Abstract
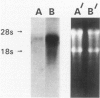
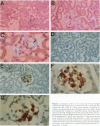
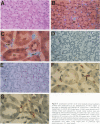
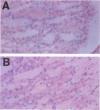
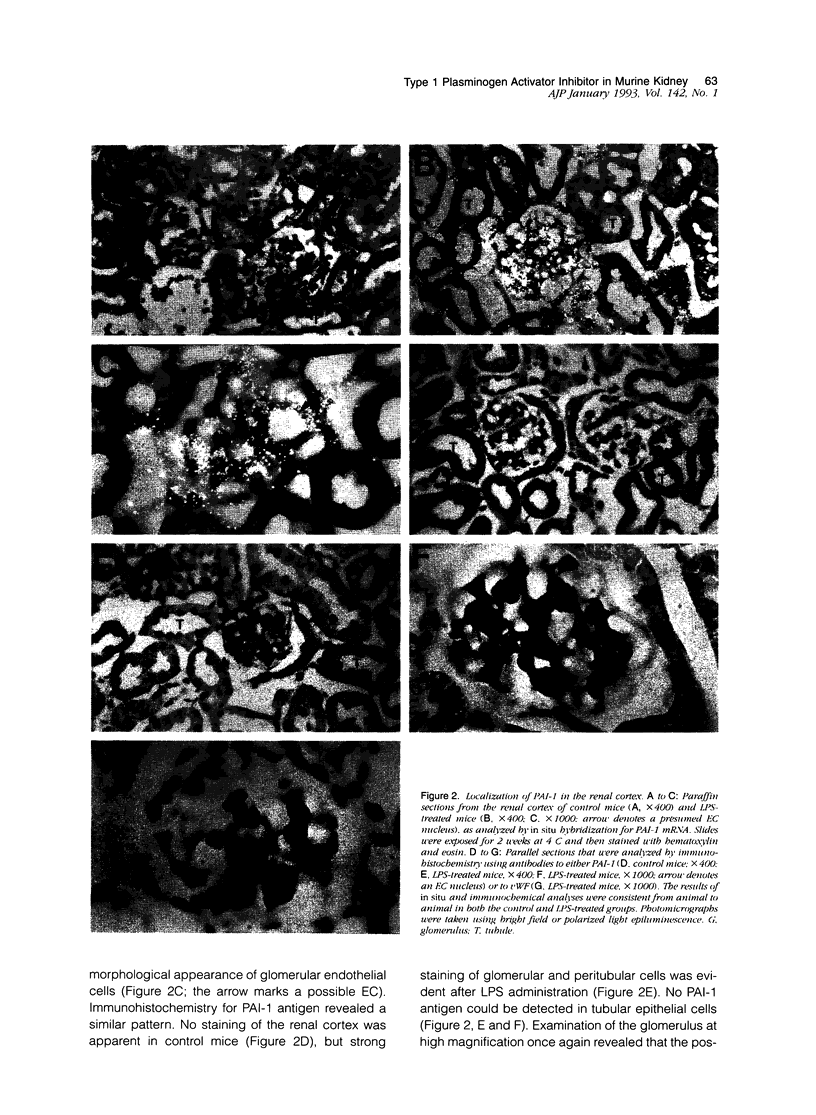
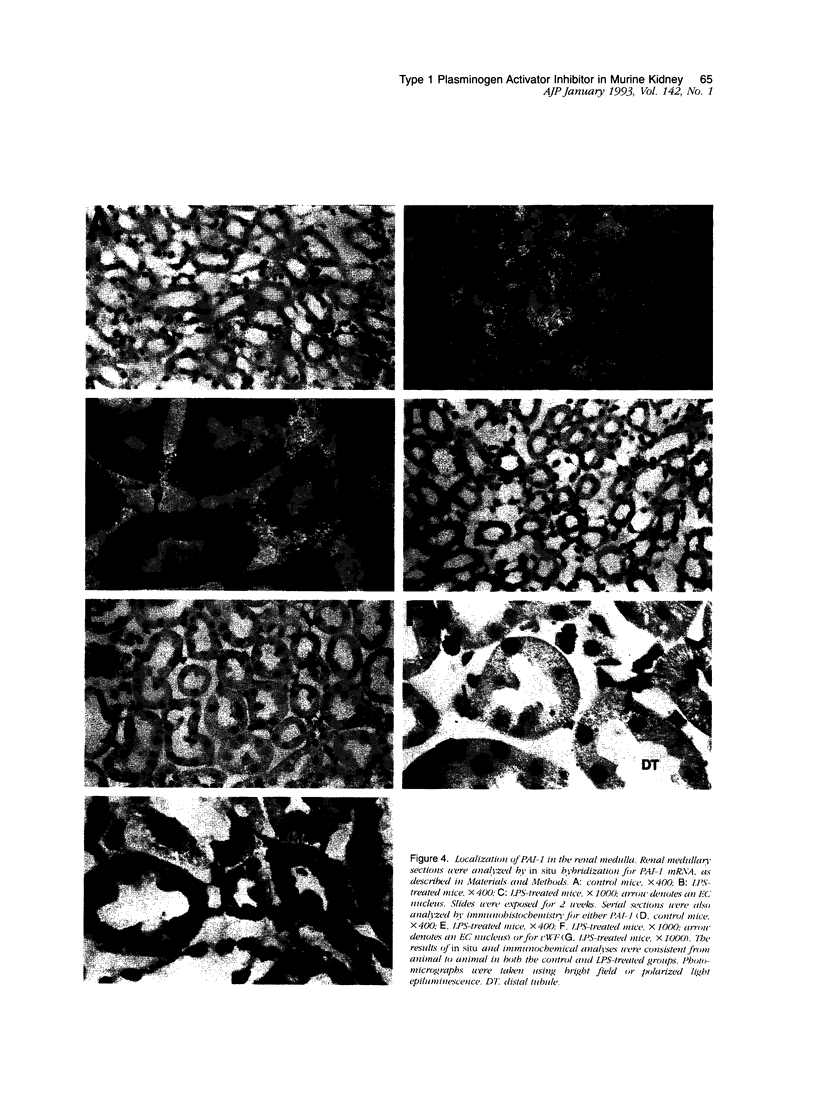
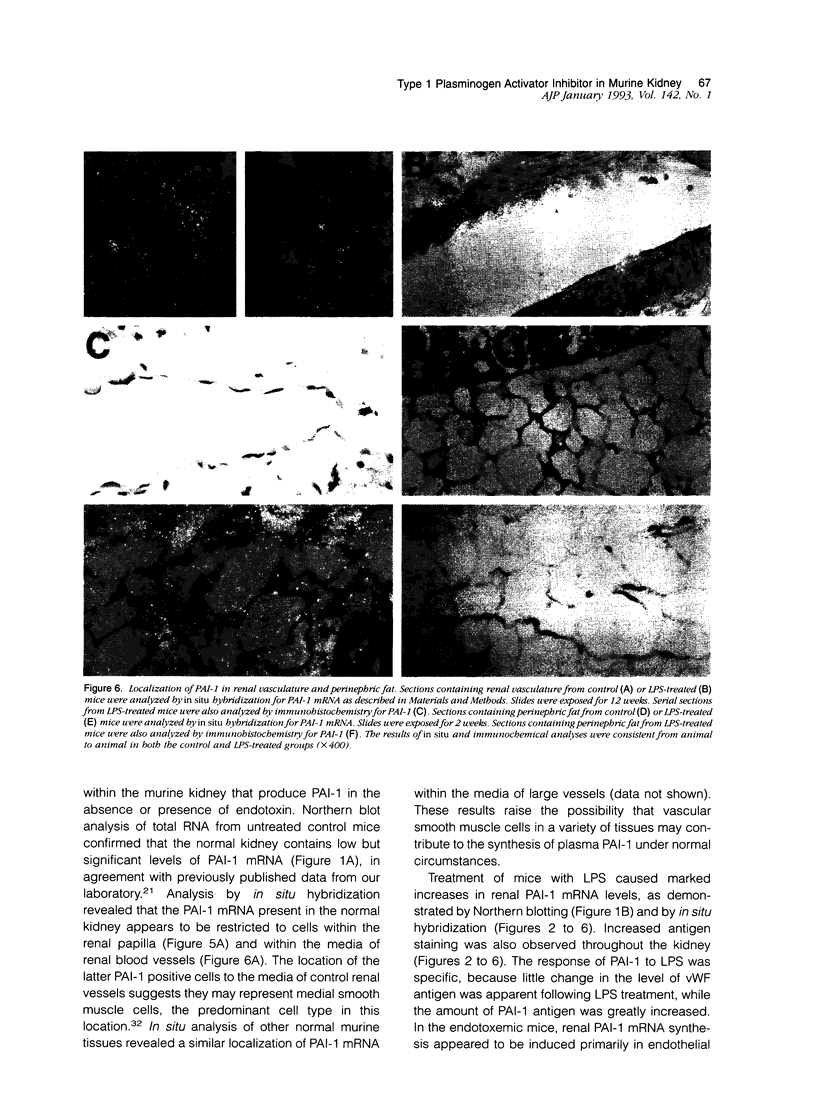
Type 1 plasminogen activator inhibitor (PAI-1) may be markedly increased in the plasma of patients with endotoxemia and/or renal disease. To investigate renal PAI-1 production during acute endotoxemia, a murine model system was used. Mice were injected with either saline alone or saline containing 50 micrograms endotoxin, and sacrificed 3 hours later and their tissues analyzed for PAI-1 messenger RNA (mRNA) and antigen. Northern blot analysis confirmed that the level of renal PAI-1 mRNA was greatly increased in the endotoxemic mice relative to the saline controls. In situ hybridization was then performed to determine the cellular localization of PAI-1 mRNA within the renal tissues. In the control kidneys, low levels of PAI-1 mRNA were detected in the renal papilla and in the muscular walls of renal arteries. However, in the endotoxemic mice, an intense hybridization signal for PAI-1 mRNA was observed in glomerular and peritubular cells. These cells also stained positively for von Willebrand factor antigen, an endothelial cell-specific marker. The PAI-1 mRNA hybridization signal could further be observed in peritubular endothelial cells in the medulla and in endothelial cells of veins and arteries throughout the kidney. Immunochemical analysis revealed that PAI-1 antigen co-localized to the cytoplasm of cells expressing PAI-1 mRNA. This study provides the first direct evidence that PAI-1 is induced in endothelial cells of the kidney during endotoxemia in vivo and suggests a role for PAI-1 in the pathogenesis of renal disease.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Almér L. O., Ohlin H. Elevated levels of the rapid inhibitor of plasminogen activator (t-PAI) in acute myocardial infarction. Thromb Res. 1987 Aug 1;47(3):335–339. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(87)90147-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertani T., Abbate M., Zoja C., Corna D., Remuzzi G. Sequence of glomerular changes in experimental endotoxemia: a possible model of hemolytic uremic syndrome. Nephron. 1989;53(4):330–337. doi: 10.1159/000185777. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bevilacqua M. P., Schleef R. R., Gimbrone M. A., Jr, Loskutoff D. J. Regulation of the fibrinolytic system of cultured human vascular endothelium by interleukin 1. J Clin Invest. 