Abstract
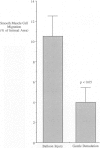
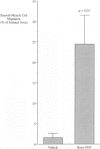
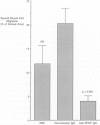
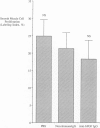
The formation of an intimal lesion in an injured artery is the consequence of the replication and migration of smooth muscle cells. Recent studies have implicated basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF) as an important mediator of replication in the arterial media, and platelet-derived growth factor as an important mediator of migration. However, the degree of arterial trauma produced during injury has a significant influence on the time of onset of intimal thickening, suggesting that factors released from damaged smooth muscle cells may affect migration. We have investigated the role of one of these factors, bFGF, in smooth muscle cell migration in vivo. We found that 1) deendothelialization of the rat carotid artery results in significantly more migration when it is accompanied by traumatic injury to the underlying smooth muscle; 2) the rate of migration in arteries that have been gently deendothelialized is significantly stimulated by systemic injection of bFGF; and 3) inhibition of bFGF with a blocking antibody significantly reduces the amount of migration after traumatic deendothelializing injury with a balloon catheter. These findings suggest that bFGF plays an important role in the mediation of smooth muscle cell migration after arterial injury.
Full text
PDF


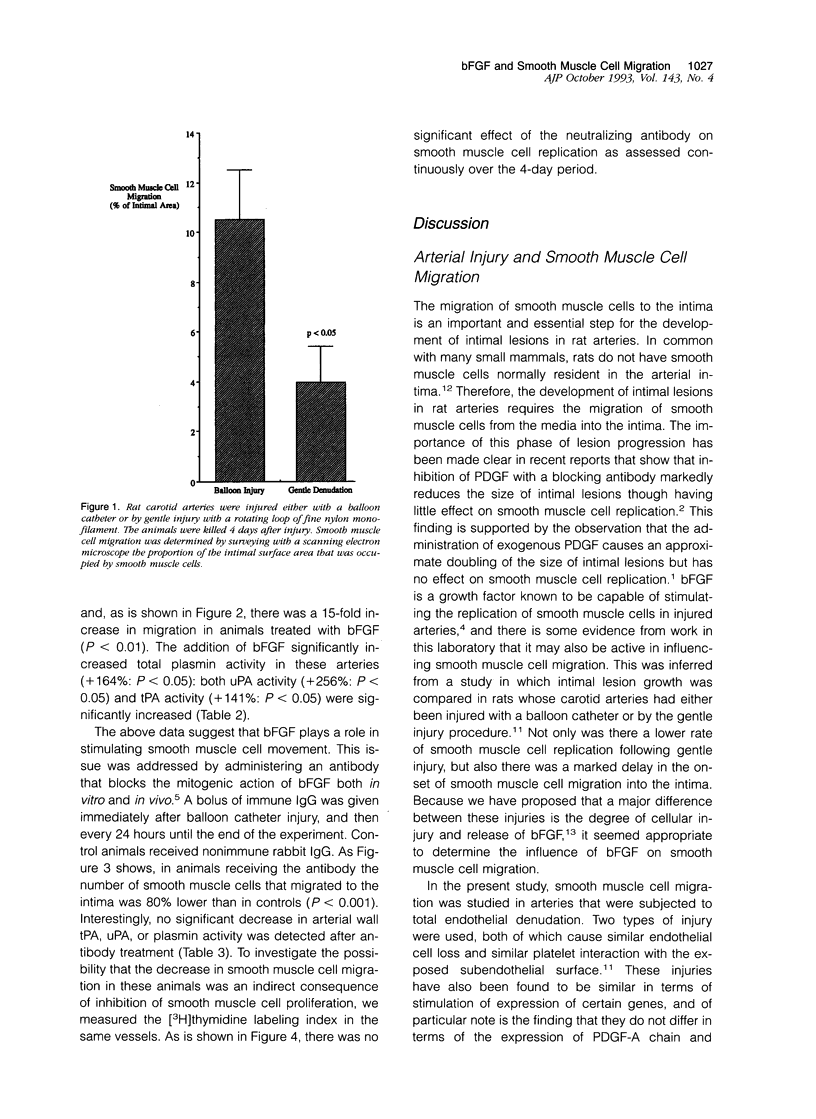
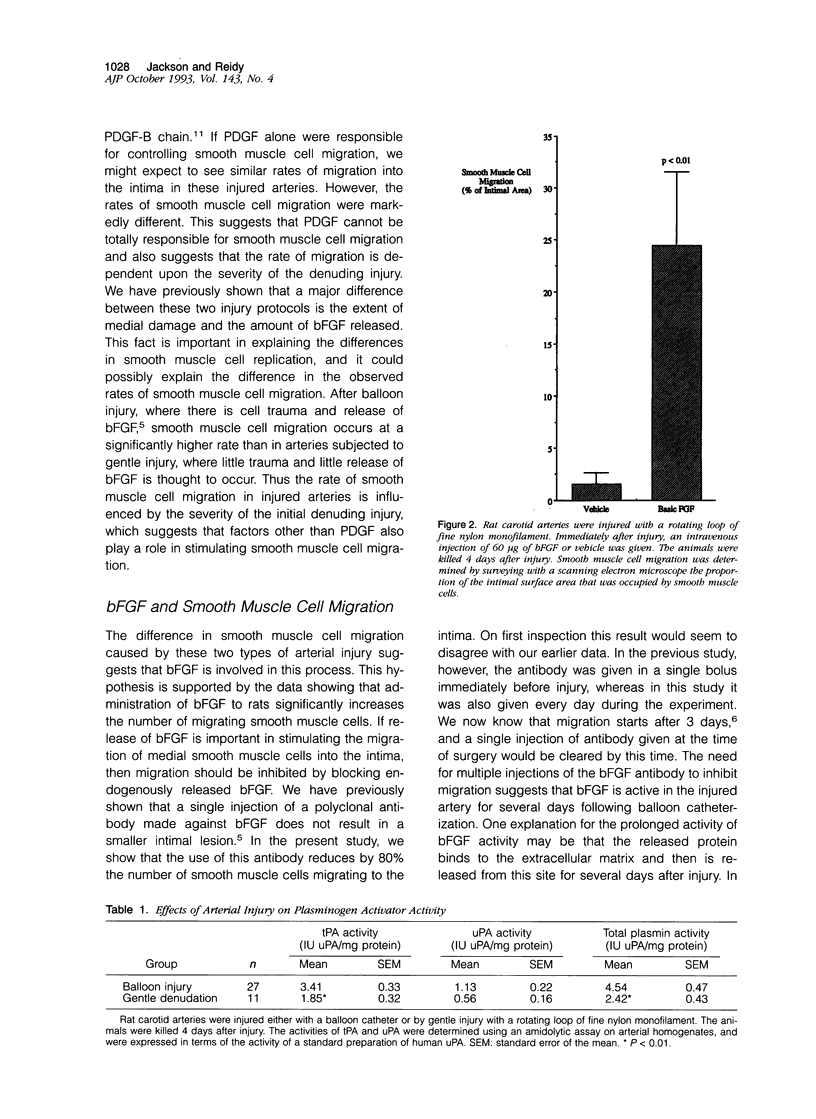
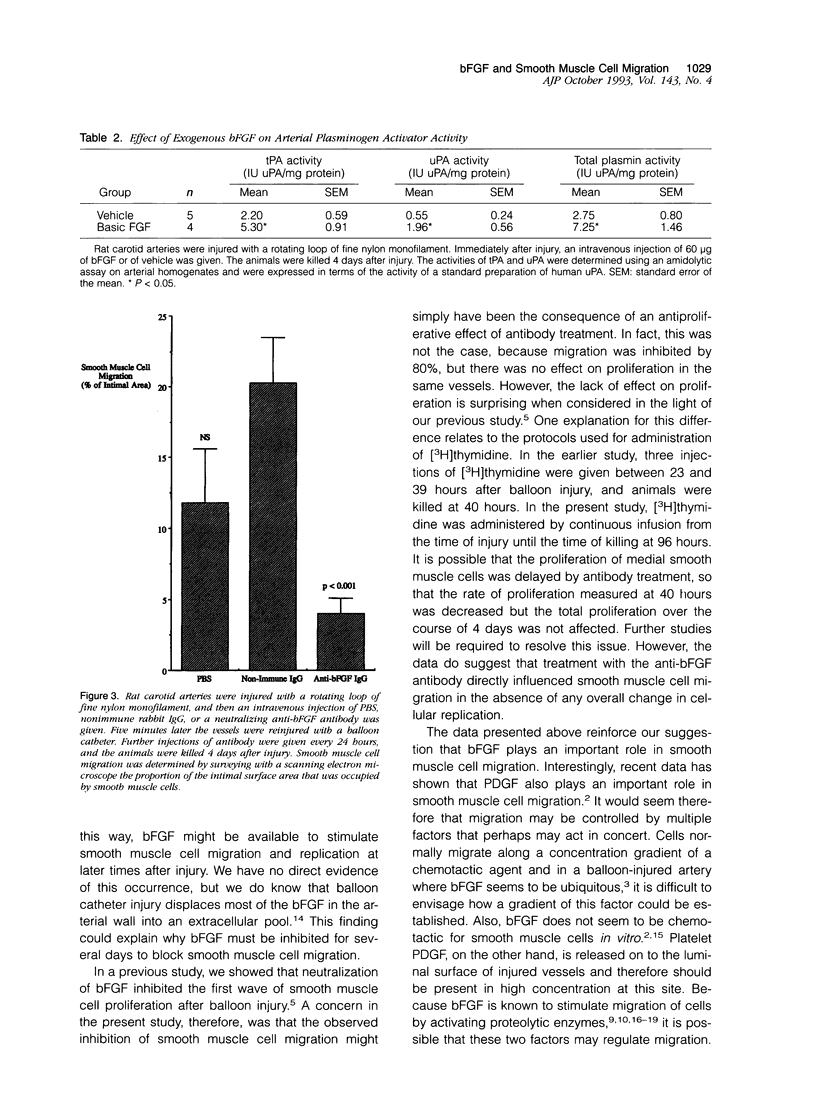
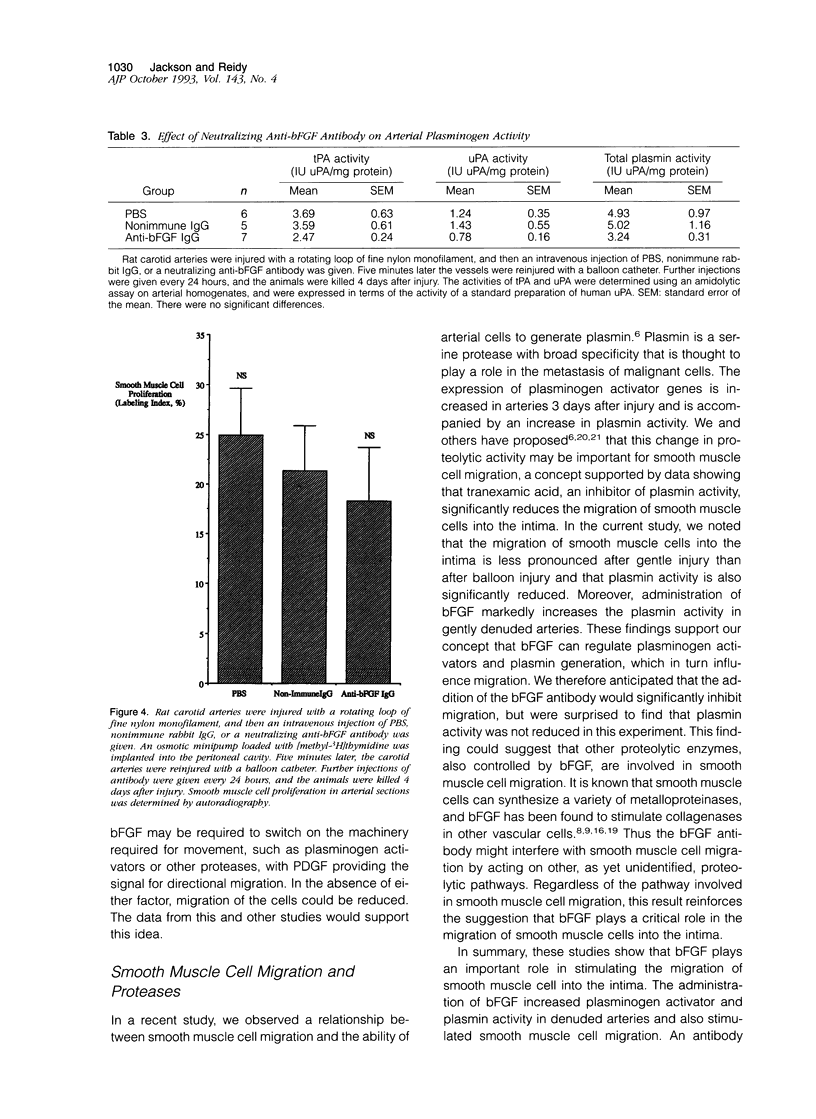

