Abstract
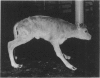
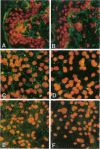
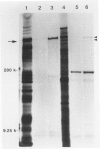
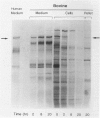
Bovine Marfan syndrome is a disorder that closely resembles human Marfan syndrome in its clinical signs and pathological lesions. The similarities between the human and bovine diseases suggest that similar metabolic defects could be responsible. Although indirect immunofluorescent assays for fibrillin in skin biopsies did not distinguish affected cattle from control animals, cultures of skin fibroblasts of affected animals were distinguished from normal, unrelated control animals and normal half-siblings on the basis of fibrillin staining. After 72 to 96 hours in culture, stained with anti-fibrillin monoclonal antibody 201, hyperconfluent fibroblast cultures of affected cattle had less immunoreactive fibrillin than control cultures, and the staining pattern was granular rather than fibrillar. Under similar culture conditions, normal bovine aortic smooth muscle cells produced large amounts of immunoreactive fibrillin, but smooth muscle cells from a single affected cow showed markedly less fibrillin staining. In pulse-chase metabolic labeling experiments with [35S]cysteine, dermal fibroblasts from 6 affected calves, incorporated far less fibrillin into the extracellular matrix than control cells. These findings are similar to those reported in human Marfan syndrome, and they suggest that the bovine Marfan syndrome, like the human disorder, is caused by a mutation in fibrillin, leading to defective microfibrillar synthesis.
Full text
PDF


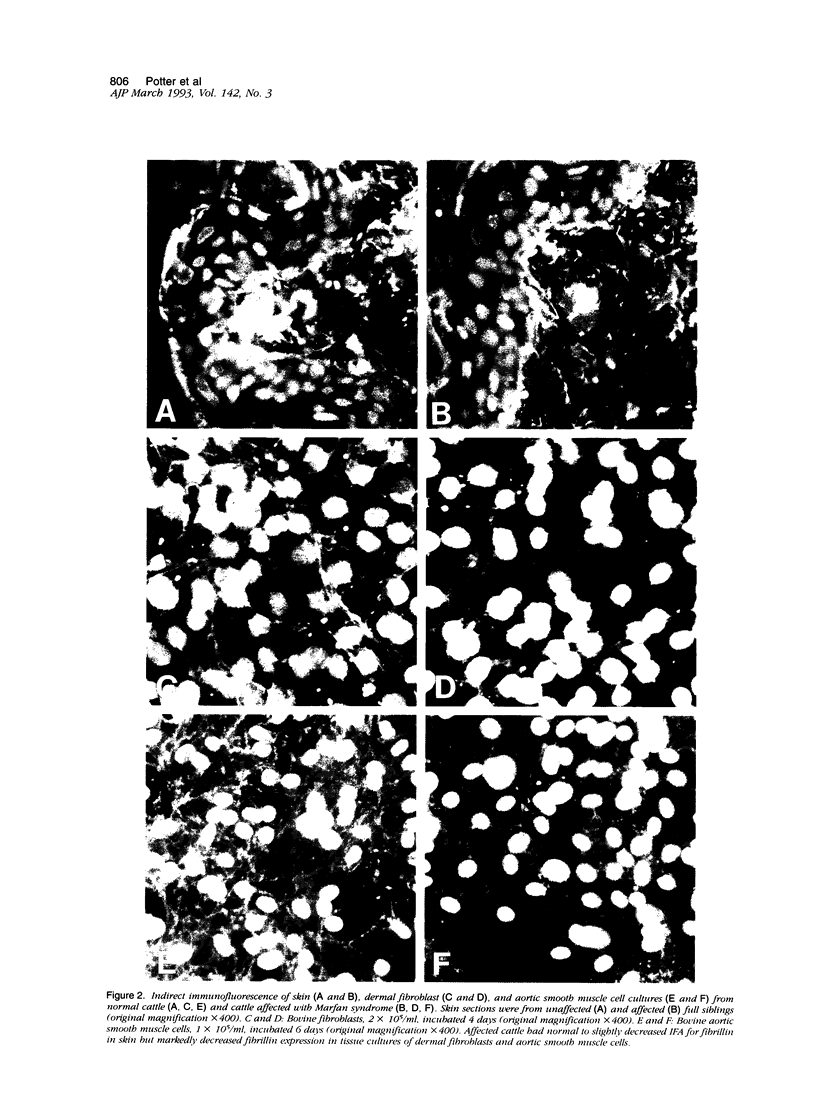
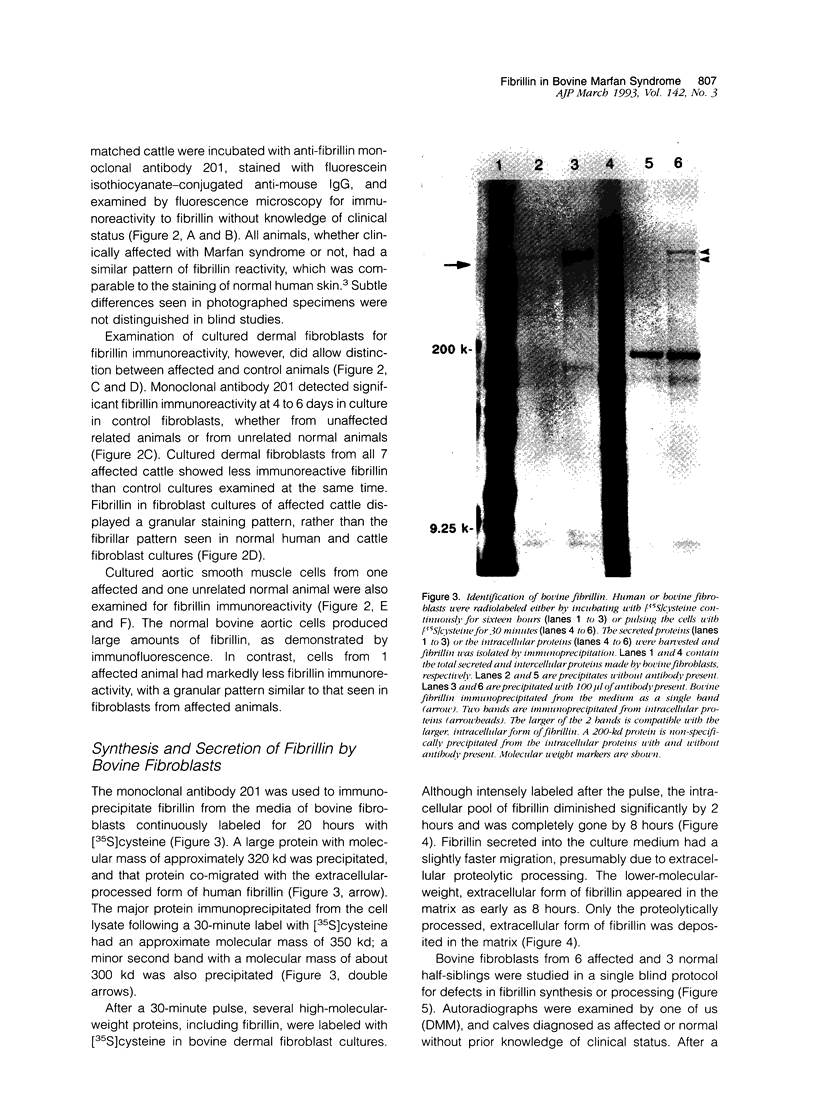
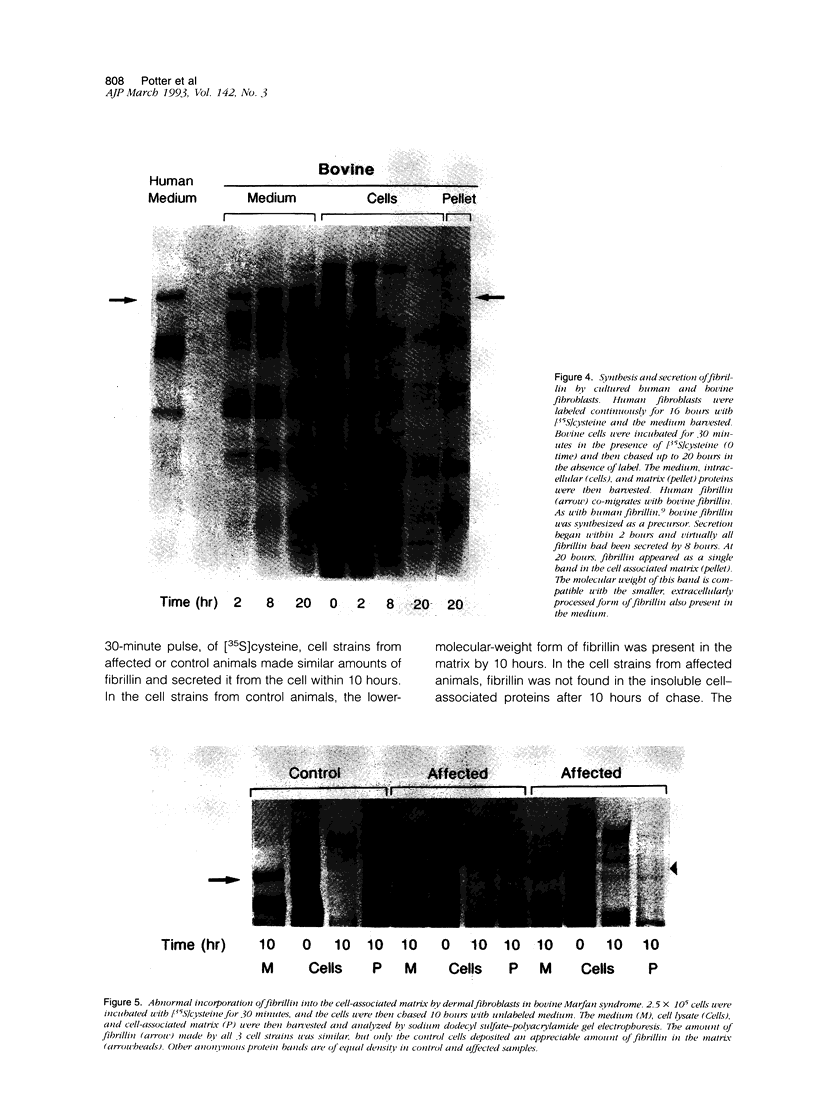


