Abstract
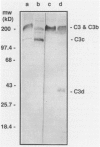
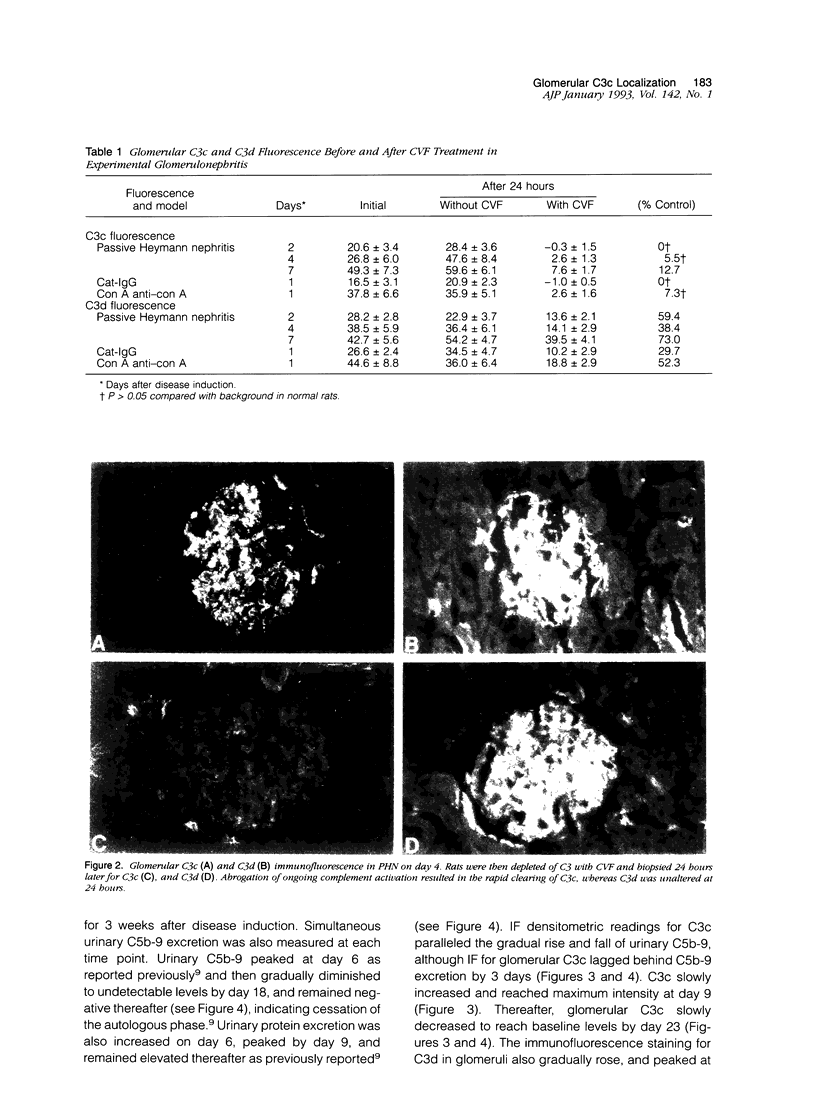
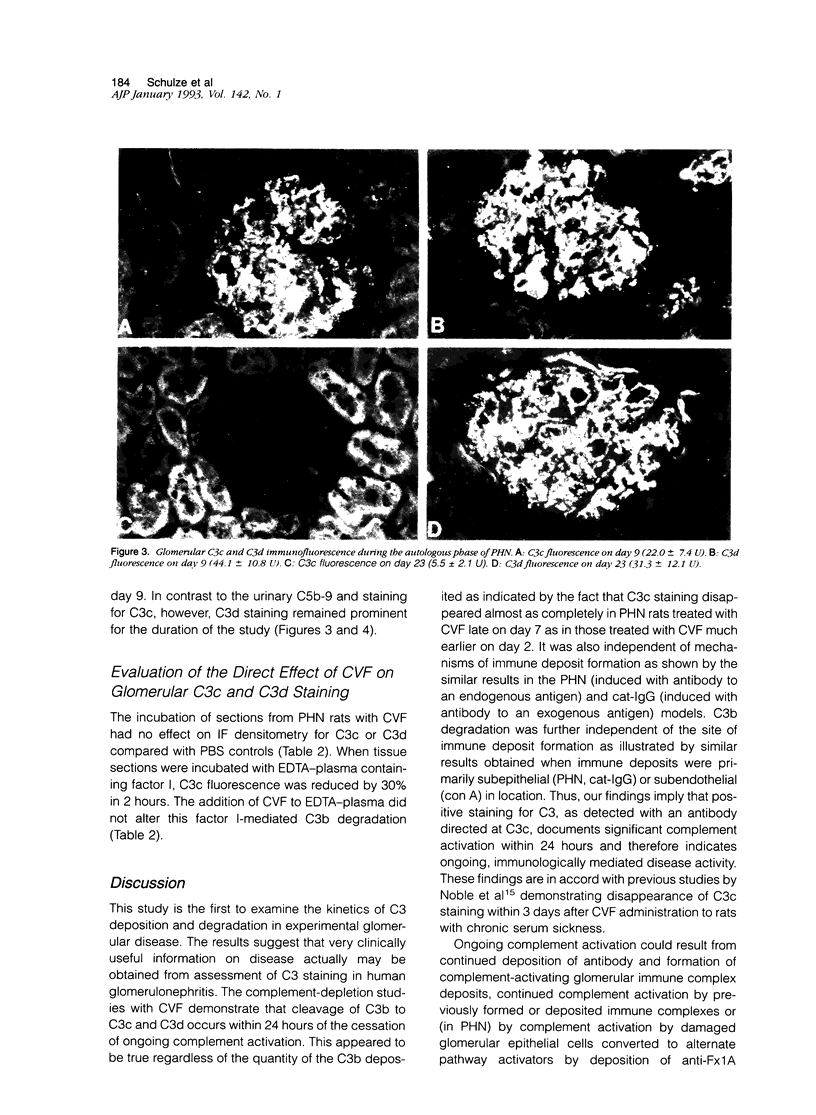
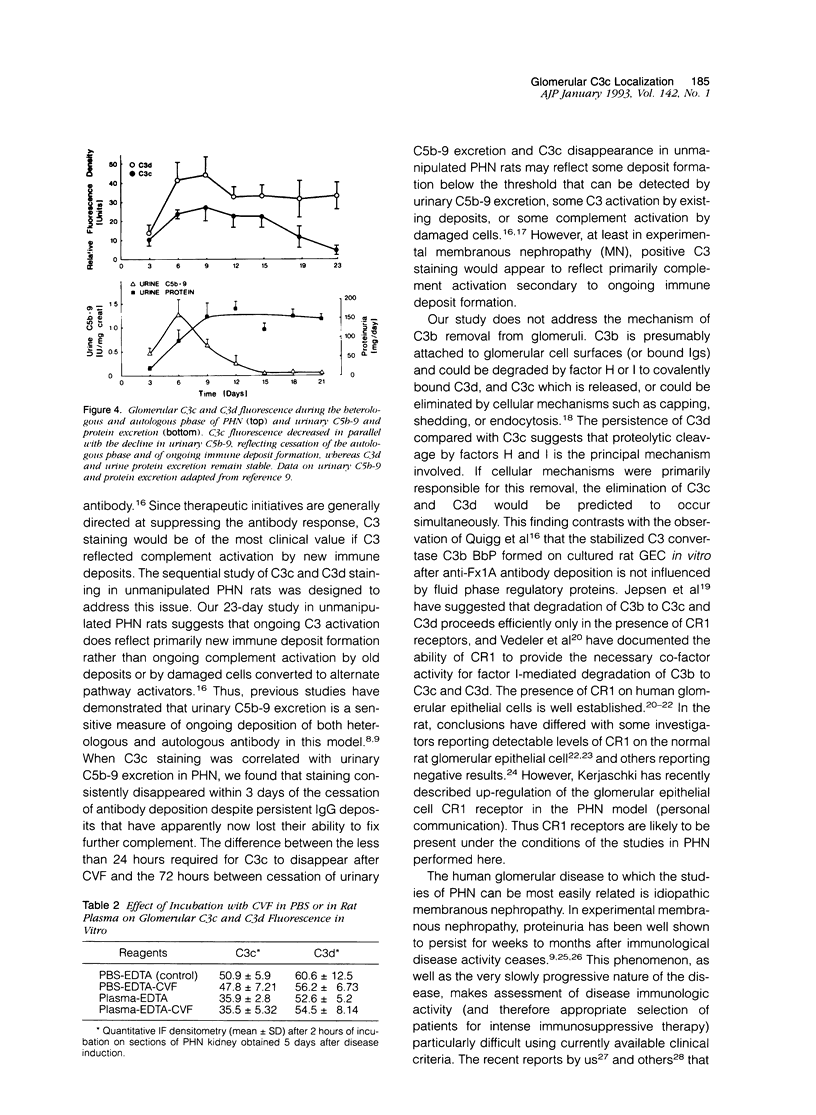
In antibody-mediated glomerular disease, deposits of C3 (C3b) are common and are degraded by factor I to C3c and C3d. However, the kinetics of C3b degradation in glomerulonephritis have not been defined. To do this, we studied three models of complement-dependent glomerulonephritis with established C3 deposits (passive Heymann nephritis, cationized immunoglobulin G membranous nephropathy, and concanavalin A-anticoncanavalin A glomerulonephritis). C3b deposition was halted by administration of cobra venom factor, and the disappearance of C3c and C3d from glomeruli was measured with specific antibodies and quantitative fluorescence densitometry. Results showed that C3c deposits were reduced by over 85% within 24 hours in all three models. C3c clearance was unaffected by site or mechanism of deposit formation. C3d deposits persisted despite lack of ongoing complement activation. In passive Heymann nephritis when disease activity was monitored by urinary C5b-9 excretion, C3c was cleared in parallel with return of urine C5b-9 excretion to normal values. We conclude that glomerular deposits of C3c are cleared within 24 hours of cessation of complement activation. Positive staining for C3 utilizing antibody specific for the C3c portion documents recent complement activation usually reflecting new immune deposit formation.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baker P. J., Adler S., Yang Y., Couser W. G. Complement activation by heat-killed human kidney cells: formation, activity, and stabilization of cell-bound C3 convertases. J Immunol. 1984 Aug;133(2):877–881. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenchley P. E., Coupes B., Short C. D., O'Donoghue D. J., Ballardie F. W., Mallick N. P. Urinary C3dg and C5b-9 indicate active immune disease in human membranous nephropathy. Kidney Int. 1992 Apr;41(4):933–937. doi: 10.1038/ki.1992.143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Couser W. G., Baker P. J., Adler S. Complement and the direct mediation of immune glomerular injury: a new perspective. Kidney Int. 1985 Dec;28(6):879–890. doi: 10.1038/ki.1985.214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Couser W. G. Mediation of immune glomerular injury. