Abstract
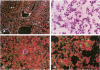
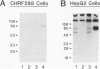
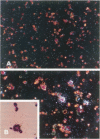
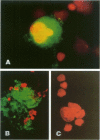
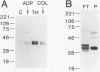
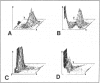
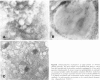
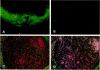
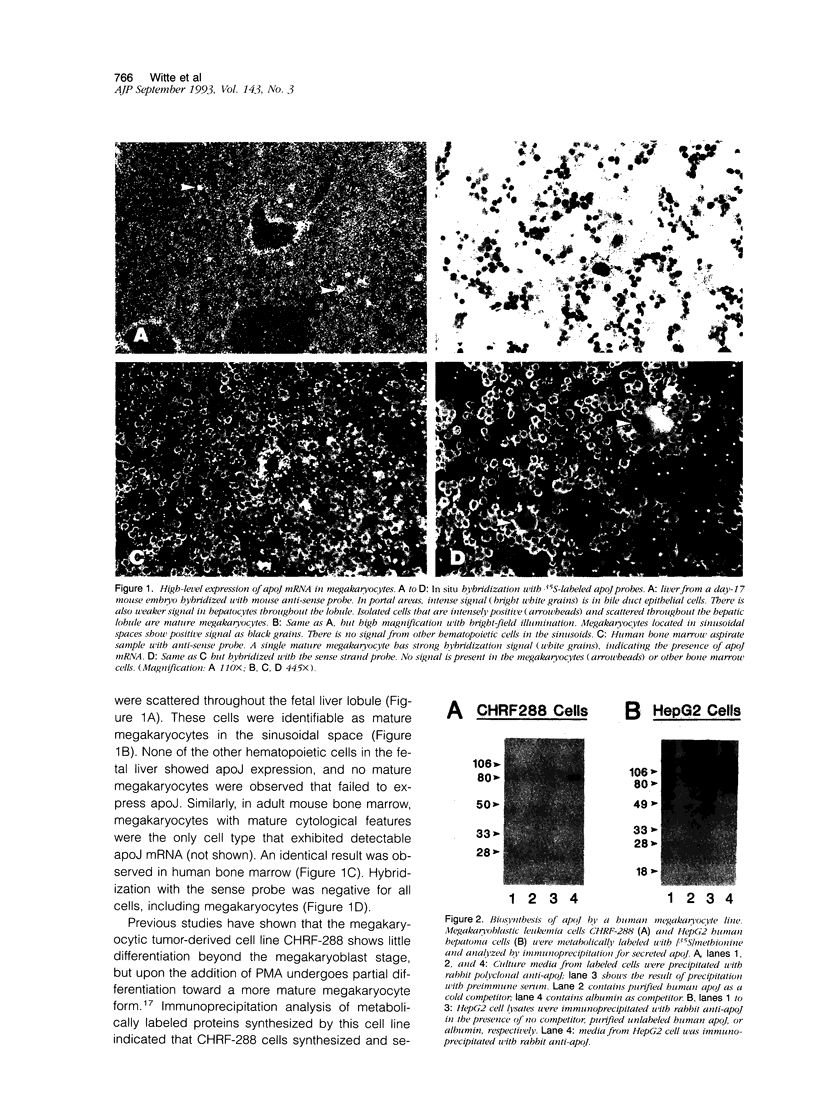
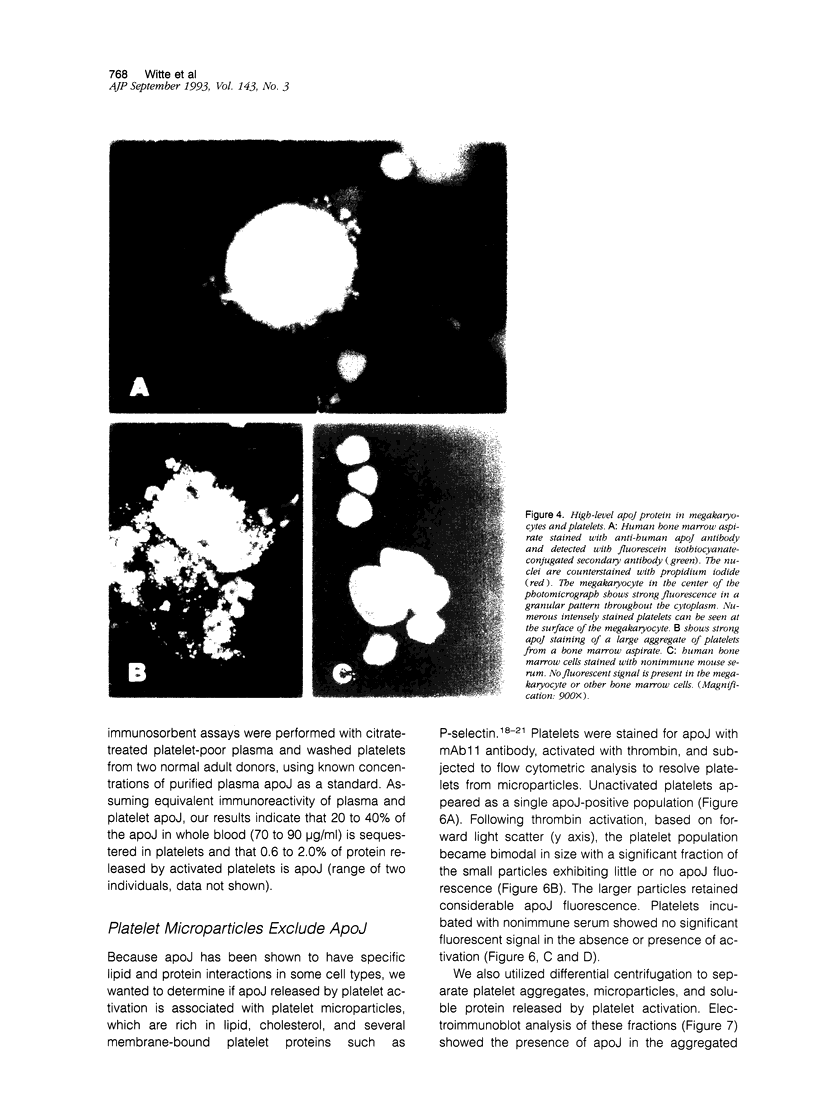
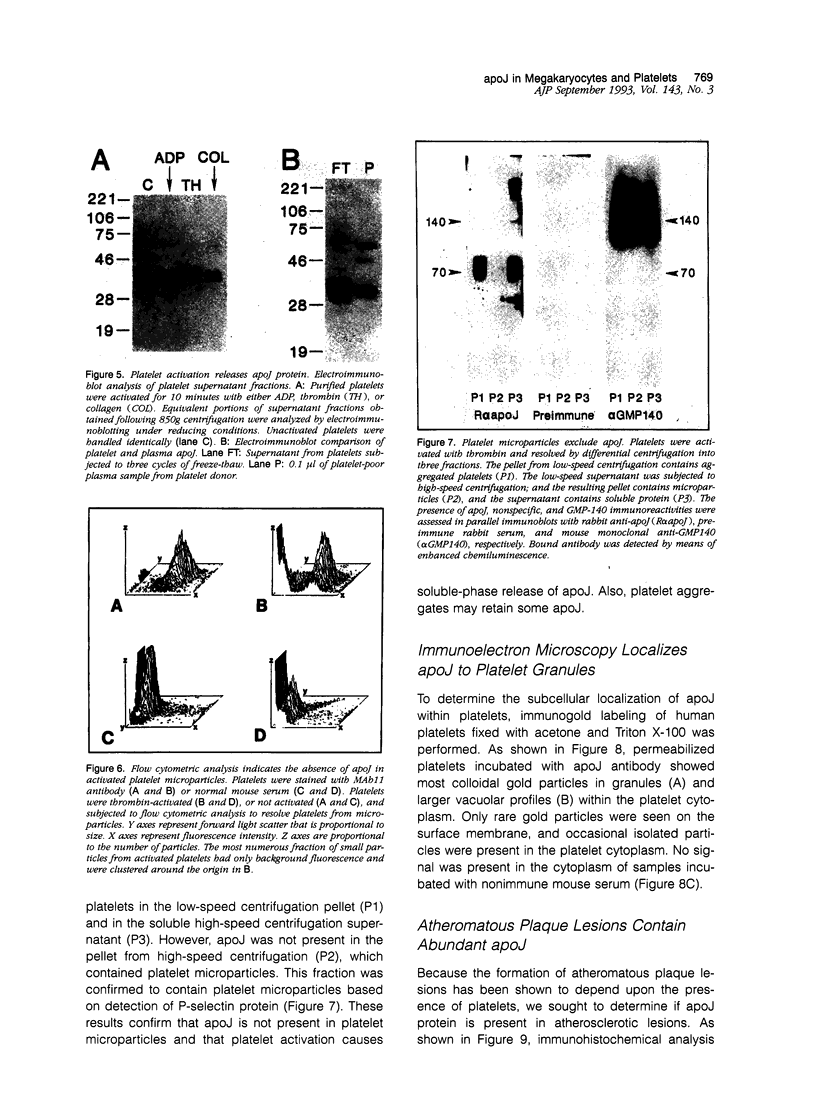
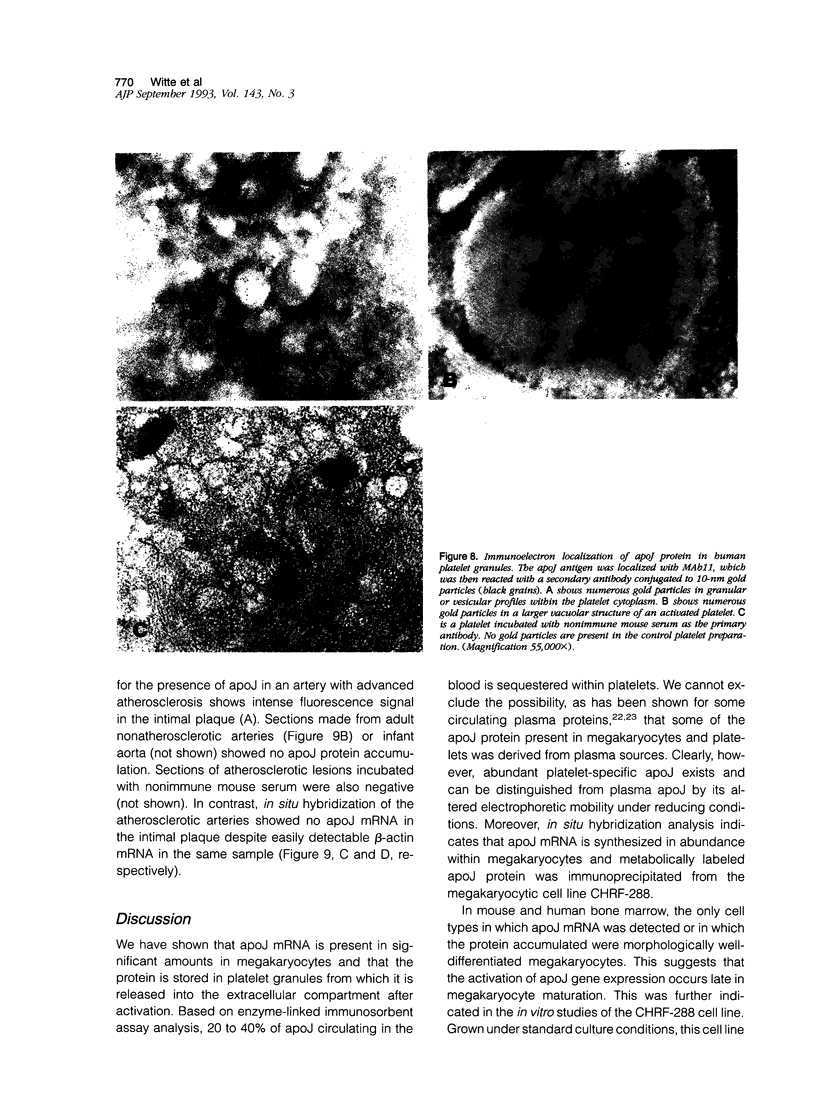
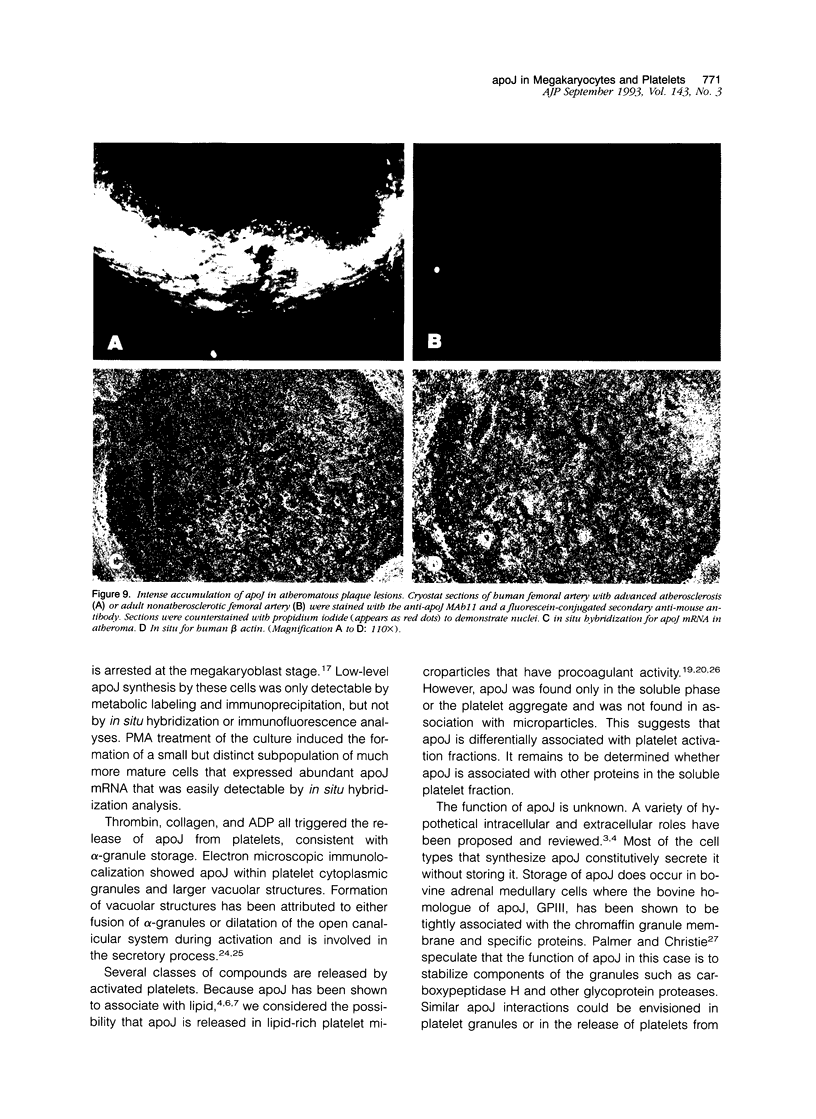
Apolipoprotein J (apoJ) is an abundant glycoprotein in many biological fluids, and its constitutive high level synthesis is characteristic of many epithelial cells exposed to harsh fluids such as urine, bile, and gastric secretions. In addition, dramatic induction of apoJ occurs in cells surrounding several kinds of pathological lesions. Because platelets and circulating inflammatory cells represent critical elements in numerous pathological processes, we evaluated bone marrow cells for the presence of apoJ. Based upon messenger RNA in situ hybridization and immunofluorescent protein detection, high-level apoJ gene expression and protein accumulation occurred exclusively in mature megakaryocytes. Our results indicate that apoJ is stored in platelet granules and is released into extracellular fluid following platelet activation. Because atheromatous plaque development involves platelet aggregation and activation, we looked for and found abundant apoJ protein in advanced human atheromatous lesions. Thus, platelet sequestration and activation may lead to the rapid deployment of apoJ into sites of vascular injury. We hypothesize that platelet-derived apoJ participates in both short-term wound repair processes and chronic pathogenic processes at vascular interfaces.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ASTER R. H., JANDL J. H. PLATELET SEQUESTRATION IN MAN. I. METHODS. J Clin Invest. 