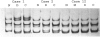Abstract
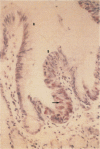
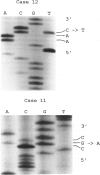
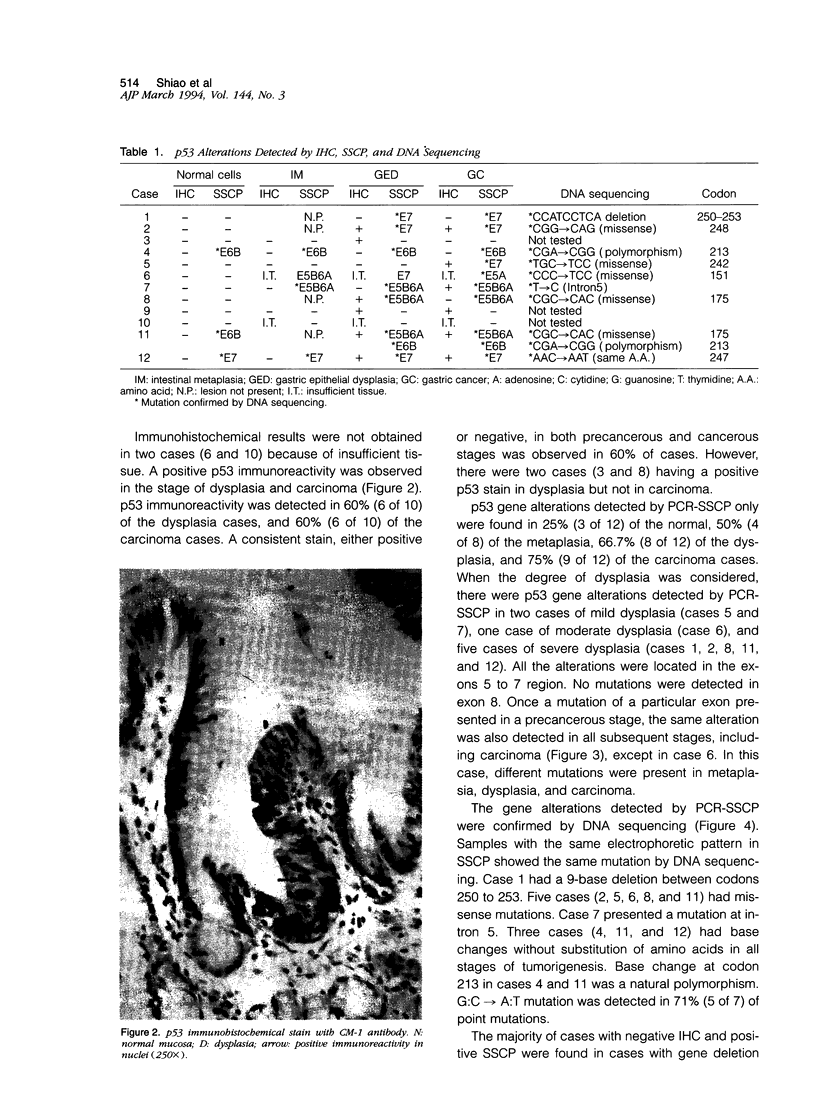
It has been postulated that chronic atrophic gastritis, intestinal metaplasia, and dysplasia are precancerous stages of stomach tumorigenesis. We investigated the timing of p53 alterations in these events of gastric tumorigenesis. Each of 12 cases of archived tissue containing precancerous and cancerous lesions were selected for the detection of p53 alterations. Accumulation of p53 protein was detected by immunohistochemistry. Exons 5 to 8 of p53 gene were examined for mutations by polymerase chain reaction-single strand conformation polymorphism and DNA sequencing. p53 immunoreactivity was detected in 60% of the dysplasia cases and in 60% of the cases with carcinomas. p53 gene alterations were found in 37.5% of the metaplasia cases, 58.3% of the dysplasia cases, and 66.7% of the cases with carcinomas. In 71% of the cases, mutations were shown as G:C-->A:T transition. We conclude that mutation of the p53 gene is an early event in stomach tumorigenesis.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ainsworth P. J., Surh L. C., Coulter-Mackie M. B. Diagnostic single strand conformational polymorphism, (SSCP): a simplified non-radioisotopic method as applied to a Tay-Sachs B1 variant. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jan 25;19(2):405–406. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.2.405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boddie A. W., Jr, McBride C. M., Balch C. M. Gastric cancer. Am J Surg. 1989 Jun;157(6):595–606. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(89)90710-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carbone D., Chiba I., Mitsudomi T. Polymorphism at codon 213 within the p53 gene. Oncogene. 1991 Sep;6(9):1691–1692. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Correa P. A human model of gastric carcinogenesis. Cancer Res. 1988 Jul 1;48(13):3554–3560. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Correa P. Human gastric carcinogenesis: a multistep and multifactorial process--First American Cancer Society Award Lecture on Cancer Epidemiology and Prevention. Cancer Res. 1992 Dec 15;52(24):6735–6740. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fritsche M., Haessler C., Brandner G. Induction of nuclear accumulation of the tumor-suppressor protein p53 by DNA-damaging agents. Oncogene. 1993 Feb;8(2):307–318. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imazeki F., Omata M., Nose H., Ohto M., Isono K. p53 gene mutations in gastric and esophageal cancers. Gastroenterology. 1992 Sep;103(3):892–896. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(92)90022-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim J. H., Takahashi T., Chiba I., Park J. G., Birrer M. J., Roh J. K., De Lee H., Kim J. P., Minna J. D., Gazdar A. F. Occurrence of p53 gene abnormalities in gastric carcinoma tumors and cell lines. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1991 Jul 3;83(13):938–943. doi: 10.1093/jnci/83.13.938. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koop B. F., Rowan L., Chen W. Q., Deshpande P., Lee H., Hood L. Sequence length and error analysis of Sequenase and automated Taq cycle sequencing methods. Biotechniques. 