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1990 Jul;1(1):13–29. doi: 10.1681/ASN.V1113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Couser W. G., Ochi R. F., Baker P. J., Schulze M., Campbell C., Johnson R. J. C6 depletion reduces proteinuria in experimental nephropathy induced by a nonglomerular antigen. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1991 Oct;2(4):894–901. doi: 10.1681/ASN.V24894. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doi T., Kanatsu K., Nagai H., Suehiro F., Kuwahara T., Hamashima Y. Demonstration of C3d deposits in membranous nephropathy. Nephron. 1984;37(4):232–235. doi: 10.1159/000183255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emancipator S. N., Ovary Z., Lamm M. E. The role of mesangial complement in the hematuria of experimental IgA nephropathy. Lab Invest. 1987 Sep;57(3):269–276. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer E., Appay M. D., Cook J., Kazatchkine M. D. Characterization of the human glomerular C3 receptor as the C3b/C4b complement type one (CR1) receptor. J Immunol. 1986 Feb 15;136(4):1373–1377. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foidart J. B., Dechenne C. A., Mahieu P., Creutz C. E., de Mey J. Tissue culture of normal rat glomeruli. Isolation and morphological characterization of two homogeneous cell lines. Invest Cell Pathol. 1979 Jan-Mar;2(1):15–26. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jennette J. C., Iskandar S. S., Dalldorf F. G. Pathologic differentiation between lupus and nonlupus membranous glomerulopathy. Kidney Int. 1983 Sep;24(3):377–385. doi: 10.1038/ki.1983.170. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jepsen H. H., Teisner B., Folkersen J., Svehag S. E. Enhancing effect of autologous human erythrocytes on generation of C3 cleavage products beyond iC3b. Complement. 1988;5(3):120–129. doi: 10.1159/000463046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. J., Klebanoff S. J., Ochi R. F., Adler S., Baker P., Sparks L., Couser W. G. Participation of the myeloperoxidase-H2O2-halide system in immune complex nephritis. Kidney Int. 1987 Sep;32(3):342–349. doi: 10.1038/ki.1987.215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasinath B. S., Maaba M. R., Schwartz M. M., Lewis E. J. Demonstration and characterization of C3 receptors on rat glomerular epithelial cells. Kidney Int. 1986 Dec;30(6):852–861. doi: 10.1038/ki.1986.265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kazatchkine M. D., Fearon D. T., Appay M. D., Mandet C., Bariety J. Immunohistochemical study of the human glomerular C3b receptor in normal kidney and in seventy-five cases of renal diseases: loss of C3b receptor antigen in focal hyalinosis and in proliferative nephritis of systemic lupus erythematosus. J Clin Invest. 