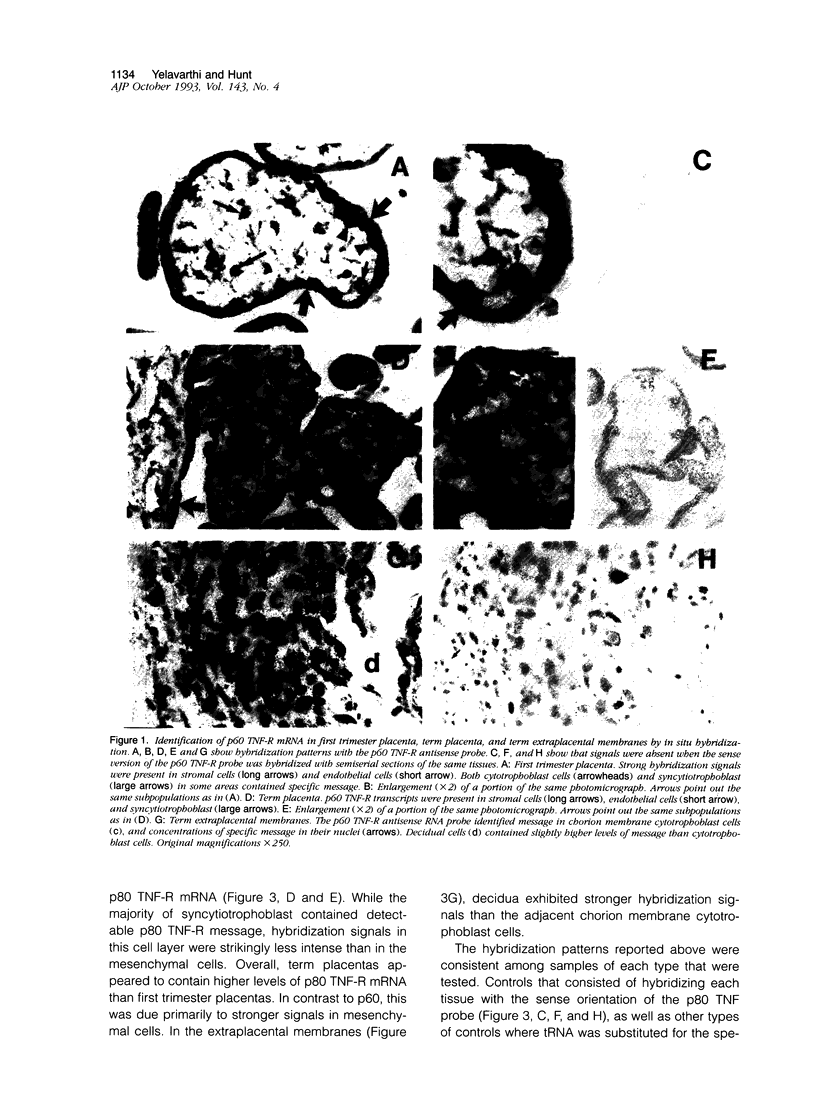
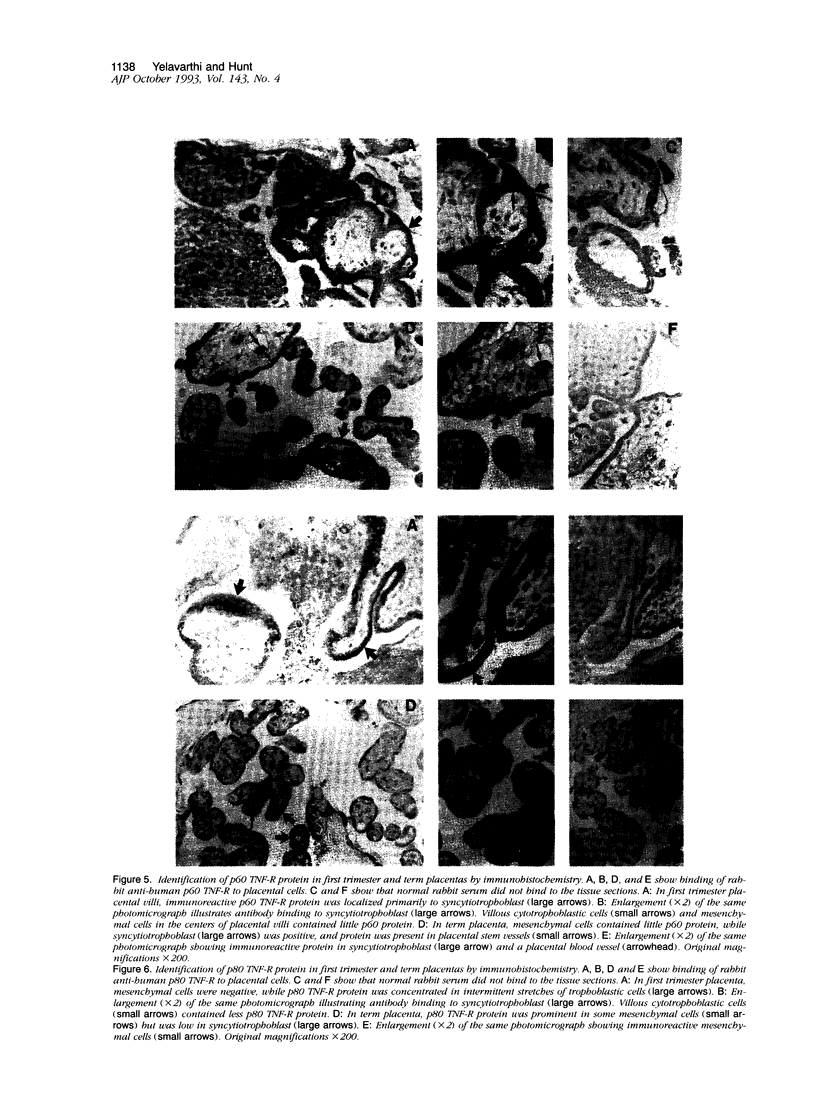
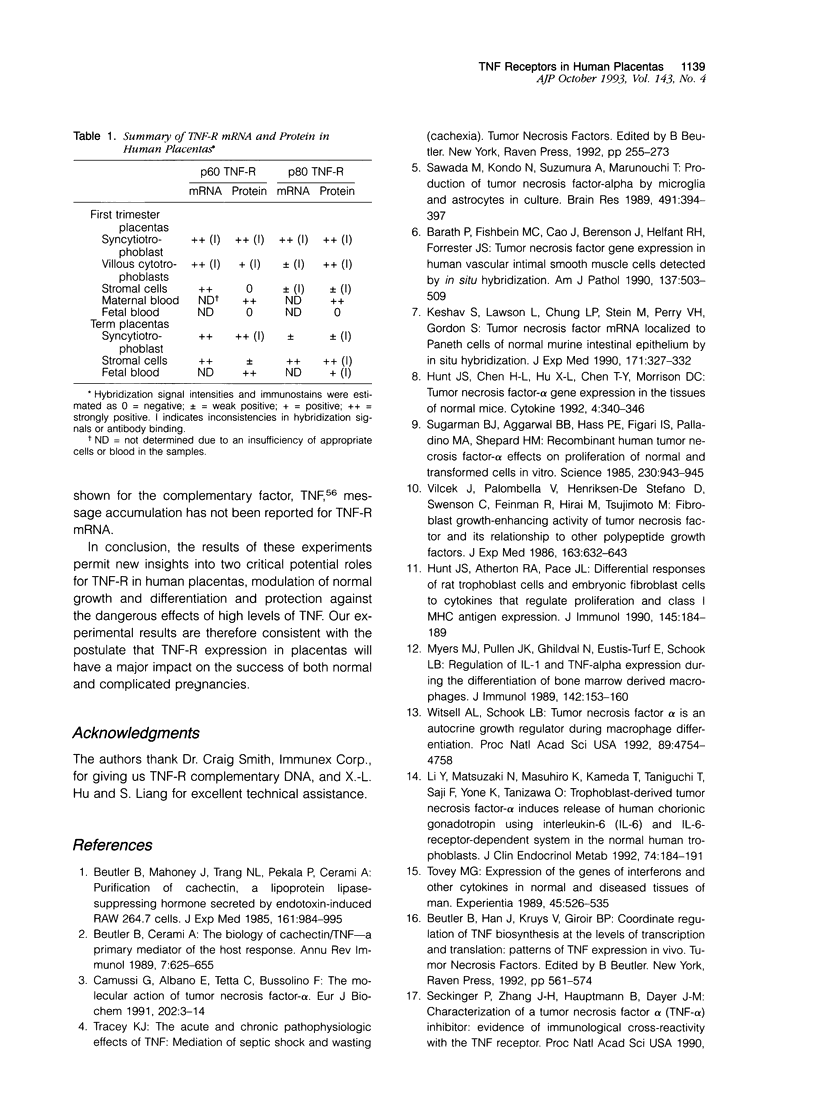
Abstract
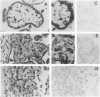
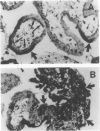
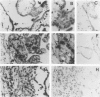
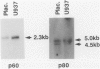
Tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF), a pleiotrophic, multifunctional polypeptide factor, has been reported in both normal and infected human placentas. To identify potential targets for this cytokine, the cells in early and late gestation placentas and extraplacental membranes that express the two TNF receptor (TNF-R) genes, p60 and p80, were identified by using in situ hybridization and immunocytochemistry. Gestation-related, cell lineage-specific differences in steady-state levels of p60 and p80 TNF-R messenger RNA were observed. p60 TNF-R messenger RNA predominated at both early and late stages of gestation, being high in both mesenchymal and trophoblastic cell lineages. By contrast, p80 TNF-R messenger RNA was abundant only in intermittent stretches of first trimester syncytiotrophoblast and term placental mesenchymal cells. Overall, intensities of the TNF-R hybridization signals were stronger in term than in first trimester tissues. Transcription of the two TNF-R genes was confirmed by Northern blot hybridization. Translation was verified in all samples by immunohistology using polyclonal antibodies specific for the receptor proteins. p60 and p80 TNF-R proteins were identified both intracellularly and in maternal and fetal blood. Because TNF-Rs exist in both membrane-bound and soluble forms, the results of this study are consistent with the postulate that placental TNF-R have two critical functions: 1) modulation of TNF utilization by specific placental cell lineages during the course of pregnancy; and 2) protection against excessive TNF produced during infections.
Full text
PDF



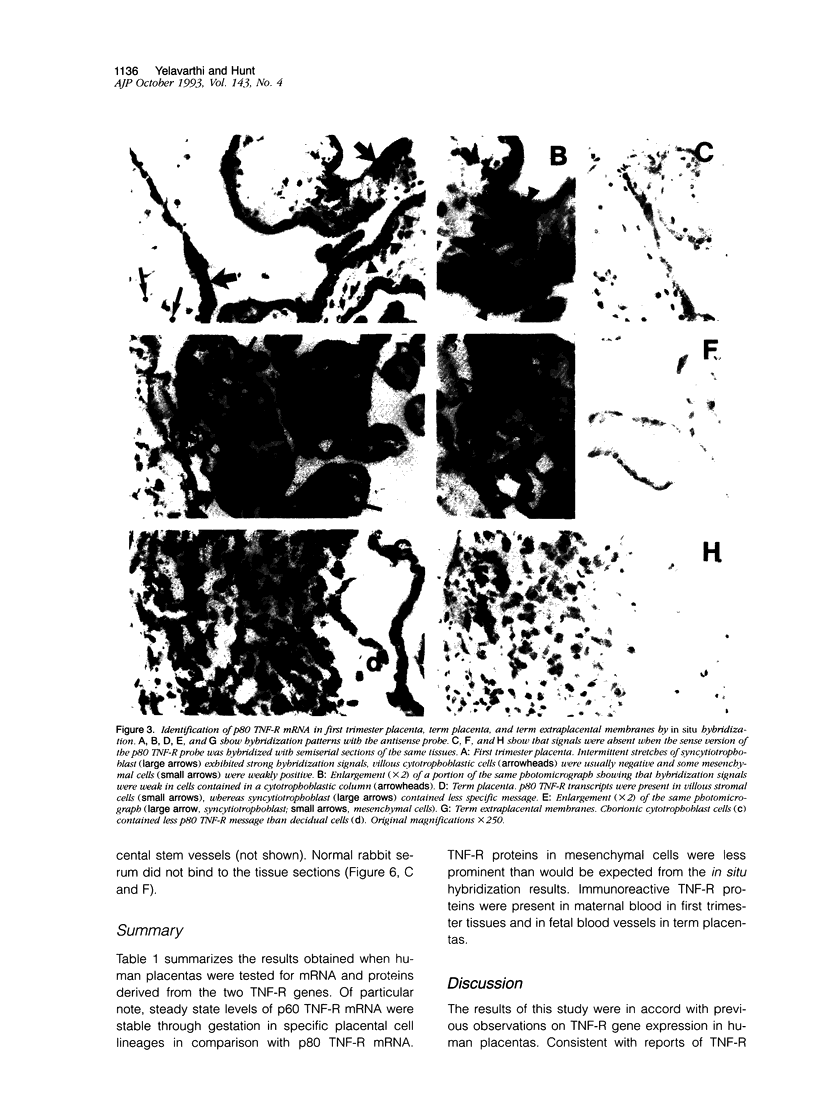



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Austgulen R., Espevik T., Mecsei R., Scott H. Expression of receptors for tumor necrosis factor in human placenta at term. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 1992 Aug;71(6):417–424. doi: 10.3109/00016349209021090. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Austgulen R., Liabakk N. B., Brockhaus M., Espevik T. Soluble TNF receptors in amniotic fluid and in urine from pregnant women. J Reprod Immunol. 