Abstract
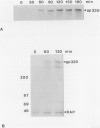
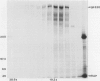
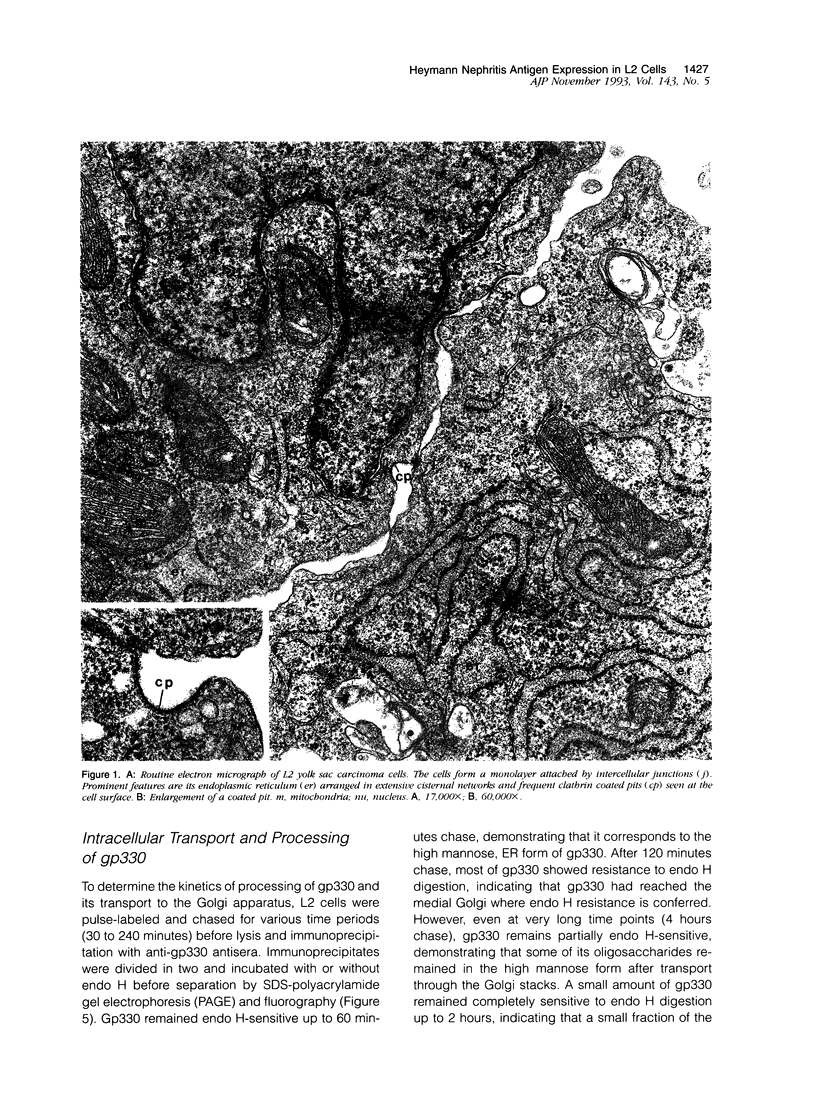
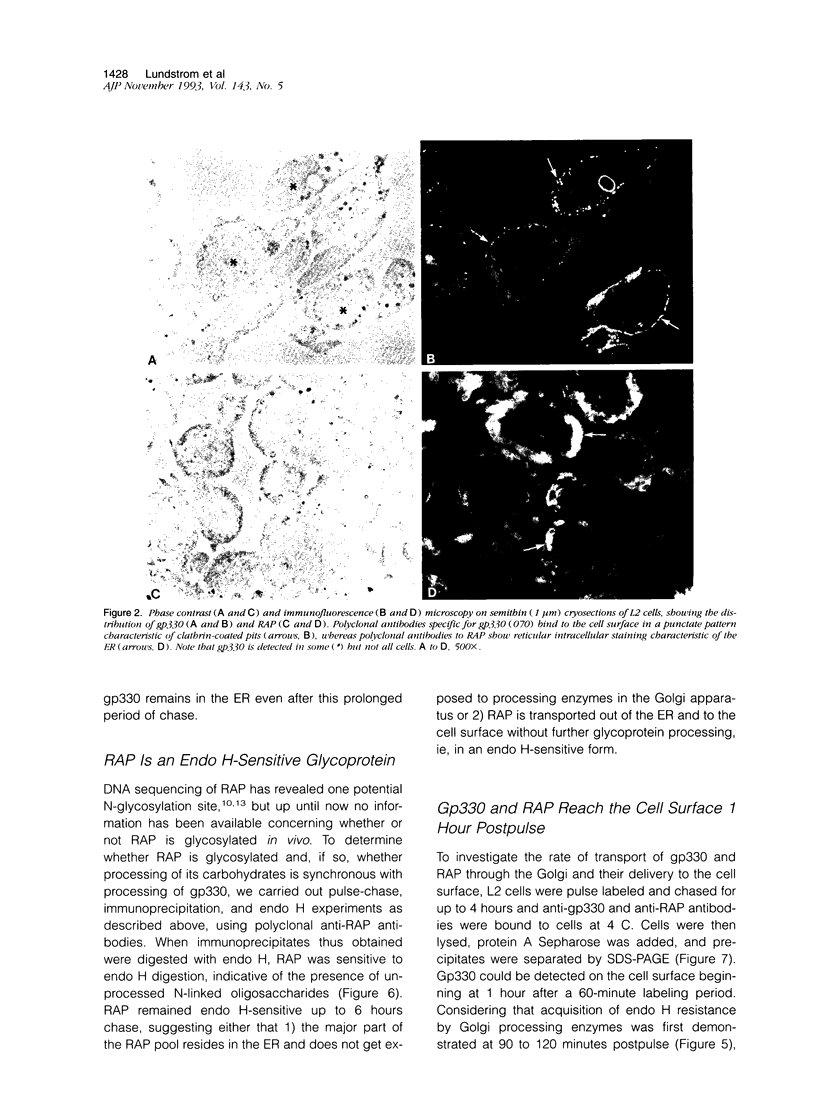
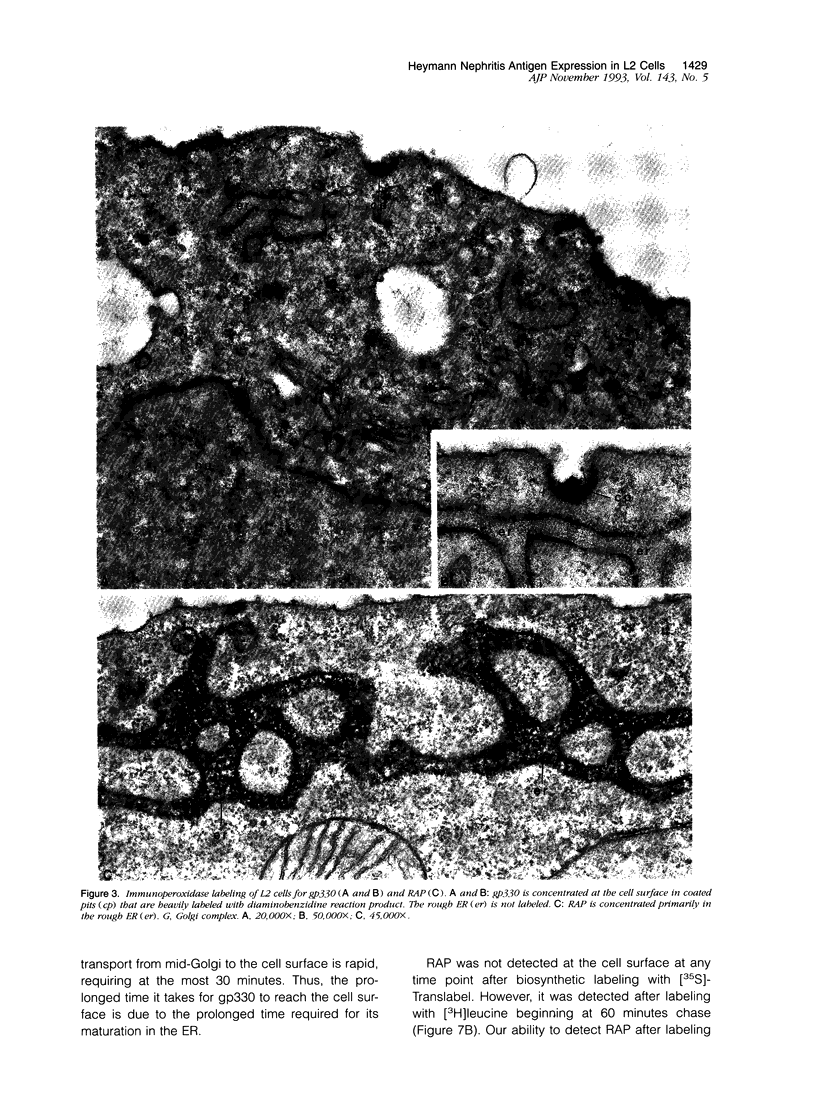
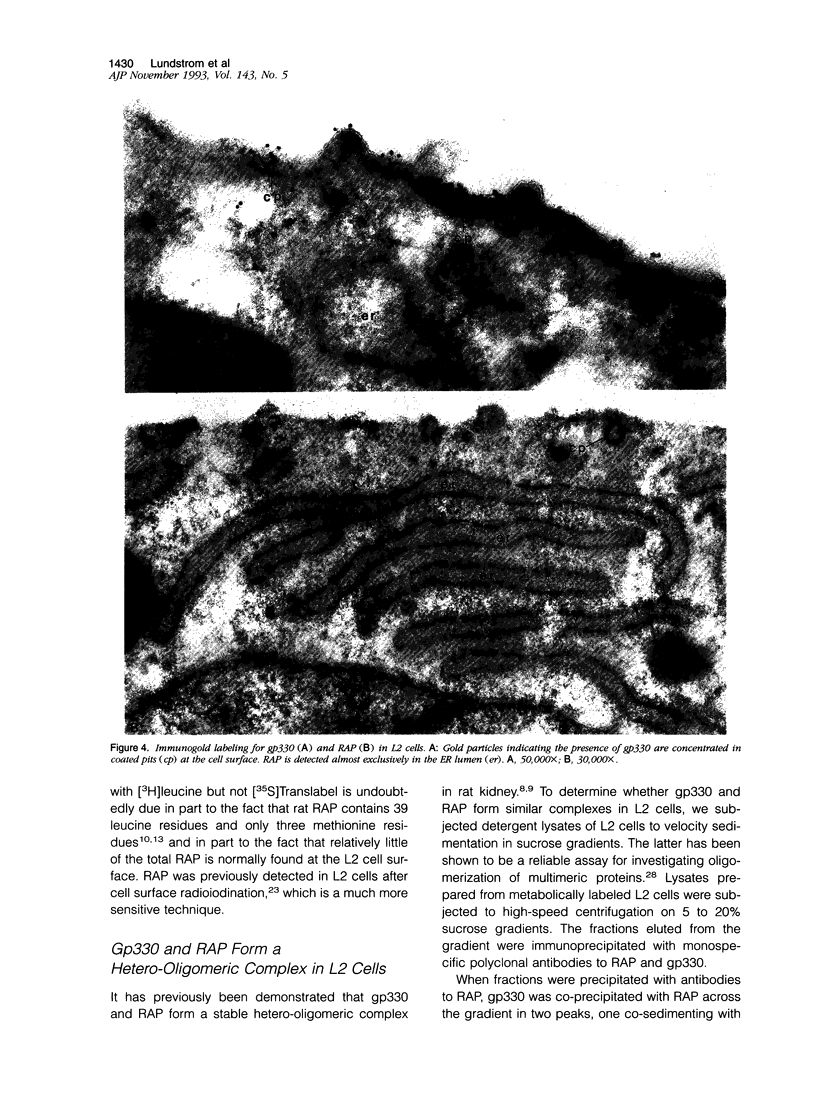
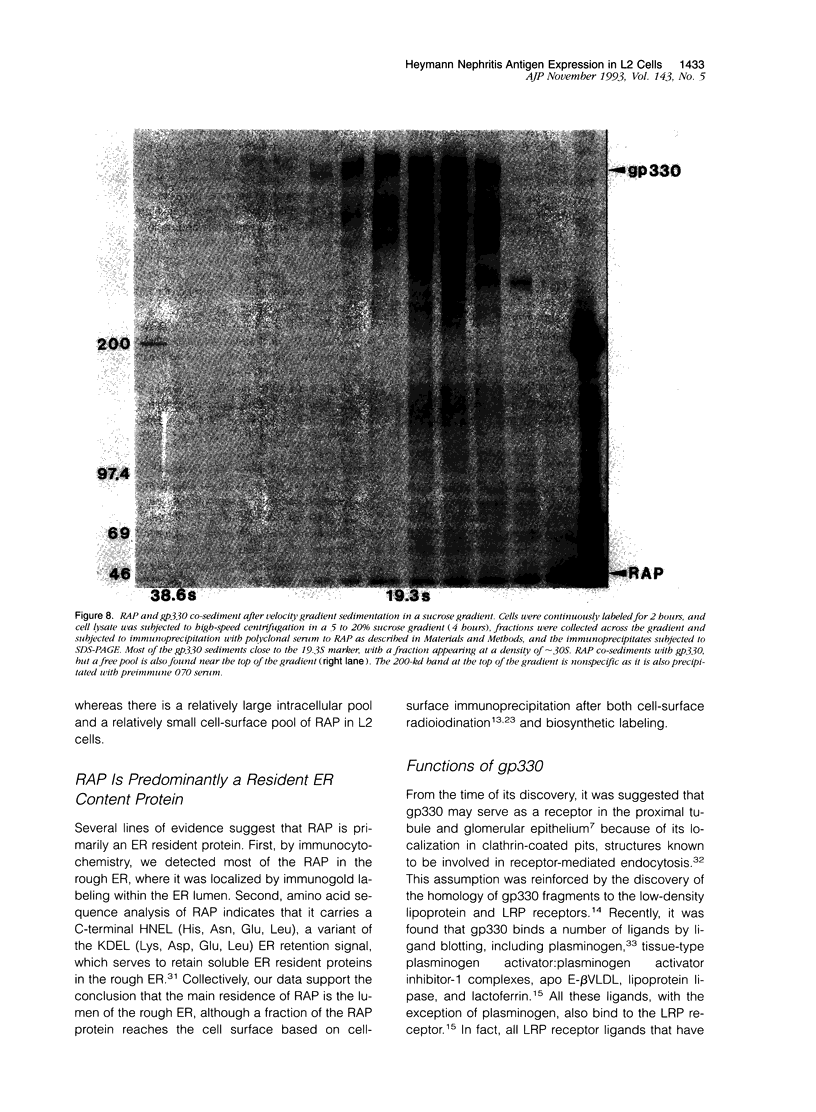
Heymann nephritis in the rat is the most widely used model of human membranous glomerulonephritis. Glycoprotein (gp)330, a large (M(r) > 550,000) membrane-associated glycoprotein, has been identified as the main antigen in this autoimmune disease. Studies of gp330 and receptor-associated protein (RAP), its 44-kd subunit, have been restricted largely to rat kidney, as no stable cultured cell line has been available that expresses gp330. We have recently identified a rat yolk sac carcinoma cell line (L2) that expresses both gp330 and RAP. In this report, we have carried out detailed morphological, immunocytochemical, and biochemical studies characterizing the biosynthesis and localization of gp330 and RAP in the L2 rat yolk sac cell line. At the electron microscope level, the L2 cells are seen to be attached by cell junctions, and their predominant morphological features include extensive networks of rough endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and numerous clathrin-coated pits found on the cell membrane. By immunocytochemistry, gp330 was localized primarily to clathrin-coated pits at the cell surface, whereas RAP was localized predominantly to the lumen of the rough ER. Pulse-chase experiments indicated that gp330 spends a prolonged time maturing in the ER of L2 cells, as transport of gp330 to the Golgi complex (based on acquisition of endoglycosidase H resistance) is slow (t1/2 = 90 to 120 minutes). Gp330 reached the L2 cell surface beginning at 2 hours after synthesis, where it could be detected by cell surface immunoprecipitation. RAP was found to be an N-linked glycoprotein, and it remained endoglycosidase H-sensitive