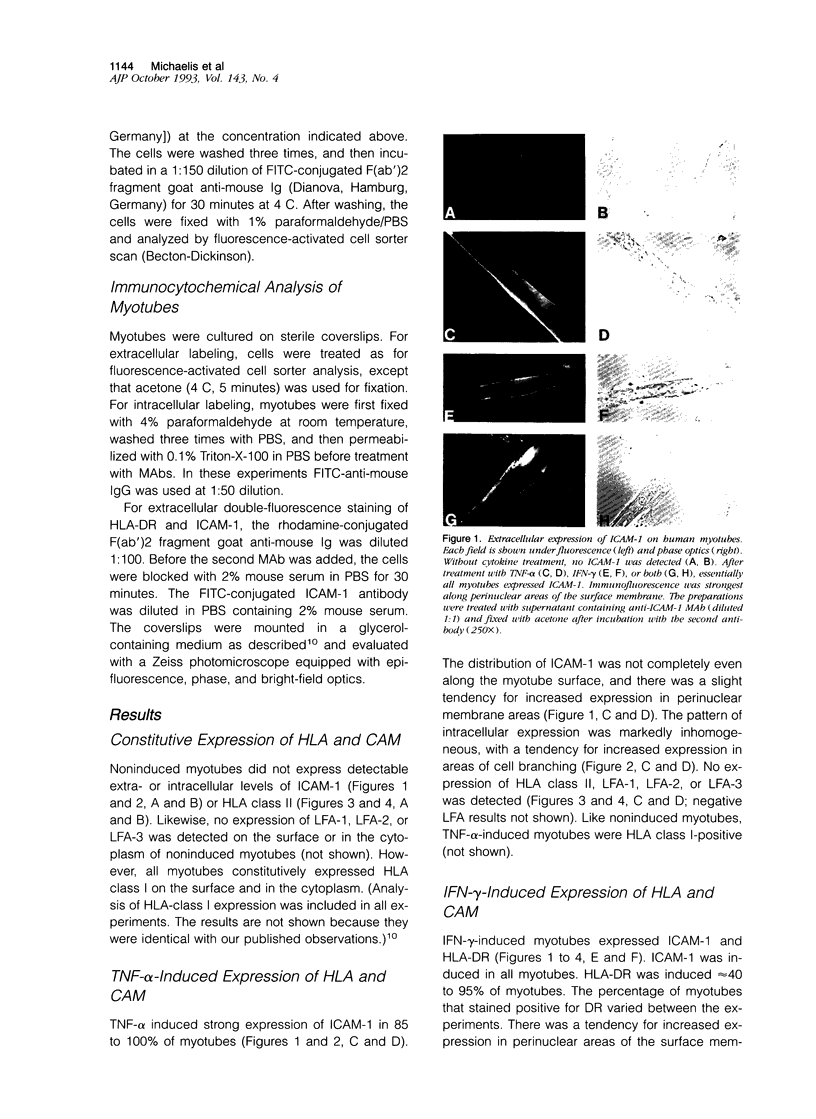
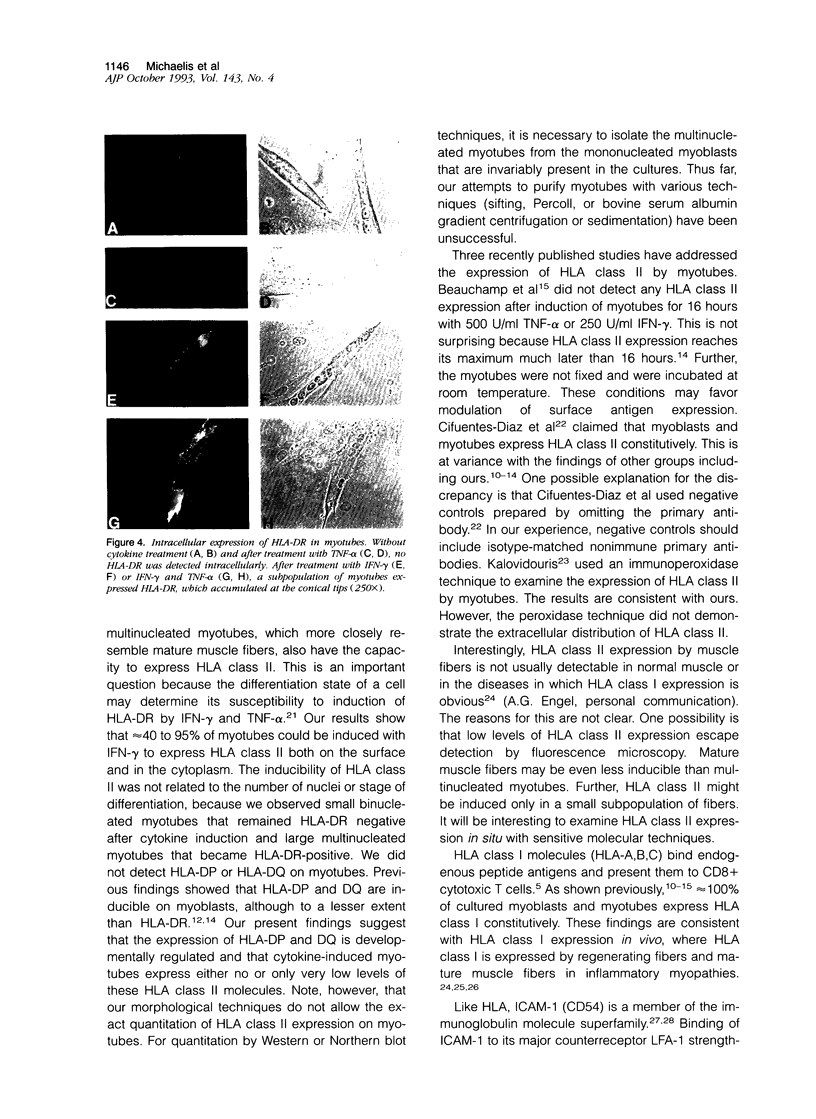
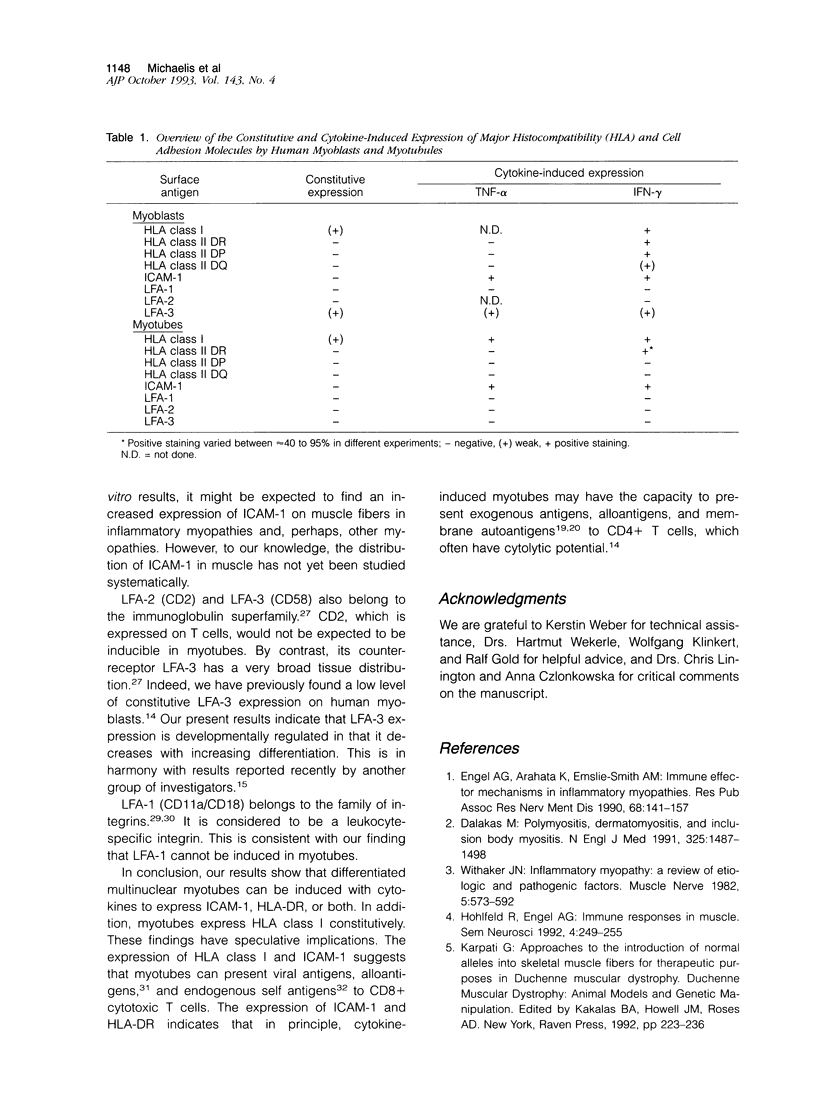
Abstract
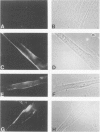
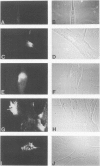
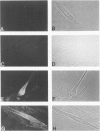
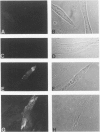
Understanding the immunobiology of muscle is relevant to muscular autoimmune diseases and to gene therapies based on myoblast transfer. We have investigated the constitutive and cytokine-induced intra- and extracellular expression of histocompatibility human leukocyte antigens (HLA) and cell adhesion molecules by multinucleated human myotubes using immunofluorescence microscopy. Myotubes constitutively expressed HLA class I but not HLA class II. Exposure to interferon-gamma, but not tumor necrosis factor-alpha, induced HLA-DR in the cytoplasm and on the surface membrane of approximately 40 to 95% of cultured myotubes. Surface expression was strongest in perinuclear membrane areas, and cytoplasmic expression was strongest at branching points and at the tips of myotubes. HLA-DP and HLA-DQ were not expressed in detectable amounts. Both interferon-gamma and tumor necrosis factor-alpha induced the intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (CD54) in the cytoplasm and on the surface of nearly all myotubes. The distribution of intercellular adhesion molecule-1 and HLA-DR was similar but not identical in double-positive myotubes. The leukocyte function-associated (LFA) adhesion molecules LFA-1 (CD11a/CD18), LFA-2 (CD2), and LFA-3 (CD58) could not be detected in the cytoplasm or on the surface. Our results indicate that cytokine-induced myotubes can participate in immune interactions with T lymphocytes.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Appleyard S. T., Dunn M. J., Dubowitz V., Rose M. L. Increased expression of HLA ABC class I antigens by muscle fibres in Duchenne muscular dystrophy, inflammatory myopathy, and other neuromuscular disorders. Lancet. 1985 Feb 16;1(8425):361–363. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)91384-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bao S. S., King N. J., dos Remedios C. G. Elevated MHC class I and II antigens in cultured human embryonic myoblasts following stimulation with gamma-interferon. Immunol Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;68(Pt 4):235–241. doi: 10.1038/icb.1990.33. