Abstract
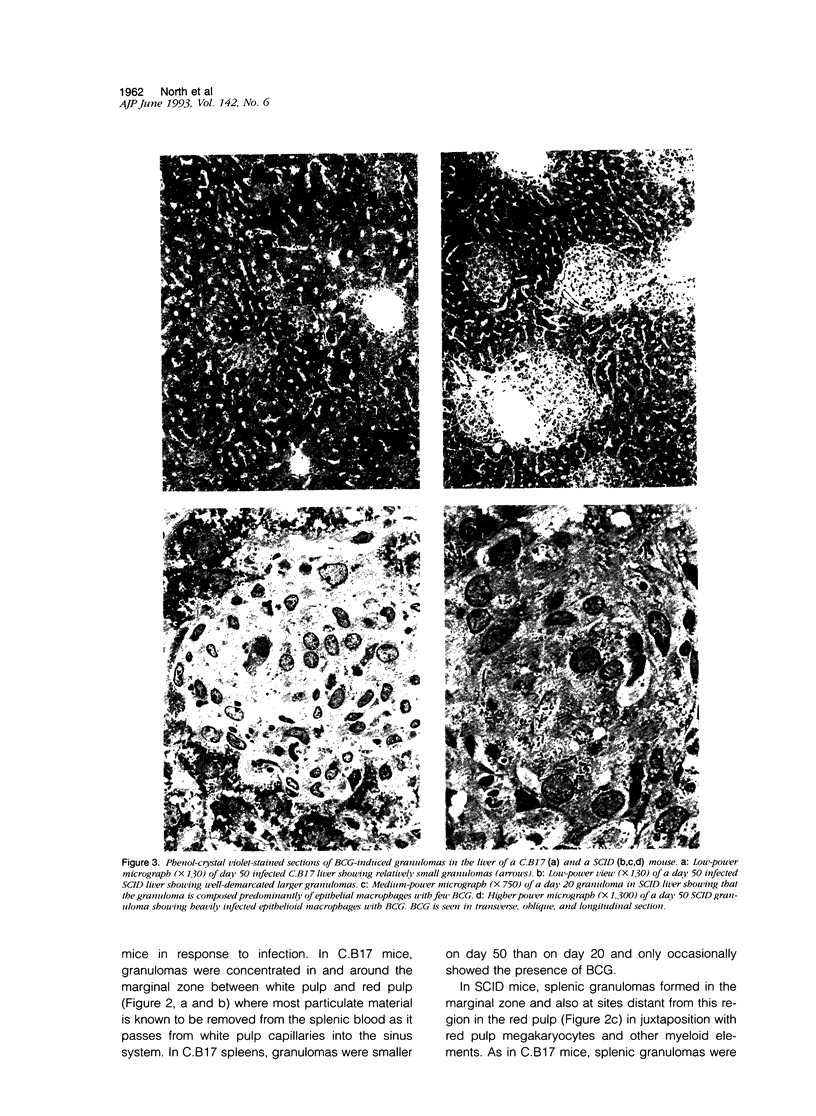
Intravenous inoculation of Mycobacterium bovis, strain bacillus Calmette-Guerin caused infection in the lungs, livers, and spleens of severe combined immunodeficient (SCID) mice and in the same organs in immunocompetent co-isogenic C.B17 mice. However, whereas infection in the latter mice was stabilized and partly resolved, it was progressive in SCID mice and eventually lethal, with the most rapid bacterial growth occurring in the lungs. Histological examination of infected organs showed that well-developed, compact epithelioid granulomas formed at sites of bacterial multiplication in livers, spleens, and lungs of C.B17 mice. Granulomas also formed in the livers and spleens of SCID mice, despite their inability to generate immunity. However, in the lungs of SCID mice, bacillus Calmette-Guerin was regionally distributed mostly in isolated alveolar macrophages and in aggregates of macrophages resembling small granulomas. The possibility that this tendency not to form granulomas in the lung is the reason for the more rapid growth of bacillus Calmette-Guerin in this organ is discussed.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amiri P., Locksley R. M., Parslow T. G., Sadick M., Rector E., Ritter D., McKerrow J. H. Tumour necrosis factor alpha restores granulomas and induces parasite egg-laying in schistosome-infected SCID mice. Nature. 1992 Apr 16;356(6370):604–607. doi: 10.1038/356604a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bosma M. J., Carroll A. M. The SCID mouse mutant: definition, characterization, and potential uses. Annu Rev Immunol. 1991;9:323–350. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.09.040191.001543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brocke S., Chakraborty T., Mohasseb I., Reichert H., Lombardi O., Hahn H., Mielke M. Protective immunity and granulomatous inflammation is mediated in vivo by T cells reactive to epitopes common to avirulent and listeriolysin-negative mutants of Listeria monocytogenes. Cell Immunol. 1992 Mar;140(1):42–53. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(92)90175-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan J., Xing Y., Magliozzo R. S., Bloom B. R. Killing of virulent Mycobacterium tuberculosis by reactive nitrogen intermediates produced by activated murine macrophages. J Exp Med. 1992 Apr 1;175(4):1111–1122. doi: 10.1084/jem.175.4.1111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deschryver-Kecskemeti K., Bancroft G. J., Bosma G. C., Bosma M. J., Unanue E. R. Pathology of Listeria infection in murine severe combined immunodeficiency. A study by immunohistochemistry and electron microscopy. Lab Invest. 1988 Jun;58(6):698–705. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douvas G. S., Looker D. L., Vatter A. E., Crowle A. J. Gamma interferon activates human macrophages to become tumoricidal and leishmanicidal but enhances replication of macrophage-associated mycobacteria. Infect Immun. 1985 Oct;50(1):1–8. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.1.1-8.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flesch I. E., Kaufmann S. H. Activation of tuberculostatic macrophage functions by gamma interferon, interleukin-4, and tumor necrosis factor. Infect Immun. 