Abstract
Immunohistochemistry was performed on lung tissue obtained from patients with severe unexplained pulmonary hypertension using an antibody to the amino-terminal end of the procollagen type I propeptide. This antibody identifies newly synthesized alpha I(I) procollagen before cleavage of the amino-terminal propeptide following secretion and, therefore, can identify sites of active collagen deposition. Procollagen was detected in the media, media and neointima, or neointima alone of a large number of small muscular arteries from hypertensive lungs. Normal adult lungs were negative. Neointimal cells in remodeled small muscular arteries stained positively for alpha-smooth muscle actin and desmin consistent with a smooth muscle lineage. These data suggest smooth muscle-like cells in small muscular arteries are actively synthesizing collagen in patients with severe unexplained pulmonary hypertension.
Full text
PDF


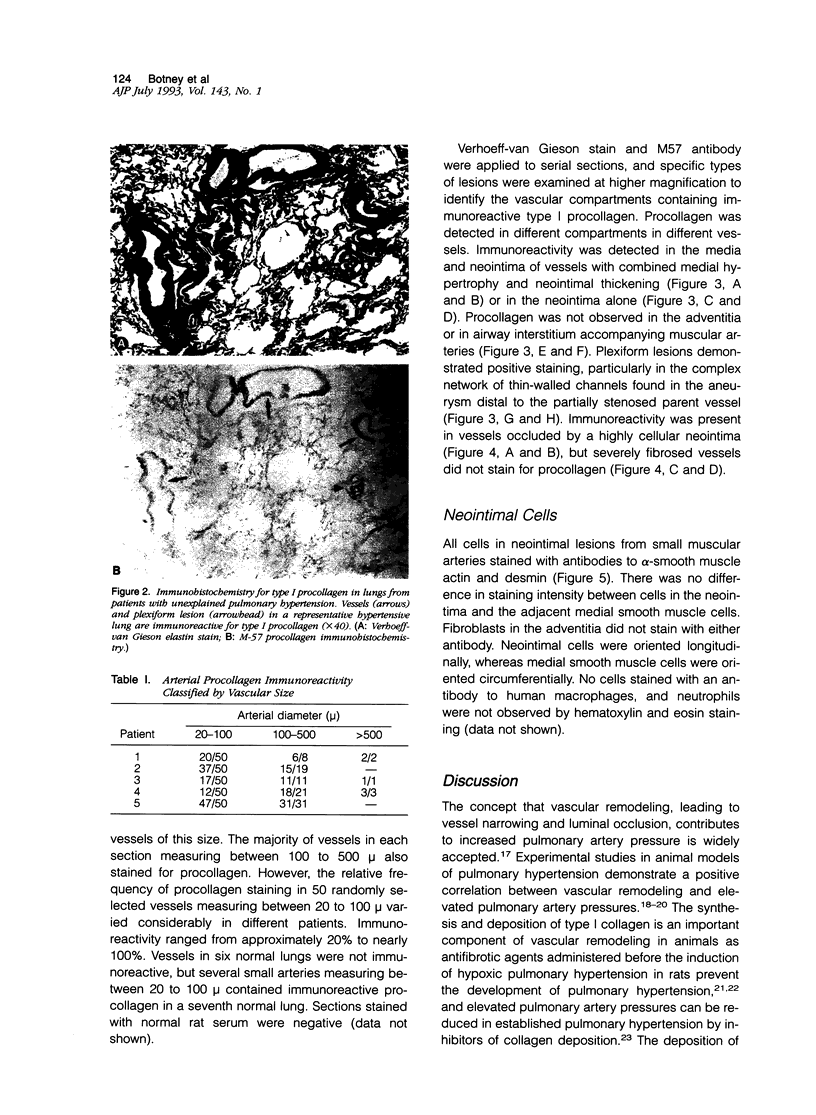





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bjornsson J., Edwards W. D. Primary pulmonary hypertension: a histopathologic study of 80 cases. Mayo Clin Proc. 1985 Jan;60(1):16–25. doi: 10.1016/s0025-6196(12)65277-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Botney M. D., Kaiser L. R., Cooper J. D., Mecham R. P., Parghi D., Roby J., Parks W. C. Extracellular matrix protein gene expression in atherosclerotic hypertensive pulmonary arteries. Am J Pathol. 1992 Feb;140(2):357–364. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu M. L., Myers J. C., Bernard M. P., Ding J. F., Ramirez F. Cloning and characterization of five overlapping cDNAs specific for the human pro alpha 1(I) collagen chain. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Oct 11;10(19):5925–5934. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.19.5925. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esterly J. A., Glagov S., Ferguson D. J. Morphogenesis of intimal obliterative hyperplasia of small arteries in experimental pulmonary hypertension. An ultrastructural study of the role of smooth-muscle cells. Am J Pathol. 1968 Feb;52(2):325–347. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gown A. M., Tsukada T., Ross R. Human atherosclerosis. II. Immunocytochemical analysis of the cellular composition of human atherosclerotic lesions. Am J Pathol. 1986 Oct;125(1):191–207. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerr J. S., Riley D. J., Frank M. M., Trelstad R. L., Frankel H. M. Reduction of chronic hypoxic pulmonary hypertension in the rat by beta-aminopropionitrile. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1984 Dec;57(6):1760–1766. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1984.57.6.1760. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhn C., 3rd, Boldt J., King T. E., Jr, Crouch E., Vartio T., McDonald J. A. An immunohistochemical study of architectural remodeling and connective tissue synthesis in pulmonary fibrosis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1989 Dec;140(6):1693–1703. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/140.6.1693. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mecham R. P., Whitehouse L. A., Wrenn D. S., Parks W. C., Griffin G. L., Senior R. M., Crouch E. C., Stenmark K. R., Voelkel N. F. Smooth muscle-mediated connective tissue remodeling in pulmonary hypertension. Science. 1987 Jul 24;237(4813):423–426. doi: 10.1126/science.3603030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyrick B., Reid L. Hypoxia-induced structural changes in the media and adventitia of the rat hilar pulmonary artery and their regression. Am J Pathol. 