Abstract
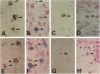
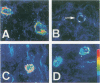
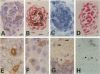
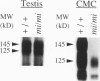
The mi locus of mice encodes a novel member of the basic-helix-loop-helix-leucine zipper protein family of transcription factors (hereafter called mi factor). In addition to microphthalmus, osteopetrosis, and lack of melanocytes, mice of mi/mi genotype are deficient in mast cells. Since the c-kit receptor tyrosine kinase plays an important role in the development of mast cells, and since the c-kit expression by cultured mast cells from mi/mi mice is deficient in both mRNA and protein levels, the mast cell deficiency of mi/mi mice has been attributed at least in part to the deficient expression of c-kit. However, it remained to be examined whether the c-kit expression was also deficient in tissues of mi/mi mice. In the present study, we examined the c-kit expression by mi/mi skin mast cells using in situ hybridization and immunohistochemistry. Moreover, we examined the c-kit expression by various cells other than mast cells in tissues of mi/mi mice. We found that the c-kit expression was deficient in mast cells but not in erythroid precursors, testicular germ cells, and neurons of mi/mi mice. This suggested that the regulation of the c-kit transcription by the mi factor was dependent on cell types. Mice of mi/mi genotype appeared to be a useful model to analyze the function of transcription factors in the whole-animal level.
Full text
PDF



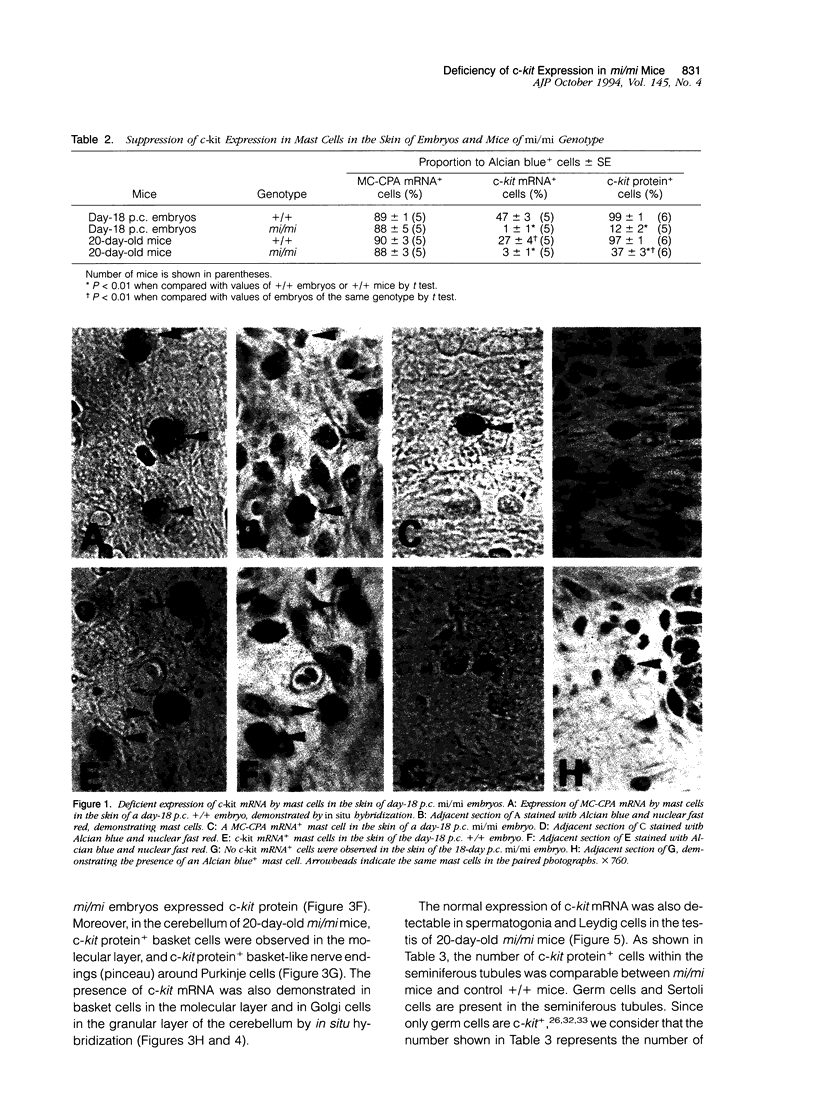

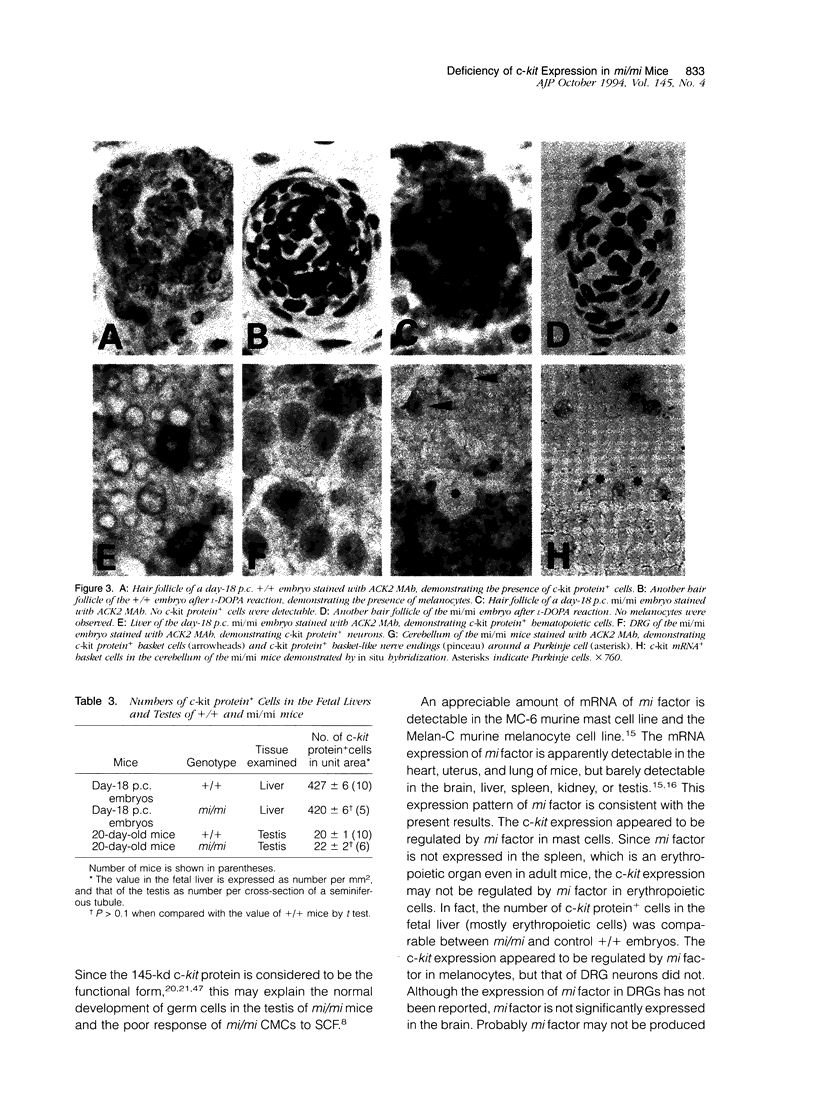
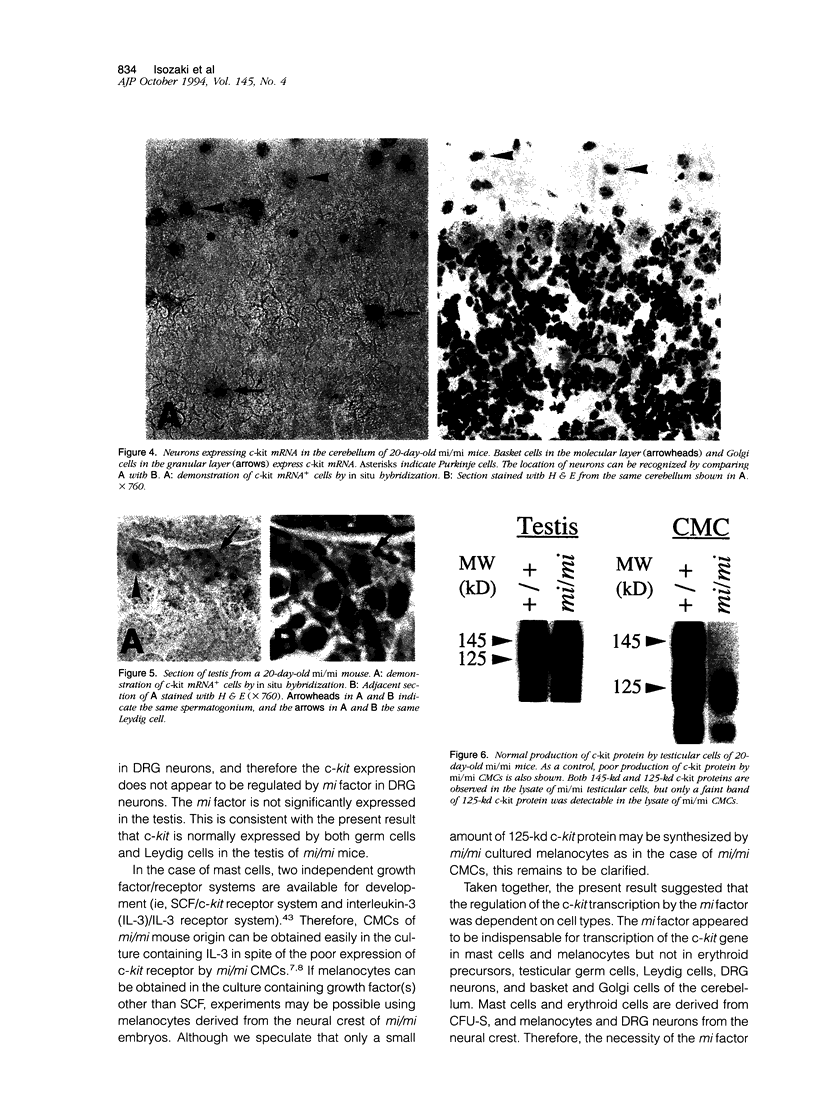


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chabot B., Stephenson D. A., Chapman V. M., Besmer P., Bernstein A. The proto-oncogene c-kit encoding a transmembrane tyrosine kinase receptor maps to the mouse W locus. Nature. 1988 Sep 1;335(6185):88–89. doi: 10.1038/335088a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dai C. H., Krantz S. B., Zsebo K. M. Human burst-forming units-erythroid need direct interaction with stem cell factor for further development. Blood. 1991 Nov 15;78(10):2493–2497. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebi Y., Kanakura Y., Jippo-Kanemoto T., Tsujimura T., Furitsu T., Ikeda H., Adachi S., Kasugai T., Nomura S., Kanayama Y. Low c-kit expression of cultured mast cells of mi/mi genotype may be involved in their defective responses to fibroblasts that express the ligand for c-kit. Blood. 1992 Sep 15;80(6):1454–1462. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebi Y., Kasugai T., Seino Y., Onoue H., Kanemoto T., Kitamura Y. Mechanism of mast cell deficiency in mutant mice of mi/mi genotype: an analysis by co-culture of mast cells and fibroblasts. Blood. 1990 Mar 15;75(6):1247–1251. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flanagan J. G., Leder P. The kit ligand: a cell surface molecule altered in steel mutant fibroblasts. Cell. 1990 Oct 5;63(1):185–194. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90299-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geissler E. N., Ryan M. A., Housman D. E. The dominant-white spotting (W) locus of the mouse encodes the c-kit proto-oncogene. Cell. 1988 Oct 7;55(1):185–192. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90020-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guenet J. L., Marchal G., Milon G., Tambourin P., Wendling F. Fertile dominant spotting in the house mouse. J Hered. 1979 Jan-Feb;70(1):9–12. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jhered.a109202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirata T., Morii E., Morimoto M., Kasugai T., Tsujimura T., Hirota S., Kanakura Y., Nomura S., Kitamura Y. Stem cell factor induces outgrowth of c-kit-positive neurites and supports the survival of c-kit-positive neurons in dorsal root ganglia of mouse embryos. Development. 1993 Sep;119(1):49–56. doi: 10.1242/dev.119.1.49. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirota S., Ito A., Morii E., Wanaka A., Tohyama M., Kitamura Y., Nomura S. Localization of mRNA for c-kit receptor and its ligand in the brain of adult rats: an analysis using in situ hybridization histochemistry. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 1992 Sep;15(1-2):47–54. doi: 10.1016/0169-328x(92)90150-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodgkinson C. A., Moore K. J., Nakayama A., Steingrímsson E., Copeland N. G., Jenkins N. A., Arnheiter H. Mutations at the mouse microphthalmia locus are associated with defects in a gene encoding a novel basic-helix-loop-helix-zipper protein. Cell. 1993 Jul 30;74(2):395–404. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90429-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang E., Nocka K., Beier D. R., Chu T. Y., Buck J., Lahm H. W., Wellner D., Leder P., Besmer P. The hematopoietic growth factor KL is encoded by the Sl locus and is the ligand of the c-kit receptor, the gene product of the W locus. Cell. 1990 Oct 5;63(1):225–233. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90303-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes M. J., Lingrel J. B., Krakowsky J. M., Anderson K. P. A helix-loop-helix transcription factor-like gene is located at the mi locus. J Biol Chem. 1993 Oct 5;268(28):20687–20690. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasugai T., Oguri K., Jippo-Kanemoto T., Morimoto M., Yamatodani A., Yoshida K., Ebi Y., Isozaki K., Tei H., Tsujimura T. Deficient differentiation of mast cells in the skin of mi/mi mice. Usefulness of in situ hybridization for evaluation of mast cell phenotype. Am J Pathol. 1993 Nov;143(5):1337–1347. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitamura Y., Go S. Decreased production of mast cells in S1/S1d anemic mice. Blood. 1979 Mar;53(3):492–497. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitamura Y., Go S., Hatanaka K. Decrease of mast cells in W/Wv mice and their increase by bone marrow transplantation. Blood. 1978 Aug;52(2):447–452. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitamura Y. Heterogeneity of mast cells and phenotypic change between subpopulations. Annu Rev Immunol. 1989;7:59–76. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.07.040189.000423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitamura Y., Kawata T., Suda O., Ezumi K. Changed differentiation pattern of parental colony-- forming cells in F1 hybrid mice suffering from graft-versus-host disease. Transplantation. 1970 Dec;10(6):455–462. doi: 10.1097/00007890-197012000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitamura Y., Shimada M., Go S. Presence of mast cell precursors in fetal liver of mice. Dev Biol. 1979 Jun;70(2):510–514. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(79)90042-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitamura Y., Yokoyama M., Matsuda H., Ohno T., Mori K. J. Spleen colony-forming cell as common precursor for tissue mast cells and granulocytes. Nature. 1981 May 14;291(5811):159–160. doi: 10.1038/291159a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCCULLOCH E. A., SIMINOVITCH L., TILL J. E. SPLEEN-COLONY FORMATION IN ANEMIC MICE OF GENOTYPE WW. Science. 1964 May 15;144(3620):844–846. doi: 10.1126/science.144.3620.844. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manova K., Bachvarova R. F. Expression of c-kit encoded at the W locus of mice in developing embryonic germ cells and presumptive melanoblasts. Dev Biol. 1991 Aug;146(2):312–324. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(91)90233-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manova K., Nocka K., Besmer P., Bachvarova R. F. Gonadal expression of c-kit encoded at the W locus of the mouse. Development. 