Abstract
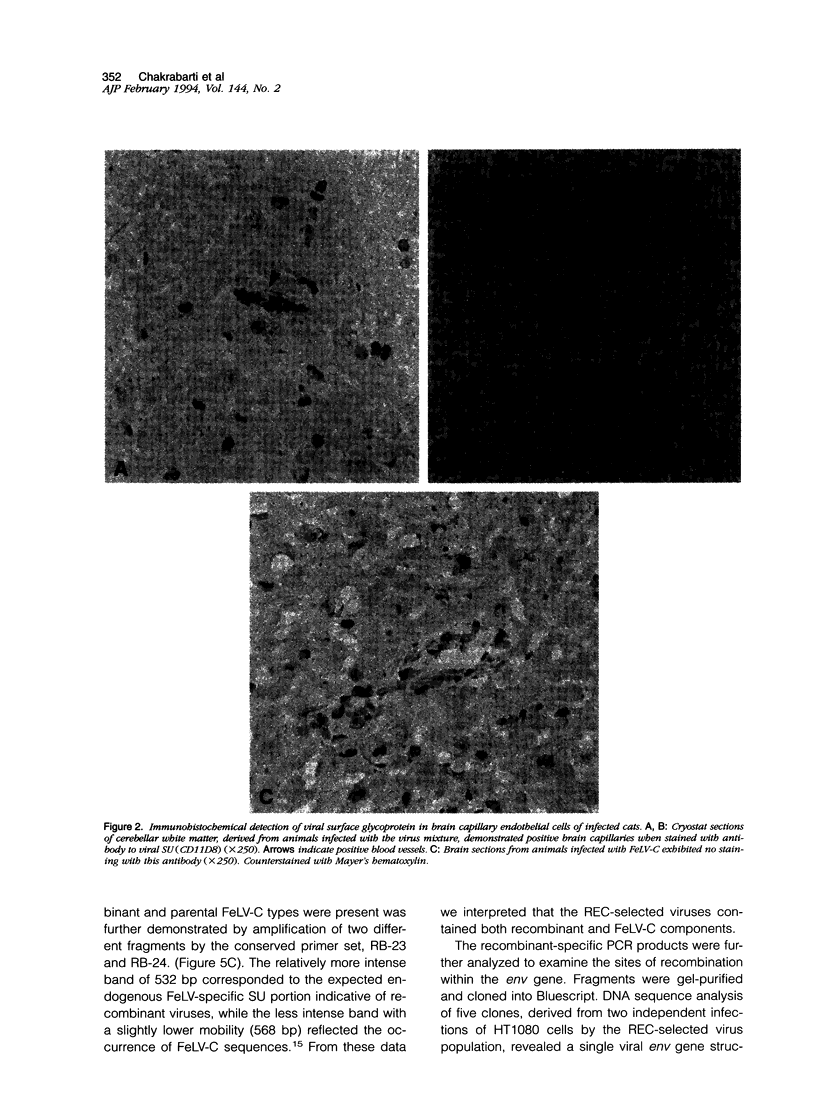
Brain tissues of domestic cats that died of aplastic anemia from infection with either parental feline leukemia virus (FeLV), subgroup C, or a mixture of FeLV-C and recombinants between FeLV-C and an endogenous FeLV provirus were examined by the immunoperoxidase staining technique using a monoclonal antibody (C11D8) directed against an epitope of the viral surface glycoprotein (SU). Positive staining of the central nervous system (CNS) capillary endothelial cells with no labeling on neuronal or glial cells was observed in cats that were inoculated with the virus mixture. This was in contrast to brain tissue of cats infected with FeLV-C alone, which showed no such staining. While non-CNS endothelial cells derived from human umbilical vein (HUVEC) could be readily infected in culture by FeLV-C, endothelial cells derived from human retina (REC) or brain (BEC) were resistant to infection by this parental virus. These latter cells in culture, however, could be infected by the viral mixture. The data suggested that at least one or more of the presumptive recombinant viruses could specifically infect CNS-derived endothelial cells. Using polymerase chain reaction and DNA sequencing strategies to amplify and analyze DNA fragments of the proviral SU region from cells infected with REC-selected viruses, we found the occurrence of a single recombinant in which two-thirds of the SU gene from the N-terminus of FeLV-C was replaced by the endogenous FeLV element. This recombinant virus, when molecularly cloned, should be useful in determining its potential in vivo neuropathogenicity.