1990 Aug;58(8):2675–2677. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.8.2675-2677.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flesch I., Kaufmann S. H. Mycobacterial growth inhibition by interferon-gamma-activated bone marrow macrophages and differential susceptibility among strains of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J Immunol. 1987 Jun 15;138(12):4408–4413. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harmsen A. G., Stankiewicz M. Requirement for CD4+ cells in resistance to Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia in mice. J Exp Med. 1990 Sep 1;172(3):937–945. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.3.937. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Izzo A. A., North R. J. Evidence for an alpha/beta T cell-independent mechanism of resistance to mycobacteria. Bacillus-Calmette-Guerin causes progressive infection in severe combined immunodeficient mice, but not in nude mice or in mice depleted of CD4+ and CD8+ T cells. J Exp Med. 1992 Aug 1;176(2):581–586. doi: 10.1084/jem.176.2.581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kindler V., Sappino A. P., Grau G. E., Piguet P. F., Vassalli P. The inducing role of tumor necrosis factor in the development of bactericidal granulomas during BCG infection. Cell. 1989 Mar 10;56(5):731–740. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90676-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LECHTMAN M. D., BARTHOLOMEW J. W., PHILLIPS A., RUSSO M. RAPID METHODS OF STAINING BACTERIAL SPORES AT ROOM TEMPERATURE. J Bacteriol. 1965 Mar;89:848–854. doi: 10.1128/jb.89.3.848-854.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leveton C., Barnass S., Champion B., Lucas S., De Souza B., Nicol M., Banerjee D., Rook G. T-cell-mediated protection of mice against virulent Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Infect Immun. 1989 Feb;57(2):390–395. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.2.390-395.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pandolph C., Poulter L. W. The staining of acid fast bacilli in sections of glycol methacrylate embedded tissues. Stain Technol. 1978 May;53(3):173–176. doi: 10.3109/10520297809111461. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedrazzini T., Hug K., Louis J. A. Importance of L3T4+ and Lyt-2+ cells in the immunologic control of infection with Mycobacterium bovis strain bacillus Calmette-Guérin in mice. Assessment by elimination of T cell subsets in vivo. J Immunol. 1987 Sep 15;139(6):2032–2037. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rook G. A., Steele J., Ainsworth M., Champion B. R. Activation of macrophages to inhibit proliferation of Mycobacterium tuberculosis: comparison of the effects of recombinant gamma-interferon on human monocytes and murine peritoneal macrophages. Immunology. 1986 Nov;59(3):333–338. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl S. M., Allen J. B., Dougherty S., Evequoz V., Pluznik D. H., Wilder R. L., Hand A. R., Wahl L. M. T lymphocyte-dependent evolution of bacterial cell wall-induced hepatic granulomas. J Immunol. 1986 Oct 1;137(7):2199–2209. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]