Abstract
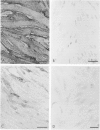
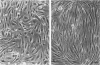
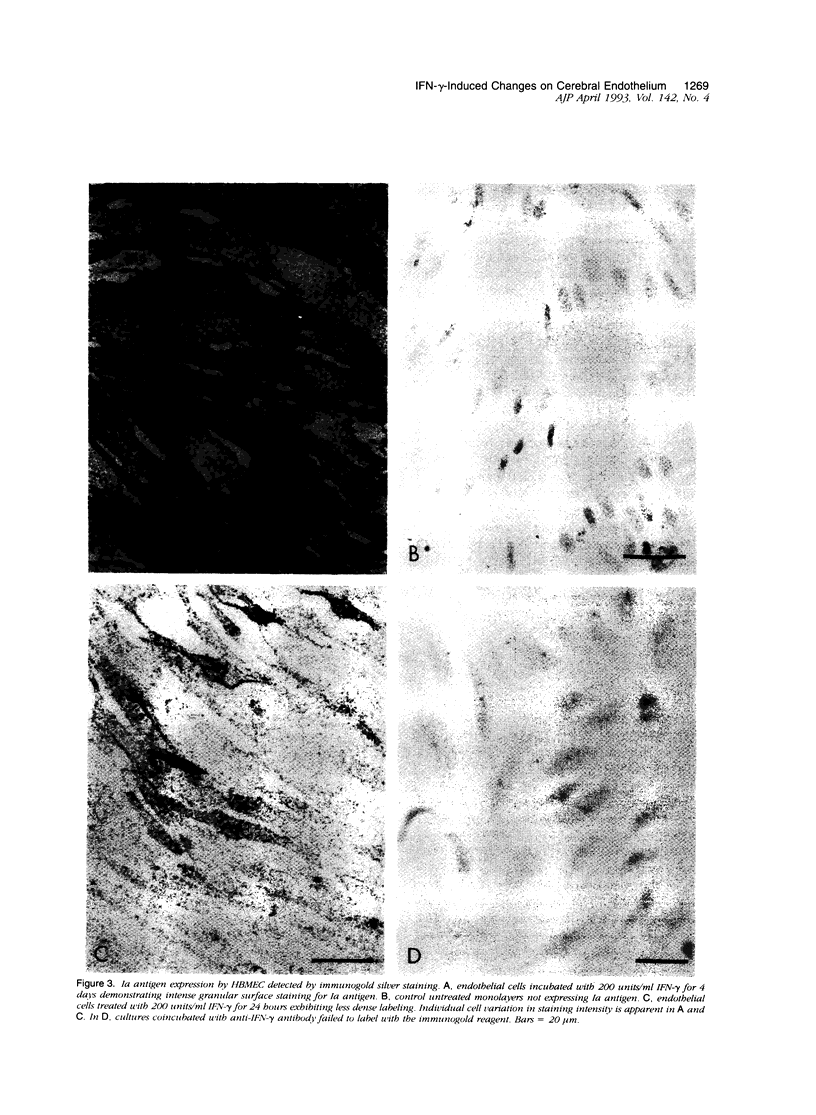
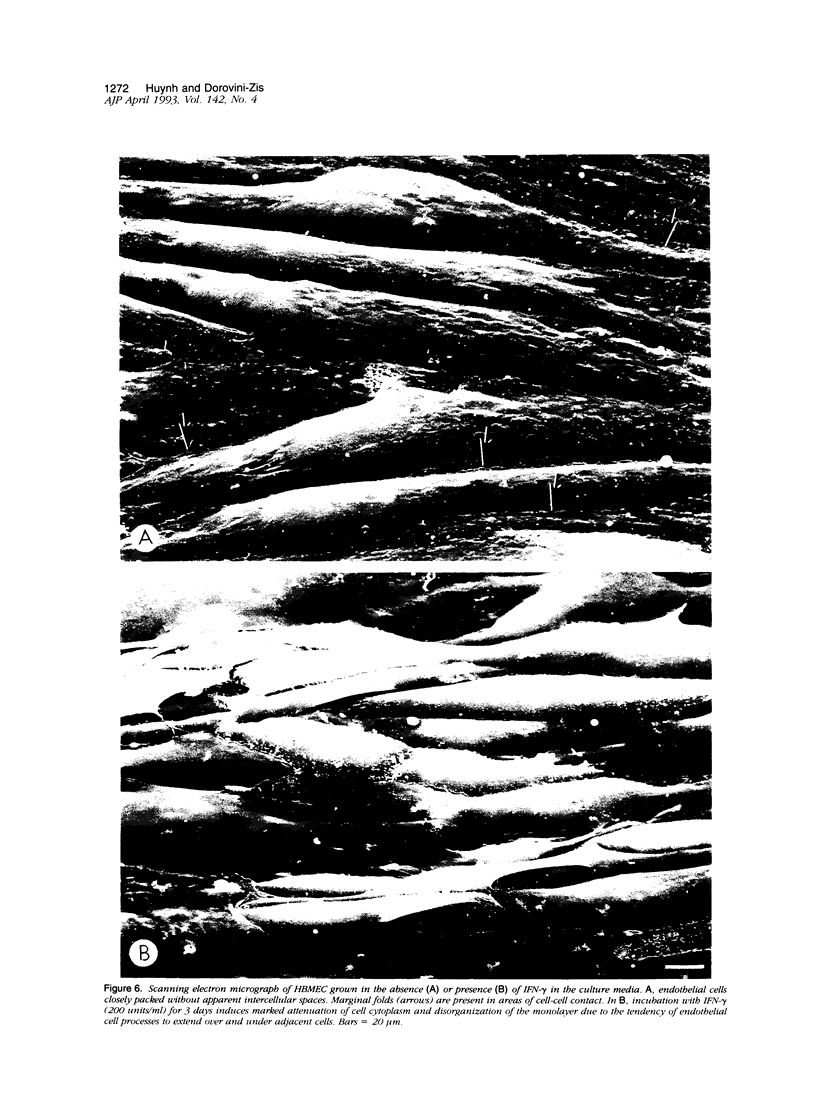
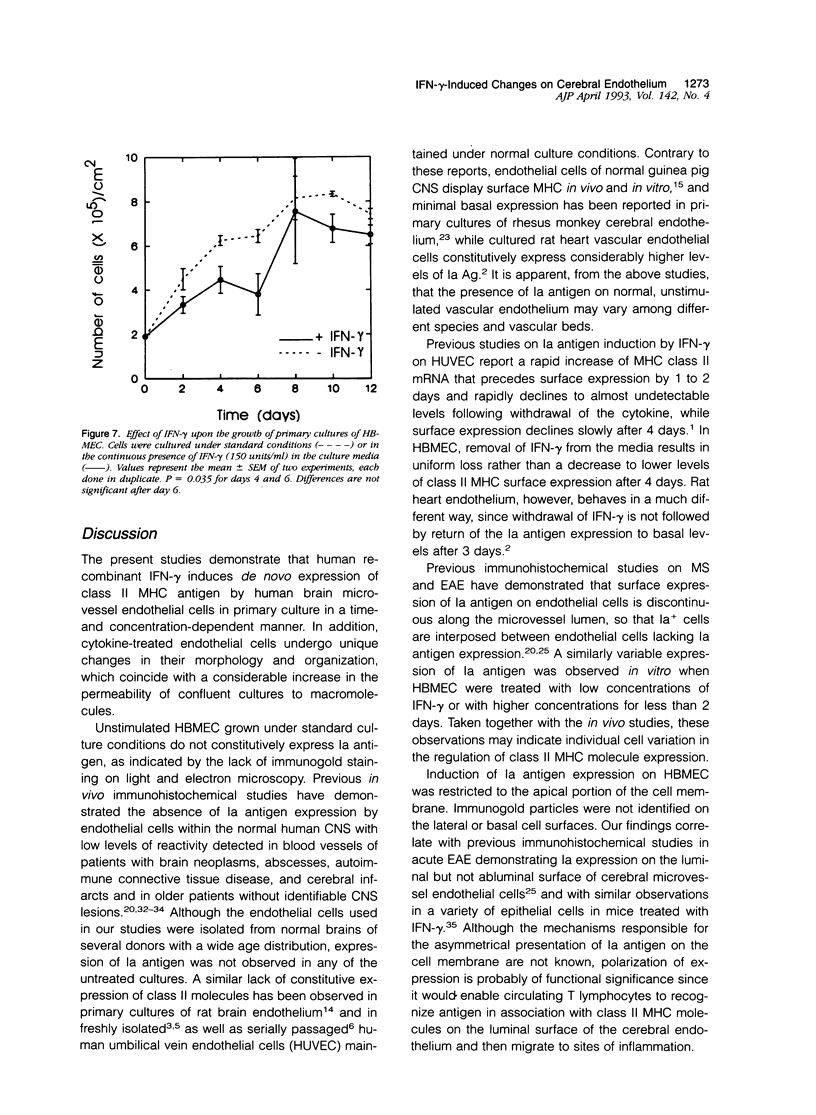
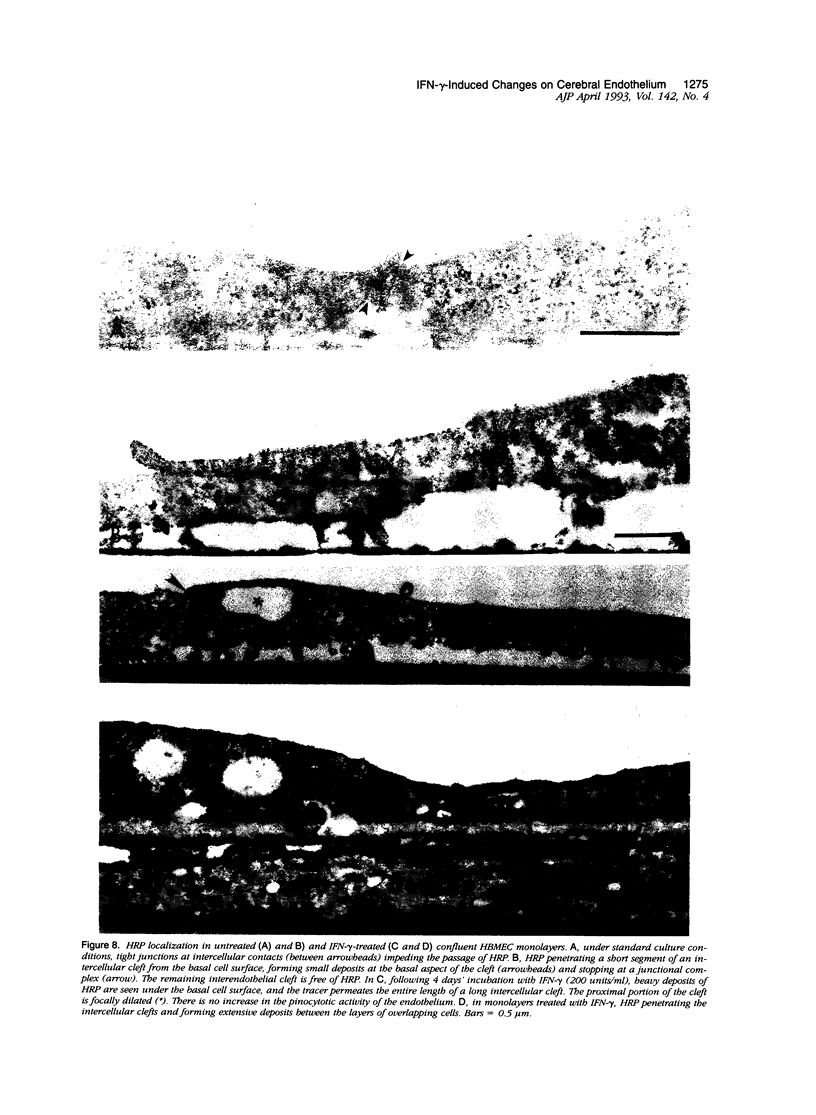
Primary cultures of human brain microvessel endothelial cells were used to study the effects of human recombinant interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma) on cerebral endothelium in vitro. Incubation of monolayers with various concentrations of IFN-gamma (10 to 200 U/ml) for 12 to 96 hours induced surface expression of class II major histocompatibility complex (Ia) antigen in a time- and concentration-dependent manner. In immunogold-stained cultures, labeling was observed as early as 12 hours, was maximal after 48 hours, and persisted at plateau levels in the continuous presence of the cytokine. Expression was blocked by coincubation with anti-IFN-gamma antibody and was reversed 4 days following removal of IFN-gamma from the culture media. Endothelial cells treated with IFN-gamma for 3 to 4 days became spindle-shaped, extensively overlapped, and frequently formed cellular whorls. These changes did not occur in the presence of anti-IFN-gamma antibody and reversed upon removal of IFN-gamma from the media. The morphological alterations were associated with increased permeability of confluent monolayers to macromolecules as compared with untreated cultures. The results of these studies indicate that human brain microvessel endothelial cells respond to in vitro cytokine stimulation by undergoing profound morphological, functional, and permeability changes. We conclude that cerebral endothelium may play an important role in the initiation and regulation of lymphocyte traffic across the blood-brain barrier in inflammatory disorders of the human central nervous system.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beilke M. A., Riding In D., Hamilton R., Stone G. A., Jordan E. K., Brashears G., Nusbaum W., Huddleston D., Gibbs C. J., Jr, Gravell M. HLA-DR expression in macaque neuroendothelial cells in vitro and during SIV encephalitis. J Neuroimmunol. 1991 Aug;33(2):129–143. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(91)90057-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brett J., Gerlach H., Nawroth P., Steinberg S., Godman G., Stern D. Tumor necrosis factor/cachectin increases permeability of endothelial cell monolayers by a mechanism involving regulatory G proteins. J Exp Med. 1989 Jun 1;169(6):1977–1991. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.6.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butter C., O'Neill J. K., Baker D., Gschmeissner S. E., Turk J. L. An immunoelectron microscopical study of the expression of class II major histocompatibility complex during chronic relapsing experimental allergic encephalomyelitis in Biozzi AB/H mice. J Neuroimmunol. 