Abstract
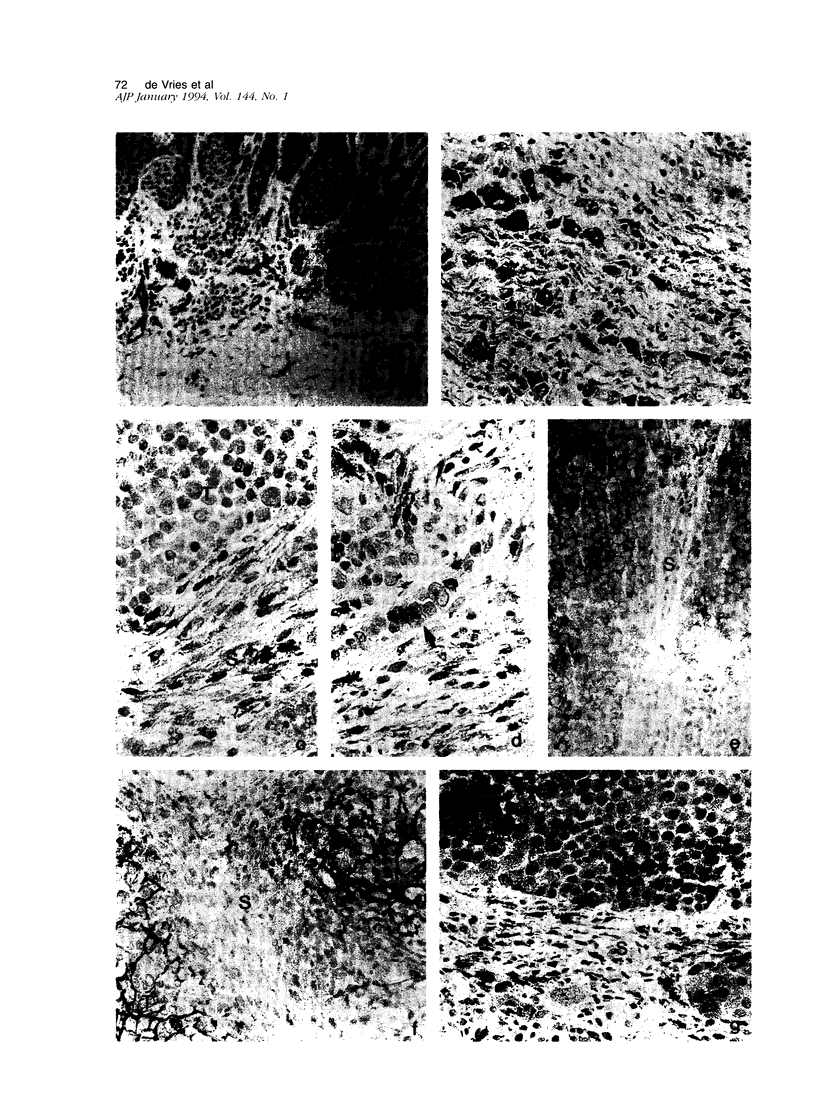
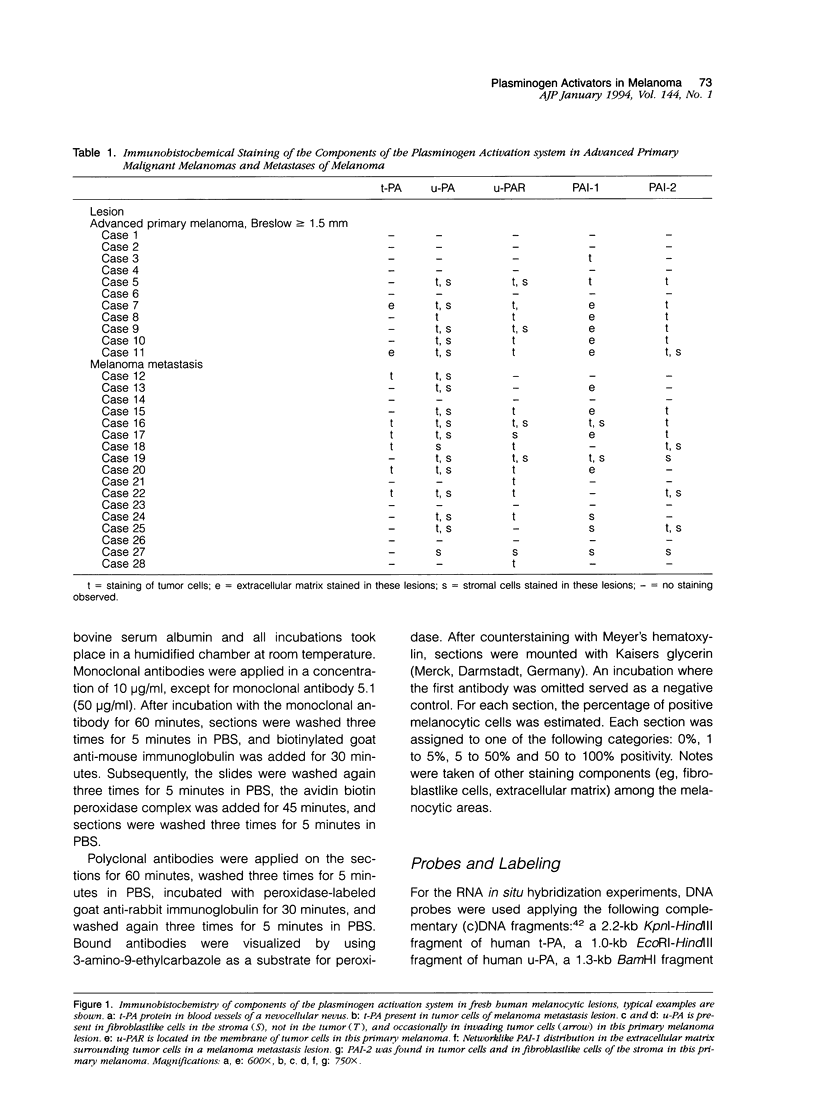
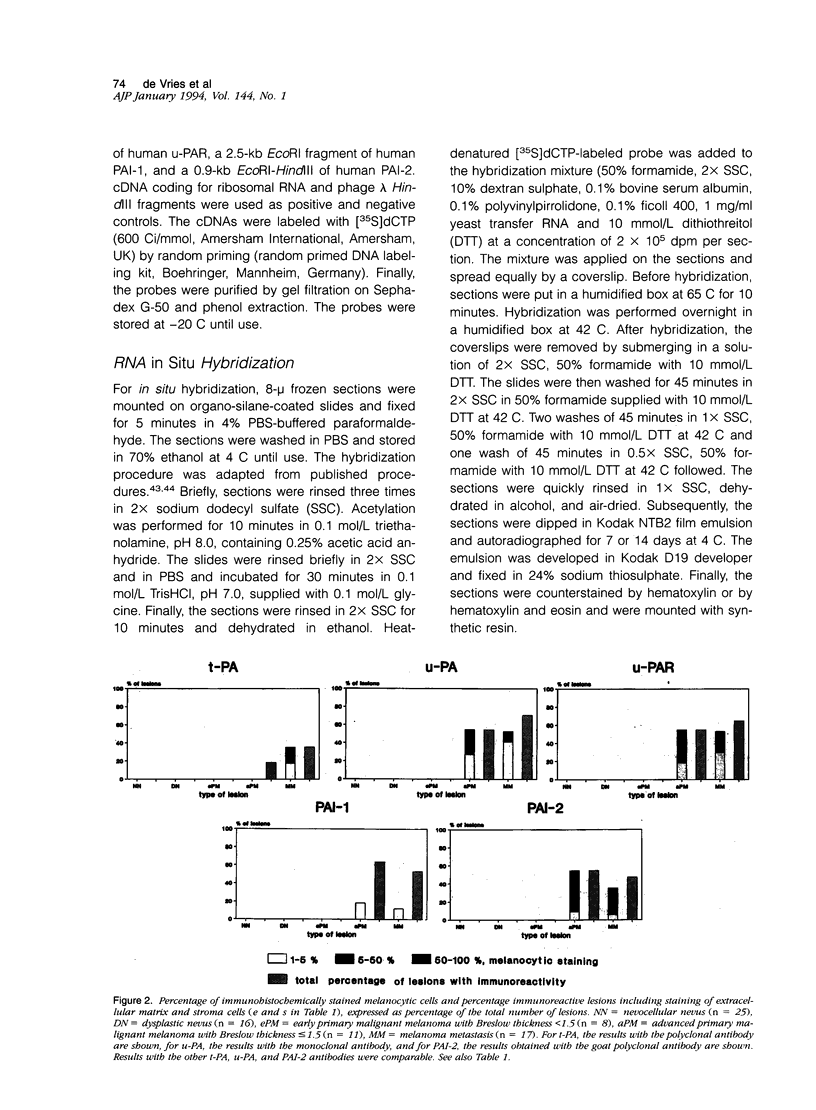
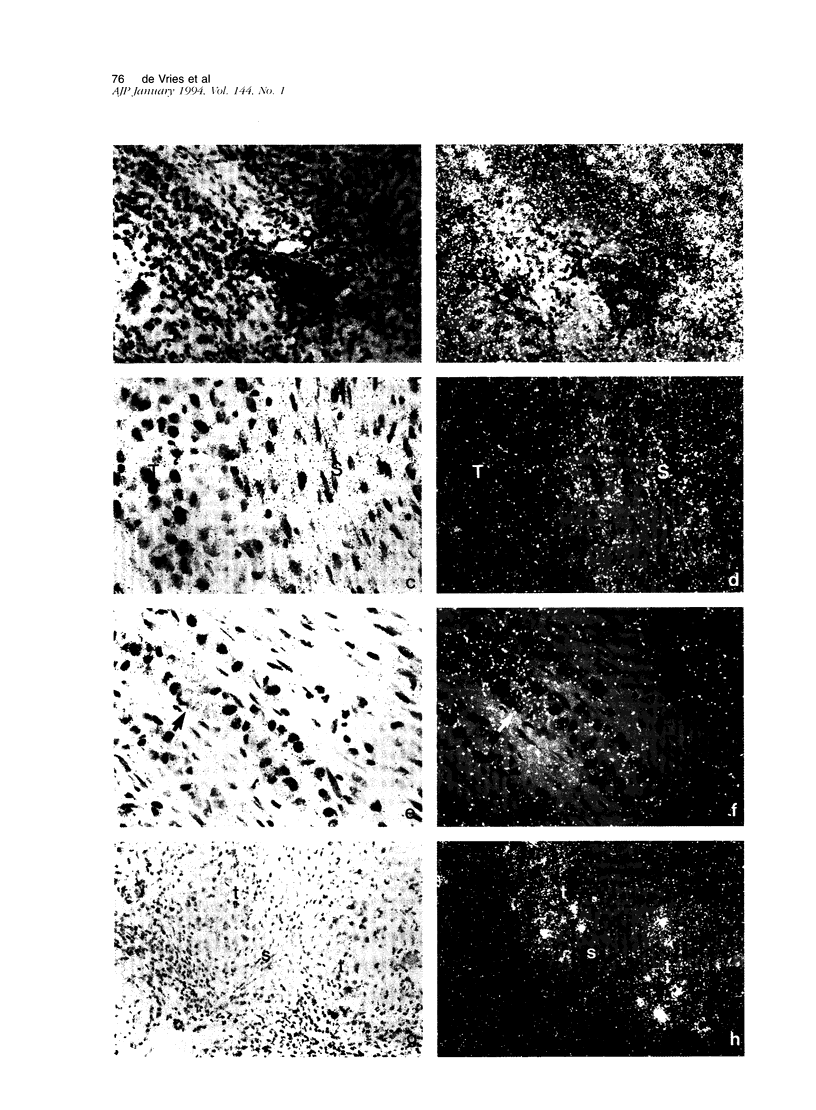
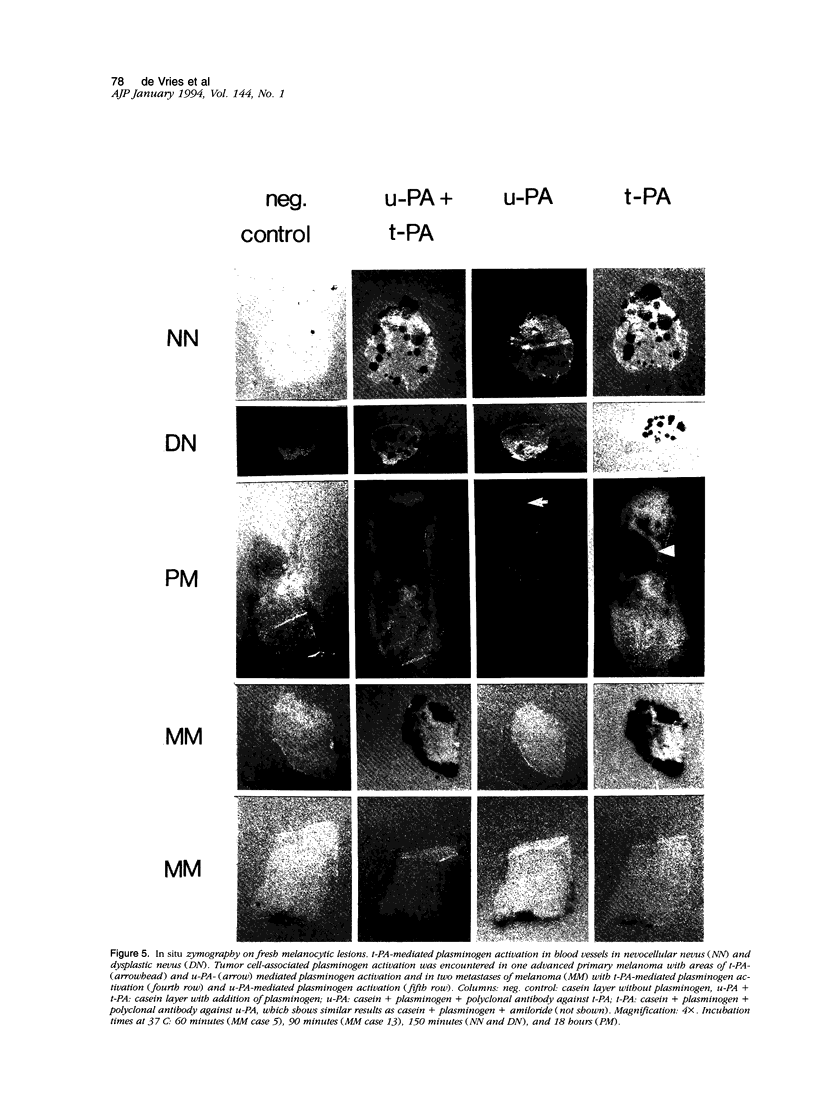
Degradation of the extracellular matrix and other tissue barriers by proteases like plasminogen activators (PAs) is a prerequisite for neoplastic growth and metastasis. Recently, we reported that highly metastatic behavior of human melanoma cells in nude mice correlates with urokinase-type PA (u-PA) expression and activity and with PA inhibitor type 1 and 2 (PAI-1, PAI-2) expression. Here we report on the occurrence of components of the PA system in the various stages of human melanoma tumor progression in situ. We studied the protein distribution on freshly frozen lesions of common nevocellular nevi (n = 25), dysplastic (= atypical) nevi (n = 16), early primary melanomas (n = 8), advanced primary melanomas (n = 11), and melanoma metastases (n = 17). Tissue-type PA was present in endothelial cells in all lesions, whereas in metastases it could be detected in tumor cells in a minority of the lesions. u-PA, its receptor, PAI-1, and PAI-2 could not be detected in benign and in early stages but appeared frequently in advanced primary melanoma and melanoma metastasis lesions. u-PA was detected in stromal cells and in tumor cells at the invasive front, the u-PA receptor and PAI-2 in tumor cells, and PAI-1 in the extracellular matrix surrounding tumor cells. Localization of the corresponding messenger RNAs and enzyme activities revealed a similar distribution. We conclude that plasminogen activation is a late event in melanoma tumor progression.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Axelrod J. H., Reich R., Miskin R. Expression of human recombinant plasminogen activators enhances invasion and experimental metastasis of H-ras-transformed NIH 3T3 cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 May;9(5):2133–2141. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.5.2133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belin D., Wohlwend A., Schleuning W. D., Kruithof E. K., Vassalli J. D. Facultative polypeptide translocation allows a single mRNA to encode the secreted and cytosolic forms of plasminogen activators inhibitor 2. EMBO J. 1989 Nov;8(11):3287–3294. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08489.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Binnema D. J., van Iersel J. J., Dooijewaard G. Quantitation of urokinase antigen in plasma and culture media by use of an ELISA. Thromb Res. 1986 Sep 1;43(5):569–577. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(86)90077-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breslow A. Thickness, cross-sectional areas and depth of invasion in the prognosis of cutaneous melanoma. Ann Surg. 1970 Nov;172(5):902–908. doi: 10.1097/00000658-197011000-00017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciambrone G. J., McKeown-Longo P. J. Vitronectin regulates the synthesis and localization of urokinase-type plasminogen activator in HT-1080 cells. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jul 5;267(19):13617–13622. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark W. H., Jr, Elder D. E., Guerry D., 4th, Epstein M. N., Greene M. H., Van Horn M. A study of tumor progression: the precursor lesions of superficial spreading and nodular melanoma. Hum Pathol. 1984 Dec;15(12):1147–1165. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(84)80310-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cubellis M. V., Wun T. C., Blasi F. Receptor-mediated internalization and degradation of urokinase is caused by its specific inhibitor PAI-1. EMBO J. 1990 Apr;9(4):1079–1085. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08213.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danø K., Andreasen P. A., Grøndahl-Hansen J., Kristensen P., Nielsen L. S., Skriver L. Plasminogen activators, tissue degradation, and cancer. Adv Cancer Res. 1985;44:139–266. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60028-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denijn M., De Weger R. A., Berends M. J., Compier-Spies P. I., Jansz H., Van Unnik J. A., Lips C. J. Detection of calcitonin-encoding mRNA by radioactive and non-radioactive in situ hybridization: improved colorimetric detection and cellular localization of mRNA in thyroid sections. J Histochem Cytochem. 1990 Mar;38(3):351–358. doi: 10.1177/38.3.2406337. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duffy M. J., Reilly D., O'Sullivan C., O'Higgins N., Fennelly J. J., Andreasen P. Urokinase-plasminogen activator, a new and independent prognostic marker in breast cancer. Cancer Res. 1990 Nov 1;50(21):6827–6829. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis V., Behrendt N., Danø K. Plasminogen activation by receptor-bound urokinase. A kinetic study with both cell-associated and isolated receptor. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jul 5;266(19):12752–12758. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Estreicher A., Mühlhauser J., Carpentier J. L., Orci L., Vassalli J. D. The receptor for urokinase type plasminogen activator polarizes expression of the protease to the leading edge of migrating monocytes and promotes degradation of enzyme inhibitor complexes. J Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;111(2):783–792. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.2.783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg R. F., Kao L. C., Haimowitz J. E., Queenan J. T., Jr, Wun T. C., Strauss J. F., 3rd, Kliman H. J. Plasminogen activator inhibitor types 1 and 2 in human trophoblasts. PAI-1 is an immunocytochemical marker of invading trophoblasts. Lab Invest. 1989 Jul;61(1):20–26. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaylis F. D., Keer H. N., Wilson M. J., Kwaan H. C., Sinha A. A., Kozlowski J. M. Plasminogen activators in human prostate cancer cell lines and tumors: correlation with the aggressive phenotype. J Urol. 1989 Jul;142(1):193–198. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5347(17)38709-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grøndahl-Hansen J., Ralfkiaer E., Kirkeby L. T., Kristensen P., Lund L. R., Danø K. Localization of urokinase-type plasminogen activator in stromal cells in adenocarcinomas of the colon in humans. Am J Pathol. 1991 Jan;138(1):111–117. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagège J., Peraldi M. N., Rondeau E., Adida C., Delarue F., Medcalf R., Schleuning W. D., Sraer J. D. Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 deposition in the extracellular matrix of cultured human mesangial cells. Am J Pathol. 1992 Jul;141(1):117–128. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasui Y., Marutsuka K., Suzumiya J., Kitada S., Osada Y., Sumiyoshi A. The content of urokinase-type plasminogen activator antigen as a prognostic factor in urinary bladder cancer. Int J Cancer. 1992 Apr 1;50(6):871–873. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910500607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hearing V. J., Law L. W., Corti A., Appella E., Blasi F. Modulation of metastatic potential by cell surface urokinase of murine melanoma cells. Cancer Res. 1988 Mar 1;48(5):1270–1278. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohga S., Harvey S. R., Weaver R. M., Markus G. Localization of plasminogen activators in human colon cancer by immunoperoxidase staining. Cancer Res. 1985 Apr;45(4):1787–1796. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kost C., Stüber W., Ehrlich H. J., Pannekoek H., Preissner K. T. Mapping of binding sites for heparin, plasminogen activator inhibitor-1, and plasminogen to vitronectin's heparin-binding region reveals a novel vitronectin-dependent feedback mechanism for the control of plasmin formation. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jun 15;267(17):12098–12105. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwaan H. C., Radosevich J. A., Xu C. G., Lastre C. Tissue plasminogen activator and inhibitors of fibrinolysis in malignant melanoma. Tumour Biol. 1988;9(6):301–306. doi: 10.1159/000217576. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markus G., Kohga S., Camiolo S. M., Madeja J. M., Ambrus J. L., Karakousis C. Plasminogen activators in human malignant melanoma. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1984 Jun;72(6):1213–1222. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matrisian L. M. Metalloproteinases and their inhibitors in matrix remodeling. Trends Genet. 1990 Apr;6(4):121–125. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(90)90126-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mignatti P., Rifkin D. B. Biology and biochemistry of proteinases in tumor invasion. Physiol Rev. 1993 Jan;73(1):161–195. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1993.73.1.161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mignatti P., Robbins E., Rifkin D. B. Tumor invasion through the human amniotic membrane: requirement for a proteinase cascade. Cell. 1986 Nov 21;47(4):487–498. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90613-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller S. J., Jensen P. J., Dzubow L. M., Lazarus G. S. Urokinase plasminogen activator is immunocytochemically detectable in squamous cell but not basal cell carcinomas. J Invest Dermatol. 1992 Mar;98(3):351–358. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12499803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura M., Konno H., Tanaka T., Maruo Y., Nishino N., Aoki K., Baba S., Sakaguchi S., Takada Y., Takada A. Possible role of plasminogen activator inhibitor 2 in the prevention of the metastasis of gastric cancer tissues. Thromb Res. 1992 Mar 15;65(6):709–719. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(92)90110-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ossowski L. Plasminogen activator dependent pathways in the dissemination of human tumor cells in the chick embryo. Cell. 1988 Feb 12;52(3):321–328. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)80025-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ossowski L., Reich E. Antibodies to plasminogen activator inhibit human tumor metastasis. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(3 Pt 2):611–619. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90093-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pyke C., Kristensen P., Ralfkiaer E., Eriksen J., Danø K. The plasminogen activation system in human colon cancer: messenger RNA for the inhibitor PAI-1 is located in endothelial cells in the tumor stroma. Cancer Res. 1991 Aug 1;51(15):4067–4071. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pyke C., Kristensen P., Ralfkiaer E., Grøndahl-Hansen J., Eriksen J., Blasi F., Danø K. Urokinase-type plasminogen activator is expressed in stromal cells and its receptor in cancer cells at invasive foci in human colon adenocarcinomas. Am J Pathol. 1991 May;138(5):1059–1067. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pöllänen J., Stephens R. W., Vaheri A. Directed plasminogen activation at the surface of normal and malignant cells. Adv Cancer Res. 1991;57:273–328. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)61002-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quax P. H., Pedersen N., Masucci M. T., Weening-Verhoeff E. J., Danø K., Verheijen J. H., Blasi F. Complementation between urokinase-producing and receptor-producing cells in extracellular matrix degradation. Cell Regul. 1991 Oct;2(10):793–803. doi: 10.1091/mbc.2.10.793. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quax P. H., van Leeuwen R. T., Verspaget H. W., Verheijen J. H. Protein and messenger RNA levels of plasminogen activators and inhibitors analyzed in 22 human tumor cell lines. Cancer Res. 1990 Mar 1;50(5):1488–1494. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quax P. H., van Muijen G. N., Weening-Verhoeff E. J., Lund L. R., Danø K., Ruiter D. J., Verheijen J. H. Metastatic behavior of human melanoma cell lines in nude mice correlates with urokinase-type plasminogen activator, its type-1 inhibitor, and urokinase-mediated matrix degradation. J Cell Biol. 1991 Oct;115(1):191–199. doi: 10.1083/jcb.115.1.191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reilly D., Christensen L., Duch M., Nolan N., Duffy M. J., Andreasen P. A. Type-1 plasminogen activator inhibitor in human breast carcinomas. Int J Cancer. 1992 Jan 21;50(2):208–214. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910500209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sappino A. P., Belin D., Huarte J., Hirschel-Scholz S., Saurat J. H., Vassalli J. D. Differential protease expression by cutaneous squamous and basal cell carcinomas. J Clin Invest. 1991 Oct;88(4):1073–1079. doi: 10.1172/JCI115406. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sappino A. P., Huarte J., Vassalli J. D., Belin D. Sites of synthesis of urokinase and tissue-type plasminogen activators in the murine kidney. J Clin Invest. 1991 Mar;87(3):962–970. doi: 10.1172/JCI115104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sier C. F., Fellbaum C., Verspaget H. W., Schmitt M., Griffioen G., Graeff H., Hôfler H., Lamers C. B. Immunolocalization of urokinase-type plasminogen activator in adenomas and carcinomas of the colorectum. Histopathology. 1991 Sep;19(3):231–237. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2559.1991.tb00027.