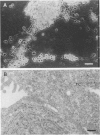
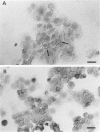
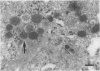
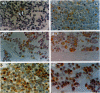
Abstract
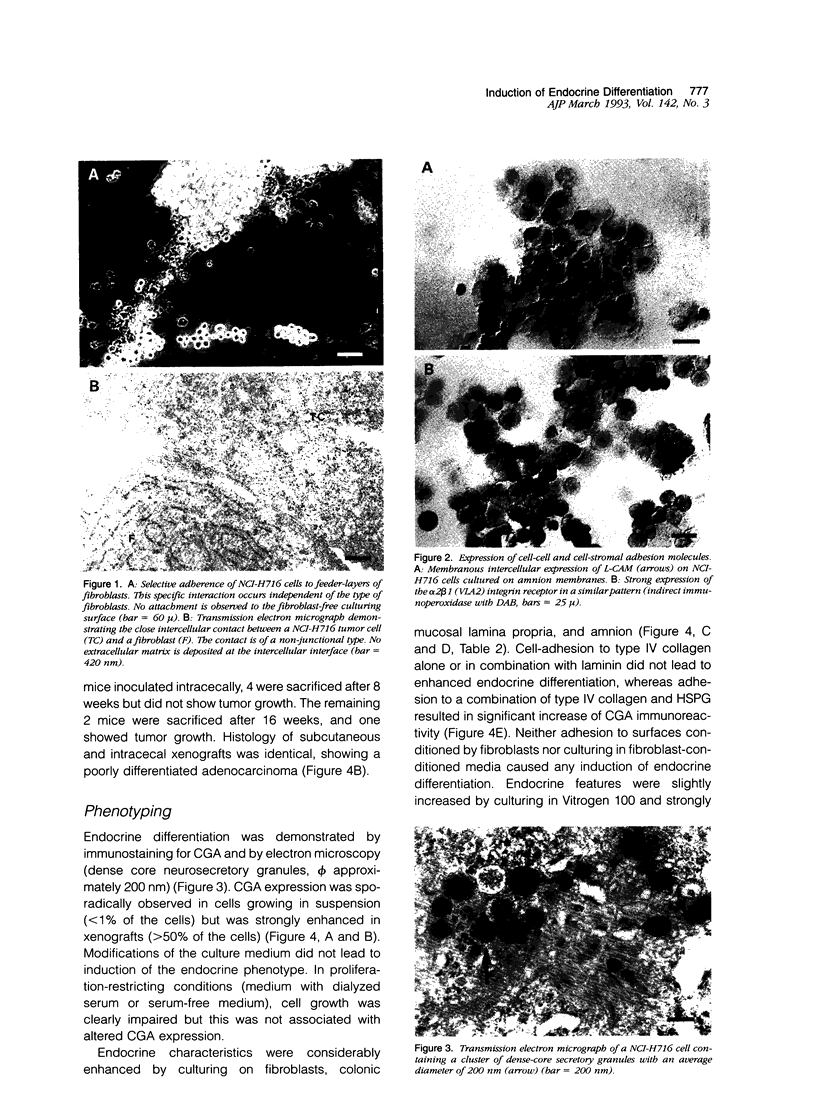
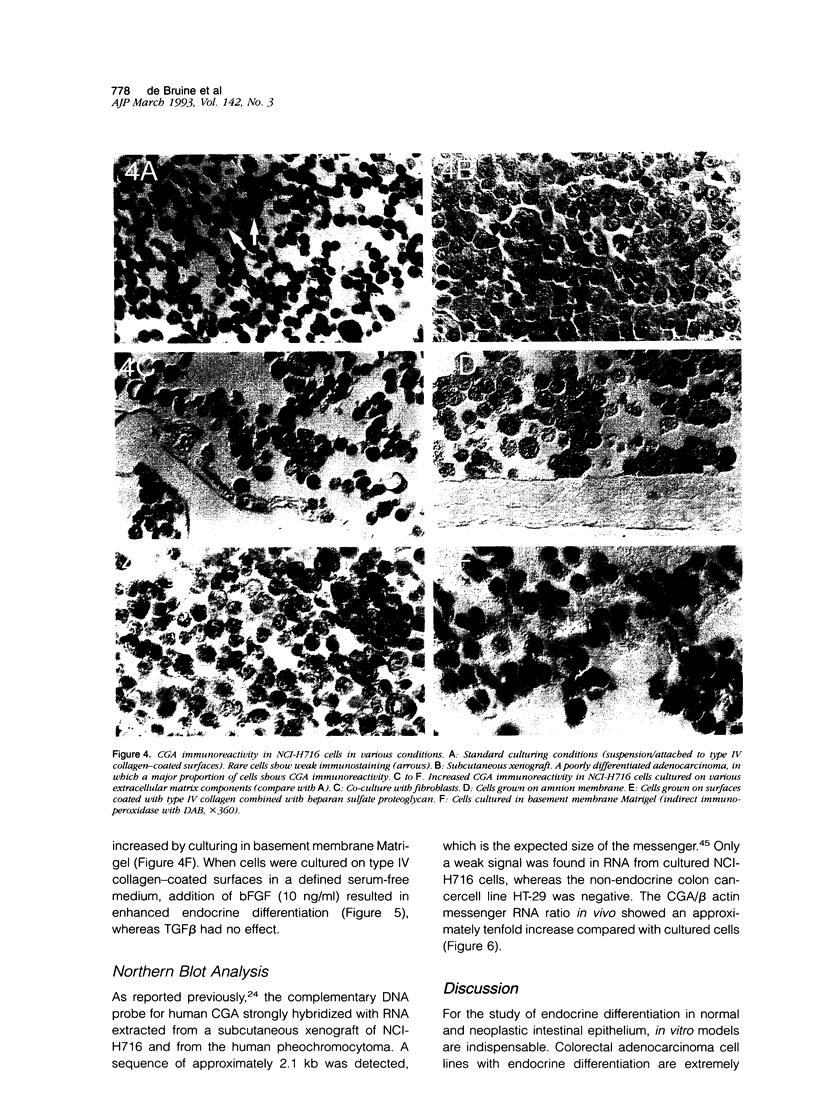
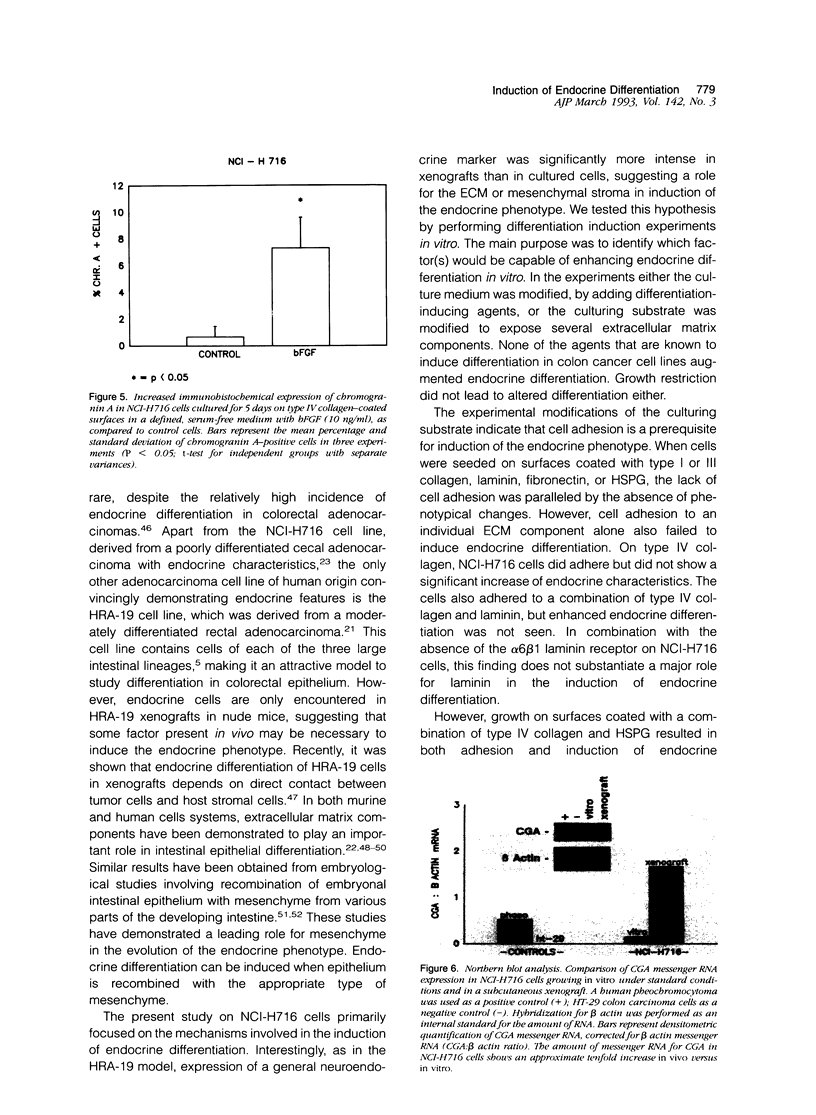
Endocrine cells occur in +/- 30% of colorectal adenocarcinomas. The significance of this phenomenon in terms of tumor behavior is still controversial. Endocrine differentiation in colorectal cancer cell lines is almost confined to tumor xenografts in vivo, suggesting that endocrine differentiation might be regulated by epithelial-stromal interactions. This hypothesis was studied in the cecal adenocarcinoma-derived cell line NCI-H716 by comparing the expression of chromogranin A protein and messenger RNA in vivo and in vitro and by attempts to induce differentiation in vitro. We found that chromogranin A expression, which was strongest in vivo, could be significantly enhanced in vitro by culturing tumor cells in the presence of native extracellular matrix, on fibroblast feeder layers, and in a defined medium with basic fibroblast growth factor. The results suggest that the extracellular matrix induces endocrine differentiation through factors (e.g., basic fibroblast-growth factor) that may be produced by stromal cells and after secretion bind to the extracellular matrix.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arends J. W., Wiggers T., Verstijnen K., Bosman F. T. The occurrence and clinicopathological significance of serotonin immunoreactive cells in large bowel carcinoma. J Pathol. 1986 Jun;149(2):97–102. doi: 10.1002/path.1711490204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buck C. A., Horwitz A. F. Cell surface receptors for extracellular matrix molecules. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1987;3:179–205. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.03.110187.001143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng H., Leblond C. P. Origin, differentiation and renewal of the four main epithelial cell types in the mouse small intestine. V. Unitarian Theory of the origin of the four epithelial cell types. Am J Anat. 1974 Dec;141(4):537–561. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001410407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohn S. M., Roth K. A., Birkenmeier E. H., Gordon J. I. Temporal and spatial patterns of transgene expression in aging adult mice provide insights about the origins, organization, and differentiation of the intestinal epithelium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 1;88(3):1034–1038. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.3.1034. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox W. F., Jr, Pierce G. B. The endodermal origin of the endocrine cells of an adenocarcinoma of the colon of the rat. Cancer. 