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barr E., Leiden J. M. Systemic delivery of recombinant proteins by genetically modified myoblasts. Science. 1991 Dec 6;254(5037):1507–1509. doi: 10.1126/science.1962212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beauchamp J. R., Abraham D. J., Bou-Gharios G., Partridge T. A., Olsen I. Expression and function of heterotypic adhesion molecules during differentiation of human skeletal muscle in culture. Am J Pathol. 1992 Feb;140(2):387–401. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chicz R. M., Urban R. G., Lane W. S., Gorga J. C., Stern L. J., Vignali D. A., Strominger J. L. Predominant naturally processed peptides bound to HLA-DR1 are derived from MHC-related molecules and are heterogeneous in size. Nature. 1992 Aug 27;358(6389):764–768. doi: 10.1038/358764a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cifuentes-Diaz C., Delaporte C., Dautréaux B., Charron D., Fardeau M. Class II MHC antigens in normal human skeletal muscle. Muscle Nerve. 1992 Mar;15(3):295–302. doi: 10.1002/mus.880150307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dai Y., Roman M., Naviaux R. K., Verma I. M. Gene therapy via primary myoblasts: long-term expression of factor IX protein following transplantation in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Nov 15;89(22):10892–10895. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.22.10892. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalakas M. C. Polymyositis, dermatomyositis and inclusion-body myositis. N Engl J Med. 1991 Nov 21;325(21):1487–1498. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199111213252107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dhawan J., Pan L. C., Pavlath G. K., Travis M. A., Lanctot A. M., Blau H. M. Systemic delivery of human growth hormone by injection of genetically engineered myoblasts. Science. 1991 Dec 6;254(5037):1509–1512. doi: 10.1126/science.1962213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emslie-Smith A. M., Arahata K., Engel A. G. Major histocompatibility complex class I antigen expression, immunolocalization of interferon subtypes, and T cell-mediated cytotoxicity in myopathies. Hum Pathol. 