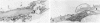Abstract
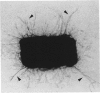
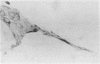
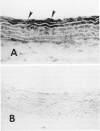
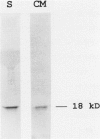
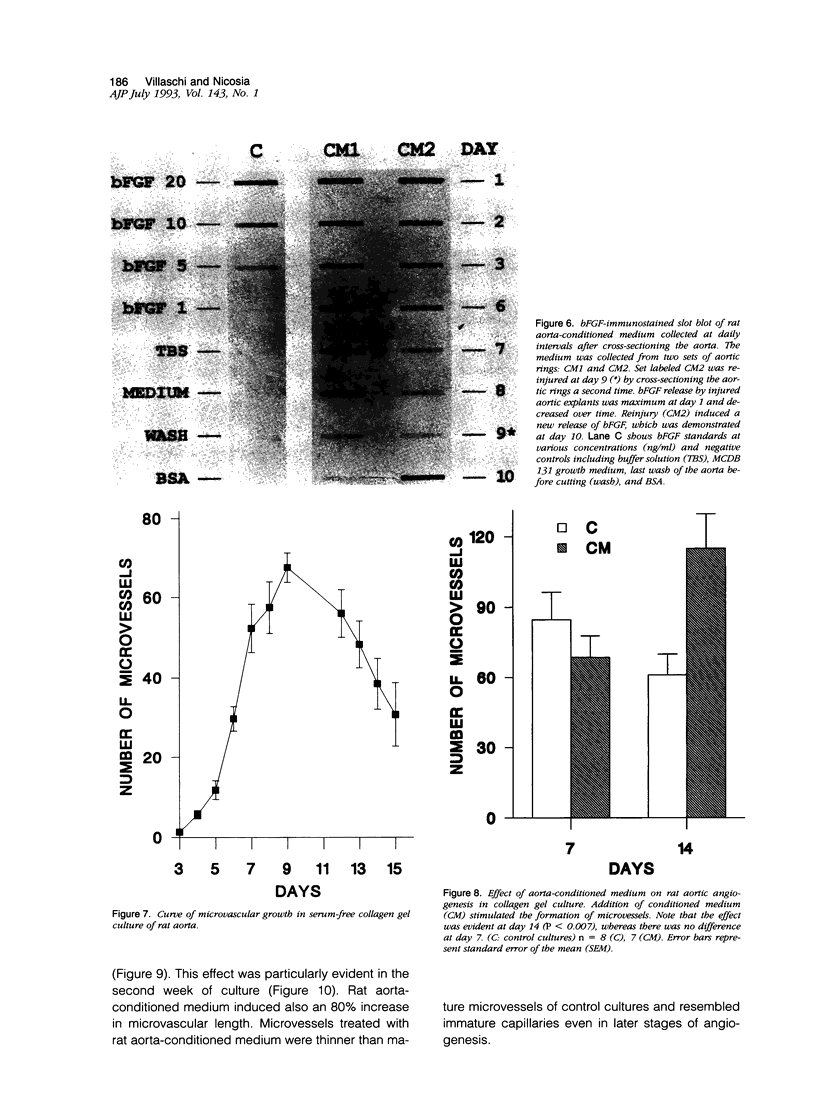
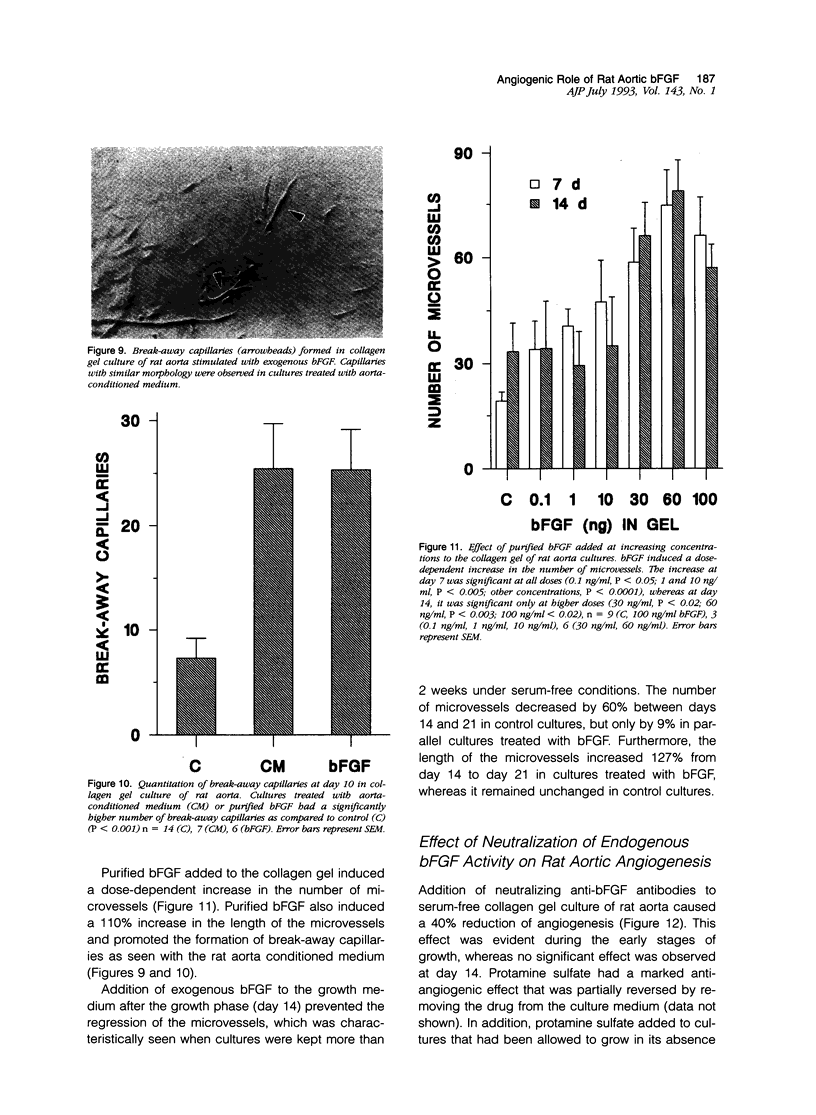
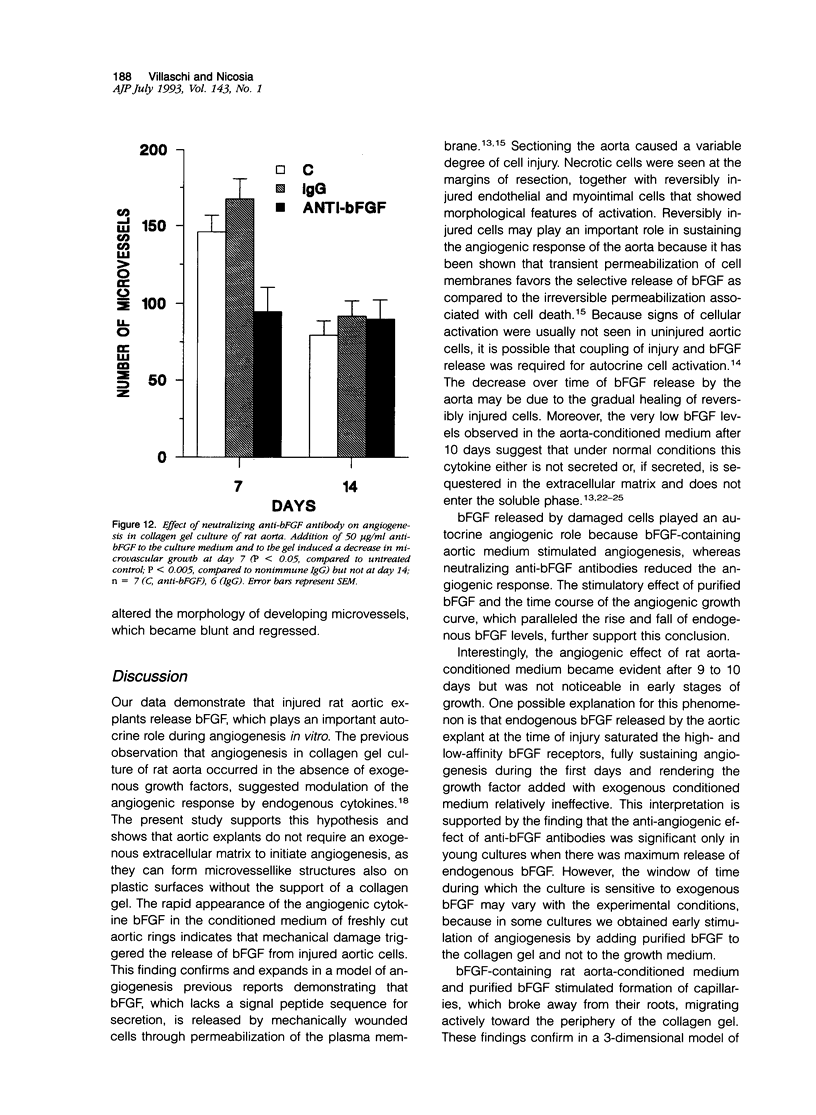
The autocrine role of basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF) in angiogenesis was studied in the rat aortic ring-collagen gel model using serum-free culture conditions. Immunohistochemical staining of the rat aorta showed bFGF in the cytoplasm of endothelial and smooth muscle cells. Aortic rings mechanically injured during the dissection procedure released bFGF, which was demonstrated in the conditioned medium by slot and Western blot analysis. bFGF-containing aorta-conditioned medium and purified bFGF increased both the number and length of microvessels sprouting from the explants. This effect was particularly evident during the second week of culture, when the release of endogenous bFGF was minimal. Neutralizing anti-bFGF antibodies induced a 40% reduction of angiogenesis. Regression of microvessels, which regularly occurred toward the end of the second week, was prevented by purified bFGF. These data support the idea that bFGF released by vascular cells plays an important role in the autoregulation of angiogenesis after injury.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abraham J. A., Mergia A., Whang J. L., Tumolo A., Friedman J., Hjerrild K. A., Gospodarowicz D., Fiddes J. C. Nucleotide sequence of a bovine clone encoding the angiogenic protein, basic fibroblast growth factor. Science. 1986 Aug 1;233(4763):545–548. doi: 10.1126/science.2425435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adams J. C. Technical considerations on the use of horseradish peroxidase as a neuronal marker. Neuroscience. 1977;2(1):141–145. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(77)90074-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Antonelli-Orlidge A., Saunders K. B., Smith S. R., D'Amore P. A. An activated form of transforming growth factor beta is produced by cocultures of endothelial cells and pericytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jun;86(12):4544–4548. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.12.4544. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ausprunk D. H., Folkman J. Migration and proliferation of endothelial cells in preformed and newly formed blood vessels during tumor angiogenesis. Microvasc Res. 1977 Jul;14(1):53–65. doi: 10.1016/0026-2862(77)90141-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavallero C., Turolla E., Ricevuti G. Cell proliferation in the atherosclerotic plaques of cholesterol-fed rabbits. 