Full text
PDF


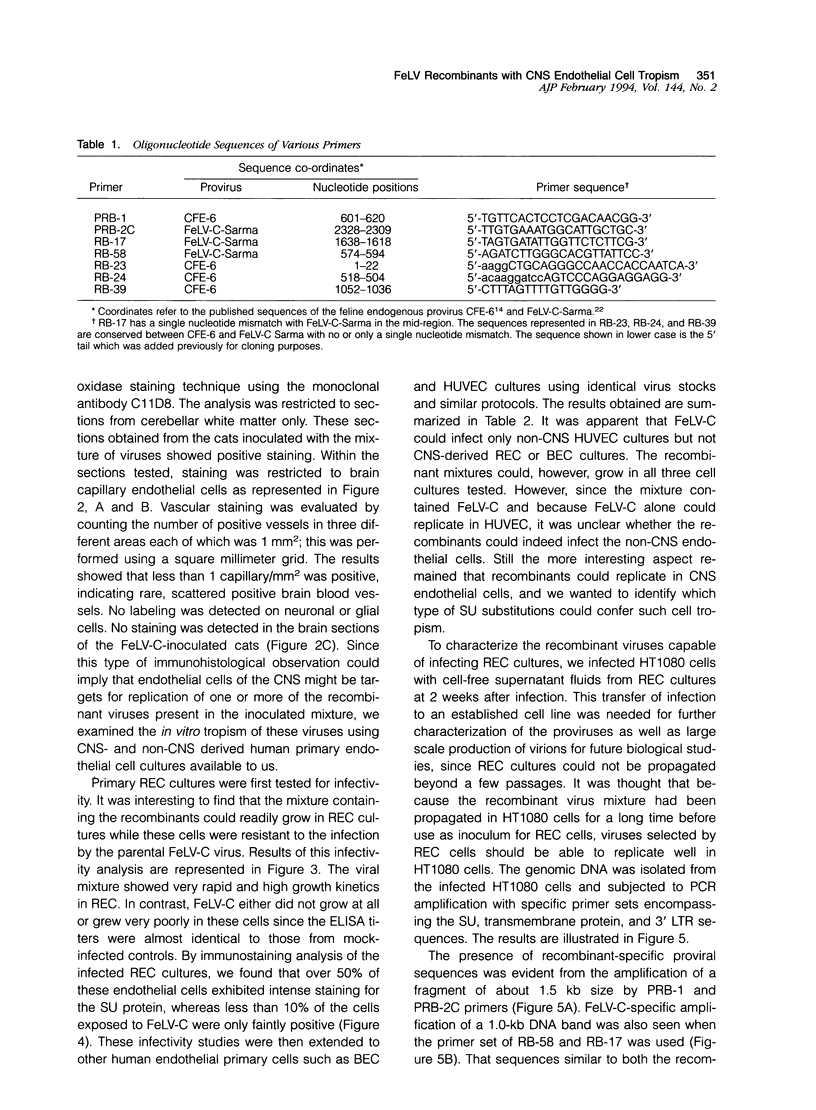




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baluda M. A., Roy-Burman P. Partial characterization of RD114 virus by DNA-RNA hybridization studies. Nat New Biol. 1973 Jul 11;244(132):59–62. doi: 10.1038/newbio244059a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baszler T. V., Zachary J. F. Murine retroviral neurovirulence correlates with an enhanced ability ofvirus to infect selectively, replicate in, and activate resident microglial cells. Am J Pathol. 1991 Mar;138(3):655–671. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Battini J. L., Heard J. M., Danos O. Receptor choice determinants in the envelope glycoproteins of amphotropic, xenotropic, and polytropic murine leukemia viruses. J Virol. 1992 Mar;66(3):1468–1475. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.3.1468-1475.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berry B. T., Ghosh A. K., Kumar D. V., Spodick D. A., Roy-Burman P. Structure and function of endogenous feline leukemia virus long terminal repeats and adjoining regions. J Virol. 1988 Oct;62(10):3631–3641. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.10.3631-3641.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brojatsch J., Kristal B. S., Viglianti G. A., Khiroya R., Hoover E. A., Mullins J. I. Feline leukemia virus subgroup C phenotype evolves through distinct alterations near the N terminus of the envelope surface glycoprotein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Sep 15;89(18):8457–8461. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.18.8457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busch M. P., Devi B. G., Soe L. H., Perbal B., Baluda M. A., Roy-Burman P. Characterization of the expression of cellular retrovirus genes and oncogenes in feline cells. Hematol Oncol. 1983 Jan-Mar;1(1):61–75. doi: 10.1002/hon.2900010108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen E. Y., Seeburg P. H. Supercoil sequencing: a fast and simple method for sequencing plasmid DNA. DNA. 1985 Apr;4(2):165–170. doi: 10.1089/dna.1985.4.165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elder J. H., McGee J. S., Munson M., Houghten R. A., Kloetzer W., Bittle J. L., Grant C. K. Localization of neutralizing regions of the envelope gene of feline leukemia virus by using anti-synthetic peptide antibodies. J Virol. 1987 Jan;61(1):8–15. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.1.8-15.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischinger P. J., Blevins C. S., Nomura S. Simple, quantitative assay for both xenotropic murine leukemia and ecotropic feline leukemia viruses. J Virol. 1974 Jul;14(1):177–179. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.1.177-179.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner M. B. Retroviral spongiform polioencephalomyelopathy. Rev Infect Dis. 1985 Jan-Feb;7(1):99–110. doi: 10.1093/clinids/7.1.99. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh A. K., Bachmann M. H., Hoover E. A., Mullins J. I. Identification of a putative receptor for subgroup A feline leukemia virus on feline T cells. J Virol. 1992 Jun;66(6):3707–3714. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.6.3707-3714.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grant C. K., Ernisse B. J., Jarrett O., Jones F. R. Feline leukemia virus envelope gp70 of subgroups B and C defined by monoclonal antibodies with cytotoxic and neutralizing functions. J Immunol. 1983 Dec;131(6):3042–3048. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman P. M., Cimino E. F., Robbins D. S., Broadwell R. D., Powers J. M., Ruscetti S. K. Cellular tropism and localization in the rodent nervous system of a neuropathogenic variant of Friend murine leukemia virus. Lab Invest. 1992 Sep;67(3):314–321. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofman F. M., Hinton D. R., Johnson K., Merrill J. E. Tumor necrosis factor identified in multiple sclerosis brain. J Exp Med. 1989 Aug 1;170(2):607–612. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.2.607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoover E. A., Kociba G. J., Hardy W. D., Jr, Yohn D. S. Erythroid hypoplasia in cats inoculated with feline leukemia virus. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1974 Nov;53(5):1271–1276. doi: 10.1093/jnci/53.5.1271. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaffe E. A., Nachman R. L., Becker C. G., Minick C. R. Culture of human endothelial cells derived from umbilical veins. Identification by morphologic and immunologic criteria. J Clin Invest. 1973 Nov;52(11):2745–2756. doi: 10.1172/JCI107470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar D. V., Berry B. T., Roy-Burman P. Nucleotide sequence and distinctive characteristics of the env gene of endogenous feline leukemia provirus. J Virol. 1989 May;63(5):2379–2384. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.5.2379-2384.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackey L., Jarrett W., Jarrett O., Laird H. Anemia associated with feline leukemia virus infection in cats. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1975 Jan;54(1):209–217. doi: 10.1093/jnci/54.1.209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchuk D., Drumm M., Saulino A., Collins F. S. Construction of T-vectors, a rapid and general system for direct cloning of unmodified PCR products. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Mar 11;19(5):1154–1154. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.5.1154. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masuda M., Remington M. P., Hoffman P. M., Ruscetti S. K. Molecular characterization of a neuropathogenic and nonerythroleukemogenic variant of Friend murine leukemia virus PVC-211. J Virol. 1992 May;66(5):2798–2806. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.5.2798-2806.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicolaisen-Strouss K., Kumar H. P., Fitting T., Grant C. K., Elder J. H. Natural feline leukemia virus variant escapes neutralization by a monoclonal antibody via an amino acid change outside the antibody-binding epitope. J Virol. 1987 Nov;61(11):3410–3415. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.11.3410-3415.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niman H. L., Akhavi M., Gardner M. B., Stephenson J. R., Roy-Burman P. Differential expression of two distinct endogenous retrovisus genomes in developing tissues of the domestic cat. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1980 Mar;64(3):587–594. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niman H. L., Stephenson J. R., Gardner M. B., Roy-Burman P. RD-114 and feline leukaemia virus genome expression in natural lymphomas of domestic cats. Nature. 1977 Mar 24;266(5600):357–360. doi: 10.1038/266357a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Onions D., Jarrett O., Testa N., Frassoni F., Toth S. Selective effect of feline leukaemia virus on early erythroid precursors. Nature. 1982 Mar 11;296(5853):156–158. doi: 10.1038/296156a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osame M., Usuku K., Izumo S., Ijichi N., Amitani H., Igata A., Matsumoto M., Tara M. HTLV-I associated myelopathy, a new clinical entity. Lancet. 1986 May 3;1(8488):1031–1032. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)91298-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Overbaugh J., Riedel N., Hoover E. A., Mullins J. I. Transduction of endogenous envelope genes by feline leukaemia virus in vitro. Nature. 