1992 Aug;22(2):105–116. doi: 10.1016/0165-0378(92)90009-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aviv H., Leder P. Purification of biologically active globin messenger RNA by chromatography on oligothymidylic acid-cellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1408–1412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barath P., Fishbein M. C., Cao J., Berenson J., Helfant R. H., Forrester J. S. Tumor necrosis factor gene expression in human vascular intimal smooth muscle cells detected by in situ hybridization. Am J Pathol. 1990 Sep;137(3):503–509. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutler B., Cerami A. The biology of cachectin/TNF--a primary mediator of the host response. Annu Rev Immunol. 1989;7:625–655. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.07.040189.003205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutler B., Mahoney J., Le Trang N., Pekala P., Cerami A. Purification of cachectin, a lipoprotein lipase-suppressing hormone secreted by endotoxin-induced RAW 264.7 cells. J Exp Med. 1985 May 1;161(5):984–995. doi: 10.1084/jem.161.5.984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bulmer J. N., Johnson P. M. Macrophage populations in the human placenta and amniochorion. Clin Exp Immunol. 1984 Aug;57(2):393–403. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camussi G., Albano E., Tetta C., Bussolino F. The molecular action of tumor necrosis factor-alpha. Eur J Biochem. 1991 Nov 15;202(1):3–14. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1991.tb16337.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen H. L., Marcinkiewicz J. L., Sancho-Tello M., Hunt J. S., Terranova P. F. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha gene expression in mouse oocytes and follicular cells. Biol Reprod. 1993 Apr;48(4):707–714. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod48.4.707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen H. L., Yang Y. P., Hu X. L., Yelavarthi K. K., Fishback J. L., Hunt J. S. Tumor necrosis factor alpha mRNA and protein are present in human placental and uterine cells at early and late stages of gestation. Am J Pathol. 1991 Aug;139(2):327–335. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daiter E., Pampfer S., Yeung Y. G., Barad D., Stanley E. R., Pollard J. W. Expression of colony-stimulating factor-1 in the human uterus and placenta. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1992 Apr;74(4):850–858. doi: 10.1210/jcem.74.4.1548350. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dayer J. M., Beutler B., Cerami A. Cachectin/tumor necrosis factor stimulates collagenase and prostaglandin E2 production by human synovial cells and dermal fibroblasts. J Exp Med. 1985 Dec 1;162(6):2163–2168. doi: 10.1084/jem.162.6.2163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eades D. K., Cornelius P., Pekala P. H. Characterization of the tumour necrosis factor receptor in human placenta. Placenta. 