1. Colchicine and (3H)thymidine studies. Atherosclerosis. 1971 Jan-Feb;13(1):9–20. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(71)90003-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cordon-Cardo C., Vlodavsky I., Haimovitz-Friedman A., Hicklin D., Fuks Z. Expression of basic fibroblast growth factor in normal human tissues. Lab Invest. 1990 Dec;63(6):832–840. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuevas P., Gonzalez A. M., Carceller F., Baird A. Vascular response to basic fibroblast growth factor when infused onto the normal adventitia or into the injured media of the rat carotid artery. Circ Res. 1991 Aug;69(2):360–369. doi: 10.1161/01.res.69.2.360. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelman E. R., Nugent M. A., Smith L. T., Karnovsky M. J. Basic fibroblast growth factor enhances the coupling of intimal hyperplasia and proliferation of vasa vasorum in injured rat arteries. J Clin Invest. 1992 Feb;89(2):465–473. doi: 10.1172/JCI115607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folkman J., Shing Y. Angiogenesis. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jun 5;267(16):10931–10934. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Form D. M., Pratt B. M., Madri J. A. Endothelial cell proliferation during angiogenesis. In vitro modulation by basement membrane components. Lab Invest. 1986 Nov;55(5):521–530. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gajdusek C. M., Carbon S. Injury-induced release of basic fibroblast growth factor from bovine aortic endothelium. J Cell Physiol. 1989 Jun;139(3):570–579. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041390317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham R. C., Jr, Karnovsky M. J. The early stages of absorption of injected horseradish peroxidase in the proximal tubules of mouse kidney: ultrastructural cytochemistry by a new technique. J Histochem Cytochem. 1966 Apr;14(4):291–302. doi: 10.1177/14.4.291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalebic T., Garbisa S., Glaser B., Liotta L. A. Basement membrane collagen: degradation by migrating endothelial cells. Science. 1983 Jul 15;221(4607):281–283. doi: 10.1126/science.6190230. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klagsbrun M., Edelman E. R. Biological and biochemical properties of fibroblast growth factors. Implications for the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis. Arteriosclerosis. 1989 May-Jun;9(3):269–278. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.9.3.269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindner V., Lappi D. A., Baird A., Majack R. A., Reidy M. A. Role of basic fibroblast growth factor in vascular lesion formation. Circ Res. 1991 Jan;68(1):106–113. doi: 10.1161/01.res.68.1.106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindner V., Majack R. A., Reidy M. A. Basic fibroblast growth factor stimulates endothelial regrowth and proliferation in denuded arteries. J Clin Invest. 1990 Jun;85(6):2004–2008. doi: 10.1172/JCI114665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNeil P. L., Ito S. Gastrointestinal cell plasma membrane wounding and resealing in vivo. Gastroenterology. 1989 May;96(5 Pt 1):1238–1248. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5085(89)80010-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNeil P. L., Muthukrishnan L., Warder E., D'Amore P. A. Growth factors are released by mechanically wounded endothelial cells. J Cell Biol. 1989 Aug;109(2):811–822. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.2.811. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mignatti P., Tsuboi R., Robbins E., Rifkin D. B. In vitro angiogenesis on the human amniotic membrane: requirement for basic fibroblast growth factor-induced proteinases. J Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;108(2):671–682. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.2.671. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montesano R., Vassalli J. D., Baird A., Guillemin R., Orci L. Basic fibroblast growth factor induces angiogenesis in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(19):7297–7301. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.19.7297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moscatelli D., Rifkin D. B. Membrane and matrix localization of proteinases: a common theme in tumor cell invasion and angiogenesis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Aug 3;948(1):67–85. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(88)90005-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muthukrishnan L., Warder E., McNeil P. L. Basic fibroblast growth factor is efficiently released from a cytolsolic storage site through plasma membrane disruptions of endothelial cells. J Cell Physiol. 1991 Jul;148(1):1–16. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041480102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neufeld G., Gospodarowicz D. Protamine sulfate inhibits mitogenic activities of the extracellular matrix and fibroblast growth factor, but potentiates that of epidermal growth factor. J Cell Physiol. 1987 Aug;132(2):287–294. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041320213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicosia R. F., Ottinetti A. Growth of microvessels in serum-free matrix culture of rat aorta. A quantitative assay of angiogenesis in vitro. Lab Invest. 1990 Jul;63(1):115–122. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicosia R. F., Tchao R., Leighton J. Histotypic angiogenesis in vitro: light microscopic, ultrastructural, and radioautographic studies. In Vitro. 1982 Jun;18(6):538–549. doi: 10.1007/BF02810077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarzani R., Brecher P., Chobanian A. V. Growth factor expression in aorta of normotensive and hypertensive rats. J Clin Invest. 1989 Apr;83(4):1404–1408. doi: 10.1172/JCI114029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato Y., Rifkin D. B. Autocrine activities of basic fibroblast growth factor: regulation of endothelial cell movement, plasminogen activator synthesis, and DNA synthesis. J Cell Biol. 1988 Sep;107(3):1199–1205. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.3.1199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stary H. C., McMillan G. C. Kinetics of cellular proliferation in experimental atherosclerosis. Radioautography with grain counts in cholesterol-fed rabbits. Arch Pathol. 1970 Feb;89(2):173–183. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor S., Folkman J. Protamine is an inhibitor of angiogenesis. Nature. 1982 May 27;297(5864):307–312. doi: 10.1038/297307a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vlodavsky I., Folkman J., Sullivan R., Fridman R., Ishai-Michaeli R., Sasse J., Klagsbrun M. Endothelial cell-derived basic fibroblast growth factor: synthesis and deposition into subendothelial extracellular matrix. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(8):2292–2296. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.8.2292. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vlodavsky I., Fridman R., Sullivan R., Sasse J., Klagsbrun M. Aortic endothelial cells synthesize basic fibroblast growth factor which remains cell associated and platelet-derived growth factor-like protein which is secreted. J Cell Physiol. 1987 Jun;131(3):402–408. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041310312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkles J. A., Friesel R., Burgess W. H., Howk R., Mehlman T., Weinstein R., Maciag T. Human vascular smooth muscle cells both express and respond to heparin-binding growth factor I (endothelial cell growth factor). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(20):7124–7128. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.20.7124. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]