1991 Jul;33(1):37–42. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(91)90032-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Claudio L., Kress Y., Factor J., Brosnan C. F. Mechanisms of edema formation in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. The contribution of inflammatory cells. Am J Pathol. 1990 Nov;137(5):1033–1045. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins T., Korman A. J., Wake C. T., Boss J. M., Kappes D. J., Fiers W., Ault K. A., Gimbrone M. A., Jr, Strominger J. L., Pober J. S. Immune interferon activates multiple class II major histocompatibility complex genes and the associated invariant chain gene in human endothelial cells and dermal fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(15):4917–4921. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.15.4917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craggs R. I., Webster H. D. Ia antigens in the normal rat nervous system and in lesions of experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. Acta Neuropathol. 1985;68(4):263–272. doi: 10.1007/BF00690828. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorovini-Zis K., Bowman P. D., Betz A. L., Goldstein G. W. Hyperosmotic urea reversibly opens the tight junctions between brain capillary endothelial cells in cell culture. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1987 Mar;46(2):130–140. doi: 10.1097/00005072-198703000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorovini-Zis K., Prameya R., Bowman P. D. Culture and characterization of microvascular endothelial cells derived from human brain. Lab Invest. 1991 Mar;64(3):425–436. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabry Z., Waldschmidt M. M., Moore S. A., Hart M. N. Antigen presentation by brain microvessel smooth muscle and endothelium. J Neuroimmunol. 1990 Jun;28(1):63–71. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(90)90041-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferry B., Halttunen J., Leszczynski D., Schellekens H., vd Meide P. H., Häyry P. Impact of class II major histocompatibility complex antigen expression on the immunogenic potential of isolated rat vascular endothelial cells. Transplantation. 1987 Oct;44(4):499–503. doi: 10.1097/00007890-198710000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank E., Pulver M., de Tribolet N. Expression of class II major histocompatibility antigens on reactive astrocytes and endothelial cells within the gliosis surrounding metastases and abscesses. J Neuroimmunol. 1986 Jul;12(1):29–36. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(86)90094-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friesel R., Komoriya A., Maciag T. Inhibition of endothelial cell proliferation by gamma-interferon. J Cell Biol. 1987 Mar;104(3):689–696. doi: 10.1083/jcb.104.3.689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haskard D. O., Cavender D., Fleck R. M., Sontheimer R., Ziff M. Human dermal microvascular endothelial cells behave like umbilical vein endothelial cells in T-cell adhesion studies. J Invest Dermatol. 1987 Mar;88(3):340–344. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12466229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heyns A. D., Eldor A., Vlodavsky I., Kaiser N., Fridman R., Panet A. The antiproliferative effect of interferon and the mitogenic activity of growth factors are independent cell cycle events. Studies with vascular smooth muscle cells and endothelial cells. Exp Cell Res. 1985 Dec;161(2):297–306. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(85)90087-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirano A., Dembitzer H. M., Becker N. H., Levine S., Zimmerman H. M. Fine structural alterations of the blood-brain barrier in experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1970 Jul;29(3):432–440. doi: 10.1097/00005072-197007000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Issekutz T. B. Effects of six different cytokines on lymphocyte adherence to microvascular endothelium and in vivo lymphocyte migration in the rat. J Immunol. 1990 Mar 15;144(6):2140–2146. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Juhler M., Barry D. I., Offner H., Konat G., Klinken L., Paulson O. B. Blood-brain and blood-spinal cord barrier permeability during the course of experimental allergic encephalomyelitis in the rat. Brain Res. 1984 Jun 8;302(2):347–355. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(84)90249-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kajiwara K., Hirozane A., Fukumoto T., Orita T., Nishizaki T., Kamiryo T., Ito H. Major histocompatibility complex expression in brain of rats with graft-versus-host disease. J Neuroimmunol. 1991 Jun;32(3):191–198. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(91)90188-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kristensson K., Wiśniewski H. M. Chronic relapsing experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. Studies in vascular permeability changes. Acta Neuropathol. 1977 Aug 31;39(3):189–194. doi: 10.1007/BF00691696. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lampson L. A., Hickey W. F. Monoclonal antibody analysis of MHC expression in human brain biopsies: tissue ranging from "histologically normal" to that showing different levels of glial tumor involvement. J Immunol. 1986 Jun 1;136(11):4054–4062. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maheshwari R. K., Srikantan V., Bhartiya D., Kleinman H. K., Grant D. S. Differential effects of interferon gamma and alpha on in vitro model of angiogenesis. J Cell Physiol. 1991 Jan;146(1):164–169. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041460121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Male D. K., Pryce G., Hughes C. C. Antigen presentation in brain: MHC induction on brain endothelium and astrocytes compared. Immunology. 1987 Mar;60(3):453–459. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masuyama J., Minato N., Kano S. Mechanisms of lymphocyte adhesion to human vascular endothelial cells in culture. T lymphocyte adhesion to endothelial cells through endothelial HLA-DR antigens induced by gamma interferon. J Clin Invest. 1986 May;77(5):1596–1605. doi: 10.1172/JCI112475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarron R. M., Kempski O., Spatz M., McFarlin D. E. Presentation of myelin basic protein by murine cerebral vascular endothelial cells. J Immunol. 1985 May;134(5):3100–3103. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarron R. M., Spatz M., Kempski O., Hogan R. N., Muehl L., McFarlin D. E. Interaction between myelin basic protein-sensitized T lymphocytes and murine cerebral vascular endothelial cells. J Immunol. 1986 Dec 1;137(11):3428–3435. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLean I. W., Nakane P. K. Periodate-lysine-paraformaldehyde fixative. A new fixation for immunoelectron microscopy. J Histochem Cytochem. 1974 Dec;22(12):1077–1083. doi: 10.1177/22.12.1077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messadi D. V., Pober J. S., Murphy G. F. Effects of recombinant gamma-interferon on HLA-DR and DQ expression by skin cells in short-term organ culture. Lab Invest. 1988 Jan;58(1):61–67. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munro J. M., Pober J. S., Cotran R. S. Tumor necrosis factor and interferon-gamma induce distinct patterns of endothelial activation and associated leukocyte accumulation in skin of Papio anubis. Am J Pathol. 1989 Jul;135(1):121–133. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oppenheimer-Marks N., Ziff M. Migration of lymphocytes through endothelial cell monolayers: augmentation by interferon-gamma. Cell Immunol. 1988 Jul;114(2):307–323. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(88)90324-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pober J. S., Collins T., Gimbrone M. A., Jr, Cotran R. S., Gitlin J. D., Fiers W., Clayberger C., Krensky A. M., Burakoff S. J., Reiss C. S. Lymphocytes recognize human vascular endothelial and dermal fibroblast Ia antigens induced by recombinant immune interferon. Nature. 