Abstract
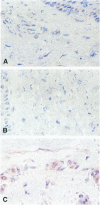
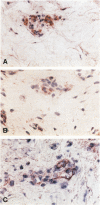
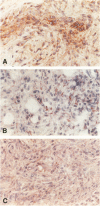
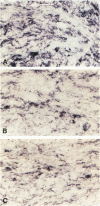
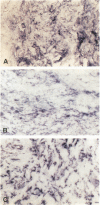
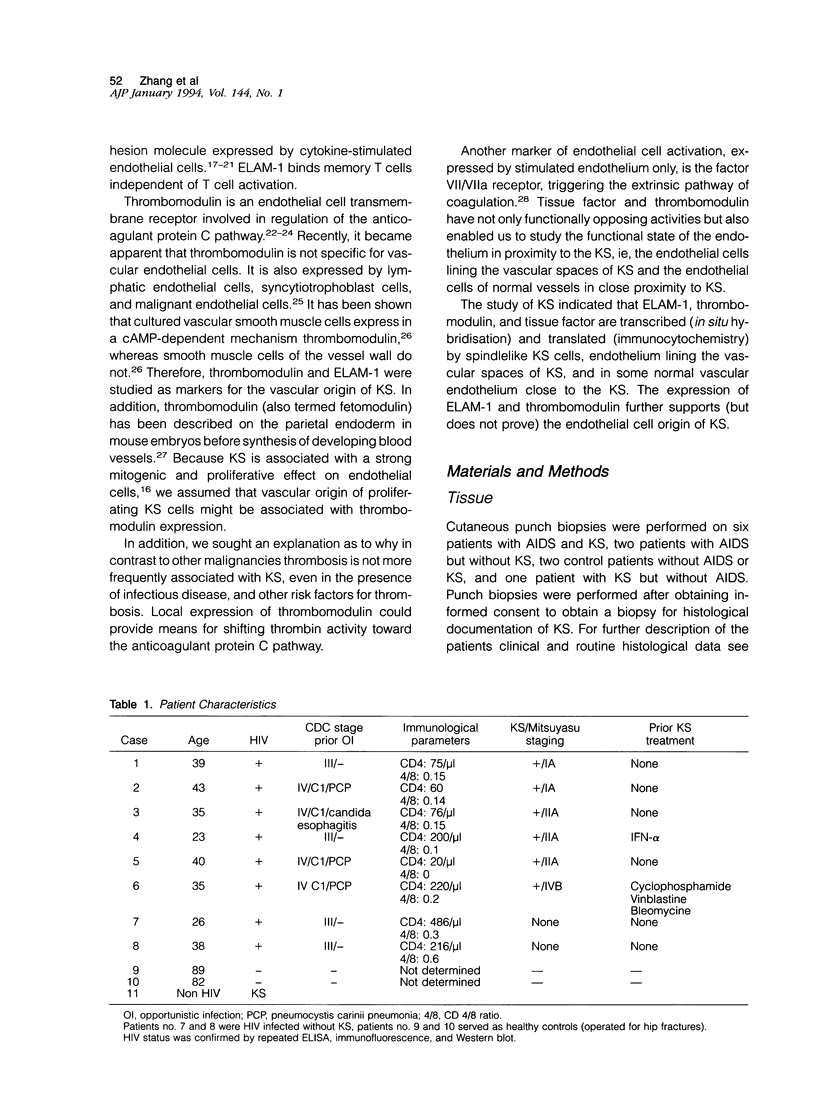
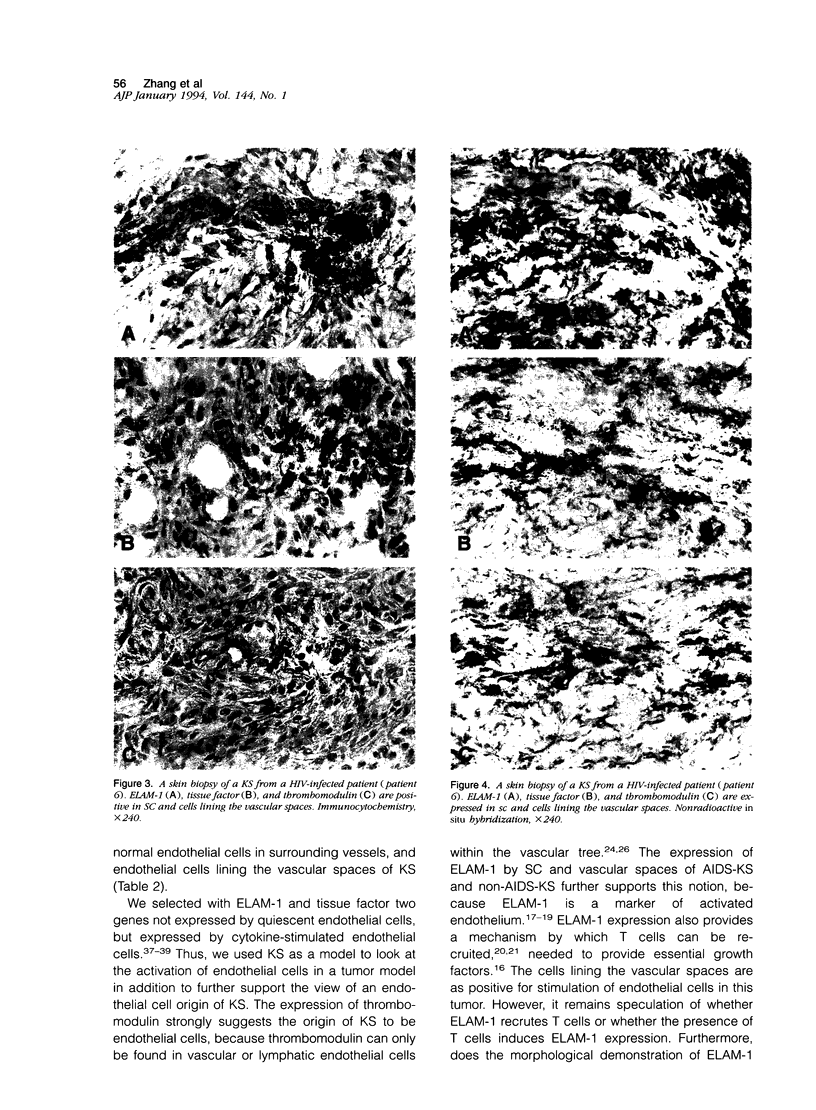
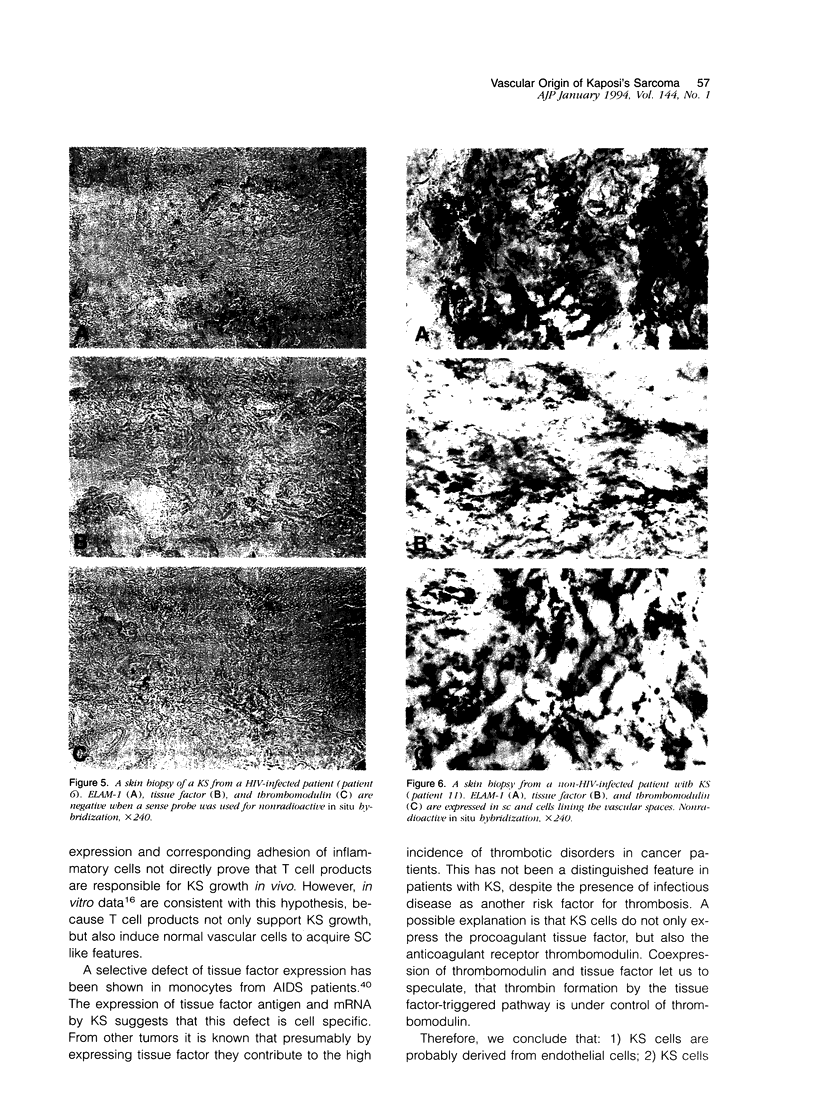
We studied seven cases of Kaposi's sarcomas (KS) obtained from patients with AIDS and one KS from a patient without HIV infection. Antigen expression was studied by immunocytochemistry and mRNA expression by in situ hybridisation. The markers tested were endothelial leukocyte adhesion molecule-1, thrombomodulin, and tissue factor. In all tumors (AIDS and non-AIDS associated) these markers reacted positive, indicating transcription and translation of these genes in KS. The synthesis and expression of tissue factor and thrombomodulin suggests that KS is a tumor that has tissue factor-mediated thrombin formation under the control of thrombomodulin. The expression of thrombomodulin and endothelial leukocyte adhesion molecule-1 provides evidence for the vascular origin of KS.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ackerman A. B. Subtle clues to diagnosis by conventional microscopy. The patch stage of Kaposi's sarcoma. Am J Dermatopathol. 1979 Summer;1(2):165–172. doi: 10.1097/00000372-197900120-00011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barillari G., Buonaguro L., Fiorelli V., Hoffman J., Michaels F., Gallo R. C., Ensoli B. Effects of cytokines from activated immune cells on vascular cell growth and HIV-1 gene expression. Implications for AIDS-Kaposi's sarcoma pathogenesis. J Immunol. 1992 Dec 1;149(11):3727–3734. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bevilacqua M. P., Gimbrone M. A., Jr Inducible endothelial functions in inflammation and coagulation. Semin Thromb Hemost. 1987 Oct;13(4):425–433. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1003519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bevilacqua M. P., Pober J. S., Mendrick D. L., Cotran R. S., Gimbrone M. A., Jr Identification of an inducible endothelial-leukocyte adhesion molecule. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(24):9238–9242. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.24.9238. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bevilacqua M. P., Pober J. S., Wheeler M. E., Cotran R. S., Gimbrone M. A., Jr Interleukin 1 acts on cultured human vascular endothelium to increase the adhesion of polymorphonuclear leukocytes, monocytes, and related leukocyte cell lines. J Clin Invest. 1985 Nov;76(5):2003–2011. doi: 10.1172/JCI112200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bevilacqua M. P., Stengelin S., Gimbrone M. A., Jr, Seed B. Endothelial leukocyte adhesion molecule 1: an inducible receptor for neutrophils related to complement regulatory proteins and lectins. Science. 1989 Mar 3;243(4895):1160–1165. doi: 10.1126/science.2466335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dittman W. A., Majerus P. W. Structure and function of thrombomodulin: a natural anticoagulant. Blood. 1990 Jan 15;75(2):329–336. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ensoli B., Barillari G., Salahuddin S. Z., Gallo R. C., Wong-Staal F. Tat protein of HIV-1 stimulates growth of cells derived from Kaposi's sarcoma lesions of AIDS patients. Nature. 1990 May 3;345(6270):84–86. doi: 10.1038/345084a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ensoli B., Nakamura S., Salahuddin S. Z., Biberfeld P., Larsson L., Beaver B., Wong-Staal F., Gallo R. C. AIDS-Kaposi's sarcoma-derived cells express cytokines with autocrine and paracrine growth effects. Science. 1989 Jan 13;243(4888):223–226. doi: 10.1126/science.2643161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ensoli B., Salahuddin S. Z., Gallo R. C. AIDS-associated Kaposi's sarcoma: a molecular model for its pathogenesis. Cancer Cells. 1989 Nov;1(3):93–96. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esmon C. T. The regulation of natural anticoagulant pathways. Science. 1987 Mar 13;235(4794):1348–1352. doi: 10.1126/science.3029867. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goerdt S., Sorg C. Endothelial heterogeneity and the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome: a paradigm for the pathogenesis of vascular disorders. Clin Investig. 1992 Feb;70(2):89–98. doi: 10.1007/BF00227347. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottlieb G. J., Ackerman A. B. Kaposi's sarcoma: an extensively disseminated form in young homosexual men. Hum Pathol. 1982 Oct;13(10):882–892. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(82)80047-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imada S., Yamaguchi H., Nagumo M., Katayanagi S., Iwasaki H., Imada M. Identification of fetomodulin, a surface marker protein of fetal development, as thrombomodulin by gene cloning and functional assays. Dev Biol. 1990 Jul;140(1):113–122. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(90)90058-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishii H., Uchiyama H., Kazama M. Soluble thrombomodulin antigen in conditioned medium is increased by damage of endothelial cells. Thromb Haemost. 1991 May 6;65(5):618–623. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lathey J. L., Agosti J. M., Nelson J. A., Corey L., Gregory S. A., Morrissey J. H., Edgington T. S., Oldstone M. B. A selective defect in tissue factor mRNA expression in monocytes from AIDS patients. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1990 Jan;54(1):1–13. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(90)90001-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maruyama I., Bell C. E., Majerus P. W. Thrombomodulin is found on endothelium of arteries, veins, capillaries, and lymphatics, and on syncytiotrophoblast of human placenta. J Cell Biol. 1985 Aug;101(2):363–371. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.2.363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miles S. A., Martínez-Maza O., Rezai A., Magpantay L., Kishimoto T., Nakamura S., Radka S. F., Linsley P. S. Oncostatin M as a potent mitogen for AIDS-Kaposi's sarcoma-derived cells. Science. 1992 Mar 13;255(5050):1432–1434. doi: 10.1126/science.1542793. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nair B. C., DeVico A. L., Nakamura S., Copeland T. D., Chen Y., Patel A., O'Neil T., Oroszlan S., Gallo R. C., Sarngadharan M. G. Identification of a major growth factor for AIDS-Kaposi's sarcoma cells as oncostatin M. Science. 1992 Mar 13;255(5050):1430–1432. doi: 10.1126/science.1542792. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nawroth P. P., Handley D. A., Esmon C. T., Stern D. M. Interleukin 1 induces endothelial cell procoagulant while suppressing cell-surface anticoagulant activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(10):3460–3464. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.10.3460. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nawroth P. P., Stern D. M. Endothelial cell procoagulant properties and the host response. Semin Thromb Hemost. 