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Clowes A. W., Clowes M. M., Au Y. P., Reidy M. A., Belin D. Smooth muscle cells express urokinase during mitogenesis and tissue-type plasminogen activator during migration in injured rat carotid artery. Circ Res. 1990 Jul;67(1):61–67. doi: 10.1161/01.res.67.1.61. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clowes A. W., Clowes M. M., Kirkman T. R., Jackson C. L., Au Y. P., Kenagy R. Heparin inhibits the expression of tissue-type plasminogen activator by smooth muscle cells in injured rat carotid artery. Circ Res. 1992 Jun;70(6):1128–1136. doi: 10.1161/01.res.70.6.1128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferns G. A., Raines E. W., Sprugel K. H., Motani A. S., Reidy M. A., Ross R. Inhibition of neointimal smooth muscle accumulation after angioplasty by an antibody to PDGF. Science. 1991 Sep 6;253(5024):1129–1132. doi: 10.1126/science.1653454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fingerle J., Au Y. P., Clowes A. W., Reidy M. A. Intimal lesion formation in rat carotid arteries after endothelial denudation in absence of medial injury. Arteriosclerosis. 1990 Nov-Dec;10(6):1082–1087. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.10.6.1082. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross J. L., Moscatelli D., Jaffe E. A., Rifkin D. B. Plasminogen activator and collagenase production by cultured capillary endothelial cells. J Cell Biol. 1982 Dec;95(3):974–981. doi: 10.1083/jcb.95.3.974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grotendorst G. R., Chang T., Seppä H. E., Kleinman H. K., Martin G. R. Platelet-derived growth factor is a chemoattractant for vascular smooth muscle cells. J Cell Physiol. 1982 Nov;113(2):261–266. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041130213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jawien A., Bowen-Pope D. F., Lindner V., Schwartz S. M., Clowes A. W. Platelet-derived growth factor promotes smooth muscle migration and intimal thickening in a rat model of balloon angioplasty. J Clin Invest. 