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beighton P., de Paepe A., Danks D., Finidori G., Gedde-Dahl T., Goodman R., Hall J. G., Hollister D. W., Horton W., McKusick V. A. International Nosology of Heritable Disorders of Connective Tissue, Berlin, 1986. Am J Med Genet. 1988 Mar;29(3):581–594. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320290316. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Besser T. E., Potter K. A., Bryan G. M., Knowlen G. G. An animal model of the Marfan syndrome. Am J Med Genet. 1990 Sep;37(1):159–165. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320370137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dietz H. C., Cutting G. R., Pyeritz R. E., Maslen C. L., Sakai L. Y., Corson G. M., Puffenberger E. G., Hamosh A., Nanthakumar E. J., Curristin S. M. Marfan syndrome caused by a recurrent de novo missense mutation in the fibrillin gene. Nature. 1991 Jul 25;352(6333):337–339. doi: 10.1038/352337a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godfrey M., Menashe V., Weleber R. G., Koler R. D., Bigley R. H., Lovrien E., Zonana J., Hollister D. W. Cosegregation of elastin-associated microfibrillar abnormalities with the Marfan phenotype in families. Am J Hum Genet. 1990 Apr;46(4):652–660. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollister D. W., Godfrey M., Sakai L. Y., Pyeritz R. E. Immunohistologic abnormalities of the microfibrillar-fiber system in the Marfan syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1990 Jul 19;323(3):152–159. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199007193230303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kainulainen K., Pulkkinen L., Savolainen A., Kaitila I., Peltonen L. Location on chromosome 15 of the gene defect causing Marfan syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1990 Oct 4;323(14):935–939. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199010043231402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee B., Godfrey M., Vitale E., Hori H., Mattei M. G., Sarfarazi M., Tsipouras P., Ramirez F., Hollister D. W. Linkage of Marfan syndrome and a phenotypically related disorder to two different fibrillin genes. Nature. 