Abstract
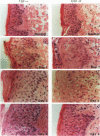
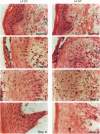
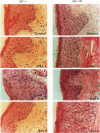
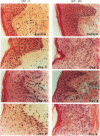
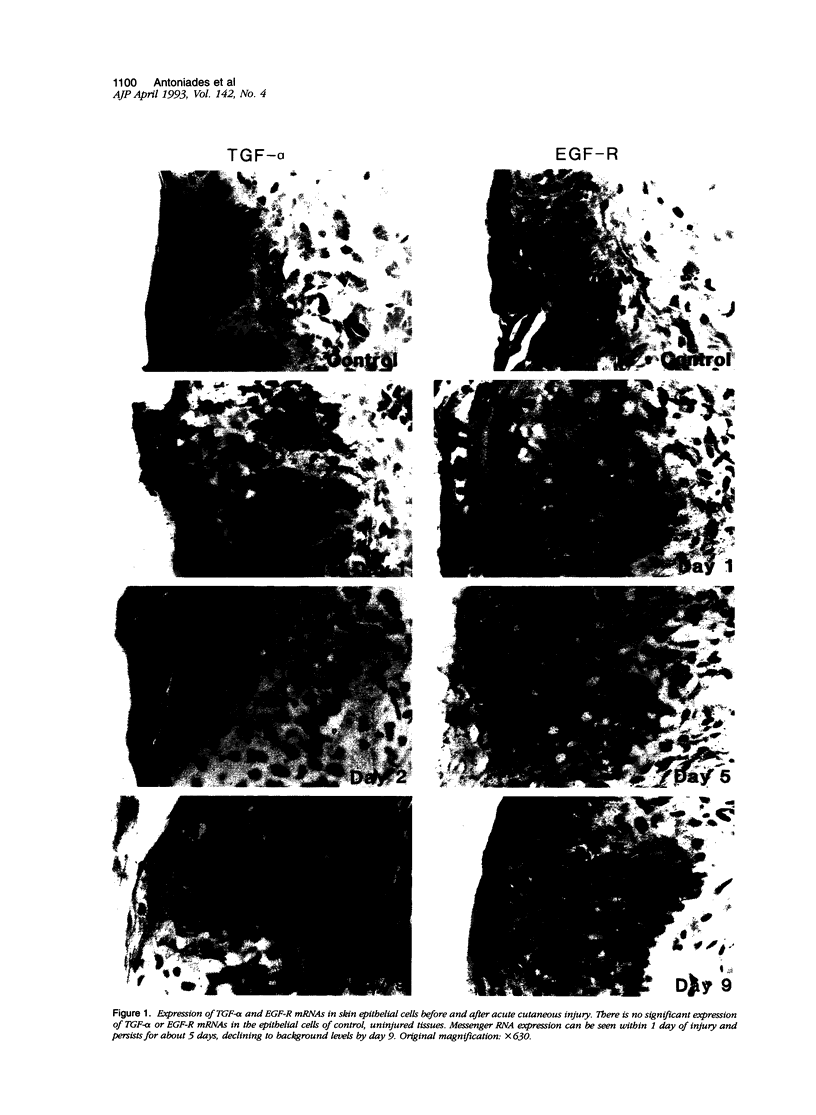
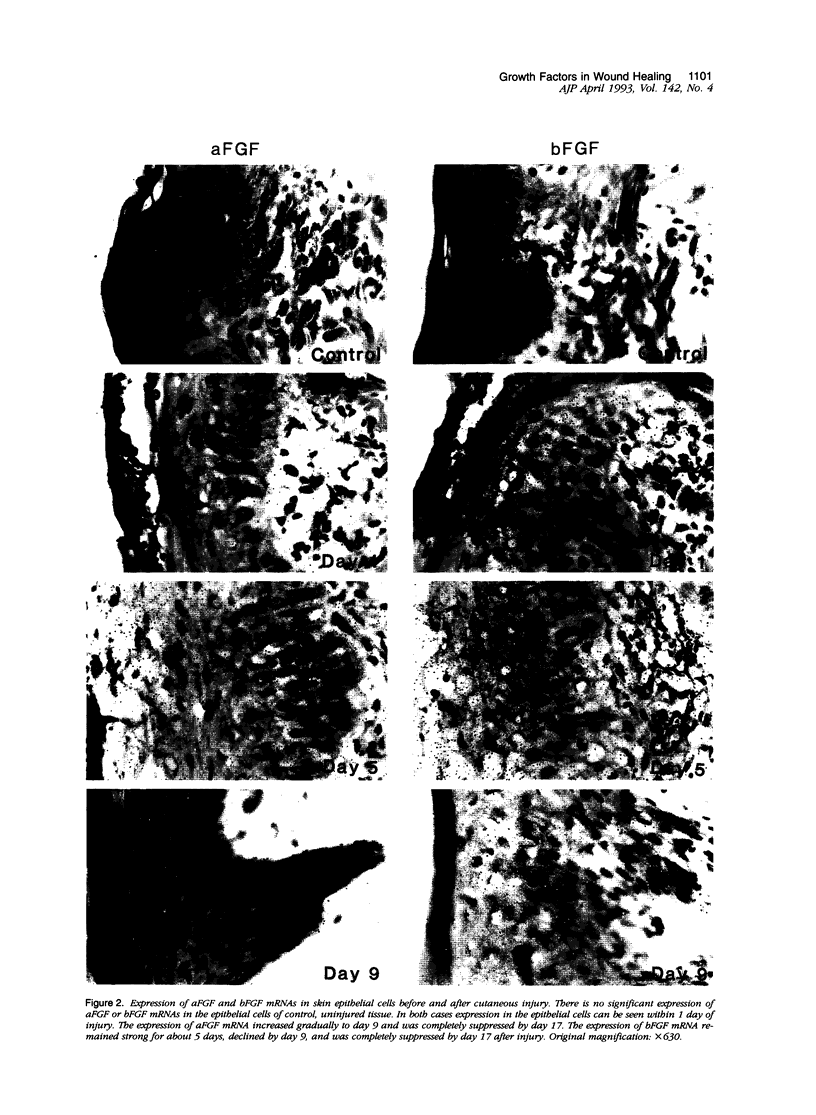
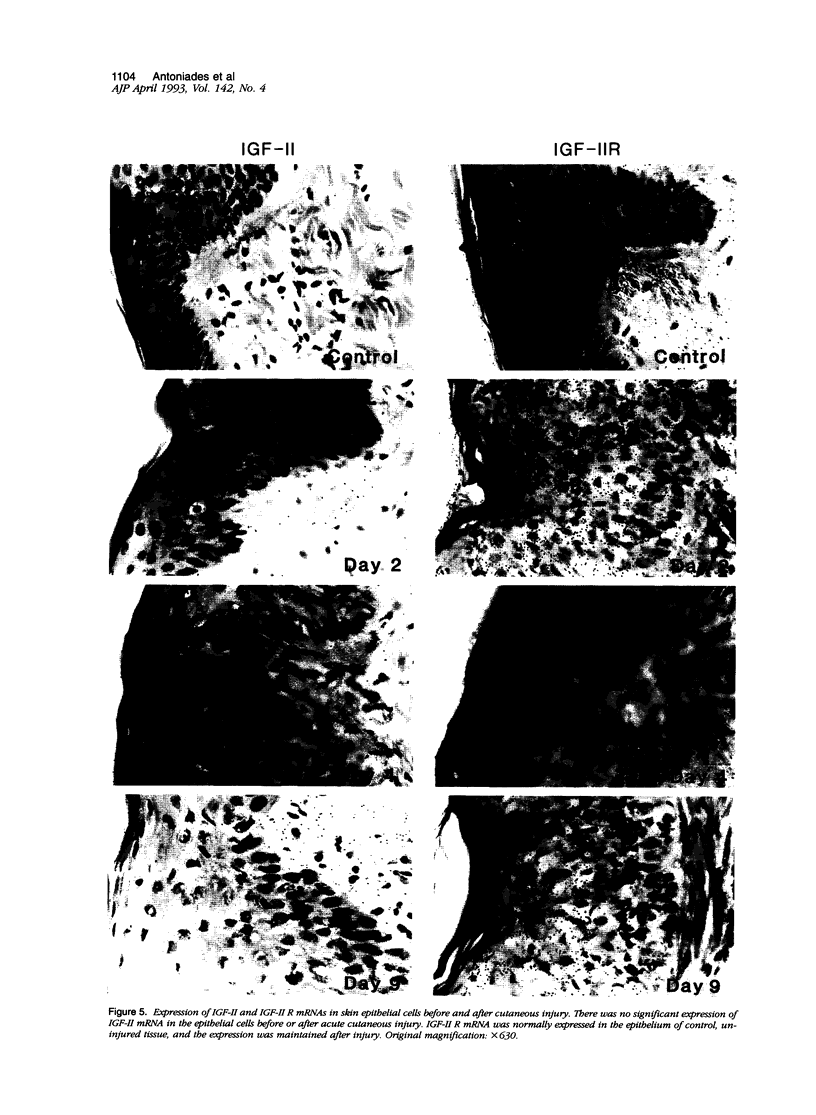
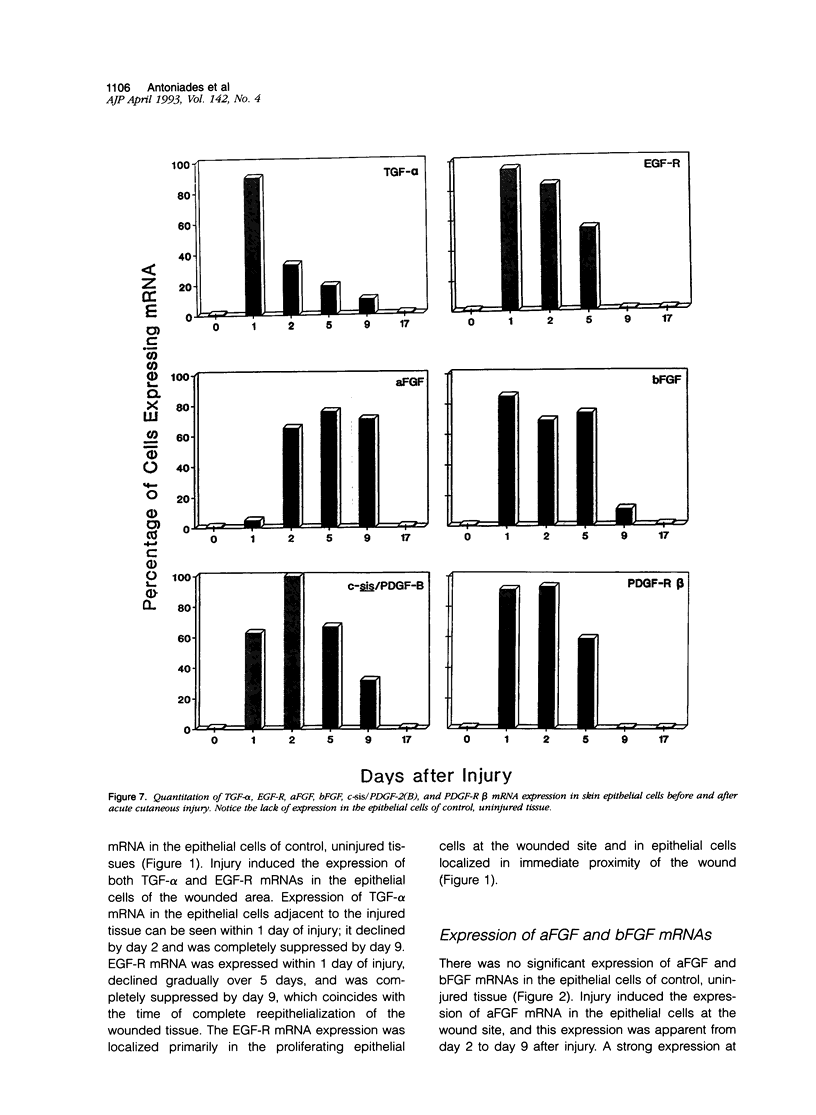
We report that acute injury induces the expression of selective growth factor and growth factor receptors in the epithelial cells of the wounded tissue. In situ hybridization analysis of skin biopsy specimens obtained after cutaneous injury in swine demonstrated the induction of the expression of transforming growth factor-alpha, its receptor, epidermal growth factor-R, acidic fibroblast growth factor, and basic fibroblast growth factor messenger RNAs in the skin epithelial cells of the wounded tissue. There was no significant expression in the epithelial cells of control, uninjured tissues. The expression levels were maximal during the period of active tissue repair (1 to 5 days after injury) and were totally suppressed upon the healing of the wounded tissues. In contrast, insulinlike growth factor-I, (IGF-I), IGF-I receptor, and IGF-II receptor messenger RNAs were expressed in the epithelial cells of both the control, uninjured tissues and in tissue specimens obtained after injury. There was no significant expression of IGF-II messenger RNA in the epithelial cells before or after injury. It seems that injury induces the coordinated expression of selective growth factor and growth factor receptor genes whose products contribute to the regulation of the complex processes involved in tissue repair and remodeling.
Full text
PDF



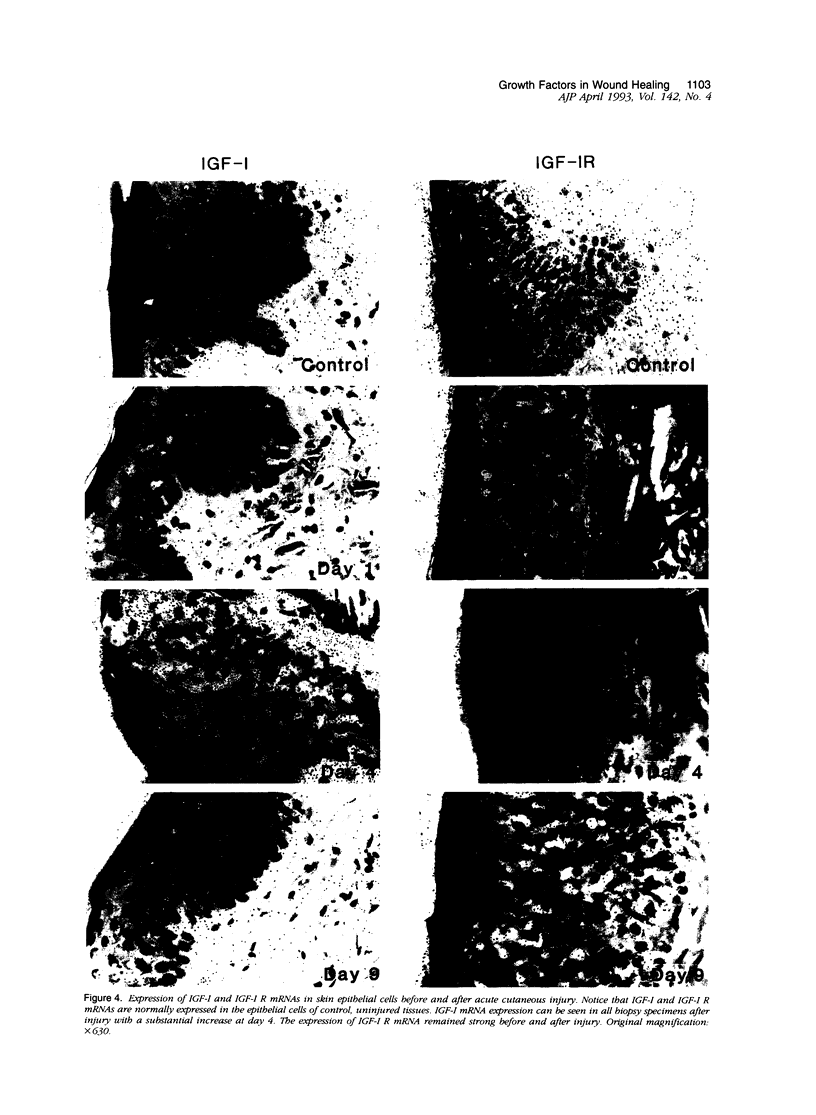




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abraham J. A., Mergia A., Whang J. L., Tumolo A., Friedman J., Hjerrild K. A., Gospodarowicz D., Fiddes J. C. Nucleotide sequence of a bovine clone encoding the angiogenic protein, basic fibroblast growth factor. Science. 1986 Aug 1;233(4763):545–548. doi: 10.1126/science.2425435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alvarez O. M., Mertz P. M., Eaglstein W. H. The effect of the proline analogue l-azetidine-2-carboxylic acid (LACA) on epidermal and dermal wound repair. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1982 Feb;69(2):284–289. doi: 10.1097/00006534-198202000-00018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Antoniades H. N., Bravo M. A., Avila R. E., Galanopoulos T., Neville-Golden J., Maxwell M., Selman M. Platelet-derived growth factor in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. J Clin Invest. 1990 Oct;86(4):1055–1064. doi: 10.1172/JCI114808. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Antoniades H. N., Galanopoulos T., Neville-Golden J., Kiritsy C. P., Lynch S. E. Injury induces in vivo expression of platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) and PDGF receptor mRNAs in skin epithelial cells and PDGF mRNA in connective tissue fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jan 15;88(2):565–569. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.2.565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Antoniades H. N., Galanopoulos T., Neville-Golden J., Maxwell M. Expression of insulin-like growth factors I and II and their receptor mRNAs in primary human astrocytomas and meningiomas; in vivo studies using in situ hybridization and immunocytochemistry. Int J Cancer. 1992 Jan 21;50(2):215–222. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910500210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Antoniades H. N., Galanopoulos T., Neville-Golden J., O'Hara C. J. Malignant epithelial cells in primary human lung carcinomas coexpress in vivo platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) and PDGF receptor mRNAs and their protein products. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 May 1;89(9):3942–3946. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.9.3942. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Antoniades H. N. Linking cellular injury to gene expression and human proliferative disorders: examples with the PDGF genes. Mol Carcinog. 