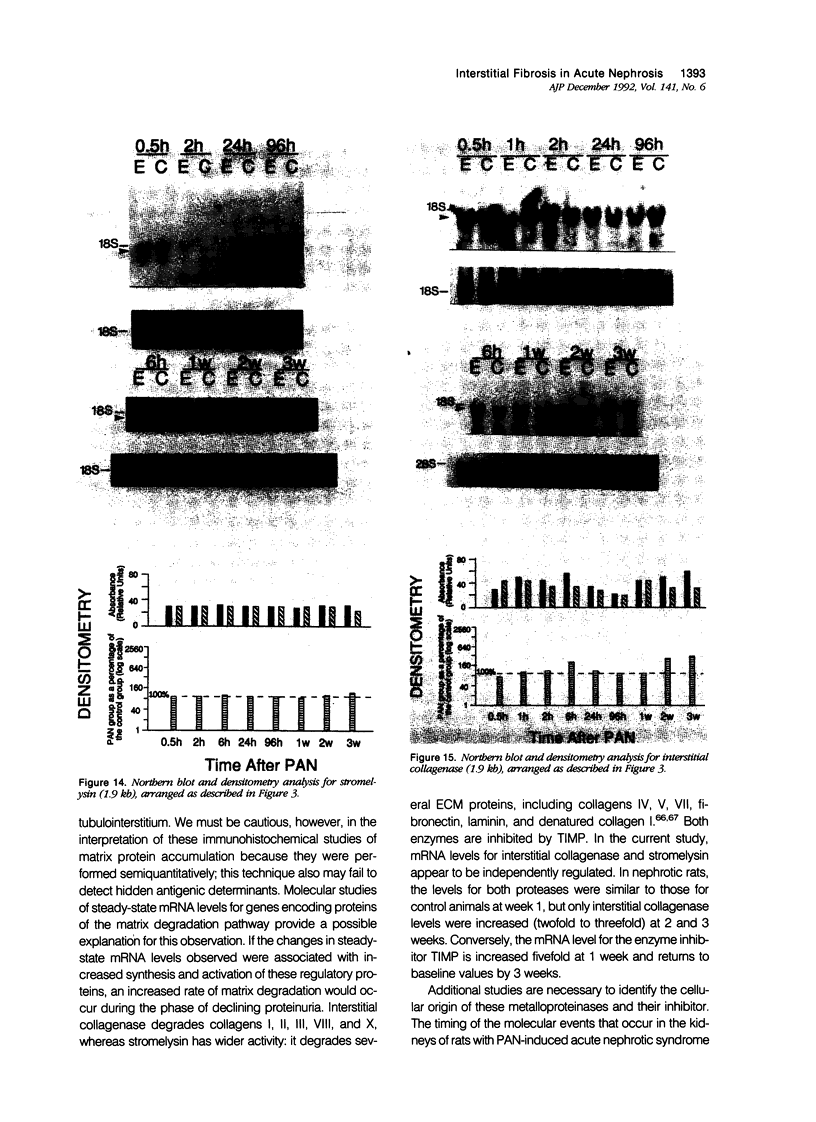
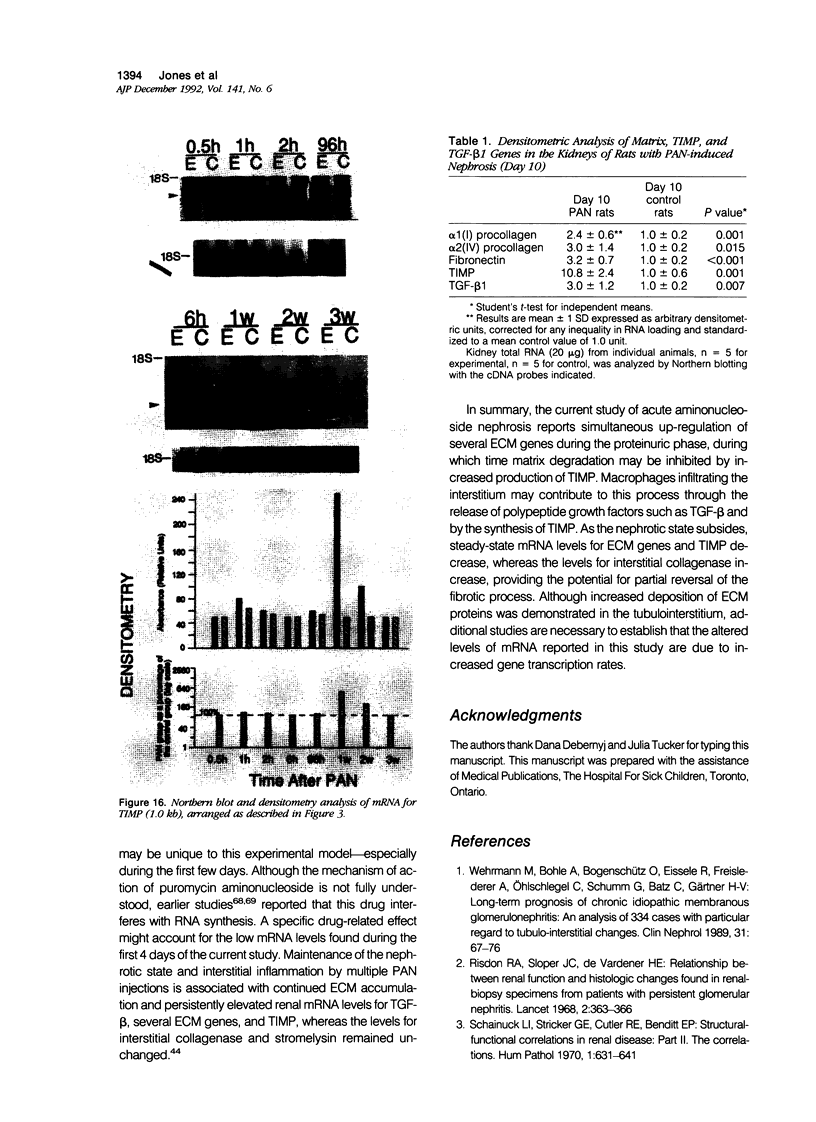
Progressive renal fibrosis is considered to be the final common pathway leading to chronic renal insufficiency. In this study, the authors examined some of the cellular and molecular mechanisms regulating the renal accumulation of extracellular matrix (ECM) proteins using rats with puromycin amino-nucleoside (PAN) nephrosis as an acute model system. Puromycin aminonucleoside rats developed reversible nephrotic syndrome accompanied by an interstitial infiltrate of monocytes. The number of interstitial fibroblasts expressing ST4 antigen did not increase. During the first 4 days, steady-state mRNA levels for all genes examined remained at or below control levels. At 1 week, nephrotic syndrome and interstitial inflammation were established, and a period of renal cell proliferation occurred, identified by increased histone mRNA levels and localized by tritiated thymine autoradiography to tubular epithelial cells and occasional interstitial cells. Transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-beta) steady-state mRNA levels were increased eightfold, but returned to control levels by 3 weeks. At week 1, there was a 10- to 20-fold increase in kidney steady-state mRNA levels for genes encoding interstitial matrix proteins collagen I and fibronectin and basement membrane collagen IV. By in situ hybridization, alpha 1(I) procollagen mRNA was localized to interstitial cells. Immunofluorescence microscopy demonstrated focal accumulation of ECM proteins in the tubulointerstitial compartment at 2 and 3 weeks, but by 6 weeks, kidney immunohistology was normal again. Steady-state mRNA levels for the matrix degrading metalloproteinase stromelysin remained at control values, whereas the levels for interstitial collagenase were normal at week 1 and increased twofold to threefold at 2 and 3 weeks. Steady-state mRNA levels for the tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases (TIMP) increased fivefold at 1 week and returned to baseline values over the next 2 weeks. The results of this study suggest that tubulointerstitial ECM accumulation occurs in rats with acute PAN nephrosis because of the activation of genes encoding several matrix proteins and inhibition of matrix degradation mediated by TIMP. These events are reversed during the phase of recovery from nephrotic syndrome. Increased mRNA levels for TGF-beta, possibly originating from inflammatory interstitial monocytes, are likely to be one of the mediators of the molecular events observed.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Avner E. D. Polypeptide growth factors and the kidney: a developmental perspective. Pediatr Nephrol. 1990 Jul;4(4):345–353. doi: 10.1007/BF00862516. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Border W. A., Okuda S., Languino L. R., Sporn M. B., Ruoslahti E. Suppression of experimental glomerulonephritis by antiserum against transforming growth factor beta 1. Nature. 1990 Jul 26;346(6282):371–374. doi: 10.1038/346371a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brodkin M., Noble B. Antibody-mediated proliferation of proximal tubule cells. Clin Exp Immunol. 1988 Jan;71(1):107–112. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castilla A., Prieto J., Fausto N. Transforming growth factors beta 1 and alpha in chronic liver disease. Effects of interferon alfa therapy. N Engl J Med. 1991 Apr 4;324(14):933–940. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199104043241401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coimbra T., Wiggins R., Noh J. W., Merritt S., Phan S. H. Transforming growth factor-beta production in anti-glomerular basement membrane disease in the rabbit. Am J Pathol. 1991 Jan;138(1):223–234. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connor T. B., Jr, Roberts A. B., Sporn M. B., Danielpour D., Dart L. L., Michels R. G., de Bustros S., Enger C., Kato H., Lansing M. Correlation of fibrosis and transforming growth factor-beta type 2 levels in the eye. J Clin Invest. 1989 May;83(5):1661–1666. doi: 10.1172/JCI114065. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deuel T. F., Kawahara R. S., Mustoe T. A., Pierce A. F. Growth factors and wound healing: platelet-derived growth factor as a model cytokine. Annu Rev Med. 1991;42:567–584. doi: 10.1146/annurev.me.42.020191.003031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond J. R., Anderson S. Irreversible tubulointerstitial damage associated with chronic aminonucleoside nephrosis. Amelioration by angiotensin I converting enzyme inhibition. Am J Pathol. 1990 Dec;137(6):1323–1332. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond J. R., Pesek I., Ruggieri S., Karnovsky M. J. Essential fatty acid deficiency during acute puromycin nephrosis ameliorates late renal injury. Am J Physiol. 1989 Nov;257(5 Pt 2):F798–F807. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1989.257.5.F798. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eddy A. A., McCulloch L., Liu E., Adams J. A relationship between proteinuria and acute tubulointerstitial disease in rats with experimental nephrotic syndrome. Am J Pathol. 1991 May;138(5):1111–1123. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eddy A. A., Michael A. F. Acute tubulointerstitial nephritis associated with aminonucleoside nephrosis. Kidney Int. 1988 Jan;33(1):14–23. doi: 10.1038/ki.1988.3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards D. R., Murphy G., Reynolds J. J., Whitham S. E., Docherty A. J., Angel P., Heath J. K. Transforming growth factor beta modulates the expression of collagenase and metalloproteinase inhibitor. EMBO J. 1987 Jul;6(7):1899–1904. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02449.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabisiak J. P., Evans J. N., Kelley J. Increased expression of PDGF-B (c-sis) mRNA in rat lung precedes DNA synthesis and tissue repair during chronic hyperoxia. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1989 Sep;1(3):181–189. doi: 10.1165/ajrcmb/1.3.181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farnham A. E., Dubin D. T. Studies on the mechanism of action of puromycin aminonucleoside in L cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Mar 29;138(1):35–50. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(67)90583-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fishman J. A., Karnovsky M. J. Effects of the aminonucleoside of puromycin on glomerular epithelial cells in vitro. Am J Pathol. 1985 Mar;118(3):398–407. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frisch S. M., Clark E. J., Werb Z. Coordinate regulation of stromelysin and collagenase genes determined with cDNA probes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(9):2600–2604. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.9.2600. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- González-Avila G., Vadillo-Ortega F., Pérez-Tamayo R. Experimental diffuse interstitial renal fibrosis. A biochemical approach. Lab Invest. 1988 Aug;59(2):245–252. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris K. P., Lefkowith J. B., Klahr S., Schreiner G. F. Essential fatty acid deficiency ameliorates acute renal dysfunction in the rat after the administration of the aminonucleoside of puromycin. J Clin Invest. 1990 Oct;86(4):1115–1123. doi: 10.1172/JCI114816. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heldin C. H., Westermark B. Platelet-derived growth factor: mechanism of action and possible in vivo function. Cell Regul. 