1987 Oct;13(4):391–397. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1003516. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nawroth P. P., Stern D. M. Modulation of endothelial cell hemostatic properties by tumor necrosis factor. J Exp Med. 1986 Mar 1;163(3):740–745. doi: 10.1084/jem.163.3.740. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connell K., Landman G., Farmer E., Edidin M. Endothelial cells transformed by SV40 T antigen cause Kaposi's sarcomalike tumors in nude mice. Am J Pathol. 1991 Oct;139(4):743–749. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Picker L. J., Kishimoto T. K., Smith C. W., Warnock R. A., Butcher E. C. ELAM-1 is an adhesion molecule for skin-homing T cells. Nature. 1991 Feb 28;349(6312):796–799. doi: 10.1038/349796a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pober J. S., Cotran R. S. The role of endothelial cells in inflammation. Transplantation. 1990 Oct;50(4):537–544. doi: 10.1097/00007890-199010000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pober J. S. Warner-Lambert/Parke-Davis award lecture. Cytokine-mediated activation of vascular endothelium. Physiology and pathology. Am J Pathol. 1988 Dec;133(3):426–433. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth W. K., Werner S., Risau W., Remberger K., Hofschneider P. H. Cultured, AIDS-related Kaposi's sarcoma cells express endothelial cell markers and are weakly malignant in vitro. Int J Cancer. 1988 Nov 15;42(5):767–773. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910420523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rutgers J. L., Wieczorek R., Bonetti F., Kaplan K. L., Posnett D. N., Friedman-Kien A. E., Knowles D. M., 2nd The expression of endothelial cell surface antigens by AIDS-associated Kaposi's sarcoma. Evidence for a vascular endothelial cell origin. Am J Pathol. 1986 Mar;122(3):493–499. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salahuddin S. Z., Nakamura S., Biberfeld P., Kaplan M. H., Markham P. D., Larsson L., Gallo R. C. Angiogenic properties of Kaposi's sarcoma-derived cells after long-term culture in vitro. Science. 1988 Oct 21;242(4877):430–433. doi: 10.1126/science.2459779. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sankey E. A., More L., Dhillon A. P. QBEnd/10: a new immunostain for the routine diagnosis of Kaposi's sarcoma. J Pathol. 