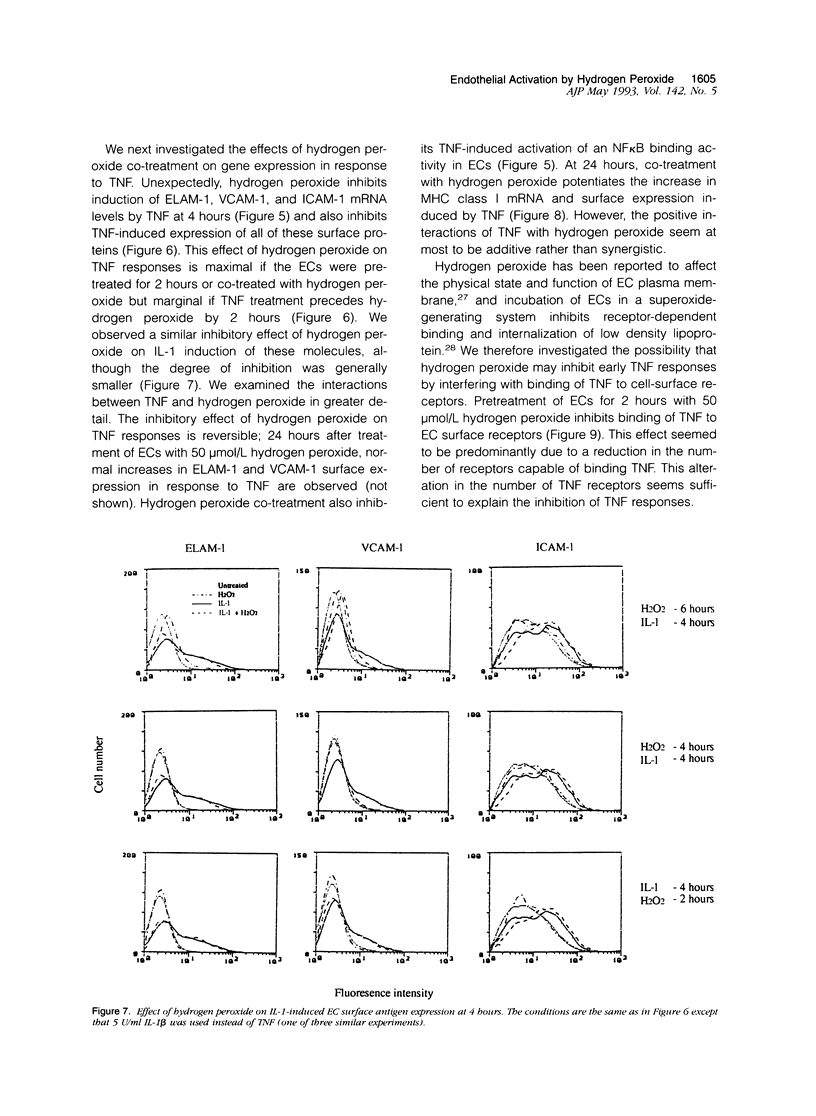
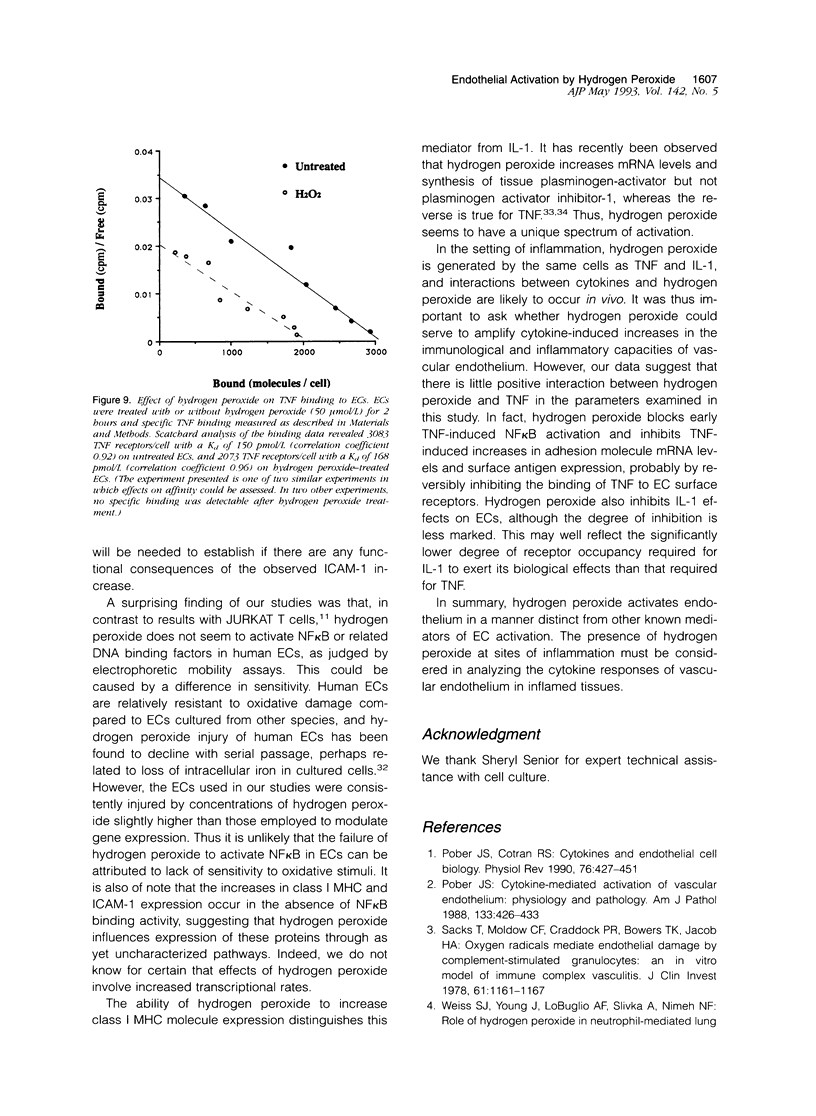
Abstract
Products of activated leukocytes may alter vascular endothelial cell (EC) function. For example, ECs respond to leukocyte-derived cytokines, such as tumor necrosis factor (TNF) or interleukin-1, by reversibly altering levels of expression of specific gene products that promote inflammation. In contrast, hydrogen peroxide, a product of TNF-activated neutrophils, can produce irreversible EC injury and death. In this study, we have investigated the effects of subinjurious concentrations of hydrogen peroxide on EC inflammatory functions. Treatment with 50 to 100 mumol/L hydrogen peroxide selectively increases surface expression of intercellular adhesion molecule-1 and major histocompatibility complex class I, but not endothelial leukocyte adhesion molecule-1 (also known as E-selectin), vascular cell adhesion molecule-1, or gp96, a constitutively expressed EC surface protein. Increased major histocompatibility complex class I and intercellular adhesion molecule-1 surface expression is associated with specifically increased messenger RNA levels, suggesting selective endothelial gene activation. Hydrogen peroxide does not activate the transcription factor Nuclear Factor kappa B, an important mediator of TNF-induced gene expression. Co-treatment with hydrogen peroxide inhibits TNF-induced gene expression at 4 hours, an effect which can be attributed to reversible inhibition of TNF binding to EC surface receptors. Hydrogen peroxide also antagonizes the actions of interleukin-1. At 24 hours, TNF and hydrogen peroxide produce, at most, additive increases in intercellular adhesion molecule-1 and major histocompatibility complex class I. These results suggest that subinjurious concentrations of hydrogen peroxide can activate endothelium and that the effects of hydrogen peroxide on ECs differ from those of inflammatory cytokines.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bevilacqua M. P., Stengelin S., Gimbrone M. A., Jr, Seed B. Endothelial leukocyte adhesion molecule 1: an inducible receptor for neutrophils related to complement regulatory proteins and lectins. Science. 1989 Mar 3;243(4895):1160–1165. doi: 10.1126/science.2466335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Block E. R. Hydrogen peroxide alters the physical state and function of the plasma membrane of pulmonary artery endothelial cells. J Cell Physiol. 1991 Mar;146(3):362–369. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041460305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brand A. H., Breeden L., Abraham J., Sternglanz R., Nasmyth K. Characterization of a "silencer" in yeast: a DNA sequence with properties opposite to those of a transcriptional enhancer. Cell. 1985 May;41(1):41–48. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90059-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cybulsky M. I., Fries J. W., Williams A. J., Sultan P., Eddy R., Byers M., Shows T., Gimbrone M. A., Jr, Collins T. Gene structure, chromosomal location, and basis for alternative mRNA splicing of the human VCAM1 gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Sep 1;88(17):7859–7863. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.17.7859. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dosne A. M., Dubor F., Lutcher F., Parant M., Chedid L. Tumor necrosis factor (TNF) stimulates plasminogen activator inhibitor (PAI) production by endothelial cells and decreases blood fibrinolytic activity in the rat. Thromb Res Suppl. 1988;8:115–122. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(88)90160-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doukas J., Pober J. S. IFN-gamma enhances endothelial activation induced by tumor necrosis factor but not IL-1. J Immunol. 1990 Sep 15;145(6):1727–1733. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gasic A. C., McGuire G., Krater S., Farhood A. I., Goldstein M. A., Smith C. W., Entman M. L., Taylor A. A. Hydrogen peroxide pretreatment of perfused canine vessels induces ICAM-1 and CD18-dependent neutrophil adherence. Circulation. 1991 Nov;84(5):2154–2166. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.84.5.2154. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gimbrone M. A., Jr Culture of vascular endothelium. Prog Hemost Thromb. 1976;3:1–28. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hohmann H. P., Brockhaus M., Baeuerle P. A., Remy R., Kolbeck R., van Loon A. P. Expression of the types A and B tumor necrosis factor (TNF) receptors is independently regulated, and both receptors mediate activation of the transcription factor NF-kappa B. TNF alpha is not needed for induction of a biological effect via TNF receptors. J Biol Chem. 1990 Dec 25;265(36):22409–22417. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hohmann H. P., Remy R., Pöschl B., van Loon A. P. Tumor necrosis factors-alpha and -beta bind to the same two types of tumor necrosis factor receptors and maximally activate the transcription factor NF-kappa B at low receptor occupancy and within minutes after receptor binding. J Biol Chem. 1990 Sep 5;265(25):15183–15188. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Israël A., Le Bail O., Hatat D., Piette J., Kieran M., Logeat F., Wallach D., Fellous M., Kourilsky P. TNF stimulates expression of mouse MHC class I genes by inducing an NF kappa B-like enhancer binding activity which displaces constitutive factors. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 1;8(12):3793–3800. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08556.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson D. R., Pober J. S. Tumor necrosis factor and immune interferon synergistically increase transcription of HLA class I heavy- and light-chain genes in vascular endothelium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jul;87(13):5183–5187. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.13.5183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis M. S., Whatley R. E., Cain P., McIntyre T. M., Prescott S. M., Zimmerman G. A. Hydrogen peroxide stimulates the synthesis of platelet-activating factor by endothelium and induces endothelial cell-dependent neutrophil adhesion. J Clin Invest. 1988 Dec;82(6):2045–2055. doi: 10.1172/JCI113825. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meichle A., Schütze S., Hensel G., Brunsing D., Krönke M. Protein kinase C-independent activation of nuclear factor kappa B by tumor necrosis factor. J Biol Chem. 1990 May 15;265(14):8339–8343. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel K. D., Zimmerman G. A., Prescott S. M., McEver R. P., McIntyre T. M. Oxygen radicals induce human endothelial cells to express GMP-140 and bind neutrophils. J Cell Biol. 1991 Feb;112(4):749–759. doi: 10.1083/jcb.112.4.749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pober J. S., Bevilacqua M. P., Mendrick D. L., Lapierre L. A., Fiers W., Gimbrone M. A., Jr Two distinct monokines, interleukin 1 and tumor necrosis factor, each independently induce biosynthesis and transient expression of the same antigen on the surface of cultured human vascular endothelial cells. J Immunol. 1986 Mar 1;136(5):1680–1687. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pober J. S., Cotran R. S. Cytokines and endothelial cell biology. Physiol Rev. 1990 Apr;70(2):427–451. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1990.70.2.427. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pober J. S. Warner-Lambert/Parke-Davis award lecture. Cytokine-mediated activation of vascular endothelium. Physiology and pathology. Am J Pathol. 1988 Dec;133(3):426–433. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poumay Y., Ronveaux-Dupal M. F. Incubation of endothelial cells in a superoxide-generating system: impaired low-density lipoprotein receptor-mediated endocytosis. J Cell Physiol. 1988 Aug;136(2):289–296. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041360211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sacks T., Moldow C. F., Craddock P. R., Bowers T. K., Jacob H. S. Oxygen radicals mediate endothelial cell damage by complement-stimulated granulocytes. An in vitro model of immune vascular damage. J Clin Invest. 