1993 Mar;14(3):442–447. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin H. M., Filipe M. I., Morris R. W., Lane D. P., Silvestre F. p53 expression and prognosis in gastric carcinoma. Int J Cancer. 1992 Apr 1;50(6):859–862. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910500604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matozaki T., Sakamoto C., Suzuki T., Matsuda K., Uchida T., Nakano O., Wada K., Nishisaki H., Konda Y., Nagao M. p53 gene mutations in human gastric cancer: wild-type p53 but not mutant p53 suppresses growth of human gastric cancer cells. Cancer Res. 1992 Aug 15;52(16):4335–4341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Midgley C. A., Fisher C. J., Bártek J., Vojtesek B., Lane D., Barnes D. M. Analysis of p53 expression in human tumours: an antibody raised against human p53 expressed in Escherichia coli. J Cell Sci. 1992 Jan;101(Pt 1):183–189. doi: 10.1242/jcs.101.1.183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen T., Brunson D., Crespi C. L., Penman B. W., Wishnok J. S., Tannenbaum S. R. DNA damage and mutation in human cells exposed to nitric oxide in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 1;89(7):3030–3034. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.7.3030. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkin D. M., Lärä E., Muir C. S. Estimates of the worldwide frequency of sixteen major cancers in 1980. Int J Cancer. 1988 Feb 15;41(2):184–197. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910410205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkin D. M., Stjernswärd J., Muir C. S. Estimates of the worldwide frequency of twelve major cancers. Bull World Health Organ. 1984;62(2):163–182. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry M. E., Levine A. J. Tumor-suppressor p53 and the cell cycle. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1993 Feb;3(1):50–54. doi: 10.1016/s0959-437x(05)80340-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prior T. W., Friedman K. J., Highsmith W. E., Jr, Perry T. R., Silverman L. M. Molecular probe protocol for determining carrier status in Duchenne and Becker muscular dystrophies. Clin Chem. 1990 Mar;36(3):441–445. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renault B., van den Broek M., Fodde R., Wijnen J., Pellegata N. S., Amadori D., Khan P. M., Ranzani G. N. Base transitions are the most frequent genetic changes at P53 in gastric cancer. Cancer Res. 1993 Jun 1;53(11):2614–2617. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rugge M., Shiao Y. H., Correa P., Baffa R., DiMario F. Immunohistochemical evidence of p53 overexpression in gastric epithelial dysplasia. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 1992 Nov-Dec;1(7):551–554. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rychlik W., Rhoads R. E. A computer program for choosing optimal oligonucleotides for filter hybridization, sequencing and in vitro amplification of DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Nov 11;17(21):8543–8551. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.21.8543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarnow P., Ho Y. S., Williams J., Levine A. J. Adenovirus E1b-58kd tumor antigen and SV40 large tumor antigen are physically associated with the same 54 kd cellular protein in transformed cells. Cell. 1982 Feb;28(2):387–394. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90356-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasano H., Date F., Imatani A., Asaki S., Nagura H. Double immunostaining for c-erbB-2 and p53 in human stomach cancer cells. Hum Pathol. 1993 Jun;24(6):584–589. doi: 10.1016/0046-8177(93)90236-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverberg E. Cancer statistics. 1986. CA Cancer J Clin. 1986 Jan-Feb;36(1):9–25. doi: 10.3322/canjclin.36.1.9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starzynska T., Bromley M., Ghosh A., Stern P. L. Prognostic significance of p53 overexpression in gastric and colorectal carcinoma. Br J Cancer. 1992 Sep;66(3):558–562. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1992.314. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugimura T., Fujimura S., Baba T. Tumor production in the glandular stomach and alimentary tract of the rat by N-methyl-N'-nitro-N-nitrosoguanidine. Cancer Res. 1970 Feb;30(2):455–465. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamura G., Kihana T., Nomura K., Terada M., Sugimura T., Hirohashi S. Detection of frequent p53 gene mutations in primary gastric cancer by cell sorting and polymerase chain reaction single-strand conformation polymorphism analysis. Cancer Res. 1991 Jun 1;51(11):3056–3058. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tatematsu M., Takahashi M., Fukushima S., Hananouchi M., Shirai T. Effects in rats of sodium chloride on experimental gastric cancers induced by N-methyl-N-nitro-N-nitrosoguanidine or 4-nitroquinoline-1-oxide. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1975 Jul;55(1):101–106. doi: 10.1093/jnci/55.1.101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tohdo H., Yokozaki H., Haruma K., Kajiyama G., Tahara E. p53 gene mutations in gastric adenomas. Virchows Arch B Cell Pathol Incl Mol Pathol. 1993;63(3):191–195. doi: 10.1007/BF02899260. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wink D. A., Kasprzak K. S., Maragos C. M., Elespuru R. K., Misra M., Dunams T. M., Cebula T. A., Koch W. H., Andrews A. W., Allen J. S. DNA deaminating ability and genotoxicity of nitric oxide and its progenitors. Science. 1991 Nov 15;254(5034):1001–1003. doi: 10.1126/science.1948068. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wynford-Thomas D. P53 in tumour pathology: can we trust immunocytochemistry? J Pathol. 1992 Apr;166(4):329–330. doi: 10.1002/path.1711660402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada Y., Yoshida T., Hayashi K., Sekiya T., Yokota J., Hirohashi S., Nakatani K., Nakano H., Sugimura T., Terada M. p53 gene mutations in gastric cancer metastases and in gastric cancer cell lines derived from metastases. Cancer Res. 1991 Nov 1;51(21):5800–5805. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokozaki H., Kuniyasu H., Kitadai Y., Nishimura K., Todo H., Ayhan A., Yasui W., Ito H., Tahara E. p53 point mutations in primary human gastric carcinomas. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 1992;119(2):67–70. doi: 10.1007/BF01209657. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]