1992;6(3):175–181. doi: 10.1002/mc.2940060302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Antoniades H. N. PDGF: a multifunctional growth factor. Baillieres Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1991 Dec;5(4):595–613. doi: 10.1016/s0950-351x(10)80005-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess W. H., Mehlman T., Friesel R., Johnson W. V., Maciag T. Multiple forms of endothelial cell growth factor. Rapid isolation and biological and chemical characterization. J Biol Chem. 1985 Sep 25;260(21):11389–11392. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derynck R., Goeddel D. V., Ullrich A., Gutterman J. U., Williams R. D., Bringman T. S., Berger W. H. Synthesis of messenger RNAs for transforming growth factors alpha and beta and the epidermal growth factor receptor by human tumors. Cancer Res. 1987 Feb 1;47(3):707–712. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derynck R. Transforming growth factor alpha. Cell. 1988 Aug 26;54(5):593–595. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)80001-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esch F., Baird A., Ling N., Ueno N., Hill F., Denoroy L., Klepper R., Gospodarowicz D., Böhlen P., Guillemin R. Primary structure of bovine pituitary basic fibroblast growth factor (FGF) and comparison with the amino-terminal sequence of bovine brain acidic FGF. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(19):6507–6511. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.19.6507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golden M. A., Au Y. P., Kenagy R. D., Clowes A. W. Growth factor gene expression by intimal cells in healing polytetrafluoroethylene grafts. J Vasc Surg. 1990 Apr;11(4):580–585. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gospodarowicz D. Isolation and characterization of acidic and basic fibroblast growth factor. Methods Enzymol. 1987;147:106–119. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)47102-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenhalgh D. G., Sprugel K. H., Murray M. J., Ross R. PDGF and FGF stimulate wound healing in the genetically diabetic mouse. Am J Pathol. 1990 Jun;136(6):1235–1246. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grotendorst G. R., Grotendorst C. A., Gilman T. Production of growth factors (PDGF & TGF-beta) at the site of tissue repair. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1988;266:47–54. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grotendorst G. R., Martin G. R., Pencev D., Sodek J., Harvey A. K. Stimulation of granulation tissue formation by platelet-derived growth factor in normal and diabetic rats. J Clin Invest. 1985 Dec;76(6):2323–2329. doi: 10.1172/JCI112243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grotendorst G. R., Soma Y., Takehara K., Charette M. EGF and TGF-alpha are potent chemoattractants for endothelial cells and EGF-like peptides are present at sites of tissue regeneration. J Cell Physiol. 1989 Jun;139(3):617–623. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041390323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansson H. A., Jennische E., Skottner A. Regenerating endothelial cells express insulin-like growth factor-I immunoreactivity after arterial injury. Cell Tissue Res. 1987 Dec;250(3):499–505. doi: 10.1007/BF00218940. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansson H. A., Jonsson R., Petruson K. Transiently increased insulin-like growth factor. I. Immunoreactivity in UVB-irradiated mouse skin. J Invest Dermatol. 1988 Oct;91(4):328–332. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12475660. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoefler H., Childers H., Montminy M. R., Lechan R. M., Goodman R. H., Wolfe H. J. In situ hybridization methods for the detection of somatostatin mRNA in tissue sections using antisense RNA probes. Histochem J. 1986 Nov-Dec;18(11-12):597–604. doi: 10.1007/BF01675295. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irminger J. C., Rosen K. M., Humbel R. E., Villa-Komaroff L. Tissue-specific expression of insulin-like growth factor II mRNAs with distinct 5' untranslated regions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Sep;84(18):6330–6334. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.18.6330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaye M., Howk R., Burgess W., Ricca G. A., Chiu I. M., Ravera M. W., O'Brien S. J., Modi W. S., Maciag T., Drohan W. N. Human endothelial cell growth factor: cloning, nucleotide sequence, and chromosome localization. Science. 1986 Aug 1;233(4763):541–545. doi: 10.1126/science.3523756. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jennische E., Skottner A., Hansson H. A. Dynamic changes in insulin-like growth factor I immunoreactivity correlate to repair events in rat ear after freeze-thaw injury. Exp Mol Pathol. 1987 Oct;47(2):193–201. doi: 10.1016/0014-4800(87)90074-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klagsbrun M., Sasse J., Sullivan R., Smith J. A. Human tumor cells synthesize an endothelial cell growth factor that is structurally related to basic fibroblast growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(8):2448–2452. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.8.2448. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence W. T., Norton J. A., Sporn M. B., Gorschboth C., Grotendorst G. R. The reversal of an Adriamycin induced healing impairment with chemoattractants and growth factors. Ann Surg. 1986 Feb;203(2):142–147. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198602000-00006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee H., Hansson H. A., Norström E., Helander H. F. Immunoreactivities for epidermal growth factor (EGF) and for EGF receptors in rats with gastric ulcers. Cell Tissue Res. 1991 Aug;265(2):211–218. doi: 10.1007/BF00398069. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin C. R., Chen W. S., Lazar C. S., Carpenter C. D., Gill G. N., Evans R. M., Rosenfeld M. G. Protein kinase C phosphorylation at Thr 654 of the unoccupied EGF receptor and EGF binding regulate functional receptor loss by independent mechanisms. Cell. 1986 Mar 28;44(6):839–848. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90006-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lynch S. E., Colvin R. B., Antoniades H. N. Growth factors in wound healing. Single and synergistic effects on partial thickness porcine skin wounds. J Clin Invest. 1989 Aug;84(2):640–646. doi: 10.1172/JCI114210. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lynch S. E., Nixon J. C., Colvin R. B., Antoniades H. N. Role of platelet-derived growth factor in wound healing: synergistic effects with other growth factors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(21):7696–7700. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.21.7696. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maciag T., Mehlman T., Friesel R., Schreiber A. B. Heparin binds endothelial cell growth factor, the principal endothelial cell mitogen in bovine brain. Science. 1984 Aug 31;225(4665):932–935. doi: 10.1126/science.6382607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massagué J. Epidermal growth factor-like transforming growth factor. II. Interaction with epidermal growth factor receptors in human placenta membranes and A431 cells. J Biol Chem. 1983 Nov 25;258(22):13614–13620. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuoka J., Grotendorst G. R. Two peptides related to platelet-derived growth factor are present in human wound fluid. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jun;86(12):4416–4420. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.12.4416. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan D. O., Edman J. C., Standring D. N., Fried V. A., Smith M. C., Roth R. A., Rutter W. J. Insulin-like growth factor II receptor as a multifunctional binding protein. Nature. 1987 Sep 24;329(6137):301–307. doi: 10.1038/329301a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mustoe T. A., Pierce G. F., Thomason A., Gramates P., Sporn M. B., Deuel T. F. Accelerated healing of incisional wounds in rats induced by transforming growth factor-beta. Science. 1987 Sep 11;237(4820):1333–1336. doi: 10.1126/science.2442813. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierce G. F., Mustoe T. A., Senior R. M., Reed J., Griffin G. L., Thomason A., Deuel T. F. In vivo incisional wound healing augmented by platelet-derived growth factor and recombinant c-sis gene homodimeric proteins. J Exp Med. 1988 Mar 1;167(3):974–987. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.3.974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotwein P. Two insulin-like growth factor I messenger RNAs are expressed in human liver. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jan;83(1):77–81. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.1.77. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreiber A. B., Winkler M. E., Derynck R. Transforming growth factor-alpha: a more potent angiogenic mediator than epidermal growth factor. Science. 