1978 May;61(5):1161–1167. doi: 10.1172/JCI109031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreck R., Rieber P., Baeuerle P. A. Reactive oxygen intermediates as apparently widely used messengers in the activation of the NF-kappa B transcription factor and HIV-1. EMBO J. 1991 Aug;10(8):2247–2258. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07761.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shasby D. M., Lind S. E., Shasby S. S., Goldsmith J. C., Hunninghake G. W. Reversible oxidant-induced increases in albumin transfer across cultured endothelium: alterations in cell shape and calcium homeostasis. Blood. 1985 Mar;65(3):605–614. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shatos M. A., Doherty J. M., Orfeo T., Hoak J. C., Collen D., Stump D. C. Modulation of the fibrinolytic response of cultured human vascular endothelium by extracellularly generated oxygen radicals. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jan 5;267(1):597–601. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staunton D. E., Marlin S. D., Stratowa C., Dustin M. L., Springer T. A. Primary structure of ICAM-1 demonstrates interaction between members of the immunoglobulin and integrin supergene families. Cell. 1988 Mar 25;52(6):925–933. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90434-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varani J., Dame M. K., Gibbs D. F., Taylor C. G., Weinberg J. M., Shayevitz J., Ward P. A. Human umbilical vein endothelial cell killing by activated neutrophils. Loss of sensitivity to injury is accompanied by decreased iron content during in vitro culture and is restored with exogenous iron. Lab Invest. 1992 Jun;66(6):708–714. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varani J., Fligiel S. E., Till G. O., Kunkel R. G., Ryan U. S., Ward P. A. Pulmonary endothelial cell killing by human neutrophils. Possible involvement of hydroxyl radical. Lab Invest. 1985 Dec;53(6):656–663. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varani J., Ginsburg I., Schuger L., Gibbs D. F., Bromberg J., Johnson K. J., Ryan U. S., Ward P. A. Endothelial cell killing by neutrophils. Synergistic interaction of oxygen products and proteases. Am J Pathol. 1989 Sep;135(3):435–438. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson J., Winter M., Shasby D. M. Oxidants, ATP depletion, and endothelial permeability to macromolecules. Blood. 1990 Dec 15;76(12):2578–2582. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Hinsbergh V. W., Kooistra T., van den Berg E. A., Princen H. M., Fiers W., Emeis J. J. Tumor necrosis factor increases the production of plasminogen activator inhibitor in human endothelial cells in vitro and in rats in vivo. Blood. 1988 Nov;72(5):1467–1473. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]