Abstract
MAP kinases (MAPK) are a family of serine/threonine (Ser/Thr) kinases that link cell surface signals to changes in enzyme activity and gene expression. They are the products of the newly described gene family referred to as extracellular signal regulated kinases (ERKs). Moreover, MAPKs phosphorylate tau in vitro at Ser/Thr Proline sites, generating a multiply phosphorylated tau protein that is similar to the hyperphosphorylated tau found in Alzheimer neurofibrillary tangles (NFTs). We studied MAPK immunoreactivity and in situ hybridization patterns of the two major genes that comprise MAPK activity, ERK1 and ERK2, in the human hippocampal formation. Our goal was to determine whether the pattern of ERK expression is consistent with the hypothesis that MAPKs contribute to NFT formation. ERK1 mRNA is present in small amounts and confined primarily to dentate gyrus granule cells. ERK2 mRNA, by contrast, gives a much stronger hybridization signal and is present in dentate gyrus granule cells and pyramidal cells throughout all hippocampal subfields and adjacent temporal neocortex. Quantitative measures of ERK2 mRNA reveal that NFT-bearing neurons contain approximately 15% less ERK2 mRNA than nearest neighbors that do not contain NFT. NFT-bearing neurons contain approximately 25% less polyA mRNA, suggesting a relative preservation of ERK2 mRNA even in metabolically compromised cells. MAPK immunoreactivity (which represents both ERK1 and ERK2) is seen in neuronal soma, dendrites, axons, and in reactive astrocytes. In Alzheimer's disease, neurons that contain NFTs are also MAPK immunoreactive, but neurons that contain the highest amounts of MAPK immunoreactivity are not necessarily vulnerable for NFT. MAPK immunoreactivity is present in the same neurons as NFT and in the same subcellular compartments as tau, supporting a role for MAPKs in tau phosphorylation in Alzheimer's disease. However, the presence of ERK immunoreactivity is not sufficient to predispose neurons to NFT formation.
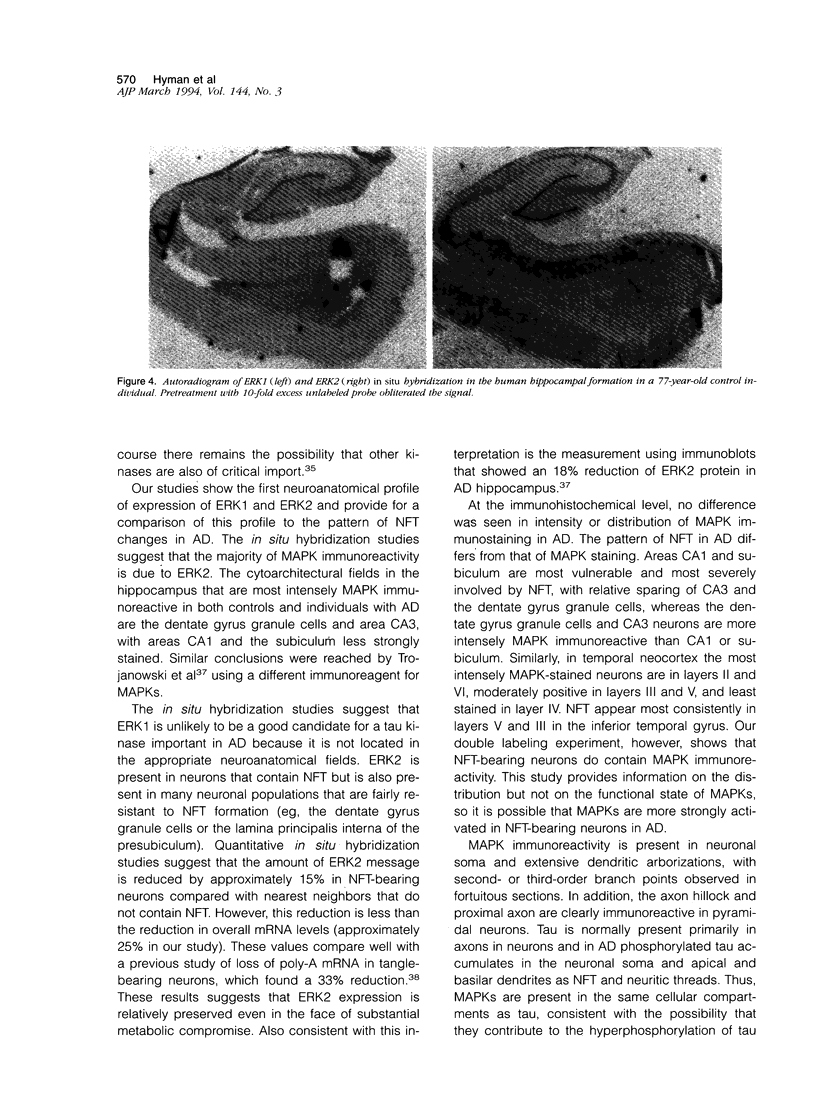
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alvarez E., Northwood I. C., Gonzalez F. A., Latour D. A., Seth A., Abate C., Curran T., Davis R. J. Pro-Leu-Ser/Thr-Pro is a consensus primary sequence for substrate protein phosphorylation. Characterization of the phosphorylation of c-myc and c-jun proteins by an epidermal growth factor receptor threonine 669 protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 15;266(23):15277–15285. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arriagada P. V., Growdon J. H., Hedley-Whyte E. T., Hyman B. T. Neurofibrillary tangles but not senile plaques parallel duration and severity of Alzheimer's disease. Neurology. 1992 Mar;42(3 Pt 1):631–639. doi: 10.1212/wnl.42.3.631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bading H., Greenberg M. E. Stimulation of protein tyrosine phosphorylation by NMDA receptor activation. Science. 1991 Aug 23;253(5022):912–914. doi: 10.1126/science.1715095. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baudier J., Cole R. D. Phosphorylation of tau proteins to a state like that in Alzheimer's brain is catalyzed by a calcium/calmodulin-dependent kinase and modulated by phospholipids. J Biol Chem. 1987 Dec 25;262(36):17577–17583. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biernat J., Gustke N., Drewes G., Mandelkow E. M., Mandelkow E. Phosphorylation of Ser262 strongly reduces binding of tau to microtubules: distinction between PHF-like immunoreactivity and microtubule binding. Neuron. 1993 Jul;11(1):153–163. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(93)90279-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boulton T. G., Nye S. H., Robbins D. J., Ip N. Y., Radziejewska E., Morgenbesser S. D., DePinho R. A., Panayotatos N., Cobb M. H., Yancopoulos G. D. ERKs: a family of protein-serine/threonine kinases that are activated and tyrosine phosphorylated in response to insulin and NGF. Cell. 1991 May 17;65(4):663–675. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90098-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boulton T. G., Yancopoulos G. D., Gregory J. S., Slaughter C., Moomaw C., Hsu J., Cobb M. H. An insulin-stimulated protein kinase similar to yeast kinases involved in cell cycle control. Science. 