1988 May-Jun;9(3):247–251. doi: 10.1016/0143-4004(88)90032-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox H., Elston C. W. Pathology of the placenta. Major Probl Pathol. 1978;7:1–491. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fràter-Schröder M., Risau W., Hallmann R., Gautschi P., Böhlen P. Tumor necrosis factor type alpha, a potent inhibitor of endothelial cell growth in vitro, is angiogenic in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(15):5277–5281. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.15.5277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein J., Braverman M., Salafia C., Buckley P. The phenotype of human placental macrophages and its variation with gestational age. Am J Pathol. 1988 Dec;133(3):648–659. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodwin R. G., Anderson D., Jerzy R., Davis T., Brannan C. I., Copeland N. G., Jenkins N. A., Smith C. A. Molecular cloning and expression of the type 1 and type 2 murine receptors for tumor necrosis factor. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jun;11(6):3020–3026. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.6.3020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heller R. A., Song K., Fan N., Chang D. J. The p70 tumor necrosis factor receptor mediates cytotoxicity. Cell. 1992 Jul 10;70(1):47–56. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90532-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Himmler A., Maurer-Fogy I., Krönke M., Scheurich P., Pfizenmaier K., Lantz M., Olsson I., Hauptmann R., Stratowa C., Adolf G. R. Molecular cloning and expression of human and rat tumor necrosis factor receptor chain (p60) and its soluble derivative, tumor necrosis factor-binding protein. DNA Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;9(10):705–715. doi: 10.1089/dna.1990.9.705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt J. S., Atherton R. A., Pace J. L. Differential responses of rat trophoblast cells and embryonic fibroblasts to cytokines that regulate proliferation and class I MHC antigen expression. J Immunol. 1990 Jul 1;145(1):184–189. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt J. S., Chen H. L., Hu X. L., Chen T. Y., Morrison D. C. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha gene expression in the tissues of normal mice. Cytokine. 1992 Sep;4(5):340–346. doi: 10.1016/1043-4666(92)90076-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt J. S., Chen H. L., Hu X. L., Tabibzadeh S. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha messenger ribonucleic acid and protein in human endometrium. Biol Reprod. 