1964 May;43:843–855. doi: 10.1172/JCI104970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aronow B. J., Lund S. D., Brown T. L., Harmony J. A., Witte D. P. Apolipoprotein J expression at fluid-tissue interfaces: potential role in barrier cytoprotection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jan 15;90(2):725–729. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.2.725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aronow W. S. Mitral annular calcification: significant and worth acting upon. Geriatrics. 1991 Apr;46(4):73-5, 79-80, 85-6. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bode A. P., Sandberg H., Dombrose F. A., Lentz B. R. Association of factor V activity with membranous vesicles released from human platelets: requirement for platelet stimulation. Thromb Res. 1985 Jul 1;39(1):49–61. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(85)90121-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burkey B. F., deSilva H. V., Harmony J. A. Intracellular processing of apolipoprotein J precursor to the mature heterodimer. J Lipid Res. 1991 Jun;32(6):1039–1048. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Escolar G., White J. G. The platelet open canalicular system: a final common pathway. Blood Cells. 1991;17(3):467–495. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman R. J., Stemerman M. B., Wenz B., Moore S., Gauldie J., Gent M., Tiell M. L., Spaet H. The effect of thrombocytopenia on experimental arteriosclerotic lesion formation in rabbits. Smooth muscle cell proliferation and re-endothelialization. J Clin Invest. 1977 Nov;60(5):1191–1201. doi: 10.1172/JCI108872. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fugman D. A., Witte D. P., Jones C. L., Aronow B. J., Lieberman M. A. In vitro establishment and characterization of a human megakaryoblastic cell line. Blood. 1990 Mar 15;75(6):1252–1261. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuster W., Bowie E. J., Lewis J. C., Fass D. N., Owen C. A., Jr, Brown A. L. Resistance to arteriosclerosis in pigs with von Willebrand's disease. Spontaneous and high cholesterol diet-induced arteriosclerosis. J Clin Invest. 