1986 Jun 6;232(4755):1250–1253. doi: 10.1126/science.2422759. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz G. S., White M., Mitchell R., Brown G., Lynch J., Twardzik D. R., Todaro G. J. Epithelial wound healing enhanced by transforming growth factor-alpha and vaccinia growth factor. Science. 1987 Jan 16;235(4786):350–352. doi: 10.1126/science.3492044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sporn M. B., Roberts A. B., Shull J. H., Smith J. M., Ward J. M., Sodek J. Polypeptide transforming growth factors isolated from bovine sources and used for wound healing in vivo. Science. 1983 Mar 18;219(4590):1329–1331. doi: 10.1126/science.6572416. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas K. A., Rios-Candelore M., Giménez-Gallego G., DiSalvo J., Bennett C., Rodkey J., Fitzpatrick S. Pure brain-derived acidic fibroblast growth factor is a potent angiogenic vascular endothelial cell mitogen with sequence homology to interleukin 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(19):6409–6413. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.19.6409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todaro G. J., Fryling C., De Larco J. E. Transforming growth factors produced by certain human tumor cells: polypeptides that interact with epidermal growth factor receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5258–5262. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5258. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich A., Gray A., Tam A. W., Yang-Feng T., Tsubokawa M., Collins C., Henzel W., Le Bon T., Kathuria S., Chen E. Insulin-like growth factor I receptor primary structure: comparison with insulin receptor suggests structural determinants that define functional specificity. EMBO J. 1986 Oct;5(10):2503–2512. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04528.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitby D. J., Ferguson M. W. Immunohistochemical localization of growth factors in fetal wound healing. Dev Biol. 1991 Sep;147(1):207–215. doi: 10.1016/s0012-1606(05)80018-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]