1992 Jul;47(1):141–147. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod47.1.141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jättelä M., Kuusela P., Saksela E. Demonstration of tumor necrosis factor in human amniotic fluids and supernatants of placental and decidual tissues. Lab Invest. 1988 Jan;58(1):48–52. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keshav S., Lawson L., Chung L. P., Stein M., Perry V. H., Gordon S. Tumor necrosis factor mRNA localized to Paneth cells of normal murine intestinal epithelium by in situ hybridization. J Exp Med. 1990 Jan 1;171(1):327–332. doi: 10.1084/jem.171.1.327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence J. B., Singer R. H. Quantitative analysis of in situ hybridization methods for the detection of actin gene expression. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Mar 11;13(5):1777–1799. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.5.1777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lessin D. L., Hunt J. S., King C. R., Wood G. W. Antigen expression by cells near the maternal-fetal interface. Am J Reprod Immunol Microbiol. 1988 Jan;16(1):1–7. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0897.1988.tb00169.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li Y., Matsuzaki N., Masuhiro K., Kameda T., Taniguchi T., Saji F., Yone K., Tanizawa O. Trophoblast-derived tumor necrosis factor-alpha induces release of human chorionic gonadotropin using interleukin-6 (IL-6) and IL-6-receptor-dependent system in the normal human trophoblasts. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1992 Jan;74(1):184–191. doi: 10.1210/jcem.74.1.1727819. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loetscher H., Pan Y. C., Lahm H. W., Gentz R., Brockhaus M., Tabuchi H., Lesslauer W. Molecular cloning and expression of the human 55 kd tumor necrosis factor receptor. Cell. 1990 Apr 20;61(2):351–359. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90815-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers M. J., Pullen J. K., Ghildyal N., Eustis-Turf E., Schook L. B. Regulation of IL-1 and TNF-alpha expression during the differentiation of bone marrow derived macrophage. J Immunol. 1989 Jan 1;142(1):153–160. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pampfer S., Daiter E., Barad D., Pollard J. W. Expression of the colony-stimulating factor-1 receptor (c-fms proto-oncogene product) in the human uterus and placenta. Biol Reprod. 1992 Jan;46(1):48–57. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod46.1.48. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollard J. W. Lymphohematopoietic cytokines in the female reproductive tract. Curr Opin Immunol. 1991 Oct;3(5):772–777. doi: 10.1016/0952-7915(91)90112-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romero R., Manogue K. R., Mitchell M. D., Wu Y. K., Oyarzun E., Hobbins J. C., Cerami A. Infection and labor. IV. Cachectin-tumor necrosis factor in the amniotic fluid of women with intraamniotic infection and preterm labor. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1989 Aug;161(2):336–341. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(89)90515-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawada M., Kondo N., Suzumura A., Marunouchi T. Production of tumor necrosis factor-alpha by microglia and astrocytes in culture. Brain Res. 1989 Jul 10;491(2):394–397. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(89)90078-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. A., Davis T., Anderson D., Solam L., Beckmann M. P., Jerzy R., Dower S. K., Cosman D., Goodwin R. G. A receptor for tumor necrosis factor defines an unusual family of cellular and viral proteins. Science. 1990 May 25;248(4958):1019–1023. doi: 10.1126/science.2160731. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugarman B. J., Aggarwal B. B., Hass P. E., Figari I. S., Palladino M. A., Jr, Shepard H. M. Recombinant human tumor necrosis factor-alpha: effects on proliferation of normal and transformed cells in vitro. Science. 1985 Nov 22;230(4728):943–945. doi: 10.1126/science.3933111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sung S. J., Walters J. A., Hudson J., Gimble J. M. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha mRNA accumulation in human myelomonocytic cell lines. Role of transcriptional regulation by DNA sequence motifs and mRNA stabilization. J Immunol. 1991 Sep 15;147(6):2047–2054. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tartaglia L. A., Goeddel D. V. Two TNF receptors. Immunol Today. 1992 May;13(5):151–153. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(92)90116-O. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tartaglia L. A., Weber R. F., Figari I. S., Reynolds C., Palladino M. A., Jr, Goeddel D. V. The two different receptors for tumor necrosis factor mediate distinct cellular responses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 15;88(20):9292–9296. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.20.9292. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tartakovsky B., Ben-Yair E. Cytokines modulate preimplantation development and pregnancy. Dev Biol. 1991 Aug;146(2):345–352. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(91)90236-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tovey M. G. Expression of the genes of interferons and other cytokines in normal and diseased tissues of man. Experientia. 1989 Jun 15;45(6):526–535. doi: 10.1007/BF01990502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umeda T., Hara T., Niijima T. Cytotoxic effect of tumor necrosis factor on human lymphocytes and specific binding of the factor to the target cells. Cell Mol Biol. 1983;29(5):349–352. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vilcek J., Palombella V. J., Henriksen-DeStefano D., Swenson C., Feinman R., Hirai M., Tsujimoto M. Fibroblast growth enhancing activity of tumor necrosis factor and its relationship to other polypeptide growth factors. J Exp Med. 1986 Mar 1;163(3):632–643. doi: 10.1084/jem.163.3.632. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vince G., Shorter S., Starkey P., Humphreys J., Clover L., Wilkins T., Sargent I., Redman C. Localization of tumour necrosis factor production in cells at the materno/fetal interface in human pregnancy. Clin Exp Immunol. 1992 Apr;88(1):174–180. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1992.tb03059.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ware C. F., Crowe P. D., Vanarsdale T. L., Andrews J. L., Grayson M. H., Jerzy R., Smith C. A., Goodwin R. G. Tumor necrosis factor (TNF) receptor expression in T lymphocytes. Differential regulation of the type I TNF receptor during activation of resting and effector T cells. J Immunol. 1991 Dec 15;147(12):4229–4238. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witsell A. L., Schook L. B. Tumor necrosis factor alpha is an autocrine growth regulator during macrophage differentiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 May 15;89(10):4754–4758. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.10.4754. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong G. H., Tartaglia L. A., Lee M. S., Goeddel D. V. Antiviral activity of tumor necrosis factor is signaled through the 55-kDa type I TNF receptor [corrected]. J Immunol. 1992 Nov 15;149(10):3350–3353. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yelavarthi K. K., Chen H. L., Yang Y. P., Cowley B. D., Jr, Fishback J. L., Hunt J. S. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha mRNA and protein in rat uterine and placental cells. J Immunol. 1991 Jun 1;146(11):3840–3848. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yelavarthi K. K., Fishback J. L., Hunt J. S. Analysis of HLA-G mRNA in human placental and extraplacental membrane cells by in situ hybridization. J Immunol. 1991 Apr 15;146(8):2847–2854. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]