1990 Jul;161(3):267–271. doi: 10.1002/path.1711610315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scarpati E. M., Wen D., Broze G. J., Jr, Miletich J. P., Flandermeyer R. R., Siegel N. R., Sadler J. E. Human tissue factor: cDNA sequence and chromosome localization of the gene. Biochemistry. 1987 Aug 25;26(17):5234–5238. doi: 10.1021/bi00391a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scully P. A., Steinman H. K., Kennedy C., Trueblood K., Frisman D. M., Voland J. R. AIDS-related Kaposi's sarcoma displays differential expression of endothelial surface antigens. Am J Pathol. 1988 Feb;130(2):244–251. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu Y., Shaw S., Graber N., Gopal T. V., Horgan K. J., Van Seventer G. A., Newman W. Activation-independent binding of human memory T cells to adhesion molecule ELAM-1. Nature. 1991 Feb 28;349(6312):799–802. doi: 10.1038/349799a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soff G. A., Jackman R. W., Rosenberg R. D. Expression of thrombomodulin by smooth muscle cells in culture: different effects of tumor necrosis factor and cyclic adenosine monophosphate on thrombomodulin expression by endothelial cells and smooth muscle cells in culture. Blood. 1991 Feb 1;77(3):515–518. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoica G., Hoffman J., Yuen P. H. Moloney murine sarcoma virus 349 induces Kaposi's sarcomalike lesions in Balb/c mice. Am J Pathol. 1990 Apr;136(4):933–947. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel J., Hinrichs S. H., Reynolds R. K., Luciw P. A., Jay G. The HIV tat gene induces dermal lesions resembling Kaposi's sarcoma in transgenic mice. Nature. 1988 Oct 13;335(6191):606–611. doi: 10.1038/335606a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weich H. A., Salahuddin S. Z., Gill P., Nakamura S., Gallo R. C., Folkmann J. AIDS-associated Kaposi's sarcoma-derived cells in long-term culture express and synthesize smooth muscle alpha-actin. Am J Pathol. 1991 Dec;139(6):1251–1258. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wen D. Z., Dittman W. A., Ye R. D., Deaven L. L., Majerus P. W., Sadler J. E. Human thrombomodulin: complete cDNA sequence and chromosome localization of the gene. Biochemistry. 1987 Jul 14;26(14):4350–4357. doi: 10.1021/bi00388a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]