Abstract
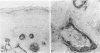
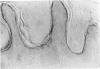
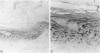
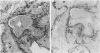
Recently we described a new epidermal serine proteinase inhibitor, skin-derived antileukoproteinase (SKALP), also known as elafin. SKALP/elafin was found to be absent in normal human epidermis, but can be induced in vitro and in vivo under hyperproliferative conditions. Here we studied the expression of SKALP/elafin in several types of epidermal tumors (basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, Bowen's disease, actinic keratosis, and keratoacanthoma). Using immunohistochemical staining SKALP/elafin appeared to be differentially expressed in these tumors. Functional measurements of anti-proteinase activity, and Western blotting of tumor extracts confirmed our findings at the histological level. In well differentiated squamous cell carcinoma, SKALP/elafin messenger RNA was demonstrated by non-radioactive in situ hybridization. We conclude that SKALP/elafin is a marker for abnormal or disturbed squamous differentiation. A possible role of SKALP/elafin in the control of tumor cell invasion is discussed.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alidina R., Kikuchi M., Kashima M., Epstein J. H., Fukuyama K. Cysteine protease and its inhibitor in experimentally produced squamous cell carcinomas in hairless mouse skin. Exp Mol Pathol. 1988 Aug;49(1):118–127. doi: 10.1016/0014-4800(88)90026-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alkemade H., van de Kerkhof P., Schalkwijk J. Demonstration of skin-derived antileukoproteinase (SKALP) in urine of psoriatic patients. J Invest Dermatol. 1992 Jul;99(1):3–7. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12611375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Basset P., Bellocq J. P., Wolf C., Stoll I., Hutin P., Limacher J. M., Podhajcer O. L., Chenard M. P., Rio M. C., Chambon P. A novel metalloproteinase gene specifically expressed in stromal cells of breast carcinomas. Nature. 1990 Dec 20;348(6303):699–704. doi: 10.1038/348699a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauer E. A., Gordon J. M., Reddick M. E., Eisen A. Z. Quantitation and immunocytochemical localization of human skin collagenase in basal cell carcinoma. J Invest Dermatol. 1977 Oct;69(4):363–367. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12510240. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blasi F., Vassalli J. D., Danø K. Urokinase-type plasminogen activator: proenzyme, receptor, and inhibitors. J Cell Biol. 1987 Apr;104(4):801–804. doi: 10.1083/jcb.104.4.801. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang A., Schalkwijk J., Happle R., van de Kerkhof P. C. Elastase-inhibiting activity in scaling skin disorders. Acta Derm Venereol. 1990;70(2):147–151. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Childers J. W., Hernandez A. D., Kim J. H., Stricklin G. P. Immunolocalization of collagenase inhibitor in normal skin and basal cell carcinoma. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1987 Dec;17(6):1025–1032. doi: 10.1016/s0190-9622(87)70293-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox K. H., DeLeon D. V., Angerer L. M., Angerer R. C. Detection of mrnas in sea urchin embryos by in situ hybridization using asymmetric RNA probes. Dev Biol. 1984 Feb;101(2):485–502. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(84)90162-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeClerck Y. A., Perez N., Shimada H., Boone T. C., Langley K. E., Taylor S. M. Inhibition of invasion and metastasis in cells transfected with an inhibitor of metalloproteinases. Cancer Res. 1992 Feb 1;52(3):701–708. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grøndahl-Hansen J., Lund L. R., Ralfkiaer E., Ottevanger V., Danø K. Urokinase- and tissue-type plasminogen activators in keratinocytes during wound reepithelialization in vivo. J Invest Dermatol. 1988 Jun;90(6):790–795. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12461511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grøndahl-Hansen J., Ralfkiaer E., Nielsen L. S., Kristensen P., Frentz G., Danø K. Immunohistochemical localization of urokinase- and tissue-type plasminogen activators in psoriatic skin. J Invest Dermatol. 1987 Jan;88(1):28–32. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12464827. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hochstrasser K., Albrecht G. J., Schönberger O. L., Rasche B., Lempart K. An elastase-specific inhibitor from human bronchial mucus. Isolation and characterization. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1981 Oct;362(10):1369–1375. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1981.362.2.1369. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen P. J., Baird J., Morioka S., Lessin S., Lazarus G. S. Epidermal plasminogen activator is abnormal in cutaneous lesions. J Invest Dermatol. 1988 Jun;90(6):777–782. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12461494. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramps J. A., Klasen E. C. Characterization of a low molecular weight anti-elastase isolated from human bronchial secretion. Exp Lung Res. 1985;9(1-2):151–165. doi: 10.3109/01902148509061534. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lammers A. M., van de Kerkhof P. C., Schalwijk J., Mier P. D. Elastase, a marker for neutrophils in skin infiltrates. Br J Dermatol. 1986 Aug;115(2):181–186. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.1986.tb05715.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liotta L. A., Steeg P. S., Stetler-Stevenson W. G. Cancer metastasis and angiogenesis: an imbalance of positive and negative regulation. Cell. 1991 Jan 25;64(2):327–336. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90642-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liotta L. A., Stetler-Stevenson W., Steeg P. S. Metastasis suppressor genes. Important Adv Oncol. 1991:85–100. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liotta L. A., Tryggvason K., Garbisa S., Hart I., Foltz C. M., Shafie S. Metastatic potential correlates with enzymatic degradation of basement membrane collagen. Nature. 1980 Mar 6;284(5751):67–68. doi: 10.1038/284067a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liotta L. The role of cellular proteases and their inhibitors in invasion and metastasis. Introductionary overview. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 1990 Dec;9(4):285–287. doi: 10.1007/BF00049519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowe F. C., Isaacs J. T. Biochemical methods for predicting metastatic ability of prostatic cancer utilizing the dunning R-3327 rat prostatic adenocarcinoma system as a model. Cancer Res. 1984 Feb;44(2):744–752. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Machovich R., Owen W. G. An elastase-dependent pathway of plasminogen activation. Biochemistry. 1989 May 16;28(10):4517–4522. doi: 10.1021/bi00436a059. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mignatti P., Robbins E., Rifkin D. B. Tumor invasion through the human amniotic membrane: requirement for a proteinase cascade. Cell. 1986 Nov 21;47(4):487–498. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90613-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller S. J., Jensen P. J., Dzubow L. M., Lazarus G. S. Urokinase plasminogen activator is immunocytochemically detectable in squamous cell but not basal cell carcinomas. J Invest Dermatol. 1992 Mar;98(3):351–358. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12499803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molhuizen H. O., Alkemade H. A., Zeeuwen P. L., de Jongh G. J., Wieringa B., Schalkwijk J. SKALP/elafin: an elastase inhibitor from cultured human keratinocytes. Purification, cDNA sequence, and evidence for transglutaminase cross-linking. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jun 5;268(16):12028–12032. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morioka S., Lazarus G. S., Baird J. L., Jensen P. J. Migrating keratinocytes express urokinase-type plasminogen activator. J Invest Dermatol. 1987 Apr;88(4):418–423. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12469754. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakajima M., Chop A. M. Tumor invasion and extracellular matrix degradative enzymes: regulation of activity by organ factors. Semin Cancer Biol. 1991 Apr;2(2):115–127. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Negi M., Matsui T., Ogawa H. Mechanism of regulation of human epidermal transglutaminase. J Invest Dermatol. 1981 Nov;77(5):389–392. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12494561. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ossowski L., Reich E. Antibodies to plasminogen activator inhibit human tumor metastasis. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(3 Pt 2):611–619. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90093-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ponton A., Coulombe B., Skup D. Decreased expression of tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases in metastatic tumor cells leading to increased levels of collagenase activity. Cancer Res. 1991 Apr 15;51(8):2138–2143. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quax P. H., van Leeuwen R. T., Verspaget H. W., Verheijen J. H. Protein and messenger RNA levels of plasminogen activators and inhibitors analyzed in 22 human tumor cell lines. Cancer Res. 1990 Mar 1;50(5):1488–1494. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quax P. H., van Muijen G. N., Weening-Verhoeff E. J., Lund L. R., Danø K., Ruiter D. J., Verheijen J. H. Metastatic behavior of human melanoma cell lines in nude mice correlates with urokinase-type plasminogen activator, its type-1 inhibitor, and urokinase-mediated matrix degradation. J Cell Biol. 1991 Oct;115(1):191–199. doi: 10.1083/jcb.115.1.191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reich R., Thompson E. W., Iwamoto Y., Martin G. R., Deason J. R., Fuller G. C., Miskin R. Effects of inhibitors of plasminogen activator, serine proteinases, and collagenase IV on the invasion of basement membranes by metastatic cells. Cancer Res. 1988 Jun 15;48(12):3307–3312. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sallenave J. M., Ryle A. P. Purification and characterization of elastase-specific inhibitor. Sequence homology with mucus proteinase inhibitor. Biol Chem Hoppe Seyler. 1991 Jan;372(1):13–21. doi: 10.1515/bchm3.1991.372.1.13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sappino A. P., Belin D., Huarte J., Hirschel-Scholz S., Saurat J. H., Vassalli J. D. Differential protease expression by cutaneous squamous and basal cell carcinomas. J Clin Invest. 1991 Oct;88(4):1073–1079. doi: 10.1172/JCI115406. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schalkwijk J., Chang A., Janssen P., De Jongh G. J., Mier P. D. Skin-derived antileucoproteases (SKALPs): characterization of two new elastase inhibitors from psoriatic epidermis. Br J Dermatol. 1990 May;122(5):631–641. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.1990.tb07285.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schalkwijk J., de Roo C., de Jongh G. J. Skin-derived antileukoproteinase (SKALP), an elastase inhibitor from human keratinocytes. Purification and biochemical properties. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Feb 22;1096(2):148–154. doi: 10.1016/0925-4439(91)90053-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schalkwijk J., van Vlijmen I. M., Alkemade J. A., de Jongh G. J. Immunohistochemical localization of SKALP/elafin in psoriatic epidermis. J Invest Dermatol. 1993 Apr;100(4):390–393. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12471990. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schägger H., von Jagow G. Tricine-sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis for the separation of proteins in the range from 1 to 100 kDa. Anal Biochem. 1987 Nov 1;166(2):368–379. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(87)90587-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuboi R., Yamaguchi T., Kurita Y., Nakao H., Ogawa H., Ishihara K. Comparison of proteinase activities in squamous cell carcinoma, basal cell epithelioma, and seborrheic keratosis. J Invest Dermatol. 1988 Jun;90(6):869–872. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12462121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsushima H., Hopsu-Havu V. K. Cysteine proteinase inhibitors in human squamous cell carcinoma. Acta Histochem. 1989;85(1):23–28. doi: 10.1016/S0065-1281(89)80092-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Roy F., Mareel M. Tumour invasion: effects of cell adhesion and motility. Trends Cell Biol. 1992 Jun;2(6):163–169. doi: 10.1016/0962-8924(92)90035-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watt F. M. Terminal differentiation of epidermal keratinocytes. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;1(6):1107–1115. doi: 10.1016/s0955-0674(89)80058-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiedow O., Lüademann J., Utecht B. Elafin is a potent inhibitor of proteinase 3. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Jan 15;174(1):6–10. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)90476-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiedow O., Schröder J. M., Gregory H., Young J. A., Christophers E. Elafin: an elastase-specific inhibitor of human skin. Purification, characterization, and complete amino acid sequence. J Biol Chem. 1990 Sep 5;265(25):14791–14795. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokouchi Y., Ohsugi K., Sasaki H., Kuroiwa A. Chicken homeobox gene Msx-1: structure, expression in limb buds and effect of retinoic acid. Development. 1991 Oct;113(2):431–444. doi: 10.1242/dev.113.2.431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeydel M., Nakagawa S., Biempica L., Takahashi S. Collagenase and elastase production by mouse mammary adenocarcinoma primary cultures and cloned cells. Cancer Res. 1986 Dec;46(12 Pt 1):6438–6445. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]