1982 Apr;69(4):900–912. doi: 10.1172/JCI110529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerjaschki D., Schulze M., Binder S., Kain R., Ojha P. P., Susani M., Horvat R., Baker P. J., Couser W. G. Transcellular transport and membrane insertion of the C5b-9 membrane attack complex of complement by glomerular epithelial cells in experimental membranous nephropathy. J Immunol. 1989 Jul 15;143(2):546–552. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kusunoki Y., Itami N., Tochimaru H., Takekoshi Y., Nagasawa S., Yoshiki T. Glomerular deposition of C4 cleavage fragment (C4d) and C4-binding protein in idiopathic membranous glomerulonephritis. Nephron. 1989;51(1):17–19. doi: 10.1159/000185234. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makker S. P., Kanalas J. J. Course of transplanted Heymann nephritis kidney in normal host. Implications for mechanism of proteinuria in membranous glomerulonephropathy. J Immunol. 1989 May 15;142(10):3406–3410. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mancini G., Carbonara A. O., Heremans J. F. Immunochemical quantitation of antigens by single radial immunodiffusion. Immunochemistry. 1965 Sep;2(3):235–254. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(65)90004-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Med M. Prenatal development of thoracic intervertebral articulation. Folia Morphol (Praha) 1977;25(2):175–177. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mollnes T. E., Lachmann P. J. Regulation of complement. Scand J Immunol. 1988 Feb;27(2):127–142. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1988.tb02331.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pangburn M. K., Müller-Eberhard H. J. The C3 convertase of the alternative pathway of human complement. Enzymic properties of the bimolecular proteinase. Biochem J. 1986 May 1;235(3):723–730. doi: 10.1042/bj2350723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierides A. M., Malasit P., Morley A. R., Willkinson R., Uldall P. R., Kerr D. N. Idiopathic membranous nephropathy. Q J Med. 1977 Apr;46(182):163–177. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pruchno C. J., Burns M. M., Schulze M., Johnson R. J., Baker P. J., Alpers C. E., Couser W. G. Urinary excretion of the C5b-9 membrane attack complex of complement is a marker of immune disease activity in autologous immune complex nephritis. Am J Pathol. 1991 Jan;138(1):203–211. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pruchno C. J., Burns M. W., Schulze M., Johnson R. J., Baker P. J., Couser W. G. Urinary excretion of C5b-9 reflects disease activity in passive Heymann nephritis. Kidney Int. 1989 Jul;36(1):65–71. doi: 10.1038/ki.1989.162. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quigg R. J., Cybulsky A. V., Salant D. J. Effect of nephritogenic antibody on complement regulation in cultured rat glomerular epithelial cells. J Immunol. 1991 Aug 1;147(3):838–845. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rauterberg E. W., Lieberknecht H. M., Wingen A. M., Ritz E. Complement membrane attack (MAC) in idiopathic IgA-glomerulonephritis. Kidney Int. 1987 Mar;31(3):820–829. doi: 10.1038/ki.1987.72. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts J. L., Wyatt R. J., Schwartz M. M., Lewis E. J. Differential characteristics of immune-bound antibodies in diffuse proliferative and membranous forms of lupus glomerulonephritis. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1983 Nov;29(2):223–241. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(83)90026-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salant D. J., Darby C., Couser W. G. Experimental membranous glomerulonephritis in rats. Quantitative studies of glomerular immune deposit formation in isolated glomeruli and whole animals. J Clin Invest. 1980 Jul;66(1):71–81. doi: 10.1172/JCI109837. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulze M., Baker P. J., Perkinson D. T., Johnson R. J., Ochi R. F., Stahl R. A., Couser W. G. Increased urinary excretion of C5b-9 distinguishes passive Heymann nephritis in the rat. Kidney Int. 1989 Jan;35(1):60–68. doi: 10.1038/ki.1989.8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulze M., Donadio J. V., Jr, Pruchno C. J., Baker P. J., Johnson R. J., Stahl R. A., Watkins S., Martin D. C., Wurzner R., Gotze O. Elevated urinary excretion of the C5b-9 complex in membranous nephropathy. Kidney Int. 1991 Sep;40(3):533–538. doi: 10.1038/ki.1991.242. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tack B. F. The beta-Cys-gamma-Glu thiolester bond in human C3, C4, and alpha 2-macroglobulin. Springer Semin Immunopathol. 1983;6(4):259–282. doi: 10.1007/BF02116276. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vedeler C. A., Matre R., Iversen B. M. Glomerular CR1 express in situ cofactor activity for degradation of C3b. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1990;92(1):60–63. doi: 10.1159/000235225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]