1990 Jul 6;249(4964):64–67. doi: 10.1126/science.2164259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark-Lewis I., Sanghera J. S., Pelech S. L. Definition of a consensus sequence for peptide substrate recognition by p44mpk, the meiosis-activated myelin basic protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 15;266(23):15180–15184. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crews C. M., Alessandrini A., Erikson R. L. The primary structure of MEK, a protein kinase that phosphorylates the ERK gene product. Science. 1992 Oct 16;258(5081):478–480. doi: 10.1126/science.1411546. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drewes G., Lichtenberg-Kraag B., Döring F., Mandelkow E. M., Biernat J., Goris J., Dorée M., Mandelkow E. Mitogen activated protein (MAP) kinase transforms tau protein into an Alzheimer-like state. EMBO J. 1992 Jun;11(6):2131–2138. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05272.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goedert M., Cohen E. S., Jakes R., Cohen P. p42 MAP kinase phosphorylation sites in microtubule-associated protein tau are dephosphorylated by protein phosphatase 2A1. Implications for Alzheimer's disease [corrected]. FEBS Lett. 1992 Nov 2;312(1):95–99. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)81418-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goedert M., Sisodia S. S., Price D. L. Neurofibrillary tangles and beta-amyloid deposits in Alzheimer's disease. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 1991 Oct;1(3):441–447. doi: 10.1016/0959-4388(91)90067-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin W. S., Ling C., White C. L., 3rd, Morrison-Bogorad M. Polyadenylated messenger RNA in paired helical filament-immunoreactive neurons in Alzheimer disease. Alzheimer Dis Assoc Disord. 1990 Summer;4(2):69–78. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gómez N., Cohen P. Dissection of the protein kinase cascade by which nerve growth factor activates MAP kinases. Nature. 1991 Sep 12;353(6340):170–173. doi: 10.1038/353170a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagestedt T., Lichtenberg B., Wille H., Mandelkow E. M., Mandelkow E. Tau protein becomes long and stiff upon phosphorylation: correlation between paracrystalline structure and degree of phosphorylation. J Cell Biol. 1989 Oct;109(4 Pt 1):1643–1651. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.4.1643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanger D. P., Hughes K., Woodgett J. R., Brion J. P., Anderton B. H. Glycogen synthase kinase-3 induces Alzheimer's disease-like phosphorylation of tau: generation of paired helical filament epitopes and neuronal localisation of the kinase. Neurosci Lett. 1992 Nov 23;147(1):58–62. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(92)90774-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyman B. T., Van Hoesen G. W., Damasio A. R. Memory-related neural systems in Alzheimer's disease: an anatomic study. Neurology. 1990 Nov;40(11):1721–1730. doi: 10.1212/wnl.40.11.1721. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishiguro K., Takamatsu M., Tomizawa K., Omori A., Takahashi M., Arioka M., Uchida T., Imahori K. Tau protein kinase I converts normal tau protein into A68-like component of paired helical filaments. J Biol Chem. 1992 May 25;267(15):10897–10901. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lange-Carter C. A., Pleiman C. M., Gardner A. M., Blumer K. J., Johnson G. L. A divergence in the MAP kinase regulatory network defined by MEK kinase and Raf. Science. 1993 Apr 16;260(5106):315–319. doi: 10.1126/science.8385802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ledesma M. D., Correas I., Avila J., Díaz-Nido J. Implication of brain cdc2 and MAP2 kinases in the phosphorylation of tau protein in Alzheimer's disease. FEBS Lett. 1992 Aug 17;308(2):218–224. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)81278-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee V. M., Balin B. J., Otvos L., Jr, Trojanowski J. Q. A68: a major subunit of paired helical filaments and derivatized forms of normal Tau. Science. 1991 Feb 8;251(4994):675–678. doi: 10.1126/science.1899488. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindwall G., Cole R. D. The purification of tau protein and the occurrence of two phosphorylation states of tau in brain. J Biol Chem. 1984 Oct 10;259(19):12241–12245. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandelkow E. M., Drewes G., Biernat J., Gustke N., Van Lint J., Vandenheede J. R., Mandelkow E. Glycogen synthase kinase-3 and the Alzheimer-like state of microtubule-associated protein tau. FEBS Lett. 1992 Dec 21;314(3):315–321. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)81496-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne D. M., Rossomando A. J., Martino P., Erickson A. K., Her J. H., Shabanowitz J., Hunt D. F., Weber M. J., Sturgill T. W. Identification of the regulatory phosphorylation sites in pp42/mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAP kinase). EMBO J. 1991 Apr;10(4):885–892. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb08021.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pulverer B. J., Kyriakis J. M., Avruch J., Nikolakaki E., Woodgett J. R. Phosphorylation of c-jun mediated by MAP kinases. Nature. 1991 Oct 17;353(6345):670–674. doi: 10.1038/353670a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roder H. M., Eden P. A., Ingram V. M. Brain protein kinase PK40erk converts TAU into a PHF-like form as found in Alzheimer's disease. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1993 Jun 15;193(2):639–647. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1993.1672. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossomando A. J., Payne D. M., Weber M. J., Sturgill T. W. Evidence that pp42, a major tyrosine kinase target protein, is a mitogen-activated serine/threonine protein kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(18):6940–6943. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.18.6940. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossomando A. J., Sanghera J. S., Marsden L. A., Weber M. J., Pelech S. L., Sturgill T. W. Biochemical characterization of a family of serine/threonine protein kinases regulated by tyrosine and serine/threonine phosphorylations. J Biol Chem. 1991 Oct 25;266(30):20270–20275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seger R., Ahn N. G., Boulton T. G., Yancopoulos G. D., Panayotatos N., Radziejewska E., Ericsson L., Bratlien R. L., Cobb M. H., Krebs E. G. Microtubule-associated protein 2 kinases, ERK1 and ERK2, undergo autophosphorylation on both tyrosine and threonine residues: implications for their mechanism of activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 15;88(14):6142–6146. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.14.6142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steiner B., Mandelkow E. M., Biernat J., Gustke N., Meyer H. E., Schmidt B., Mieskes G., Söling H. D., Drechsel D., Kirschner M. W. Phosphorylation of microtubule-associated protein tau: identification of the site for Ca2(+)-calmodulin dependent kinase and relationship with tau phosphorylation in Alzheimer tangles. EMBO J. 1990 Nov;9(11):3539–3544. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07563.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stratton K. R., Worley P. F., Litz J. S., Parsons S. J., Huganir R. L., Baraban J. M. Electroconvulsive treatment induces a rapid and transient increase in tyrosine phosphorylation of a 40-kilodalton protein associated with microtubule-associated protein 2 kinase activity. J Neurochem. 1991 Jan;56(1):147–152. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1991.tb02574.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi M., Tomizawa K., Ishiguro K., Sato K., Omori A., Sato S., Shiratsuchi A., Uchida T., Imahori K. A novel brain-specific 25 kDa protein (p25) is phosphorylated by a Ser/Thr-Pro kinase (TPK II) from tau protein kinase fractions. FEBS Lett. 1991 Sep 2;289(1):37–43. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80903-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trojanowski J. Q., Mawal-Dewan M., Schmidt M. L., Martin J., Lee V. M. Localization of the mitogen activated protein kinase ERK2 in Alzheimer's disease neurofibrillary tangles and senile plaque neurites. Brain Res. 1993 Aug 6;618(2):333–337. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(93)91286-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vincent I. J., Davies P. A protein kinase associated with paired helical filaments in Alzheimer disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 1;89(7):2878–2882. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.7.2878. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]