1991 Jul 25;352(6333):330–334. doi: 10.1038/352330a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magenis R. E., Maslen C. L., Smith L., Allen L., Sakai L. Y. Localization of the fibrillin (FBN) gene to chromosome 15, band q21.1. Genomics. 1991 Oct;11(2):346–351. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(91)90142-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maslen C. L., Corson G. M., Maddox B. K., Glanville R. W., Sakai L. Y. Partial sequence of a candidate gene for the Marfan syndrome. Nature. 1991 Jul 25;352(6333):334–337. doi: 10.1038/352334a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milewicz D. M., Pyeritz R. E., Crawford E. S., Byers P. H. Marfan syndrome: defective synthesis, secretion, and extracellular matrix formation of fibrillin by cultured dermal fibroblasts. J Clin Invest. 1992 Jan;89(1):79–86. doi: 10.1172/JCI115589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penner J. D., Prieur D. J. A comparative study of the lesions in cultured fibroblasts of humans and four species of animals with Chediak-Higashi syndrome. Am J Med Genet. 1987 Oct;28(2):445–454. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320280222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pyeritz R. E., McKusick V. A. The Marfan syndrome: diagnosis and management. N Engl J Med. 1979 Apr 5;300(14):772–777. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197904053001406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakai L. Y., Keene D. R., Engvall E. Fibrillin, a new 350-kD glycoprotein, is a component of extracellular microfibrils. J Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;103(6 Pt 1):2499–2509. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.6.2499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]