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sier C. F., Verspaget H. W., Griffioen G., Verheijen J. H., Quax P. H., Dooijewaard G., De Bruin P. A., Lamers C. B. Imbalance of plasminogen activators and their inhibitors in human colorectal neoplasia. Implications of urokinase in colorectal carcinogenesis. Gastroenterology. 1991 Dec;101(6):1522–1528. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(91)90387-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sprengers E. D., Kluft C. Plasminogen activator inhibitors. Blood. 1987 Feb;69(2):381–387. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens R. W., Pöllänen J., Tapiovaara H., Leung K. C., Sim P. S., Salonen E. M., Rønne E., Behrendt N., Danø K., Vaheri A. Activation of pro-urokinase and plasminogen on human sarcoma cells: a proteolytic system with surface-bound reactants. J Cell Biol. 1989 May;108(5):1987–1995. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.5.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoppelli M. P., Tacchetti C., Cubellis M. V., Corti A., Hearing V. J., Cassani G., Appella E., Blasi F. Autocrine saturation of pro-urokinase receptors on human A431 cells. Cell. 1986 Jun 6;45(5):675–684. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90782-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tryggvason K., Höyhtyä M., Salo T. Proteolytic degradation of extracellular matrix in tumor invasion. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Nov 25;907(3):191–217. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(87)90006-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Bruin P. A., Griffioen G., Verspaget H. W., Verheijen J. H., Dooijewaard G., van den Ingh H. F., Lamers C. B. Plasminogen activator profiles in neoplastic tissues of the human colon. Cancer Res. 1988 Aug 15;48(16):4520–4524. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van den Heuvel L. P., van den Born J., van de Velden T. J., Veerkamp J. H., Monnens L. A., Schroder C. H., Berden J. H. Isolation and partial characterization of heparan sulphate proteoglycan from the human glomerular basement membrane. Biochem J. 1989 Dec 1;264(2):457–465. doi: 10.1042/bj2640457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]