1989 Mar;20(3):224–231. doi: 10.1016/0046-8177(89)90128-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engel A. G., Arahata K., Emslie-Smith A. Immune effector mechanisms in inflammatory myopathies. Res Publ Assoc Res Nerv Ment Dis. 1990;68:141–157. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goebels N., Michaelis D., Wekerle H., Hohlfeld R. Human myoblasts as antigen-presenting cells. J Immunol. 1992 Jul 15;149(2):661–667. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogg N., Bates P. A., Harvey J. Structure and function of intercellular adhesion molecule-1. Chem Immunol. 1991;50:98–115. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hohlfeld R., Engel A. G. Induction of HLA-DR expression on human myoblasts with interferon-gamma. Am J Pathol. 1990 Mar;136(3):503–508. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hohlfeld R., Engel A. G. Lysis of myotubes by alloreactive cytotoxic T cells and natural killer cells. Relevance to myoblast transplantation. J Clin Invest. 1990 Jul;86(1):370–374. doi: 10.1172/JCI114711. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hohlfeld R. Neurological autoimmune disease and the trimolecular complex of T-lymphocytes. Ann Neurol. 1989 Jun;25(6):531–538. doi: 10.1002/ana.410250602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hynes R. O. Integrins: versatility, modulation, and signaling in cell adhesion. Cell. 1992 Apr 3;69(1):11–25. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90115-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Illa I., Leon-Monzon M., Dalakas M. C. Regenerating and denervated human muscle fibers and satellite cells express neural cell adhesion molecule recognized by monoclonal antibodies to natural killer cells. Ann Neurol. 1992 Jan;31(1):46–52. doi: 10.1002/ana.410310109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jardetzky T. S., Lane W. S., Robinson R. A., Madden D. R., Wiley D. C. Identification of self peptides bound to purified HLA-B27. Nature. 1991 Sep 26;353(6342):326–329. doi: 10.1038/353326a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalovidouris A. E. The role of cytokines in polymyositis: interferon-gamma induces class II and enhances class I major histocompatibility complex antigen expression on cultured human muscle cells. J Lab Clin Med. 1992 Aug;120(2):244–251. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karpati G., Pouliot Y., Carpenter S. Expression of immunoreactive major histocompatibility complex products in human skeletal muscles. Ann Neurol. 