Abstract
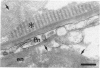
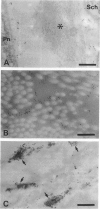
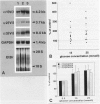
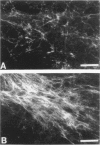
Electron microscopy of peripheral nerves obtained from two diabetic patients revealed large deposits of microfibrils and the presence of Luse bodies in the vicinity of perineurial cells. Microfibrils were found to accumulate also in the sciatic nerves of diabetic BB rats; these microfibrillar deposits were shown to contain type VI collagen by immunoelectron microscopy. Connective tissue cells cultured from rat sciatic nerves were exposed to high glucose concentrations. High glucose concentrations up-regulated the mRNA steady-state levels of alpha 1(VI), alpha 2(VI), and alpha 3(VI) chains of type VI collagen and caused accumulation of type VI collagen-containing fibrils in the cultures. Immunostaining and in situ hybridizations demonstrated that perineurial cells, Schwann cells, and fibroblasts expressed type VI collagen at the mRNA and protein levels. The results suggest that the turnover and supramolecular assembly of type VI collagen are perturbed in diabetic nerves and that glucose per se increases the expression of type VI collagen in vitro.
Full text
PDF











Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ayo S. H., Radnik R. A., Glass W. F., 2nd, Garoni J. A., Rampt E. R., Appling D. R., Kreisberg J. I. Increased extracellular matrix synthesis and mRNA in mesangial cells grown in high-glucose medium. Am J Physiol. 1991 Feb;260(2 Pt 2):F185–F191. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1991.260.2.F185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bischoff A. Diabetic neuropathy. Morbid anatomy, patho-physiology and pathogenesis based on electron-microscopic findings. Ger Med Mon. 1968 May;13(5):214–passim. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruneval P., Foidart J. M., Nochy D., Camilleri J. P., Bariety J. Glomerular matrix proteins in nodular glomerulosclerosis in association with light chain deposition disease and diabetes mellitus. Hum Pathol. 1985 May;16(5):477–484. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(85)80086-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruns R. R., Press W., Engvall E., Timpl R., Gross J. Type VI collagen in extracellular, 100-nm periodic filaments and fibrils: identification by immunoelectron microscopy. J Cell Biol. 1986 Aug;103(2):393–404. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.2.393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cagliero E., Maiello M., Boeri D., Roy S., Lorenzi M. Increased expression of basement membrane components in human endothelial cells cultured in high glucose. J Clin Invest. 1988 Aug;82(2):735–738. doi: 10.1172/JCI113655. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu M. L., Mann K., Deutzmann R., Pribula-Conway D., Hsu-Chen C. C., Bernard M. P., Timpl R. Characterization of three constituent chains of collagen type VI by peptide sequences and cDNA clones. Eur J Biochem. 1987 Oct 15;168(2):309–317. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb13422.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engel J., Furthmayr H., Odermatt E., von der Mark H., Aumailley M., Fleischmajer R., Timpl R. Structure and macromolecular organization of type VI collagen. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1985;460:25–37. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1985.tb51154.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engel J., Odermatt E., Engel A., Madri J. A., Furthmayr H., Rohde H., Timpl R. Shapes, domain organizations and flexibility of laminin and fibronectin, two multifunctional proteins of the extracellular matrix. J Mol Biol. 1981 Jul 25;150(1):97–120. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90326-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fort P., Marty L., Piechaczyk M., el Sabrouty S., Dani C., Jeanteur P., Blanchard J. M. Various rat adult tissues express only one major mRNA species from the glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate-dehydrogenase multigenic family. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Mar 11;13(5):1431–1442. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.5.1431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson M. A., Sandberg L. B., Grosso L. E., Cleary E. G. Complementary DNA cloning establishes microfibril-associated glycoprotein (MAGP) to be a discrete component of the elastin-associated microfibrils. J Biol Chem. 1991 Apr 25;266(12):7596–7601. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatamochi A., Aumailley M., Mauch C., Chu M. L., Timpl R., Krieg T. Regulation of collagen VI expression in fibroblasts. Effects of cell density, cell-matrix interactions, and chemical transformation. J Biol Chem. 1989 Feb 25;264(6):3494–3499. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heckmann M., Aumailley M., Hatamochi A., Chu M. L., Timpl R., Krieg T. Down-regulation of alpha 3(VI) chain expression by gamma-interferon decreases synthesis and deposition of collagen type VI. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Jul 1;182(3):719–726. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb14884.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hessle H., Engvall E. Type VI collagen. Studies on its localization, structure, and biosynthetic form with monoclonal antibodies. J Biol Chem. 1984 Mar 25;259(6):3955–3961. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horrigan S. K., Rich C. B., Streeten B. W., Li Z. Y., Foster J. A. Characterization of an associated microfibril protein through recombinant DNA techniques. J Biol Chem. 1992 May 15;267(14):10087–10095. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu H. C., Churg J. Glomerular microfibrils in renal disease: a comparative electron microscopic study. Kidney Int. 1979 Oct;16(4):497–504. doi: 10.1038/ki.1979.155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaakkola S., Peltonen J., Riccardi V., Chu M. L., Uitto J. Type 1 neurofibromatosis: selective expression of extracellular matrix genes by Schwann cells, perineurial cells, and fibroblasts in mixed cultures. J Clin Invest. 1989 Jul;84(1):253–261. doi: 10.1172/JCI114148. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaakkola S., Peltonen J., Uitto J. J. Perineurial cells coexpress genes encoding interstitial collagens and basement membrane zone components. J Cell Biol. 1989 Mar;108(3):1157–1163. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.3.1157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson P. C., Brendel K., Meezan E. Human diabetic perineurial cell basement membrane thickening. Lab Invest. 1981 Mar;44(3):265–270. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keene D. R., Engvall E., Glanville R. W. Ultrastructure of type VI collagen in human skin and cartilage suggests an anchoring function for this filamentous network. J Cell Biol. 1988 Nov;107(5):1995–2006. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.5.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kielty C. M., Boot-Handford R. P., Ayad S., Shuttleworth C. A., Grant M. E. Molecular composition of type VI collagen. Evidence for chain heterogeneity in mammalian tissues and cultured cells. Biochem J. 1990 Dec 15;272(3):787–795. doi: 10.1042/bj2720787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi R., Tashima Y., Masuda H., Shozawa T., Numata Y., Miyauchi K., Hayakawa T. Isolation and characterization of a new 36-kDa microfibril-associated glycoprotein from porcine aorta. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 15;264(29):17437–17444. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LUSE S. A. Electron microscopic studies of brain tumors. Neurology. 1960 Oct;10:881–905. doi: 10.1212/wnl.10.10.881. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marliss E. B., Nakhooda A. F., Poussier P., Sima A. A. The diabetic syndrome of the 'BB' Wistar rat: possible relevance to type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetes in man. Diabetologia. 1982 Apr;22(4):225–232. doi: 10.1007/BF00281296. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mauer S. M., Steffes M. W., Ellis E. N., Sutherland D. E., Brown D. M., Goetz F. C. Structural-functional relationships in diabetic nephropathy. J Clin Invest. 1984 Oct;74(4):1143–1155. doi: 10.1172/JCI111523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohan P. S., Carter W. G., Spiro R. G. Occurrence of type VI collagen in extracellular matrix of renal glomeruli and its increase in diabetes. Diabetes. 1990 Jan;39(1):31–37. doi: 10.2337/diacare.39.1.31. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muona P., Jaakkola S., Salonen V., Peltonen J. Diabetes induces the formation of large diameter collagen fibrils in the sciatic nerves of BB rats. Matrix. 1989 Jan;9(1):62–67. doi: 10.1016/s0934-8832(89)80020-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muona P., Peltonen J., Jaakkola S., Uitto J. Increased matrix gene expression by glucose in rat neural connective tissue cells in culture. Diabetes. 1991 May;40(5):605–611. doi: 10.2337/diab.40.5.605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muona P., Sollberg S., Peltonen J., Uitto J. Glucose transporters of rat peripheral nerve. Differential expression of GLUT1 gene by Schwann cells and perineural cells in vivo and in vitro. Diabetes. 1992 Dec;41(12):1587–1596. doi: 10.2337/diab.41.12.1587. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oda Y., Kawahara E., Minamoto T., Ueda Y., Ikeda K., Nagai Y., Nakanishi I. Immunohistochemical studies on the tissue localization of collagen types I, III, IV, V and VI in schwannomas. Correlation with ultrastructural features of the extracellular matrix. Virchows Arch B Cell Pathol Incl Mol Pathol. 1988;56(3):153–163. doi: 10.1007/BF02890013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odermatt E., Risteli J., van Delden V., Timpl R. Structural diversity and domain composition of a unique collagenous fragment (intima collagen) obtained from human placenta. Biochem J. 1983 May 1;211(2):295–302. doi: 10.1042/bj2110295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okada Y., Naka K., Minamoto T., Ueda Y., Oda Y., Nakanishi I., Timpl R. localization of type VI collagen in the lining cell layer of normal and rheumatoid synovium. Lab Invest. 