1983 Oct 20;305(5936):726–729. doi: 10.1038/305726a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pober J. S., Gimbrone M. A., Jr, Cotran R. S., Reiss C. S., Burakoff S. J., Fiers W., Ault K. A. Ia expression by vascular endothelium is inducible by activated T cells and by human gamma interferon. J Exp Med. 1983 Apr 1;157(4):1339–1353. doi: 10.1084/jem.157.4.1339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pober J. S., Gimbrone M. A., Jr Expression of Ia-like antigens by human vascular endothelial cells is inducible in vitro: demonstration by monoclonal antibody binding and immunoprecipitation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(21):6641–6645. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.21.6641. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pryce G., Male D., Sedgwick J. Antigen presentation in brain: brain endothelial cells are poor stimulators of T-cell proliferation. Immunology. 1989 Feb;66(2):207–212. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruszczak Z., Detmar M., Imcke E., Orfanos C. E. Effects of rIFN alpha, beta, and gamma on the morphology, proliferation, and cell surface antigen expression of human dermal microvascular endothelial cells in vitro. J Invest Dermatol. 1990 Dec;95(6):693–699. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12514496. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saegusa Y., Ziff M., Welkovich L., Cavender D. Effect of inflammatory cytokines on human endothelial cell proliferation. J Cell Physiol. 1990 Mar;142(3):488–495. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041420307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakai K., Tabira T., Endoh M., Steinman L. Ia expression in chronic relapsing experimental allergic encephalomyelitis induced by long-term cultured T cell lines in mice. Lab Invest. 1986 Mar;54(3):345–352. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sethna M. P., Lampson L. A. Immune modulation within the brain: recruitment of inflammatory cells and increased major histocompatibility antigen expression following intracerebral injection of interferon-gamma. J Neuroimmunol. 1991 Nov;34(2-3):121–132. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(91)90121-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skoskiewicz M. J., Colvin R. B., Schneeberger E. E., Russell P. S. Widespread and selective induction of major histocompatibility complex-determined antigens in vivo by gamma interferon. J Exp Med. 1985 Nov 1;162(5):1645–1664. doi: 10.1084/jem.162.5.1645. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobel R. A., Ames M. B. Major histocompatibility complex molecule expression in the human central nervous system: immunohistochemical analysis of 40 patients. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1988 Jan;47(1):19–28. doi: 10.1097/00005072-198801000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobel R. A., Natale J. M., Schneeberger E. E. The immunopathology of acute experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. IV. An ultrastructural immunocytochemical study of class II major histocompatibility complex molecule (Ia) expression. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1987 May;46(3):239–249. doi: 10.1097/00005072-198705000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stolpen A. H., Guinan E. C., Fiers W., Pober J. S. Recombinant tumor necrosis factor and immune interferon act singly and in combination to reorganize human vascular endothelial cell monolayers. Am J Pathol. 1986 Apr;123(1):16–24. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thornhill M. H., Kyan-Aung U., Lee T. H., Haskard D. O. T cells and neutrophils exhibit differential adhesion to cytokine-stimulated endothelial cells. Immunology. 1990 Feb;69(2):287–292. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traugott U., Raine C. S. Multiple sclerosis. Evidence for antigen presentation in situ by endothelial cells and astrocytes. J Neurol Sci. 1985 Jul;69(3):365–370. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(85)90147-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traugott U., Scheinberg L. C., Raine C. S. On the presence of Ia-positive endothelial cells and astrocytes in multiple sclerosis lesions and its relevance to antigen presentation. J Neuroimmunol. 1985 Apr;8(1):1–14. doi: 10.1016/s0165-5728(85)80043-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuruoka N., Sugiyama M., Tawaragi Y., Tsujimoto M., Nishihara T., Goto T., Sato N. Inhibition of in vitro angiogenesis by lymphotoxin and interferon-gamma. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Aug 30;155(1):429–435. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)81104-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vass K., Lassmann H., Wekerle H., Wisniewski H. M. The distribution of Ia antigen in the lesions of rat acute experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. Acta Neuropathol. 1986;70(2):149–160. doi: 10.1007/BF00691433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner C. R., Vetto R. M., Burger D. R. Expression of I-region-associated antigen (Ia) and interleukin 1 by subcultured human endothelial cells. Cell Immunol. 1985 Jun;93(1):91–104. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(85)90391-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilcox C. E., Baker D., Butter C., Willoughby D. A., Turk J. L. Differential expression of guinea pig class II major histocompatibility complex antigens on vascular endothelial cells in vitro and in experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. Cell Immunol. 1989 Apr 15;120(1):82–91. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(89)90176-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]