up to 4 hours after synthesis. Co-precipitation and co-sedimentation experiments demonstrated that gp330 and RAP form a large heterodimer (M(r) approximately 669,000) immediately after biosynthesis and are further assembled into a large hetero-oligomer in the ER. These findings demonstrate that the localization and the kinetics of assembly of gp330 and RAP into the Heymann nephritis antigenic complex are similar in both L2 cells and rat kidney. They also provide new information on the intracellular processing of these two molecules and their delivery to the cell surface. Thus, the L2 cell system should facilitate further characterization of the functions and interactions of gp330 and RAP, which may shed light on the cellular and molecular mechanisms of Heymann nephritis.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Biemesderfer D., Dekan G., Aronson P. S., Farquhar M. G. Biosynthesis of the gp330/44-kDa Heymann nephritis antigenic complex: assembly takes place in the ER. Am J Physiol. 1993 Jun;264(6 Pt 2):F1011–F1020. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1993.264.6.F1011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brentjens J. R., Andres G. Interaction of antibodies with renal cell surface antigens. Kidney Int. 1989 Apr;35(4):954–968. doi: 10.1038/ki.1989.79. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen E. I., Gliemann J., Moestrup S. K. Renal tubule gp330 is a calcium binding receptor for endocytic uptake of protein. J Histochem Cytochem. 1992 Oct;40(10):1481–1490. doi: 10.1177/40.10.1382088. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Copeland C. S., Doms R. W., Bolzau E. M., Webster R. G., Helenius A. Assembly of influenza hemagglutinin trimers and its role in intracellular transport. J Cell Biol. 1986 Oct;103(4):1179–1191. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.4.1179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Couser W. G. Mechanisms of glomerular injury in immune-complex disease. Kidney Int. 1985 Sep;28(3):569–583. doi: 10.1038/ki.1985.167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein J. L., Brown M. S., Anderson R. G., Russell D. W., Schneider W. J. Receptor-mediated endocytosis: concepts emerging from the LDL receptor system. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1985;1:1–39. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.01.110185.000245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEYMANN W., HACKEL D. B., HARWOOD S., WILSON S. G., HUNTER J. L. Production of nephrotic syndrome in rats by Freund's adjuvants and rat kidney suspensions. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1959 Apr;100(4):660–664. doi: 10.3181/00379727-100-24736. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herz J., Goldstein J. L., Strickland D. K., Ho Y. K., Brown M. S. 39-kDa protein modulates binding of ligands to low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein/alpha 2-macroglobulin receptor. J Biol Chem. 1991 Nov 5;266(31):21232–21238. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanalas J. J., Makker S. P. Identification of the rat Heymann nephritis autoantigen (GP330) as a receptor site for plasminogen. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jun 15;266(17):10825–10829. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerjaschki D., Farquhar M. G. Immunocytochemical localization of the Heymann nephritis antigen (GP330) in glomerular epithelial cells of normal Lewis rats. J Exp Med. 1983 Feb 1;157(2):667–686. doi: 10.1084/jem.157.2.667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerjaschki D., Farquhar M. G. The pathogenic antigen of Heymann nephritis is a membrane glycoprotein of the renal proximal tubule brush border. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Sep;79(18):5557–5561. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.18.5557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerjaschki D., Miettinen A., Farquhar M. G. Initial events in the formation of immune deposits in passive Heymann nephritis. gp330-anti-gp330 immune complexes form in epithelial coated pits and rapidly become attached to the glomerular basement membrane. J Exp Med. 1987 Jul 1;166(1):109–128. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.1.109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerjaschki D., Noronha-Blob L., Sacktor B., Farquhar M. G. Microdomains of distinctive glycoprotein composition in the kidney proximal tubule brush border. J Cell Biol. 1984 Apr;98(4):1505–1513. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.4.1505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerjaschki D. The pathogenesis of membranous glomerulonephritis: from morphology to molecules. Virchows Arch B Cell Pathol Incl Mol Pathol. 1990;58(4):253–271. doi: 10.1007/BF02890080. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerjaschki D., Ullrich R., Diem K., Pietromonaco S., Orlando R. A., Farquhar M. G. Identification of a pathogenic epitope involved in initiation of Heymann nephritis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Dec 1;89(23):11179–11183. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.23.11179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leung C. C., Cheewatrakoolpong B., O'Mara T., Black M. Passive Heymann nephritis induced by rabbit antiserum to membrane antigens isolated from rat visceral yolk-sac microvilli. Am J Anat. 1987 Jun;179(2):169–174. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001790209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miettinen A., Dekan G., Farquhar M. G. Monoclonal antibodies against membrane proteins of the rat glomerulus. Immunochemical specificity and immunofluorescence distribution of the antigens. Am J Pathol. 1990 Oct;137(4):929–944. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miettinen A., Törnroth T., Ekblom P., Virtanen I., Linder E. Nephritogenic and non-nephritogenic epithelial antigens in autoimmune and passive Heymann nephritis. Lab Invest. 1984 Apr;50(4):435–446. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moestrup S. K., Gliemann J., Pallesen G. Distribution of the alpha 2-macroglobulin receptor/low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein in human tissues. Cell Tissue Res. 1992 Sep;269(3):375–382. doi: 10.1007/BF00353892. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orlando R. A., Farquhar M. G. Identification of a cell line that expresses a cell surface and a soluble form of the gp330/receptor-associated protein (RAP) Heymann nephritis antigenic complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 May 1;90(9):4082–4086. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.9.4082. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orlando R. A., Kerjaschki D., Kurihara H., Biemesderfer D., Farquhar M. G. gp330 associates with a 44-kDa protein in the rat kidney to form the Heymann nephritis antigenic complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 1;89(15):6698–6702. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.15.6698. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R. Control of protein exit from the endoplasmic reticulum. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1989;5:1–23. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.05.110189.000245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pietromonaco S., Kerjaschki D., Binder S., Ullrich R., Farquhar M. G. Molecular cloning of a cDNA encoding a major pathogenic domain of the Heymann nephritis antigen gp330. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Mar;87(5):1811–1815. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.5.1811. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raychowdhury R., Niles J. L., McCluskey R. T., Smith J. A. Autoimmune target in Heymann nephritis is a glycoprotein with homology to the LDL receptor. Science. 