1990 Nov;63(5):647–656. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PILLAI P. A. A BANDED STRUCTURE IN THE CONNECTIVE TISSUE OF NERVE. J Ultrastruct Res. 1964 Dec;11:455–468. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(64)80076-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peltonen J., Jaakkola S., Gay K., Olsen D. R., Chu M. L., Uitto J. Expression of extracellular matrix genes by cultured human cells: localization of messenger RNAs and antigenic epitopes. Anal Biochem. 1989 Apr;178(1):184–193. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(89)90377-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peltonen J., Jaakkola S., Hsiao L. L., Timpl R., Chu M. L., Uitto J. Type VI collagen. In situ hybridizations and immunohistochemistry reveal abundant mRNA and protein levels in human neurofibroma, schwannoma and normal peripheral nerve tissues. Lab Invest. 1990 Apr;62(4):487–492. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peltonen J., Jaakkola S., Uitto J. In situ hybridization and immunodetection techniques for simultaneous localization of messenger RNAs and protein epitopes in tissue sections and cultured cells. Methods Enzymol. 1991;203:476–484. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)03026-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peltonen J., Jaakkola S., Virtanen I., Pelliniemi L. Perineurial cells in culture. An immunocytochemical and electron microscopic study. Lab Invest. 1987 Nov;57(5):480–488. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ponte P., Gunning P., Blau H., Kedes L. Human actin genes are single copy for alpha-skeletal and alpha-cardiac actin but multicopy for beta- and gamma-cytoskeletal genes: 3' untranslated regions are isotype specific but are conserved in evolution. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Oct;3(10):1783–1791. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.10.1783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell H. C., Rosoff J., Myers R. R. Microangiopathy in human diabetic neuropathy. Acta Neuropathol. 1985;68(4):295–305. doi: 10.1007/BF00690832. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell H., Knox D., Lee S., Charters A. C., Orloff M., Garrett R., Lampert P. Alloxan diabetic neuropathy: electron microscopic studies. Neurology. 1977 Jan;27(1):60–66. doi: 10.1212/wnl.27.1.60. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakai L. Y., Keene D. R., Engvall E. Fibrillin, a new 350-kD glycoprotein, is a component of extracellular microfibrils. J Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;103(6 Pt 1):2499–2509. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.6.2499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sohar E., Ravid M., Ben-Shaul Y., Reshef T., Gafni J. Diabetic fibrillosis. A report of three cases. Am J Med. 1970 Jul;49(1):64–69. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9343(70)80114-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sollberg S., Muona P., Lebwohl M., Peltonen J., Uitto J. Presence of type I and VI collagen mRNAs in endothelial cells in cutaneous neurofibromas. Lab Invest. 1991 Aug;65(2):237–242. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternberg M., Cohen-Forterre L., Peyroux J. Connective tissue in diabetes mellitus: biochemical alterations of the intercellular matrix with special reference to proteoglycans, collagens and basement membranes. Diabete Metab. 1985 Feb;11(1):27–50. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stokes D. G., Saitta B., Timpl R., Chu M. L. Human alpha 3(VI) collagen gene. Characterization of exons coding for the amino-terminal globular domain and alternative splicing in normal and tumor cells. J Biol Chem. 1991 May 5;266(13):8626–8633. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trüeb B., Schreier T., Bruckner P., Winterhalter K. H. Type VI collagen represents a major fraction of connective tissue collagens. Eur J Biochem. 1987 Aug 3;166(3):699–703. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb13568.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yurchenco P. D., Schittny J. C. Molecular architecture of basement membranes. FASEB J. 1990 Apr 1;4(6):1577–1590. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.4.6.2180767. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziyadeh F. N., Snipes E. R., Watanabe M., Alvarez R. J., Goldfarb S., Haverty T. P. High glucose induces cell hypertrophy and stimulates collagen gene transcription in proximal tubule. Am J Physiol. 1990 Oct;259(4 Pt 2):F704–F714. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1990.259.4.F704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von der Mark H., Aumailley M., Wick G., Fleischmajer R., Timpl R. Immunochemistry, genuine size and tissue localization of collagen VI. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Aug 1;142(3):493–502. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08313.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]