Abstract
Murine gammaherpesvirus is a natural pathogen of wild rodents. In the laboratory it establishes an infection of epithelial cells and persists in B lymphocytes in a latent form. Inbred mice chronically infected with the virus develop a lymphoproliferative disease (LPD) similar to that seen in patients infected with Epstein-Barr virus. The frequency of LPD over a period of 3 years was 9% of all infected animals, with 50% of these displaying high grade lymphomas. The incidence of LPD was greatly increased when infected mice were treated with cyclosporin A. The majority of mice used in the experiments were BALB/c, although lymphomas were detected in mice on other genetic backgrounds, ie, CBA and B10Br. Lymphomas were associated with both lymphoid and nonlymphoid tissues (liver, lung, and kidney). In all cases of lymphomas studied thus far, there was a mixed B cell (B220+ve) and T cell (CD3+ve) phenotype. The B cells were light chain restricted, indicative of a clonal origin. Variable numbers of virus genome-positive cells were detected by in situ hybridization in and around the lymphomas. In contrast, no lytic antigen-positive cells were detected, indicating that genome-positive cells were either latently infected or undergoing an abortive infection. These observations suggest that murine gammaherpesvirus-infected mice may be an important model to study the pathogenesis of LPD associated with other gammaherpesviruses, such as Epstein-Barr virus.
Full text
PDF


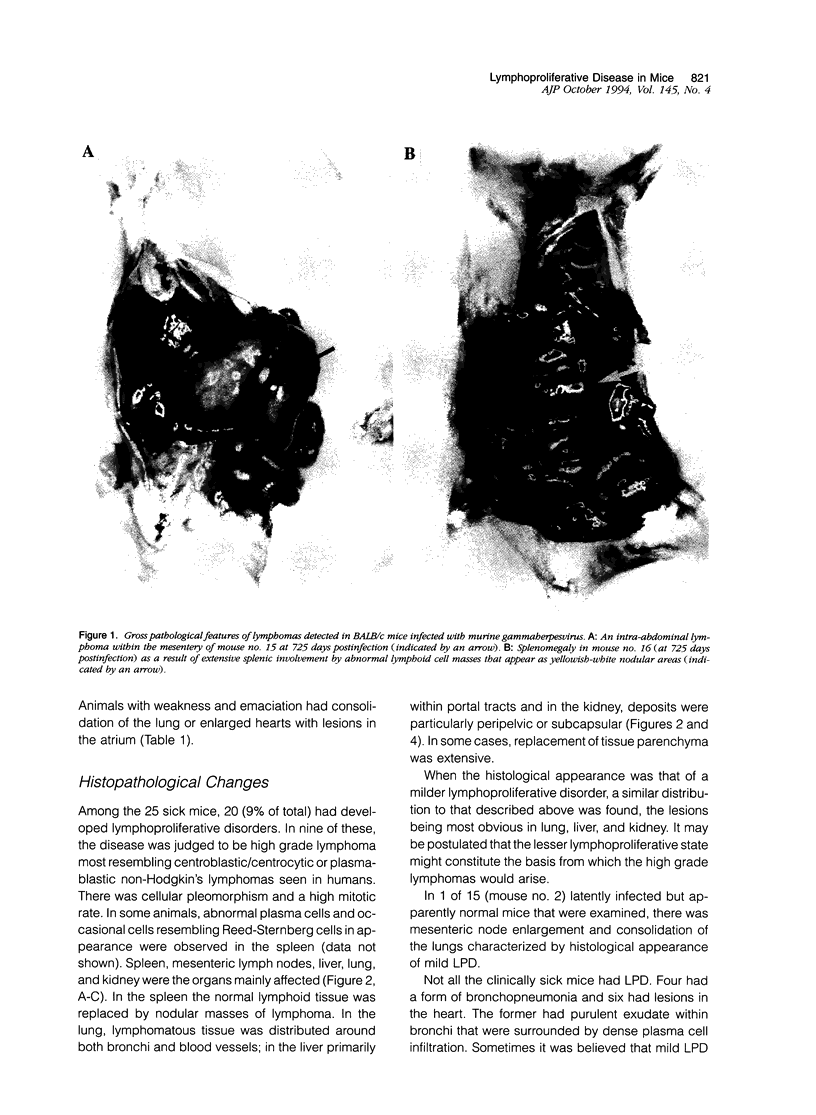
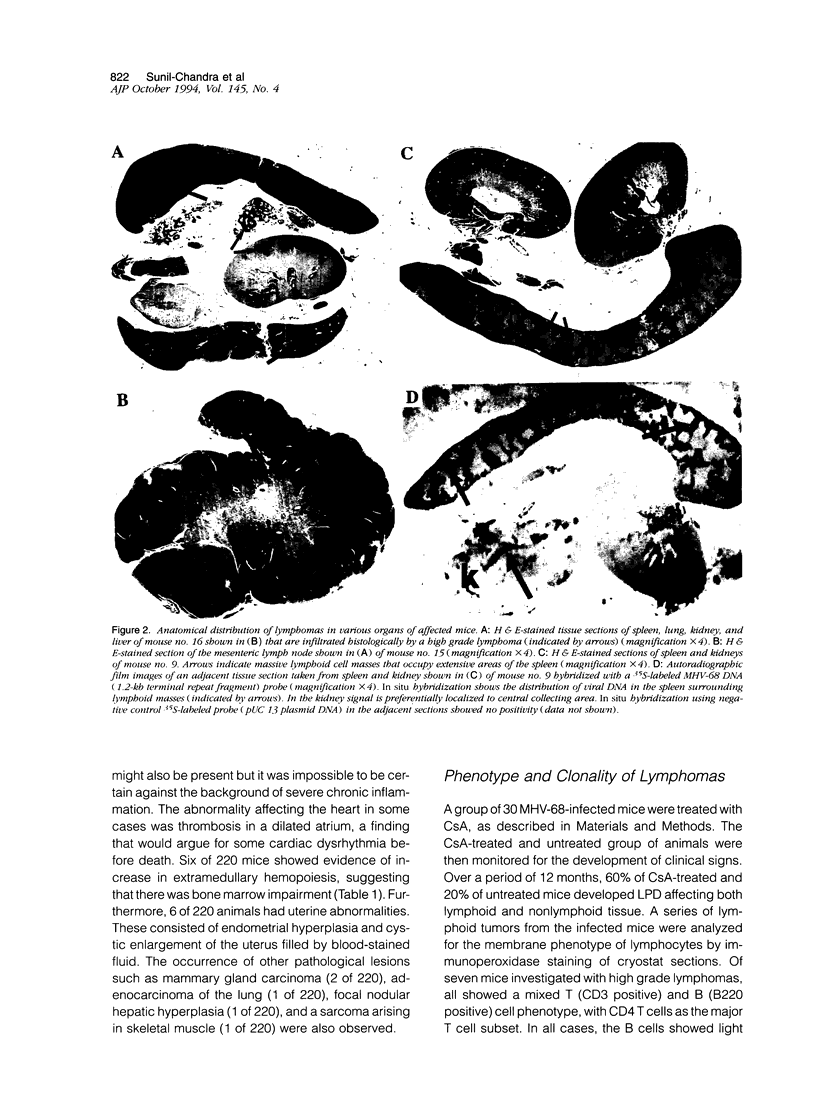

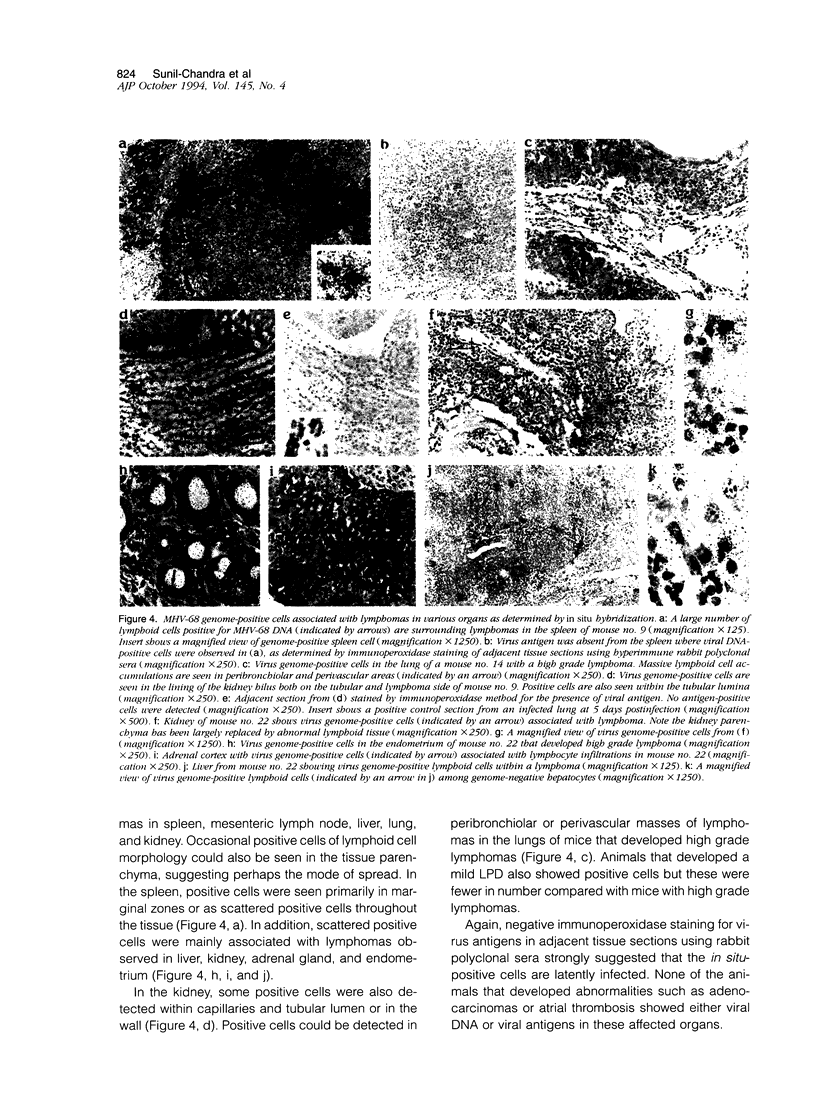


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blaskovic D., Stanceková M., Svobodová J., Mistríková J. Isolation of five strains of herpesviruses from two species of free living small rodents. Acta Virol. 1980 Dec;24(6):468–468. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borisch-Chappuis B., Nezelof C., Müller H., Müller-Hermelink H. K. Different Epstein-Barr virus expression in lymphomas from immunocompromised and immunocompetent patients. Am J Pathol. 1990 Apr;136(4):751–758. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cannon M. J., Pisa P., Fox R. I., Cooper N. R. Epstein-Barr virus induces aggressive lymphoproliferative disorders of human B cell origin in SCID/hu chimeric mice. J Clin Invest. 1990 Apr;85(4):1333–1337. doi: 10.1172/JCI114573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deacon E. M., Pallesen G., Niedobitek G., Crocker J., Brooks L., Rickinson A. B., Young L. S. Epstein-Barr virus and Hodgkin's disease: transcriptional analysis of virus latency in the malignant cells. J Exp Med. 1993 Feb 1;177(2):339–349. doi: 10.1084/jem.177.2.339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Efstathiou S., Ho Y. M., Hall S., Styles C. J., Scott S. D., Gompels U. A. Murine herpesvirus 68 is genetically related to the gammaherpesviruses Epstein-Barr virus and herpesvirus saimiri. J Gen Virol. 1990 Jun;71(Pt 6):1365–1372. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-71-6-1365. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Efstathiou S., Ho Y. M., Minson A. C. Cloning and molecular characterization of the murine herpesvirus 68 genome. J Gen Virol. 1990 Jun;71(Pt 6):1355–1364. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-71-6-1355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frizzera G., Hanto D. W., Gajl-Peczalska K. J., Rosai J., McKenna R. W., Sibley R. K., Holahan K. P., Lindquist L. L. Polymorphic diffuse B-cell hyperplasias and lymphomas in renal transplant recipients. Cancer Res. 1981 Nov;41(11 Pt 1):4262–4279. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanto D. W., Frizzera G., Purtilo D. T., Sakamoto K., Sullivan J. L., Saemundsen A. K., Klein G., Simmons R. L., Najarian J. S. Clinical spectrum of lymphoproliferative disorders in renal transplant recipients and evidence for the role of Epstein-Barr virus. Cancer Res. 1981 Nov;41(11 Pt 1):4253–4261. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howe J. G., Steitz J. A. Localization of Epstein-Barr virus-encoded small RNAs by in situ hybridization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(23):9006–9010. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.23.9006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nalesnik M. A. Lymphoproliferative disease in organ transplant recipients. Springer Semin Immunopathol. 1991;13(2):199–216. doi: 10.1007/BF00201469. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Randhawa P. S., Markin R. S., Starzl T. E., Demetris A. J. Epstein-Barr virus-associated syndromes in immunosuppressed liver transplant recipients. Clinical profile and recognition on routine allograft biopsy. Am J Surg Pathol. 1990 Jun;14(6):538–547. doi: 10.1097/00000478-199006000-00004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe M., Young L. S., Crocker J., Stokes H., Henderson S., Rickinson A. B. Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-associated lymphoproliferative disease in the SCID mouse model: implications for the pathogenesis of EBV-positive lymphomas in man. J Exp Med. 1991 Jan 1;173(1):147–158. doi: 10.1084/jem.173.1.147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shope T., Dechairo D., Miller G. Malignant lymphoma in cottontop marmosets after inoculation with Epstein-Barr virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Sep;70(9):2487–2491. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.9.2487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sunil-Chandra N. P., Efstathiou S., Arno J., Nash A. A. Virological and pathological features of mice infected with murine gamma-herpesvirus 68. J Gen Virol. 1992 Sep;73(Pt 9):2347–2356. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-73-9-2347. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sunil-Chandra N. P., Efstathiou S., Nash A. A. Interactions of murine gammaherpesvirus 68 with B and T cell lines. Virology. 1993 Apr;193(2):825–833. doi: 10.1006/viro.1993.1191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sunil-Chandra N. P., Efstathiou S., Nash A. A. Murine gammaherpesvirus 68 establishes a latent infection in mouse B lymphocytes in vivo. J Gen Virol. 1992 Dec;73(Pt 12):3275–3279. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-73-12-3275. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas J. A., Hotchin N. A., Allday M. J., Amlot P., Rose M., Yacoub M., Crawford D. H. Immunohistology of Epstein-Barr virus-associated antigens in B cell disorders from immunocompromised individuals. Transplantation. 1990 May;49(5):944–953. doi: 10.1097/00007890-199005000-00022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss L. M., Movahed L. A. In situ demonstration of Epstein-Barr viral genomes in viral-associated B cell lymphoproliferations. Am J Pathol. 1989 Mar;134(3):651–659. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young L. S., Finerty S., Brooks L., Scullion F., Rickinson A. B., Morgan A. J. Epstein-Barr virus gene expression in malignant lymphomas induced by experimental virus infection of cottontop tamarins. J Virol. 1989 May;63(5):1967–1974. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.5.1967-1974.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young L., Alfieri C., Hennessy K., Evans H., O'Hara C., Anderson K. C., Ritz J., Shapiro R. S., Rickinson A., Kieff E. Expression of Epstein-Barr virus transformation-associated genes in tissues of patients with EBV lymphoproliferative disease. N Engl J Med. 1989 Oct 19;321(16):1080–1085. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198910193211604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]