Abstract
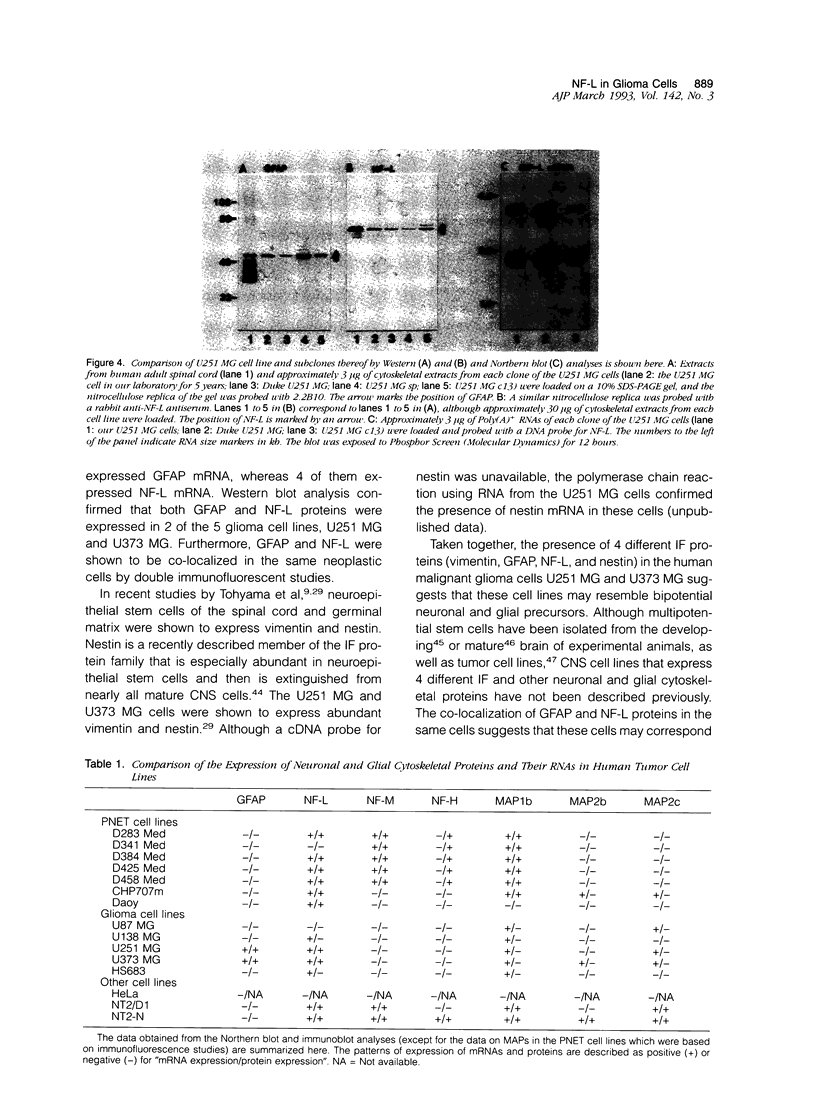
This report describes the expression of glial and neuronal cytoskeletal proteins and their messenger RNAs (mRNAs) in established cell lines derived from human primitive neuroectodermal tumors (PNETs) and malignant gliomas. Northern blot analyses revealed neurofilament (NF) protein mRNAs in 6 of 7 PNET cell lines but no glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) mRNA. Six of these cell lines contained mRNA for the microtubule-associated protein (MAP) known as MAP1b, whereas MAP2 mRNAs were detected only in 1 of the PNET cell lines. These findings closely paralleled previously published data on the expression of these cytoskeletal proteins in the same group of PNET cell lines. Although GFAP mRNA was detected in only 2 of 5 glioma cell lines, 4 of these cell lines contained mRNAs for the low-molecular-weight (M(r)) NF protein (NF-L). Western blot analysis confirmed the expression of both GFAP and NF-L protein in 2 of the glioma cell lines (U251 MG and U373 MG) that contained GFAP and NF-L mRNAs. Further, double immunofluorescence studies showed that GFAP and NF-L co-localized in the same glioma cells. In contrast, neither the middle- (NF-M) or high- (NF-H) M(r) NF proteins or their mRNAs were detected in any of these glioma cell lines. Finally, MAP1b mRNA was expressed in all 5 glioma cell lines, whereas MAP2 mRNAs were detected in only 3 of the cell lines. This is the first documentation of the expression of both glial-specific and neuron-specific cytoskeletal proteins in human malignant glioma-derived cell lines. These data may reflect the aberrant induction of neuron-specific gene products in some neoplastic glial cell lines. Alternatively, our findings may indicate that some glioma cell lines correspond to transformed bipotential human central nervous system precursors of cells restricted to a neuronal or glial lineage.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baker D. L., Reddy U. R., Pleasure S., Hardy M., Williams M., Tartaglione M., Biegel J. A., Emanuel B. S., Lo Presti P., Kreider B. Human central nervous system primitive neuroectodermal tumor expressing nerve growth factor receptors: CHP707m. Ann Neurol. 1990 Aug;28(2):136–145. doi: 10.1002/ana.410280205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bigner D. D., Bigner S. H., Pontén J., Westermark B., Mahaley M. S., Ruoslahti E., Herschman H., Eng L. F., Wikstrand C. J. Heterogeneity of Genotypic and phenotypic characteristics of fifteen permanent cell lines derived from human gliomas. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1981 May;40(3):201–229. doi: 10.1097/00005072-198105000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bilzer T., Stavrou D., Dahme E., Keiditsch E., Bürrig K. F., Anzil A. P., Wechsler W. Morphological, immunocytochemical and growth characteristics of three human glioblastomas established in vitro. Virchows Arch A Pathol Anat Histopathol. 1991;418(4):281–293. doi: 10.1007/BF01600156. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodey B., Cosgrove M., Gonzalez-Gomez I., Siegel S. E., Martin S. E., Gilles F. H. Co-expression of four intermediate filament subclasses in childhood glial neoplasms. Mod Pathol. 1991 Nov;4(6):742–749. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodey B., Zeltzer P. M., Saldivar V., Kemshead J. Immunophenotyping of childhood astrocytomas with a library of monoclonal antibodies. Int J Cancer. 1990 Jun 15;45(6):1079–1087. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910450617. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bongcam-Rudloff E., Nistér M., Betsholtz C., Wang J. L., Stenman G., Huebner K., Croce C. M., Westermark B. Human glial fibrillary acidic protein: complementary DNA cloning, chromosome localization, and messenger RNA expression in human glioma cell lines of various phenotypes. Cancer Res. 1991 Mar 1;51(5):1553–1560. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carden M. J., Trojanowski J. Q., Schlaepfer W. W., Lee V. M. Two-stage expression of neurofilament polypeptides during rat neurogenesis with early establishment of adult phosphorylation patterns. J Neurosci. 1987 Nov;7(11):3489–3504. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.07-11-03489.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charrière-Bertrand C., Garner C., Tardy M., Nunez J. Expression of various microtubule-associated protein 2 forms in the developing mouse brain and in cultured neurons and astrocytes. J Neurochem. 1991 Feb;56(2):385–391. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1991.tb08163.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cruz-Sánchez F. F., Rossi M. L., Hughes J. T., Moss T. H. Differentiation in embryonal neuroepithelial tumors of the central nervous system. Cancer. 1991 Feb 15;67(4):965–976. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19910215)67:4<965::aid-cncr2820670419>3.0.co;2-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Debus E., Weber K., Osborn M. Monoclonal antibodies specific for glial fibrillary acidic (GFA) protein and for each of the neurofilament triplet polypeptides. Differentiation. 1983;25(2):193–203. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.1984.tb01355.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Escurat M., Djabali K., Huc C., Landon F., Bécourt C., Boitard C., Gros F., Portier M. M. Origin of the beta cells of the islets of Langerhans is further questioned by the expression of neuronal intermediate filament proteins, peripherin and NF-L, in the rat insulinoma RIN5F cell line. Dev Neurosci. 1991;13(6):424–432. doi: 10.1159/000112194. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frederiksen K., Jat P. S., Valtz N., Levy D., McKay R. Immortalization of precursor cells from the mammalian CNS. Neuron. 1988 Aug;1(6):439–448. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(88)90175-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman H. S., Burger P. C., Bigner S. H., Trojanowski J. Q., Brodeur G. M., He X. M., Wikstrand C. J., Kurtzberg J., Berens M. E., Halperin E. C. Phenotypic and genotypic analysis of a human medulloblastoma cell line and transplantable xenograft (D341 Med) demonstrating amplification of c-myc. Am J Pathol. 1988 Mar;130(3):472–484. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman H. S., Burger P. C., Bigner S. H., Trojanowski J. Q., Wikstrand C. J., Halperin E. C., Bigner D. D. Establishment and characterization of the human medulloblastoma cell line and transplantable xenograft D283 Med. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1985 Nov;44(6):592–605. doi: 10.1097/00005072-198511000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fults D., Pedone C. A., Morse H. G., Rose J. W., McKay R. D. Establishment and characterization of a human primitive neuroectodermal tumor cell line from the cerebral hemisphere. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1992 May;51(3):272–280. doi: 10.1097/00005072-199205000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garner C. C., Brugg B., Matus A. A 70-kilodalton microtubule-associated protein (MAP2c), related to MAP2. J Neurochem. 1988 Feb;50(2):609–615. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1988.tb02954.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geisert E. E., Jr, Johnson H. G., Binder L. I. Expression of microtubule-associated protein 2 by reactive astrocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 May;87(10):3967–3971. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.10.3967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gould V. E., Jansson D. S., Molenaar W. M., Rorke L. B., Trojanowski J. Q., Lee V. M., Packer R. J., Franke W. W. Primitive neuroectodermal tumors of the central nervous system. Patterns of expression of neuroendocrine markers, and all classes of intermediate filament proteins. Lab Invest. 