Abstract
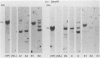
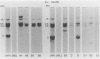
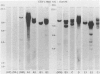
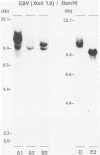
To improve the diagnostic accuracy and understanding of the pathogenesis of lymphoproliferative diseases (LPDs) occurring in immunosuppressed transplant recipients (post-transplantation LPD), clonality of Epstein-Barr virus-induced human LPDs in mice with severe combined immunodeficiency was examined by analyzing: 1) human immunoglobulin genes and their products, 2) the clonality of Epstein-Barr virus DNA, and 3) genetic alteration of c-myc or bcl-2 genes. A spectrum of clonality was found in the LPDs comparable with that reported for post-transplantation LPDs, although rearrangements of c-myc or bcl-2 genes were not detected. It is confirmed that this system is useful in terms of clonality for understanding the early phases in the pathogenesis of post-transplantation LPD or LPD in immune deficient patients.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bosma G. C., Custer R. P., Bosma M. J. A severe combined immunodeficiency mutation in the mouse. Nature. 1983 Feb 10;301(5900):527–530. doi: 10.1038/301527a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canioni D., MacKelvie P., Debure A., Nezelof C. Lymphadenopathy in renal transplant patients treated with immunosuppressive antibodies (OKT3 and anti-thymocyte globulin). A report of nine cases. Am J Surg Pathol. 1989 Feb;13(2):87–96. doi: 10.1097/00000478-198902000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cannon M. J., Pisa P., Fox R. I., Cooper N. R. Epstein-Barr virus induces aggressive lymphoproliferative disorders of human B cell origin in SCID/hu chimeric mice. J Clin Invest. 1990 Apr;85(4):1333–1337. doi: 10.1172/JCI114573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleary M. L., Galili N., Trela M., Levy R., Sklar J. Single cell origin of bigenotypic and biphenotypic B cell proliferations in human follicular lymphomas. J Exp Med. 1988 Feb 1;167(2):582–597. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.2.582. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleary M. L., Nalesnik M. A., Shearer W. T., Sklar J. Clonal analysis of transplant-associated lymphoproliferations based on the structure of the genomic termini of the Epstein-Barr virus. Blood. 1988 Jul;72(1):349–352. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cossman J., Uppenkamp M., Sundeen J., Coupland R., Raffeld M. Molecular genetics and the diagnosis of lymphoma. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1988 Feb;112(2):117–127. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davey D. D., Kamat D., Laszewski M., Goeken J. A., Kemp J. D., Trigg M. E., Purtilo D. T., Davis J., Dick F. R. Epstein-Barr virus-related lymphoproliferative disorders following bone marrow transplantation: an immunologic and genotypic analysis. Mod Pathol. 1989 Jan;2(1):27–34. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frizzera G., Hanto D. W., Gajl-Peczalska K. J., Rosai J., McKenna R. W., Sibley R. K., Holahan K. P., Lindquist L. L. Polymorphic diffuse B-cell hyperplasias and lymphomas in renal transplant recipients. Cancer Res. 1981 Nov;41(11 Pt 1):4262–4279. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanto D. W., Birkenbach M., Frizzera G., Gajl-Peczalska K. J., Simmons R. L., Schubach W. H. Confirmation of the heterogeneity of posttransplant Epstein-Barr virus-associated B cell proliferations by immunoglobulin gene rearrangement analyses. Transplantation. 1989 Mar;47(3):458–464. doi: 10.1097/00007890-198903000-00012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hieter P. A., Hollis G. F., Korsmeyer S. J., Waldmann T. A., Leder P. Clustered arrangement of immunoglobulin lambda constant region genes in man. Nature. 1981 Dec 10;294(5841):536–540. doi: 10.1038/294536a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hieter P. A., Maizel J. V., Jr, Leder P. Evolution of human immunoglobulin kappa J region genes. J Biol Chem. 1982 Feb 10;257(3):1516–1522. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu S. M., Raine L., Fanger H. Use of avidin-biotin-peroxidase complex (ABC) in immunoperoxidase techniques: a comparison between ABC and unlabeled antibody (PAP) procedures. J Histochem Cytochem. 1981 Apr;29(4):577–580. doi: 10.1177/29.4.6166661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katamine S., Otsu M., Tada K., Tsuchiya S., Sato T., Ishida N., Honjo T., Ono Y. Epstein-Barr virus transforms precursor B cells even before immunoglobulin gene rearrangements. Nature. 1984 May 24;309(5966):369–372. doi: 10.1038/309369a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz B. Z., Raab-Traub N., Miller G. Latent and replicating forms of Epstein-Barr virus DNA in lymphomas and lymphoproliferative diseases. J Infect Dis. 1989 Oct;160(4):589–598. doi: 10.1093/infdis/160.4.589. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Locker J., Nalesnik M. Molecular genetic analysis of lymphoid tumors arising after organ transplantation. Am J Pathol. 1989 Dec;135(6):977–987. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malynn B. A., Blackwell T. K., Fulop G. M., Rathbun G. A., Furley A. J., Ferrier P., Heinke L. B., Phillips R. A., Yancopoulos G. D., Alt F. W. The scid defect affects the final step of the immunoglobulin VDJ recombinase mechanism. Cell. 1988 Aug 12;54(4):453–460. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90066-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masih A., Weisenburger D., Duggan M., Armitage J., Bashir R., Mitchell D., Wickert R., Purtilo D. T. Epstein-Barr viral genome in lymph nodes from patients with Hodgkin's disease may not be specific to Reed-Sternberg cells. Am J Pathol. 1991 Jul;139(1):37–43. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller G., Lipman M. Release of infectious Epstein-Barr virus by transformed marmoset leukocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Jan;70(1):190–194. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.1.190. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitus A. J., Stein R., Rappeport J. M., Antin J. H., Weinstein H. J., Alper C. A., Smith B. R. Monoclonal and oligoclonal gammopathy after bone marrow transplantation. Blood. 1989 Dec;74(8):2764–2768. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosier D. E., Gulizia R. J., Baird S. M., Spector S., Spector D., Kipps T. J., Fox R. I., Carson D. A., Cooper N., Richman D. D. Studies of HIV infection and the development of Epstein-Barr virus-related B cell lymphomas following transfer of human lymphocytes to mice with severe combined immunodeficiency. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1989;152:195–199. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-74974-2_23. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosier D. E., Gulizia R. J., Baird S. M., Wilson D. B. Transfer of a functional human immune system to mice with severe combined immunodeficiency. Nature. 1988 Sep 15;335(6187):256–259. doi: 10.1038/335256a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamine H., Okano M., Taguchi Y., Pirruccello S. J., Davis J. R., Beisel K. W., Kleveland K., Sanger W. G., Fordyce R. R., Purtilo D. T. Hematopathologic features of Epstein-Barr virus-induced human B-lymphoproliferation in mice with severe combined immunodeficiency. A model of lymphoproliferative diseases in immunocompromised patients. Lab Invest. 1991 Oct;65(4):389–399. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nalesnik M. A., Jaffe R., Starzl T. E., Demetris A. J., Porter K., Burnham J. A., Makowka L., Ho M., Locker J. The pathology of posttransplant lymphoproliferative disorders occurring in the setting of cyclosporine A-prednisone immunosuppression. Am J Pathol. 1988 Oct;133(1):173–192. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okano M., Taguchi Y., Nakamine H., Pirruccello S. J., Davis J. R., Beisel K. W., Kleveland K. L., Sanger W. G., Fordyce R. R., Purtilo D. T. Characterization of Epstein-Barr virus-induced lymphoproliferation derived from human peripheral blood mononuclear cells transferred to severe combined immunodeficient mice. Am J Pathol. 1990 Sep;137(3):517–522. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patton D. F., Wilkowski C. W., Hanson C. A., Shapiro R., Gajl-Peczalska K. J., Filipovich A. H., McClain K. L. Epstein-Barr virus--determined clonality in posttransplant lymphoproliferative disease. Transplantation. 1990 Jun;49(6):1080–1084. doi: 10.1097/00007890-199006000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purtilo D. T., Cassel C. K., Yang J. P., Harper R. X-linked recessive progressive combined variable immunodeficiency (Duncan's disease). Lancet. 1975 Apr 26;1(7913):935–940. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)92004-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purtilo D. T. Epstein-Barr-virus-induced oncogenesis in immune-deficient individuals. Lancet. 1980 Feb 9;1(8163):300–303. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(80)90792-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purtilo D. T., Falk K., Pirruccello S. J., Nakamine H., Kleveland K., Davis J. R., Okano M., Taguchi Y., Sanger W. G., Beisel K. W. SCID mouse model of Epstein-Barr virus-induced lymphomagenesis of immunodeficient humans. Int J Cancer. 1991 Feb 20;47(4):510–517. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910470407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purtilo D. T., Grierson H. L. Methods of detection of new families with X-linked lymphoproliferative disease. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 1991 Feb;51(2):143–153. doi: 10.1016/0165-4608(91)90127-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raab-Traub N., Flynn K. The structure of the termini of the Epstein-Barr virus as a marker of clonal cellular proliferation. Cell. 1986 Dec 26;47(6):883–889. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90803-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe M., Young L. S., Crocker J., Stokes H., Henderson S., Rickinson A. B. Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-associated lymphoproliferative disease in the SCID mouse model: implications for the pathogenesis of EBV-positive lymphomas in man. J Exp Med. 1991 Jan 1;173(1):147–158. doi: 10.1084/jem.173.1.147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegelman M. H., Cleary M. L., Warnke R., Sklar J. Frequent biclonality and Ig gene alterations among B cell lymphomas that show multiple histologic forms. J Exp Med. 1985 Apr 1;161(4):850–863. doi: 10.1084/jem.161.4.850. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starzl T. E., Nalesnik M. A., Porter K. A., Ho M., Iwatsuki S., Griffith B. P., Rosenthal J. T., Hakala T. R., Shaw B. W., Jr, Hardesty R. L. Reversibility of lymphomas and lymphoproliferative lesions developing under cyclosporin-steroid therapy. Lancet. 1984 Mar 17;1(8377):583–587. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)90994-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsujimoto Y., Cossman J., Jaffe E., Croce C. M. Involvement of the bcl-2 gene in human follicular lymphoma. Science. 1985 Jun 21;228(4706):1440–1443. doi: 10.1126/science.3874430. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsujimoto Y., Croce C. M. Analysis of the structure, transcripts, and protein products of bcl-2, the gene involved in human follicular lymphoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(14):5214–5218. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.14.5214. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zelenetz A. D., Chen T. T., Levy R. Histologic transformation of follicular lymphoma to diffuse lymphoma represents tumor progression by a single malignant B cell. J Exp Med. 1991 Jan 1;173(1):197–207. doi: 10.1084/jem.173.1.197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]