Abstract
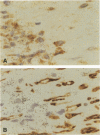
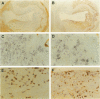
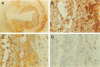
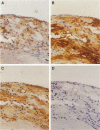
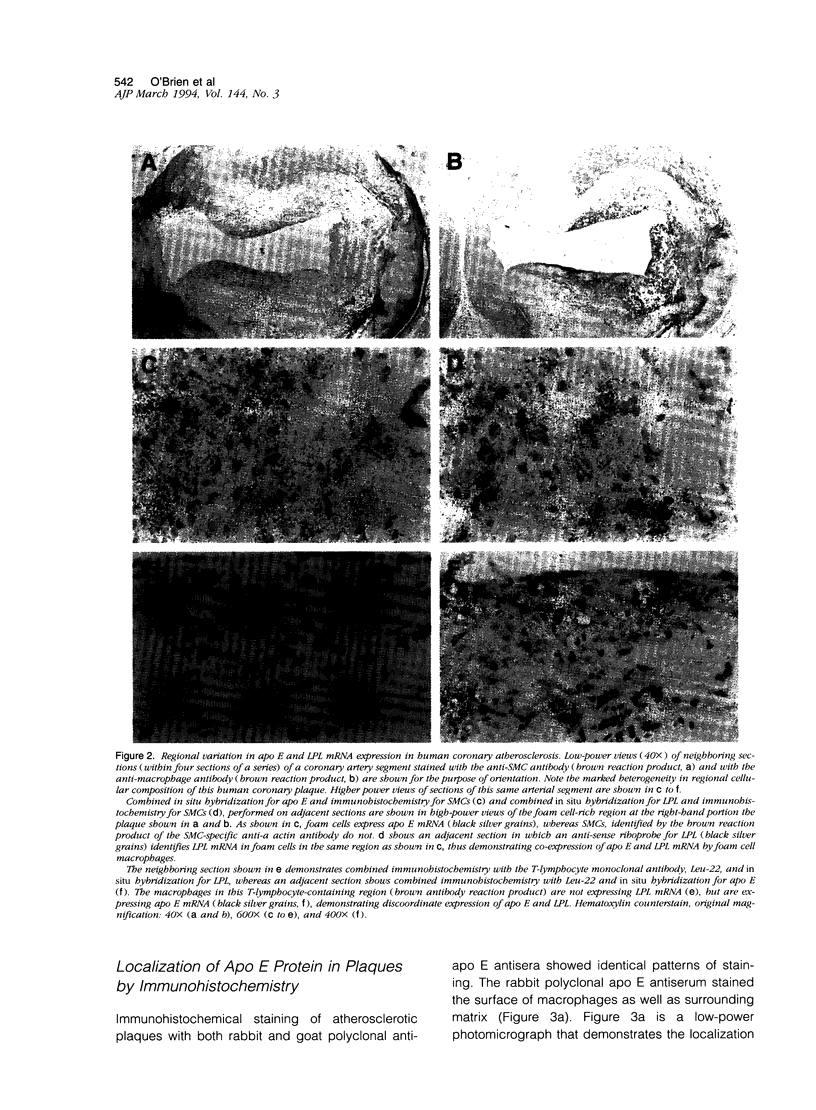
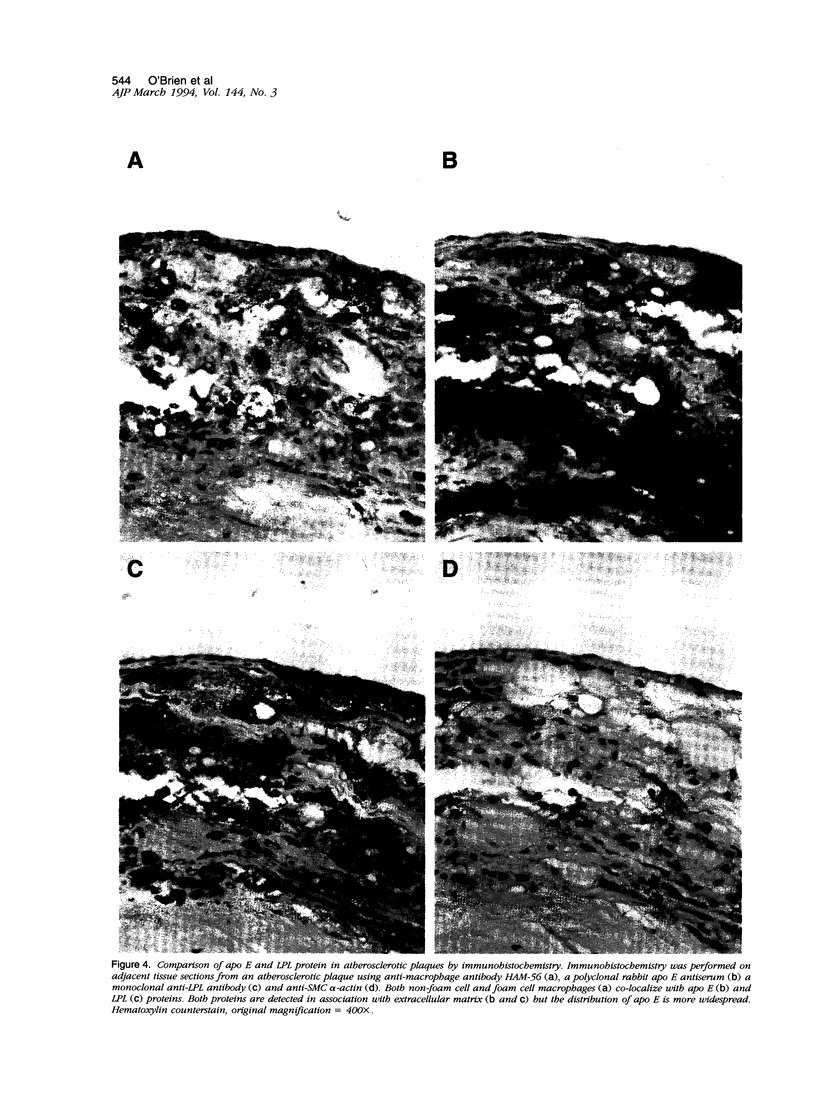
Apolipoprotein E (apo E) mediates both lipid accumulation by and removal from cells and may be secreted by both macrophages and smooth muscle cells in vitro, but its cellular source in atherosclerotic plaques is not known. Lipoprotein lipase (LPL) also enhances cell lipid accumulation and is synthesized by macrophage foam cells in atherosclerotic plaques. To determine the cellular source of apo E in human coronary atherosclerotic lesions and its relationship to LPL synthesis, in situ hybridization and immunohistochemistry were performed on 12 atherosclerotic plaques and six nondiseased coronary artery segments from 10 cardiac transplant recipients. Apo E messenger RNA was localized to both non-foam cell and foam cell macrophages in plaques, but not to other cell types, and was not detected in nonatherosclerotic arteries. Half of the regions with non-foam cell macrophages expressed neither apo E nor LPL messenger RNA, whereas 86% of macrophage foam cell-containing regions contained both messenger RNAs. Polyclonal antisera raised against human apo E localized apo E protein to the surface of macrophages and surrounding matrix in plaques but not in control coronary segments. An LPL-specific monoclonal antibody demonstrated that, similar to apo E, LPL protein on foam cell and non-foam cell macrophages was detected in atherosclerotic lesions, but LPL was also localized to intimal muscle smooth muscle cells and was not distributed as widely in association with matrix as was apo E. The expression of both apo E and LPL in atherosclerotic lesions but not in normal intima suggest that these molecules play a role in lipid metabolism in atherosclerosis.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Auwerx J. H., Deeb S., Brunzell J. D., Peng R., Chait A. Transcriptional activation of the lipoprotein lipase and apolipoprotein E genes accompanies differentiation in some human macrophage-like cell lines. Biochemistry. 1988 Apr 19;27(8):2651–2655. doi: 10.1021/bi00408a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aviram M., Bierman E. L., Chait A. Modification of low density lipoprotein by lipoprotein lipase or hepatic lipase induces enhanced uptake and cholesterol accumulation in cells. J Biol Chem. 1988 Oct 25;263(30):15416–15422. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Basheeruddin K., Rechtoris C., Mazzone T. Transcriptional and post-transcriptional control of apolipoprotein E gene expression in differentiating human monocytes. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jan 15;267(2):1219–1224. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Basu S. K., Brown M. S., Ho Y. K., Havel R. J., Goldstein J. L. Mouse macrophages synthesize and secrete a protein resembling apolipoprotein E. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Dec;78(12):7545–7549. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.12.7545. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Basu S. K., Goldstein J. L., Brown M. S. Independent pathways for secretion of cholesterol and apolipoprotein E by macrophages. Science. 1983 Feb 18;219(4586):871–873. doi: 10.1126/science.6823554. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Basu S. K., Ho Y. K., Brown M. S., Bilheimer D. W., Anderson R. G., Goldstein J. L. Biochemical and genetic studies of the apoprotein E secreted by mouse macrophages and human monocytes. J Biol Chem. 1982 Aug 25;257(16):9788–9795. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beisiegel U., Weber W., Bengtsson-Olivecrona G. Lipoprotein lipase enhances the binding of chylomicrons to low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 1;88(19):8342–8346. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.19.8342. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clinton S. K., Underwood R., Hayes L., Sherman M. L., Kufe D. W., Libby P. Macrophage colony-stimulating factor gene expression in vascular cells and in experimental and human atherosclerosis. Am J Pathol. 1992 Feb;140(2):301–316. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crespo P., González C., Ordovás J. M., Ortiz J. M., Rodriguez J. C., León J. Induction of apolipoprotein E gene expression in human and experimental atherosclerotic lesions. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Apr 30;168(2):733–740. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)92383-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtiss L. K., Edgington T. S. Differential sensitivity of lymphocyte subpopulations to suppression by low density lipoprotein inhibitor, an immunoregulatory human serum low density lipoprotein. J Clin Invest. 1979 Feb;63(2):193–201. doi: 10.1172/JCI109289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtiss L. K., Edgington T. S. Effect of LDL-In, a normal immunoregulatory human serum low density lipoprotein, on the interaction of macrophages with lymphocytes proliferating in response to mitogen and allogeneic stimulation. J Immunol. 1977 Jun;118(6):1966–1970. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuthbert J. A., Lipsky P. E. Modulation of human lymphocyte responses by low density lipoproteins (LDL): enhancement but not immunosuppression is mediated by LDL receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(14):4539–4543. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.14.4539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon D., Reidy M. A., Benditt E. P., Schwartz S. M. Cell proliferation in human coronary arteries. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(12):4600–4604. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.12.4600. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gown A. M., Tsukada T., Ross R. Human atherosclerosis. II. Immunocytochemical analysis of the cellular composition of human atherosclerotic lesions. Am J Pathol. 1986 Oct;125(1):191–207. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonasson L., Hansson G. K., Bondjers G., Noe L., Etienne J. Interferon-gamma inhibits lipoprotein lipase in human monocyte-derived macrophages. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Jun 12;1053(1):43–48. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(90)90024-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindqvist P., Ostlund-Lindqvist A. M., Witztum J. L., Steinberg D., Little J. A. The role of lipoprotein lipase in the metabolism of triglyceride-rich lipoproteins by macrophages. J Biol Chem. 1983 Aug 10;258(15):9086–9092. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahley R. W. Apolipoprotein E: cholesterol transport protein with expanding role in cell biology. Science. 1988 Apr 29;240(4852):622–630. doi: 10.1126/science.3283935. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majack R. A., Castle C. K., Goodman L. V., Weisgraber K. H., Mahley R. W., Shooter E. M., Gebicke-Haerter P. J. Expression of apolipoprotein E by cultured vascular smooth muscle cells is controlled by growth state. J Cell Biol. 1988 Sep;107(3):1207–1213. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.3.1207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menju M., Tajima S., Yamamoto A. Expression of the apolipoprotein E gene in a human macrophage-like cell line, THP-1. J Biochem. 1989 Sep;106(3):505–510. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a122882. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mori N., Gotoda T., Ishibashi S., Shimano H., Harada K., Inaba T., Takaku F., Yazaki Y., Yamada N. Effects of human recombinant macrophage colony-stimulating factor on the secretion of lipoprotein lipase from macrophages. Arterioscler Thromb. 1991 Sep-Oct;11(5):1315–1321. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.11.5.1315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulder M., Lombardi P., Jansen H., van Berkel T. J., Frants R. R., Havekes L. M. Heparan sulphate proteoglycans are involved in the lipoprotein lipase-mediated enhancement of the cellular binding of very low density and low density lipoproteins. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Jun 15;185(2):582–587. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(92)91664-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien K. D., Gordon D., Deeb S., Ferguson M., Chait A. Lipoprotein lipase is synthesized by macrophage-derived foam cells in human coronary atherosclerotic plaques. J Clin Invest. 1992 May;89(5):1544–1550. doi: 10.1172/JCI115747. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson J., Fujimoto W. Y., Brunzell J. D. Human lipoprotein lipase: relationship of activity, heparin affinity, and conformation as studied with monoclonal antibodies. J Lipid Res. 1992 Aug;33(8):1165–1170. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plump A. S., Smith J. D., Hayek T., Aalto-Setälä K., Walsh A., Verstuyft J. G., Rubin E. M., Breslow J. L. Severe hypercholesterolemia and atherosclerosis in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice created by homologous recombination in ES cells. Cell. 1992 Oct 16;71(2):343–353. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90362-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Querfeld U., Ong J. M., Prehn J., Carty J., Saffari B., Jordan S. C., Kern P. A. Effects of cytokines on the production of lipoprotein lipase in cultured human macrophages. J Lipid Res. 1990 Aug;31(8):1379–1386. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenfeld M. E., Butler S., Ord V. A., Lipton B. A., Dyer C. A., Curtiss L. K., Palinski W., Witztum J. L. Abundant expression of apoprotein E by macrophages in human and rabbit atherosclerotic lesions. Arterioscler Thromb. 1993 Sep;13(9):1382–1389. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.13.9.1382. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rumsey S. C., Obunike J. C., Arad Y., Deckelbaum R. J., Goldberg I. J. Lipoprotein lipase-mediated uptake and degradation of low density lipoproteins by fibroblasts and macrophages. J Clin Invest. 1992 Oct;90(4):1504–1512. doi: 10.1172/JCI116018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Said J. W., Stoll P. N., Shintaku P., Bindl J. M., Butmarc J. R., Pinkus G. S. Leu-22: a preferential marker for T-lymphocytes in paraffin sections. Staining profile in T- and B-cell lymphomas, Hodgkin's disease, other lymphoproliferative disorders, myeloproliferative diseases, and various neoplastic processes. Am J Clin Pathol. 1989 May;91(5):542–549. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/91.5.542. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salomon R. N., Underwood R., Doyle M. V., Wang A., Libby P. Increased apolipoprotein E and c-fms gene expression without elevated interleukin 1 or 6 mRNA levels indicates selective activation of macrophage functions in advanced human atheroma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 1;89(7):2814–2818. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.7.2814. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saxena U., Klein M. G., Vanni T. M., Goldberg I. J. Lipoprotein lipase increases low density lipoprotein retention by subendothelial cell matrix. J Clin Invest. 1992 Feb;89(2):373–380. doi: 10.1172/JCI115595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuler G., Hambrecht R., Schlierf G., Niebauer J., Hauer K., Neumann J., Hoberg E., Drinkmann A., Bacher F., Grunze M. Regular physical exercise and low-fat diet. Effects on progression of coronary artery disease. Circulation. 1992 Jul;86(1):1–11. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.86.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skalli O., Ropraz P., Trzeciak A., Benzonana G., Gillessen D., Gabbiani G. A monoclonal antibody against alpha-smooth muscle actin: a new probe for smooth muscle differentiation. J Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;103(6 Pt 2):2787–2796. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.6.2787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vance J. E., Khoo J. C., Steinberg D. Lipoprotein lipase in cultured pig aortic smooth muscle cells. Arteriosclerosis. 1982 Sep-Oct;2(5):390–395. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.2.5.390. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werb Z., Chin J. R., Takemura R., Oropeza R. L., Bainton D. F., Stenberg P., Taylor J. M., Reardon C. The cell and molecular biology of apolipoprotein E synthesis by macrophages. Ciba Found Symp. 1986;118:155–171. doi: 10.1002/9780470720998.ch11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werb Z., Takemura R., Stenberg P. E., Bainton D. F. Directed exocytosis of secretory granules containing apolipoprotein E to the adherent surface and basal vacuoles of macrophages spreading on immobile immune complexes. Am J Pathol. 1989 Mar;134(3):661–670. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams K. J., Fless G. M., Petrie K. A., Snyder M. L., Brocia R. W., Swenson T. L. Mechanisms by which lipoprotein lipase alters cellular metabolism of lipoprotein(a), low density lipoprotein, and nascent lipoproteins. Roles for low density lipoprotein receptors and heparan sulfate proteoglycans. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jul 5;267(19):13284–13292. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada N., Inoue I., Kawamura M., Harada K., Watanabe Y., Shimano H., Gotoda T., Shimada M., Kohzaki K., Tsukada T. Apolipoprotein E prevents the progression of atherosclerosis in Watanabe heritable hyperlipidemic rabbits. J Clin Invest. 1992 Feb;89(2):706–711. doi: 10.1172/JCI115639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ylä-Herttuala S., Lipton B. A., Rosenfeld M. E., Goldberg I. J., Steinberg D., Witztum J. L. Macrophages and smooth muscle cells express lipoprotein lipase in human and rabbit atherosclerotic lesions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 15;88(22):10143–10147. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.22.10143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang S. H., Reddick R. L., Piedrahita J. A., Maeda N. Spontaneous hypercholesterolemia and arterial lesions in mice lacking apolipoprotein E. Science. 1992 Oct 16;258(5081):468–471. doi: 10.1126/science.1411543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]