1989 Jun 9;244(4909):1163–1165. doi: 10.1126/science.2786251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodman J. S., Seidman L., Farquhar M. G. The membrane composition of coated pits, microvilli, endosomes, and lysosomes is distinctive in the rat kidney proximal tubule cell. J Cell Biol. 1986 Jan;102(1):77–87. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.1.77. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strickland D. K., Ashcom J. D., Williams S., Burgess W. H., Migliorini M., Argraves W. S. Sequence identity between the alpha 2-macroglobulin receptor and low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein suggests that this molecule is a multifunctional receptor. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 15;265(29):17401–17404. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tokuyasu K. T. Application of cryoultramicrotomy to immunocytochemistry. J Microsc. 1986 Aug;143(Pt 2):139–149. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2818.1986.tb02772.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trimble R. B., Maley F. Optimizing hydrolysis of N-linked high-mannose oligosaccharides by endo-beta-N-acetylglucosaminidase H. Anal Biochem. 1984 Sep;141(2):515–522. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90080-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wewer U. Characterization of a rat yolk sac carcinoma cell line. Dev Biol. 1982 Oct;93(2):416–421. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(82)90128-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willnow T. E., Goldstein J. L., Orth K., Brown M. S., Herz J. Low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein and gp330 bind similar ligands, including plasminogen activator-inhibitor complexes and lactoferrin, an inhibitor of chylomicron remnant clearance. J Biol Chem. 1992 Dec 25;267(36):26172–26180. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]