1978 Mar;61(3):722–730. doi: 10.1172/JCI108985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handagama P. J., George J. N., Shuman M. A., McEver R. P., Bainton D. F. Incorporation of a circulating protein into megakaryocyte and platelet granules. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Feb;84(3):861–865. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.3.861. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harding M. A., Chadwick L. J., Gattone V. H., 2nd, Calvet J. P. The SGP-2 gene is developmentally regulated in the mouse kidney and abnormally expressed in collecting duct cysts in polycystic kidney disease. Dev Biol. 1991 Aug;146(2):483–490. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(91)90249-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison P., Wilbourn B., Debili N., Vainchenker W., Breton-Gorius J., Lawrie A. S., Masse J. M., Savidge G. F., Cramer E. M. Uptake of plasma fibrinogen into the alpha granules of human megakaryocytes and platelets. J Clin Invest. 1989 Oct;84(4):1320–1324. doi: 10.1172/JCI114300. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James R. W., Hochstrasser A. C., Borghini I., Martin B., Pometta D., Hochstrasser D. Characterization of a human high density lipoprotein-associated protein, NA1/NA2. Identity with SP-40,40, an inhibitor of complement-mediated cytolysis. Arterioscler Thromb. 1991 May-Jun;11(3):645–652. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.11.3.645. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Javors M. A., Liu M., Cuvelier B. S., Bowden C. L. Characterization of the effect of the adenosine agonist cyclohexyladenosine on platelet activating factor-induced increases in [Ca2+]i in human platelets in vitro. Cell Calcium. 1990 Nov-Dec;11(10):647–653. doi: 10.1016/0143-4160(90)90019-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenne D. E., Lowin B., Peitsch M. C., Böttcher A., Schmitz G., Tschopp J. Clusterin (complement lysis inhibitor) forms a high density lipoprotein complex with apolipoprotein A-I in human plasma. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jun 15;266(17):11030–11036. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenne D. E., Tschopp J. Clusterin: the intriguing guises of a widely expressed glycoprotein. Trends Biochem Sci. 1992 Apr;17(4):154–159. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(92)90325-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenne D. E., Tschopp J. Molecular structure and functional characterization of a human complement cytolysis inhibitor found in blood and seminal plasma: identity to sulfated glycoprotein 2, a constituent of rat testis fluid. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(18):7123–7127. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.18.7123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- May P. C., Lampert-Etchells M., Johnson S. A., Poirier J., Masters J. N., Finch C. E. Dynamics of gene expression for a hippocampal glycoprotein elevated in Alzheimer's disease and in response to experimental lesions in rat. Neuron. 1990 Dec;5(6):831–839. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90342-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore S., Friedman R. J., Singal D. P., Gauldie J., Blajchman M. A., Roberts R. S. Inhibition of injury induced thromboatherosclerotic lesions by anti-platelet serum in rabbits. Thromb Haemost. 1976 Feb 29;35(1):70–81. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan B. P. Isolation and characterization of the complement-inhibiting protein CD59 antigen from platelet membranes. Biochem J. 1992 Mar 1;282(Pt 2):409–413. doi: 10.1042/bj2820409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy B. F., Davies D. J., Morrow W., d'Apice A. J. Localization of terminal complement components S-protein and SP-40,40 in renal biopsies. Pathology. 1989 Oct;21(4):275–278. doi: 10.3109/00313028909061073. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholson-Weller A., March J. P., Rosen C. E., Spicer D. B., Austen K. F. Surface membrane expression by human blood leukocytes and platelets of decay-accelerating factor, a regulatory protein of the complement system. Blood. 1985 May;65(5):1237–1244. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer D. J., Christie D. L. Identification of molecular aggregates containing glycoproteins III, J, K (carboxypeptidase H), and H (Kex2-related proteases) in the soluble and membrane fractions of adrenal medullary chromaffin granules. J Biol Chem. 1992 Oct 5;267(28):19806–19812. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross R. The pathogenesis of atherosclerosis--an update. N Engl J Med. 1986 Feb 20;314(8):488–500. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198602203140806. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandberg H., Bode A. P., Dombrose F. A., Hoechli M., Lentz B. R. Expression of coagulant activity in human platelets: release of membranous vesicles providing platelet factor 1 and platelet factor 3. Thromb Res. 1985 Jul 1;39(1):63–79. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(85)90122-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shattil S. J., Cunningham M., Hoxie J. A. Detection of activated platelets in whole blood using activation-dependent monoclonal antibodies and flow cytometry. Blood. 1987 Jul;70(1):307–315. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sims P. J., Rollins S. A., Wiedmer T. Regulatory control of complement on blood platelets. Modulation of platelet procoagulant responses by a membrane inhibitor of the C5b-9 complex. J Biol Chem. 1989 Nov 15;264(32):19228–19235. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sims P. J., Wiedmer T. The response of human platelets to activated components of the complement system. Immunol Today. 1991 Sep;12(9):338–342. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(91)90012-I. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skarlatos S. I., Amende L. M., Chao F. F., Blanchette-Mackie E. J., Gamble W., Kruth H. S. Biochemical characterization of isolated cholesterol-phospholipid particles continuously released from rat and human platelets after activation. Lab Invest. 1988 Sep;59(3):344–352. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenberg P. E., McEver R. P., Shuman M. A., Jacques Y. V., Bainton D. F. A platelet alpha-granule membrane protein (GMP-140) is expressed on the plasma membrane after activation. J Cell Biol. 1985 Sep;101(3):880–886. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.3.880. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watts M. J., Dankert J. R., Morgan E. P. Isolation and characterization of a membrane-attack-complex-inhibiting protein present in human serum and other biological fluids. Biochem J. 1990 Jan 15;265(2):471–477. doi: 10.1042/bj2650471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witte D. P., Wiginton D. A., Hutton J. J., Aronow B. J. Coordinate developmental regulation of purine catabolic enzyme expression in gastrointestinal and postimplantation reproductive tracts. J Cell Biol. 1991 Oct;115(1):179–190. doi: 10.1083/jcb.115.1.179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu G. H., Holers V. M., Seya T., Ballard L., Atkinson J. P. Identification of a third component of complement-binding glycoprotein of human platelets. J Clin Invest. 1986 Aug;78(2):494–501. doi: 10.1172/JCI112601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Silva H. V., Harmony J. A., Stuart W. D., Gil C. M., Robbins J. Apolipoprotein J: structure and tissue distribution. Biochemistry. 1990 Jun 5;29(22):5380–5389. doi: 10.1021/bi00474a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Silva H. V., Stuart W. D., Duvic C. R., Wetterau J. R., Ray M. J., Ferguson D. G., Albers H. W., Smith W. R., Harmony J. A. A 70-kDa apolipoprotein designated ApoJ is a marker for subclasses of human plasma high density lipoproteins. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 5;265(22):13240–13247. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]