1982 Oct 15;50(8):1530–1538. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19821015)50:8<1530::aid-cncr2820500813>3.0.co;2-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Amore P. A. Modes of FGF release in vivo and in vitro. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 1990 Nov;9(3):227–238. doi: 10.1007/BF00046362. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dayal Y., DeLellis R. A., Wolfe H. J. Hyperplastic lesions of the gastrointestinal endocrine cells. Am J Surg Pathol. 1987;11 (Suppl 1):87–101. doi: 10.1097/00000478-198700111-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Del Buono R., Pignatelli M., Hall P. A. Control of differentiation in a rectal adenocarcinoma cell line: the role of diffusable and cell-associated factors. J Pathol. 1991 May;164(1):59–66. doi: 10.1002/path.1711640111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinjens W. N., Ten Kate J., Kirch J. A., Tanke H. J., Van der Linden E. P., Van den Ingh H. F., Van Steenbrugge G. J., Meera Khan P., Bosman F. T. Adenosine deaminase complexing protein (ADCP) expression and metastatic potential in prostatic adenocarcinomas. J Pathol. 1990 Mar;160(3):195–201. doi: 10.1002/path.1711600303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elices M. J., Hemler M. E. The human integrin VLA-2 is a collagen receptor on some cells and a collagen/laminin receptor on others. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(24):9906–9910. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.24.9906. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. "A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity". Addendum. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;137(1):266–267. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90381-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folkman J., Klagsbrun M., Sasse J., Wadzinski M., Ingber D., Vlodavsky I. A heparin-binding angiogenic protein--basic fibroblast growth factor--is stored within basement membrane. Am J Pathol. 1988 Feb;130(2):393–400. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukamachi H., Mizuno T., Kim Y. S. Gland formation of human colon cancer cells combined with foetal rat mesenchyme in organ culture: an ultrastructural study. J Cell Sci. 1987 Jun;87(Pt 5):615–621. doi: 10.1242/jcs.87.5.615. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez A. M., Buscaglia M., Ong M., Baird A. Distribution of basic fibroblast growth factor in the 18-day rat fetus: localization in the basement membranes of diverse tissues. J Cell Biol. 1990 Mar;110(3):753–765. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.3.753. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gospodarowicz D. Fibroblast growth factor and its involvement in developmental processes. Curr Top Dev Biol. 1990;24:57–93. doi: 10.1016/s0070-2153(08)60084-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths D. F., Davies S. J., Williams D., Williams G. T., Williams E. D. Demonstration of somatic mutation and colonic crypt clonality by X-linked enzyme histochemistry. Nature. 1988 Jun 2;333(6172):461–463. doi: 10.1038/333461a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn U., Stallmach A., Hahn E. G., Riecken E. O. Basement membrane components are potent promoters of rat intestinal epithelial cell differentiation in vitro. Gastroenterology. 1990 Feb;98(2):322–335. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(90)90821-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamada Y., Oishi A., Shoji T., Takada H., Yamamura M., Hioki K., Yamamoto M. Endocrine cells and prognosis in patients with colorectal carcinoma. Cancer. 1992 Jun 1;69(11):2641–2646. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19920601)69:11<2641::aid-cncr2820691104>3.0.co;2-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Havenith M. G., Cleutjens J. P., Beek C., vd Linden E., De Goeij A. F., Bosman F. T. Human specific anti-type IV collagen monoclonal antibodies, characterization and immunohistochemical application. Histochemistry. 1987;87(2):123–128. doi: 10.1007/BF00533396. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helman L. J., Ahn T. G., Levine M. A., Allison A., Cohen P. S., Cooper M. J., Cohn D. V., Israel M. A. Molecular cloning and primary structure of human chromogranin A (secretory protein I) cDNA. J Biol Chem. 1988 Aug 15;263(23):11559–11563. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho S. B., Itzkowitz S. H., Friera A. M., Jiang S. H., Kim Y. S. Cell lineage markers in premalignant and malignant colonic mucosa. Gastroenterology. 1989 Aug;97(2):392–404. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(89)90075-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoosein N. M., Kiener P. A., Curry R. C., Brattain M. G. Evidence for autocrine growth stimulation of cultured colon tumor cells by a gastrin/cholecystokinin-like peptide. Exp Cell Res. 1990 Jan;186(1):15–21. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(90)90204-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hynes R. O. Integrins: a family of cell surface receptors. Cell. 1987 Feb 27;48(4):549–554. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90233-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jansson D., Gould V. E., Gooch G. T., Rittenhouse H. G., Shin S. S., Manderino G. L., Tomita J. T., Staren E. D. Immunohistochemical analysis of colon carcinomas applying exocrine and neuroendocrine markers. APMIS. 1988 Dec;96(12):1129–1139. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1988.tb00991.