1988 Jan;23(1):64–72. doi: 10.1002/ana.410230111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kropshofer H., Max H., Müller C. A., Hesse F., Stevanovic S., Jung G., Kalbacher H. Self-peptide released from class II HLA-DR1 exhibits a hydrophobic two-residue contact motif. J Exp Med. 1992 Jun 1;175(6):1799–1803. doi: 10.1084/jem.175.6.1799. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mantegazza R., Hughes S. M., Mitchell D., Travis M., Blau H. M., Steinman L. Modulation of MHC class II antigen expression in human myoblasts after treatment with IFN-gamma. Neurology. 1991 Jul;41(7):1128–1132. doi: 10.1212/wnl.41.7.1128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller A. D. Human gene therapy comes of age. Nature. 1992 Jun 11;357(6378):455–460. doi: 10.1038/357455a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roy R., Dansereau G., Tremblay J. P., Belles-Isles M., Huard J., Labrecque C., Bouchard J. P. Expression of major histocompatibility complex antigens on human myoblasts. Transplant Proc. 1991 Feb;23(1 Pt 1):799–801. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruoslahti E. Integrins. J Clin Invest. 1991 Jan;87(1):1–5. doi: 10.1172/JCI114957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schubert W., Zimmermann K., Cramer M., Starzinski-Powitz A. Lymphocyte antigen Leu-19 as a molecular marker of regeneration in human skeletal muscle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jan;86(1):307–311. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.1.307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Springer T. A. Adhesion receptors of the immune system. Nature. 1990 Aug 2;346(6283):425–434. doi: 10.1038/346425a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe Y., Jacob C. O. Regulation of MHC class II antigen expression. Opposing effects of tumor necrosis factor-alpha on IFN-gamma-induced HLA-DR and Ia expression depends on the maturation and differentiation stage of the cell. J Immunol. 1991 Feb 1;146(3):899–905. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitaker J. N. Inflammatory myopathy: a review of etiologic and pathogenetic factors. Muscle Nerve. 1982 Oct;5(8):573–592. doi: 10.1002/mus.880050802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]