1980 Jul;100(1):151–178. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyrick B., Reid L. The effect of continued hypoxia on rat pulmonary arterial circulation. An ultrastructural study. Lab Invest. 1978 Feb;38(2):188–200. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pietra G. G., Edwards W. D., Kay J. M., Rich S., Kernis J., Schloo B., Ayres S. M., Bergofsky E. H., Brundage B. H., Detre K. M. Histopathology of primary pulmonary hypertension. A qualitative and quantitative study of pulmonary blood vessels from 58 patients in the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, Primary Pulmonary Hypertension Registry. Circulation. 1989 Nov;80(5):1198–1206. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.80.5.1198. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poiani G. J., Tozzi C. A., Choe J. K., Yohn S. E., Riley D. J. An antifibrotic agent reduces blood pressure in established pulmonary hypertension in the rat. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1990 Apr;68(4):1542–1547. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1990.68.4.1542. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poiani G. J., Tozzi C. A., Yohn S. E., Pierce R. A., Belsky S. A., Berg R. A., Yu S. Y., Deak S. B., Riley D. J. Collagen and elastin metabolism in hypertensive pulmonary arteries of rats. Circ Res. 1990 Apr;66(4):968–978. doi: 10.1161/01.res.66.4.968. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prosser I. W., Stenmark K. R., Suthar M., Crouch E. C., Mecham R. P., Parks W. C. Regional heterogeneity of elastin and collagen gene expression in intralobar arteries in response to hypoxic pulmonary hypertension as demonstrated by in situ hybridization. Am J Pathol. 1989 Dec;135(6):1073–1088. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabinovitch M., Gamble W., Nadas A. S., Miettinen O. S., Reid L. Rat pulmonary circulation after chronic hypoxia: hemodynamic and structural features. Am J Physiol. 1979 Jun;236(6):H818–H827. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1979.236.6.H818. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rich S., Dantzker D. R., Ayres S. M., Bergofsky E. H., Brundage B. H., Detre K. M., Fishman A. P., Goldring R. M., Groves B. M., Koerner S. K. Primary pulmonary hypertension. A national prospective study. Ann Intern Med. 1987 Aug;107(2):216–223. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-107-2-216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P., Heath D. Electron microscopy of the plexiform lesion. Thorax. 1979 Apr;34(2):177–186. doi: 10.1136/thx.34.2.177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobin S. S., Tremer H. M., Hardy J. D., Chiodi H. P. Changes in arteriole in acute and chronic hypoxic pulmonary hypertension and recovery in rat. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1983 Nov;55(5):1445–1455. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1983.55.5.1445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenmark K. R., Fasules J., Hyde D. M., Voelkel N. F., Henson J., Tucker A., Wilson H., Reeves J. T. Severe pulmonary hypertension and arterial adventitial changes in newborn calves at 4,300 m. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1987 Feb;62(2):821–830. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1987.62.2.821. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagenvoort C. A. Lung biopsy specimens in the evaluation of pulmonary vascular disease. Chest. 1980 May;77(5):614–625. doi: 10.1378/chest.77.5.614. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]