1986 Aug;78(2):587–591. doi: 10.1172/JCI112613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Border W. A., Okuda S., Languino L. R., Sporn M. B., Ruoslahti E. Suppression of experimental glomerulonephritis by antiserum against transforming growth factor beta 1. Nature. 1990 Jul 26;346(6282):371–374. doi: 10.1038/346371a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler T., Rahman H., Al-Mahmud K. A., Islam M., Bardhan P., Kabir I., Rahman M. M. An animal model of haemolytic--uraemic syndrome in shigellosis: lipopolysaccharides of Shigella dysenteriae I and S. flexneri produce leucocyte-mediated renal cortical necrosis in rabbits. Br J Exp Pathol. 1985 Feb;66(1):7–15. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cajot J. F., Bamat J., Bergonzelli G. E., Kruithof E. K., Medcalf R. L., Testuz J., Sordat B. Plasminogen-activator inhibitor type 1 is a potent natural inhibitor of extracellular matrix degradation by fibrosarcoma and colon carcinoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Sep;87(18):6939–6943. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.18.6939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chart H., Scotland S. M., Rowe B. Serum antibodies to Escherichia coli serotype O157:H7 in patients with hemolytic uremic syndrome. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Feb;27(2):285–290. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.2.285-290.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colucci M., Paramo J. A., Collen D. Generation in plasma of a fast-acting inhibitor of plasminogen activator in response to endotoxin stimulation. J Clin Invest. 1985 Mar;75(3):818–824. doi: 10.1172/JCI111777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond J. R., Karnovsky M. J. Focal and segmental glomerulosclerosis: analogies to atherosclerosis. Kidney Int. 1988 May;33(5):917–924. doi: 10.1038/ki.1988.87. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emeis J. J., Kooistra T. Interleukin 1 and lipopolysaccharide induce an inhibitor of tissue-type plasminogen activator in vivo and in cultured endothelial cells. J Exp Med. 1986 May 1;163(5):1260–1266. doi: 10.1084/jem.163.5.1260. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ey P. L., Prowse S. J., Jenkin C. R. Isolation of pure IgG1, IgG2a and IgG2b immunoglobulins from mouse serum using protein A-sepharose. Immunochemistry. 1978 Jul;15(7):429–436. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(78)90070-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hekman C. M., Loskutoff D. J. Kinetic analysis of the interactions between plasminogen activator inhibitor 1 and both urokinase and tissue plasminogen activator. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1988 Apr;262(1):199–210. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(88)90182-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaffe E. A., Nachman R. L., Becker C. G., Minick C. R. Culture of human endothelial cells derived from umbilical veins. Identification by morphologic and immunologic criteria. J Clin Invest. 1973 Nov;52(11):2745–2756. doi: 10.1172/JCI107470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kruithof E. K., Tran-Thang C., Gudinchet A., Hauert J., Nicoloso G., Genton C., Welti H., Bachmann F. Fibrinolysis in pregnancy: a study of plasminogen activator inhibitors. Blood. 1987 Feb;69(2):460–466. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin D. L., MacDonald K. L., White K. E., Soler J. T., Osterholm M. T. The epidemiology and clinical aspects of the hemolytic uremic syndrome in Minnesota. N Engl J Med. 1990 Oct 25;323(17):1161–1167. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199010253231703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathison J. C., Wolfson E., Ulevitch R. J. Participation of tumor necrosis factor in the mediation of gram negative bacterial lipopolysaccharide-induced injury in rabbits. J Clin Invest. 1988 Jun;81(6):1925–1937. doi: 10.1172/JCI113540. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mimuro J., Loskutoff D. J. Binding of type 1 plasminogen activator inhibitor to the extracellular matrix of cultured bovine endothelial cells. J Biol Chem. 1989 Mar 25;264(9):5058–5063. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okuda S., Languino L. R., Ruoslahti E., Border W. A. Elevated expression of transforming growth factor-beta and proteoglycan production in experimental glomerulonephritis. Possible role in expansion of the mesangial extracellular matrix. J Clin Invest. 1990 Aug;86(2):453–462. doi: 10.1172/JCI114731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paramo J. A., de Boer A., Colucci M., Jonker J. J., Collen D. Plasminogen activator inhibitor (PA-inhibitor) activity in the blood of patients with deep vein thrombosis. Thromb Haemost. 1985 Oct 30;54(3):725–725. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prendergast G. C., Diamond L. E., Dahl D., Cole M. D. The c-myc-regulated gene mrl encodes plasminogen activator inhibitor 1. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Mar;10(3):1265–1269. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.3.1265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quax P. H., van den Hoogen C. M., Verheijen J. H., Padro T., Zeheb R., Gelehrter T. D., van Berkel T. J., Kuiper J., Emeis J. J. Endotoxin induction of plasminogen activator and plasminogen activator inhibitor type 1 mRNA in rat tissues in vivo. J Biol Chem. 1990 Sep 15;265(26):15560–15563. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remick D. G., Strieter R. M., Lynch J. P., 3rd, Nguyen D., Eskandari M., Kunkel S. L. In vivo dynamics of murine tumor necrosis factor-alpha gene expression. Kinetics of dexamethasone-induced suppression. Lab Invest. 1989 Jun;60(6):766–771. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruggeri Z. M., Zimmerman T. S. The complex multimeric composition of factor VIII/von Willebrand factor. Blood. 1981 Jun;57(6):1140–1143. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruggeri Z. M., Zimmerman T. S. Variant von Willebrand's disease: characterization of two subtypes by analysis of multimeric composition of factor VIII/von Willebrand factor in plasma and platelets. J Clin Invest. 1980 Jun;65(6):1318–1325. doi: 10.1172/JCI109795. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawdey M. S., Loskutoff D. J. Regulation of murine type 1 plasminogen activator inhibitor gene expression in vivo. Tissue specificity and induction by lipopolysaccharide, tumor necrosis factor-alpha, and transforming growth factor-beta. J Clin Invest. 1991 Oct;88(4):1346–1353. doi: 10.1172/JCI115440. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawdey M., Podor T. J., Loskutoff D. J. Regulation of type 1 plasminogen activator inhibitor gene expression in cultured bovine aortic endothelial cells. Induction by transforming growth factor-beta, lipopolysaccharide, and tumor necrosis factor-alpha. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jun 25;264(18):10396–10401. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suffredini A. F., Harpel P. C., Parrillo J. E. Promotion and subsequent inhibition of plasminogen activation after administration of intravenous endotoxin to normal subjects. N Engl J Med. 1989 May 4;320(18):1165–1172. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198905043201802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner D. D., Olmsted J. B., Marder V. J. Immunolocalization of von Willebrand protein in Weibel-Palade bodies of human endothelial cells. J Cell Biol. 1982 Oct;95(1):355–360. doi: 10.1083/jcb.95.1.355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilcox J. N., Gee C. E., Roberts J. L. In situ cDNA:mRNA hybridization: development of a technique to measure mRNA levels in individual cells. Methods Enzymol. 1986;124:510–533. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(86)24037-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilcox J. N., Smith K. M., Schwartz S. M., Gordon D. Localization of tissue factor in the normal vessel wall and in the atherosclerotic plaque. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(8):2839–2843. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.8.2839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]