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson L. R. Regulation of gastrointestinal mucosal growth. Physiol Rev. 1988 Apr;68(2):456–502. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1988.68.2.456. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karnes W. E., Jr, Walsh J. H., Wu S. V., Kim R. S., Martin M. G., Wong H. C., Mendelsohn J., Park J. G., Cuttitta F. Autonomous proliferation of colon cancer cells that coexpress transforming growth factor alpha and its receptor. Variable effects of receptor-blocking antibody. Gastroenterology. 1992 Feb;102(2):474–485. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(92)90093-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirkland S. C. Clonal origin of columnar, mucous, and endocrine cell lineages in human colorectal epithelium. Cancer. 1988 Apr 1;61(7):1359–1363. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19880401)61:7<1359::aid-cncr2820610714>3.0.co;2-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirkland S. C. Endocrine differentiation by a human rectal adenocarcinoma cell line (HRA-19). Differentiation. 1986;33(2):148–155. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.1986.tb00420.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klagsbrun M., Baird A. A dual receptor system is required for basic fibroblast growth factor activity. Cell. 1991 Oct 18;67(2):229–231. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90173-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koretz K., Schlag P., Boumsell L., Möller P. Expression of VLA-alpha 2, VLA-alpha 6, and VLA-beta 1 chains in normal mucosa and adenomas of the colon, and in colon carcinomas and their liver metastases. Am J Pathol. 1991 Mar;138(3):741–750. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer B., Andrew A., Rawdon B. B., Becker P. The effect of pancreatic mesenchyme on the differentiation of endocrine cells from gastric endoderm. Development. 1987 Aug;100(4):661–671. doi: 10.1242/dev.100.4.661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Languino L. R., Gehlsen K. R., Wayner E., Carter W. G., Engvall E., Ruoslahti E. Endothelial cells use alpha 2 beta 1 integrin as a laminin receptor. J Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;109(5):2455–2462. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.5.2455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewin K. J. The endocrine cells of the gastrointestinal tract. The normal endocrine cells and their hyperplasias. Part I. Pathol Annu. 1986;21(Pt 1):1–27. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lloyd R. V., Wilson B. S. Specific endocrine tissue marker defined by a monoclonal antibody. Science. 1983 Nov 11;222(4624):628–630. doi: 10.1126/science.6635661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moerkerk P. T., Kessels H. J., ten Kate J., de Goeij A. F., Bosman F. T. Southern and dot blot analysis of DNA from formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissue samples from colonic carcinomas. Virchows Arch B Cell Pathol Incl Mol Pathol. 