1992 Feb;89(2):507–511. doi: 10.1172/JCI115613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindner V., Lappi D. A., Baird A., Majack R. A., Reidy M. A. Role of basic fibroblast growth factor in vascular lesion formation. Circ Res. 1991 Jan;68(1):106–113. doi: 10.1161/01.res.68.1.106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindner V., Reidy M. A., Fingerle J. Regrowth of arterial endothelium. Denudation with minimal trauma leads to complete endothelial cell regrowth. Lab Invest. 1989 Nov;61(5):556–563. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindner V., Reidy M. A. Proliferation of smooth muscle cells after vascular injury is inhibited by an antibody against basic fibroblast growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 1;88(9):3739–3743. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.9.3739. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mignatti P., Tsuboi R., Robbins E., Rifkin D. B. In vitro angiogenesis on the human amniotic membrane: requirement for basic fibroblast growth factor-induced proteinases. J Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;108(2):671–682. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.2.671. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moscatelli D., Presta M., Rifkin D. B. Purification of a factor from human placenta that stimulates capillary endothelial cell protease production, DNA synthesis, and migration. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(7):2091–2095. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.7.2091. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson N. E., Chao S., Lindner V., Reidy M. A. Intimal smooth muscle cell proliferation after balloon catheter injury. The role of basic fibroblast growth factor. Am J Pathol. 1992 May;140(5):1017–1023. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pepper M. S., Belin D., Montesano R., Orci L., Vassalli J. D. Transforming growth factor-beta 1 modulates basic fibroblast growth factor-induced proteolytic and angiogenic properties of endothelial cells in vitro. J Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;111(2):743–755. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.2.743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Presta M., Moscatelli D., Joseph-Silverstein J., Rifkin D. B. Purification from a human hepatoma cell line of a basic fibroblast growth factor-like molecule that stimulates capillary endothelial cell plasminogen activator production, DNA synthesis, and migration. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Nov;6(11):4060–4066. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.11.4060. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reidy M. A., Schwartz S. M. Endothelial regeneration. III. Time course of intimal changes after small defined injury to rat aortic endothelium. Lab Invest. 1981 Apr;44(4):301–308. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato Y., Hamanaka R., Ono J., Kuwano M., Rifkin D. B., Takaki R. The stimulatory effect of PDGF on vascular smooth muscle cell migration is mediated by the induction of endogenous basic FGF. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Feb 14;174(3):1260–1266. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)91557-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato Y., Rifkin D. B. Autocrine activities of basic fibroblast growth factor: regulation of endothelial cell movement, plasminogen activator synthesis, and DNA synthesis. J Cell Biol. 1988 Sep;107(3):1199–1205. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.3.1199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuboi R., Sato Y., Rifkin D. B. Correlation of cell migration, cell invasion, receptor number, proteinase production, and basic fibroblast growth factor levels in endothelial cells. J Cell Biol. 1990 Feb;110(2):511–517. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.2.511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]