1990 Jul;1(8):555–566. doi: 10.1091/mbc.1.8.555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humes H. D., Beals T. F., Cieslinski D. A., Sanchez I. O., Page T. P. Effects of transforming growth factor-beta, transforming growth factor-alpha, and other growth factors on renal proximal tubule cells. Lab Invest. 1991 Apr;64(4):538–545. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ignotz R. A., Massagué J. Transforming growth factor-beta stimulates the expression of fibronectin and collagen and their incorporation into the extracellular matrix. J Biol Chem. 1986 Mar 25;261(9):4337–4345. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaffer F., Saunders C., Shultz P., Throckmorton D., Weinshell E., Abboud H. E. Regulation of mesangial cell growth by polypeptide mitogens. Inhibitory role of transforming growth factor beta. Am J Pathol. 1989 Aug;135(2):261–269. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
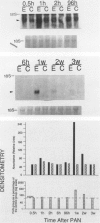
- Jones C. L., Buch S., Post M., McCulloch L., Liu E., Eddy A. A. Pathogenesis of interstitial fibrosis in chronic purine aminonucleoside nephrosis. Kidney Int. 1991 Dec;40(6):1020–1031. doi: 10.1038/ki.1991.310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanda S., Nomata K., Saha P. K., Nishimura N., Yamada J., Kanetake H., Saito Y. A study of growth regulators of renal cortical tubular cells in the rabbit liver. Kidney Int. 1990 Mar;37(3):875–879. doi: 10.1038/ki.1990.61. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khalil N., Bereznay O., Sporn M., Greenberg A. H. Macrophage production of transforming growth factor beta and fibroblast collagen synthesis in chronic pulmonary inflammation. J Exp Med. 1989 Sep 1;170(3):727–737. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.3.727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khokha R., Denhardt D. T. On the use of anti-sense RNA: down-regulation of mRNA encoding a metalloproteinase inhibitor. Anticancer Res. 1987 Jul-Aug;7(4A):653–660. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kujubu D. A., Fine L. G. Physiology and cell biology update: polypeptide growth factors and their relation to renal disease. Am J Kidney Dis. 1989 Jul;14(1):61–73. doi: 10.1016/s0272-6386(89)80096-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuncio G. S., Neilson E. G., Haverty T. Mechanisms of tubulointerstitial fibrosis. Kidney Int. 1991 Mar;39(3):550–556. doi: 10.1038/ki.1991.63. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurkinen M., Bernard M. P., Barlow D. P., Chow L. T. Characterization of 64-, 123- and 182-base-pair exons in the mouse alpha 2(IV) collagen gene. Nature. 1985 Sep 12;317(6033):177–179. doi: 10.1038/317177a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyons R. M., Moses H. L. Transforming growth factors and the regulation of cell proliferation. Eur J Biochem. 1990 Feb 14;187(3):467–473. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb15327.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matrisian L. M. Metalloproteinases and their inhibitors in matrix remodeling. Trends Genet. 1990 Apr;6(4):121–125. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(90)90126-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merritt S. E., Killen P. D., Phan S. H., Wiggins R. C. Analysis of alpha 1 (I) procollagen alpha 1 (IV) collagen, and beta-actin mRNA in glomerulus and cortex of rabbits with experimental anti-glomerular basement membrane disease. Evidence for early extraglomerular collagen biosynthesis. Lab Invest. 1990 Dec;63(6):762–769. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura T., Ebihara I., Fukui M., Tomino Y., Koide H. Effects of methylprednisolone on glomerular and medullary mRNA levels for extracellular matrices in puromycin aminonucleoside nephrosis. Kidney Int. 1991 Nov;40(5):874–881. doi: 10.1038/ki.1991.288. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura T., Ebihara I., Shirato I., Tomino Y., Koide H. Modulation of basement membrane component gene expression in glomeruli of aminonucleoside nephrosis. Lab Invest. 1991 May;64(5):640–647. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakatsukasa H., Nagy P., Evarts R. P., Hsia C. C., Marsden E., Thorgeirsson S. S. Cellular distribution of transforming growth factor-beta 1 and procollagen types I, III, and IV transcripts in carbon tetrachloride-induced rat liver fibrosis. J Clin Invest. 1990 Jun;85(6):1833–1843. doi: 10.1172/JCI114643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakatsukasa H., Nagy P., Evarts R. P., Hsia C. C., Marsden E., Thorgeirsson S. S. Cellular distribution of transforming growth factor-beta 1 and procollagen types I, III, and IV transcripts in carbon tetrachloride-induced rat liver fibrosis. J Clin Invest. 1990 Jun;85(6):1833–1843. doi: 10.1172/JCI114643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan C. F. Secretory products of macrophages. J Clin Invest. 1987 Feb;79(2):319–326. doi: 10.1172/JCI112815. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nevins T. E., Gaston T., Basgen J. M. Quantitative indexes of aminonucleoside-induced nephrotic syndrome. Am J Pathol. 1984 Oct;117(1):30–36. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nugent M. A., Newman M. J. Inhibition of normal rat kidney cell growth by transforming growth factor-beta is mediated by collagen. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 25;264(30):18060–18067. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Postlethwaite A. E., Keski-Oja J., Moses H. L., Kang A. H. Stimulation of the chemotactic migration of human fibroblasts by transforming growth factor beta. J Exp Med. 1987 Jan 1;165(1):251–256. doi: 10.1084/jem.165.1.251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qian S. W., Kondaiah P., Roberts A. B., Sporn M. B. cDNA cloning by PCR of rat transforming growth factor beta-1. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 May 25;18(10):3059–3059. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.10.3059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quaglino D., Jr, Nanney L. B., Kennedy R., Davidson J. M. Transforming growth factor-beta stimulates wound healing and modulates extracellular matrix gene expression in pig skin. I. Excisional wound model. Lab Invest. 1990 Sep;63(3):307–319. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raghow R., Postlethwaite A. E., Keski-Oja J., Moses H. L., Kang A. H. Transforming growth factor-beta increases steady state levels of type I procollagen and fibronectin messenger RNAs posttranscriptionally in cultured human dermal fibroblasts. J Clin Invest. 1987 Apr;79(4):1285–1288. doi: 10.1172/JCI112950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rifkin D. B., Moscatelli D. Recent developments in the cell biology of basic fibroblast growth factor. J Cell Biol. 1989 Jul;109(1):1–6. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Risdon R. A., Sloper J. C., De Wardener H. E. Relationship between renal function and histological changes found in renal-biopsy specimens from patients with persistent glomerular nephritis. Lancet. 1968 Aug 17;2(7564):363–366. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(68)90589-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts A. B., Anzano M. A., Wakefield L. M., Roche N. S., Stern D. F., Sporn M. B. Type beta transforming growth factor: a bifunctional regulator of cellular growth. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(1):119–123. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.1.119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts A. B., Sporn M. B., Assoian R. K., Smith J. M., Roche N. S., Wakefield L. M., Heine U. I., Liotta L. A., Falanga V., Kehrl J. H. Transforming growth factor type beta: rapid induction of fibrosis and angiogenesis in vivo and stimulation of collagen formation in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(12):4167–4171. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.12.4167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schainuck L. I., Striker G. E., Cutler R. E., Benditt E. P. Structural-functional correlations in renal disease. II. The correlations. Hum Pathol. 1970 Dec;1(4):631–641. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(70)80061-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarzbauer J. E., Tamkun J. W., Lemischka I. R., Hynes R. O. Three different fibronectin mRNAs arise by alternative splicing within the coding region. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(2 Pt 1):421–431. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90175-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segal R., Fine L. G. Polypeptide growth factors and the kidney. Kidney Int Suppl. 1989 Nov;27:S2–10. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sierra F., Lichtler A., Marashi F., Rickles R., Van Dyke T., Clark S., Wells J., Stein G., Stein J. Organization of human histone genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Mar;79(6):1795–1799. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.6.1795. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sporn M. B., Roberts A. B., Wakefield L. M., de Crombrugghe B. Some recent advances in the chemistry and biology of transforming growth factor-beta. J Cell Biol. 1987 Sep;105(3):1039–1045. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.3.1039. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinhausen M., Endlich K., Wiegman D. L. Glomerular blood flow. Kidney Int. 1990 Nov;38(5):769–784. doi: 10.1038/ki.1990.271. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan A. K., Claxton D., Shematek G., Wang H. Cellular composition of rat bone marrow stroma. Antigen-defined subpopulations. Lab Invest. 1989 May;60(5):667–676. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas K. A. Fibroblast growth factors. FASEB J. 1987 Dec;1(6):434–440. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.1.6.3315806. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaage J., Lindblad W. J. Production of collagen type I by mouse peritoneal macrophages. J Leukoc Biol. 1990 Sep;48(3):274–280. doi: 10.1002/jlb.48.3.274. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl S. M., Hunt D. A., Wakefield L. M., McCartney-Francis N., Wahl L. M., Roberts A. B., Sporn M. B. Transforming growth factor type beta induces monocyte chemotaxis and growth factor production. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(16):5788–5792. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.16.5788. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl S. M., McCartney-Francis N., Mergenhagen S. E. Inflammatory and immunomodulatory roles of TGF-beta. Immunol Today. 1989 Aug;10(8):258–261. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(89)90136-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wehrmann M., Bohle A., Bogenschütz O., Eissele R., Freislederer A., Ohlschlegel C., Schumm G., Batz C., Gärtner H. V. Long-term prognosis of chronic idiopathic membranous glomerulonephritis. An analysis of 334 cases with particular regard to tubulo-interstitial changes. Clin Nephrol. 1989 Feb;31(2):67–76. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woessner J. F., Jr Matrix metalloproteinases and their inhibitors in connective tissue remodeling. FASEB J. 1991 May;5(8):2145–2154. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamashita A., Hattori Y., Kotani M., Miyasaka M., Fukumoto T. A novel monoclonal antibody, Mar 1, directed specifically against mononuclear phagocyte system cells in rats. Immunology. 1990 Jun;70(2):262–271. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]