1988 Apr 21;332(6166):731–734. doi: 10.1038/332731a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pandey R., Ghosh A. K., Kumar D. V., Bachman B. A., Shibata D., Roy-Burman P. Recombination between feline leukemia virus subgroup B or C and endogenous env elements alters the in vitro biological activities of the viruses. J Virol. 1991 Dec;65(12):6495–6508. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.12.6495-6508.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portis J. L. Wild mouse retrovirus: pathogenesis. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1990;160:11–27. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-75267-4_2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riedel N., Hoover E. A., Gasper P. W., Nicolson M. O., Mullins J. I. Molecular analysis and pathogenesis of the feline aplastic anemia retrovirus, feline leukemia virus C-Sarma. J Virol. 1986 Oct;60(1):242–250. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.1.242-250.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby M. A., Rojko J. L., Stewart M. A., Kociba G. J., Cheney C. M., Rezanka L. J., Mathes L. E., Hartke J. R., Jarrett O., Neil J. C. Partial dissociation of subgroup C phenotype and in vivo behaviour in feline leukaemia viruses with chimeric envelope genes. J Gen Virol. 1992 Nov;73(Pt 11):2839–2847. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-73-11-2839. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rymaszewski Z., Cohen R. M., Chomczynski P. Human growth hormone stimulates proliferation of human retinal microvascular endothelial cells in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jan 15;88(2):617–621. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.2.617. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarma P. S., Log T. Subgroup classification of feline leukemia and sarcoma viruses by viral interference and neutralization tests. Virology. 1973 Jul;54(1):160–169. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90125-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheets R. L., Pandey R., Jen W. C., Roy-Burman P. Recombinant feline leukemia virus genes detected in naturally occurring feline lymphosarcomas. J Virol. 1993 Jun;67(6):3118–3125. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.6.3118-3125.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheets R. L., Pandey R., Klement V., Grant C. K., Roy-Burman P. Biologically selected recombinants between feline leukemia virus (FeLV) subgroup A and an endogenous FeLV element. Virology. 1992 Oct;190(2):849–855. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90924-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soe L. H., Devi B. G., Mullins J. I., Roy-Burman P. Molecular cloning and characterization of endogenous feline leukemia virus sequences from a cat genomic library. J Virol. 1983 Jun;46(3):829–840. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.3.829-840.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soe L. H., Devi B. G., Mullins J. I., Roy-Burman P. Molecular cloning and characterization of endogenous feline leukemia virus sequences from a cat genomic library. J Virol. 1983 Jun;46(3):829–840. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.3.829-840.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeuchi Y., Vile R. G., Simpson G., O'Hara B., Collins M. K., Weiss R. A. Feline leukemia virus subgroup B uses the same cell surface receptor as gibbon ape leukemia virus. J Virol. 1992 Feb;66(2):1219–1222. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.2.1219-1222.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vernant J. C., Maurs L., Gessain A., Barin F., Gout O., Delaporte J. M., Sanhadji K., Buisson G., de-Thé G. Endemic tropical spastic paraparesis associated with human T-lymphotropic virus type I: a clinical and seroepidemiological study of 25 cases. Ann Neurol. 1987 Feb;21(2):123–130. doi: 10.1002/ana.410210204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]