1990 Apr;62(4):498–509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gould V. E., Rorke L. B., Jansson D. S., Molenaar W. M., Trojanowski J. Q., Lee V. M., Packer R. J., Franke W. W. Primitive neuroectodermal tumors of the central nervous system express neuroendocrine markers and may express all classes of intermediate filaments. Hum Pathol. 1990 Mar;21(3):245–252. doi: 10.1016/0046-8177(90)90223-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- He X. M., Skapek S. X., Wikstrand C. J., Friedman H. S., Trojanowski J. Q., Kemshead J. T., Coakham H. B., Bigner S. H., Bigner D. D. Phenotypic analysis of four human medulloblastoma cell lines and transplantable xenografts. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1989 Jan;48(1):48–68. doi: 10.1097/00005072-198901000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- He X. M., Wikstrand C. J., Friedman H. S., Bigner S. H., Pleasure S., Trojanowski J. Q., Bigner D. D. Differentiation characteristics of newly established medulloblastoma cell lines (D384 Med, D425 Med, and D458 Med) and their transplantable xenografts. Lab Invest. 1991 Jun;64(6):833–843. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobsen P. F., Jenkyn D. J., Papadimitriou J. M. Establishment of a human medulloblastoma cell line and its heterotransplantation into nude mice. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1985 Sep;44(5):472–485. doi: 10.1097/00005072-198509000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones-Villeneuve E. M., McBurney M. W., Rogers K. A., Kalnins V. I. Retinoic acid induces embryonal carcinoma cells to differentiate into neurons and glial cells. J Cell Biol. 1982 Aug;94(2):253–262. doi: 10.1083/jcb.94.2.253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly B. M., Gillespie C. S., Sherman D. L., Brophy P. J. Schwann cells of the myelin-forming phenotype express neurofilament protein NF-M. J Cell Biol. 1992 Jul;118(2):397–410. doi: 10.1083/jcb.118.2.397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleinert R. Immunohistochemical characterization of primitive neuroectodermal tumors and their possible relationship to the stepwise ontogenetic development of the central nervous system. 1. Ontogenetic studies. Acta Neuropathol. 1991;82(6):502–507. doi: 10.1007/BF00293385. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleinert R. Immunohistochemical characterization of primitive neuroectodermal tumors and their possible relationship to the stepwise ontogenetic development of the central nervous system. 2. Tumor studies. Acta Neuropathol. 1991;82(6):508–515. doi: 10.1007/BF00293386. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaRocca R. V., Rosenblum M., Westermark B., Israel M. A. Patterns of proto-oncogene expression in human glioma cell lines. J Neurosci Res. 1989 Sep;24(1):97–106. doi: 10.1002/jnr.490240114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee V. M., Carden M. J., Schlaepfer W. W., Trojanowski J. Q. Monoclonal antibodies distinguish several differentially phosphorylated states of the two largest rat neurofilament subunits (NF-H and NF-M) and demonstrate their existence in the normal nervous system of adult rats. J Neurosci. 1987 Nov;7(11):3474–3488. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.07-11-03474.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee V. M., Page C. D., Wu H. L., Schlaepfer W. W. Monoclonal antibodies to gel-excised glial filament protein and their reactivities with other intermediate filament proteins. J Neurochem. 1984 Jan;42(1):25–32. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1984.tb09692.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lendahl U., Zimmerman L. B., McKay R. D. CNS stem cells express a new class of intermediate filament protein. Cell. 1990 Feb 23;60(4):585–595. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90662-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis S. A., Balcarek J. M., Krek V., Shelanski M., Cowan N. J. Sequence of a cDNA clone encoding mouse glial fibrillary acidic protein: structural conservation of intermediate filaments. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(9):2743–2746. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.9.2743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis S. A., Wang D. H., Cowan N. J. Microtubule-associated protein MAP2 shares a microtubule binding motif with tau protein. Science. 1988 Nov 11;242(4880):936–939. doi: 10.1126/science.3142041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mark J., Westermark B., Pontén J., Hugosson R. Banding patterns in human glioma cell lines. Hereditas. 1977;87(2):243–260. doi: 10.1111/j.1601-5223.1978.tb01267.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matus A. Microtubule-associated proteins: their potential role in determining neuronal morphology. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1988;11:29–44. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.11.030188.000333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molenaar W. M., Jansson D. S., Gould V. E., Rorke L. B., Franke W. W., Lee V. M., Packer R. J., Trojanowski J. Q. Molecular markers of primitive neuroectodermal tumors and other pediatric central nervous system tumors. Monoclonal antibodies to neuronal and glial antigens distinguish subsets of primitive neuroectodermal tumors. Lab Invest. 1989 Dec;61(6):635–643. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers M. W., Lazzarini R. A., Lee V. M., Schlaepfer W. W., Nelson D. L. The human mid-size neurofilament subunit: a repeated protein sequence and the relationship of its gene to the intermediate filament gene family. EMBO J. 1987 Jun;6(6):1617–1626. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02409.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noble M., Lewis S. A., Cowan N. J. The microtubule binding domain of microtubule-associated protein MAP1B contains a repeated sequence motif unrelated to that of MAP2 and tau. J Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;109(6 Pt 2):3367–3376. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.6.3367. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papandrikopoulou A., Doll T., Tucker R. P., Garner C. C., Matus A. Embryonic MAP2 lacks the cross-linking sidearm sequences and dendritic targeting signal of adult MAP2. Nature. 1989 Aug 24;340(6235):650–652. doi: 10.1038/340650a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pleasure S. J., Lee V. M., Nelson D. L. Site-specific phosphorylation of the middle molecular weight human neurofilament protein in transfected non-neuronal cells. J Neurosci. 1990 Jul;10(7):2428–2437. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.10-07-02428.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pleasure S. J., Page C., Lee V. M. Pure, postmitotic, polarized human neurons derived from NTera 2 cells provide a system for expressing exogenous proteins in terminally differentiated neurons. J Neurosci. 1992 May;12(5):1802–1815. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.12-05-01802.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeves S. A., Helman L. J., Allison A., Israel M. A. Molecular cloning and primary structure of human glial fibrillary acidic protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(13):5178–5182. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.13.5178. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds B. A., Weiss S. Generation of neurons and astrocytes from isolated cells of the adult mammalian central nervous system. Science. 1992 Mar 27;255(5052):1707–1710. doi: 10.1126/science.1553558. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riederer B., Cohen R., Matus A. MAP5: a novel brain microtubule-associated protein under strong developmental regulation. J Neurocytol. 