1990;58(5):351–355. doi: 10.1007/BF02890091. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park J. G., Oie H. K., Sugarbaker P. H., Henslee J. G., Chen T. R., Johnson B. E., Gazdar A. Characteristics of cell lines established from human colorectal carcinoma. Cancer Res. 1987 Dec 15;47(24 Pt 1):6710–6718. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rawdon B. B., Andrew A. Can proventricular mesenchyme promote differentiation of endocrine cells in gizzard endoderm? Cell Differ Dev. 1988 Nov;25(2):135–143. doi: 10.1016/0922-3371(88)90006-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redman B. G., Pazdur R. Colonic small cell undifferentiated carcinoma: a distinct pathological diagnosis with therapeutic implications. Am J Gastroenterol. 1987 Apr;82(4):382–385. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santoro S. A., Rajpara S. M., Staatz W. D., Woods V. L., Jr Isolation and characterization of a platelet surface collagen binding complex related to VLA-2. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 May 31;153(1):217–223. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)81211-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sjölund K., Sandén G., Håkanson R., Sundler F. Endocrine cells in human intestine: an immunocytochemical study. Gastroenterology. 1983 Nov;85(5):1120–1130. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solcia E., Usellini L., Buffa R., Rindi G., Villani L., Zampatti C., Silini E. Endocrine cells producing regulatory peptides. Experientia. 1987 Jul 15;43(7):839–850. doi: 10.1007/BF01945362. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonnenberg A., Modderman P. W., Hogervorst F. Laminin receptor on platelets is the integrin VLA-6. Nature. 1988 Dec 1;336(6198):487–489. doi: 10.1038/336487a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Springer T. A. Adhesion receptors of the immune system. Nature. 1990 Aug 2;346(6283):425–434. doi: 10.1038/346425a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staatz W. D., Fok K. F., Zutter M. M., Adams S. P., Rodriguez B. A., Santoro S. A. Identification of a tetrapeptide recognition sequence for the alpha 2 beta 1 integrin in collagen. J Biol Chem. 1991 Apr 25;266(12):7363–7367. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staatz W. D., Rajpara S. M., Wayner E. A., Carter W. G., Santoro S. A. The membrane glycoprotein Ia-IIa (VLA-2) complex mediates the Mg++-dependent adhesion of platelets to collagen. J Cell Biol. 1989 May;108(5):1917–1924. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.5.1917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stallmach A., Hahn U., Merker H. J., Hahn E. G., Riecken E. O. Differentiation of rat intestinal epithelial cells is induced by organotypic mesenchymal cells in vitro. Gut. 1989 Jul;30(7):959–970. doi: 10.1136/gut.30.7.959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein B., Andrew A. Differentiation of endocrine cells in chick allantoic epithelium combined with pancreatic mesenchyme. Cell Differ Dev. 1989 May;26(3):173–180. doi: 10.1016/0922-3371(89)90748-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeichi M. Cadherin cell adhesion receptors as a morphogenetic regulator. Science. 1991 Mar 22;251(5000):1451–1455. doi: 10.1126/science.2006419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walling J. M., Blackmore M., Hickman J. A., Townsend K. M. Role of the extracellular matrix on the growth and differentiated phenotype of murine colonic adenocarcinoma cells in vitro. Int J Cancer. 1991 Mar 12;47(5):776–783. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910470526. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber S., Engel J., Wiedemann H., Glanville R. W., Timpl R. Subunit structure and assembly of the globular domain of basement-membrane collagen type IV. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Mar 1;139(2):401–410. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08019.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westermann R., Johannsen M., Unsicker K., Grothe C. Basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF) immunoreactivity is present in chromaffin granules. J Neurochem. 1990 Jul;55(1):285–292. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1990.tb08850.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitehead R. H., Brown A., Bhathal P. S. A method for the isolation and culture of human colonic crypts in collagen gels. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol. 1987 Jun;23(6):436–442. doi: 10.1007/BF02623860. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiedenmann B., Huttner W. B. Synaptophysin and chromogranins/secretogranins--widespread constituents of distinct types of neuroendocrine vesicles and new tools in tumor diagnosis. Virchows Arch B Cell Pathol Incl Mol Pathol. 1989;58(2):95–121. doi: 10.1007/BF02890062. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Bruïne A. P., Dinjens W. N., Pijls M. M., vd Linden E. P., Rousch M. J., Moerkerk P. T., de Goeij A. F., Bosman F. T. NCI-H716 cells as a model for endocrine differentiation in colorectal cancer. Virchows Arch B Cell Pathol Incl Mol Pathol. 1992;62(5):311–320. doi: 10.1007/BF02899698. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Bruïne A. P., Dinjens W. N., Zijlema J. H., Lenders M. H., Bosman F. T. Renewal of enterochromaffin cells in the rat caecum. Anat Rec. 1992 May;233(1):75–82. doi: 10.1002/ar.1092330110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]