1986 Dec;15(6):763–775. doi: 10.1007/BF01625193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rorke L. B., Gilles F. H., Davis R. L., Becker L. E. Revision of the World Health Organization classification of brain tumors for childhood brain tumors. Cancer. 1985 Oct 1;56(7 Suppl):1869–1886. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19851001)56:7+<1869::aid-cncr2820561330>3.0.co;2-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rorke L. B. The cerebellar medulloblastoma and its relationship to primitive neuroectodermal tumors. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1983 Jan;42(1):1–15. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rutka J. T., Giblin J. R., Dougherty D. Y., Liu H. C., McCulloch J. R., Bell C. W., Stern R. S., Wilson C. B., Rosenblum M. L. Establishment and characterization of five cell lines derived from human malignant gliomas. Acta Neuropathol. 1987;75(1):92–103. doi: 10.1007/BF00686798. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shneidman P. S., Carden M. J., Lees J. F., Lazzarini R. A. The structure of the largest murine neurofilament protein (NF-H) as revealed by cDNA and genomic sequences. Brain Res. 1988 Nov;464(3):217–231. doi: 10.1016/0169-328x(88)90028-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinert P. M., Liem R. K. Intermediate filament dynamics. Cell. 1990 Feb 23;60(4):521–523. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90651-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamura K., Shimizu K., Yamada M., Okamoto Y., Matsui Y., Park K. C., Mabuchi E., Moriuchi S., Mogami H. Expression of major histocompatibility complex on human medulloblastoma cells with neuronal differentiation. Cancer Res. 1989 Oct 1;49(19):5380–5384. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tohyama T., Lee V. M., Rorke L. B., Marvin M., McKay R. D., Trojanowski J. Q. Nestin expression in embryonic human neuroepithelium and in human neuroepithelial tumor cells. Lab Invest. 1992 Mar;66(3):303–313. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trojanowski J. Q., Friedman H. S., Burger P. C., Bigner D. D. A rapidly dividing human medulloblastoma cell line (D283 MED) expresses all three neurofilament subunits. Am J Pathol. 1987 Feb;126(2):358–363. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trojanowski J. Q., Kelsten M. L., Lee V. M. Phosphate-dependent and independent neurofilament protein epitopes are expressed throughout the cell cycle in human medulloblastoma (D283 MED) cells. Am J Pathol. 1989 Oct;135(4):747–758. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trojanowski J. Q., Tohyama T., Lee V. M. Medulloblastomas and related primitive neuroectodermal brain tumors of childhood recapitulate molecular milestones in the maturation of neuroblasts. Mol Chem Neuropathol. 1992 Oct;17(2):121–135. doi: 10.1007/BF03159987. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tucker R. P., Binder L. I., Viereck C., Hemmings B. A., Matus A. I. The sequential appearance of low- and high-molecular-weight forms of MAP2 in the developing cerebellum. J Neurosci. 1988 Dec;8(12):4503–4512. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.08-12-04503.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tucker R. P. The roles of microtubule-associated proteins in brain morphogenesis: a review. Brain Res Brain Res Rev. 1990 May-Aug;15(2):101–120. doi: 10.1016/0165-0173(90)90013-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westphal M., Nausch H., Herrmann H. D. Antigenic staining patterns of human glioma cultures: primary cultures, long-term cultures and cell lines. J Neurocytol. 1990 Aug;19(4):466–477. doi: 10.1007/BF01257237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiche G., Oberkanins C., Himmler A. Molecular structure and function of microtubule-associated proteins. Int Rev Cytol. 1991;124:217–273. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)61528-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]