1990 Dec;110(4):1057–1069. doi: 10.1242/dev.110.4.1057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin F. H., Suggs S. V., Langley K. E., Lu H. S., Ting J., Okino K. H., Morris C. F., McNiece I. K., Jacobsen F. W., Mendiaz E. A. Primary structure and functional expression of rat and human stem cell factor DNAs. Cell. 1990 Oct 5;63(1):203–211. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90301-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Motro B., van der Kooy D., Rossant J., Reith A., Bernstein A. Contiguous patterns of c-kit and steel expression: analysis of mutations at the W and Sl loci. Development. 1991 Dec;113(4):1207–1221. doi: 10.1242/dev.113.4.1207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakahata T., Spicer S. S., Cantey J. R., Ogawa M. Clonal assay of mouse mast cell colonies in methylcellulose culture. Blood. 1982 Aug;60(2):352–361. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakayama H., Kuroda H., Fujita J., Kitamura Y. Studies of Sl/Sld in equilibrium with +/+ mouse aggregation chimaeras. I. Different distribution patterns between melanocytes and mast cells in the skin. Development. 1988 Jan;102(1):107–116. doi: 10.1242/dev.102.1.107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishikawa S., Kusakabe M., Yoshinaga K., Ogawa M., Hayashi S., Kunisada T., Era T., Sakakura T., Nishikawa S. In utero manipulation of coat color formation by a monoclonal anti-c-kit antibody: two distinct waves of c-kit-dependency during melanocyte development. EMBO J. 1991 Aug;10(8):2111–2118. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07744.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nocka K., Tan J. C., Chiu E., Chu T. Y., Ray P., Traktman P., Besmer P. Molecular bases of dominant negative and loss of function mutations at the murine c-kit/white spotting locus: W37, Wv, W41 and W. EMBO J. 1990 Jun;9(6):1805–1813. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08305.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogawa M., Matsuzaki Y., Nishikawa S., Hayashi S., Kunisada T., Sudo T., Kina T., Nakauchi H., Nishikawa S. Expression and function of c-kit in hemopoietic progenitor cells. J Exp Med. 1991 Jul 1;174(1):63–71. doi: 10.1084/jem.174.1.63. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okada S., Nakauchi H., Nagayoshi K., Nishikawa S., Nishikawa S., Miura Y., Suda T. Enrichment and characterization of murine hematopoietic stem cells that express c-kit molecule. Blood. 1991 Oct 1;78(7):1706–1712. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Onoue H., Maeyama K., Nomura S., Kasugai T., Tei H., Kim H. M., Watanabe T., Kitamura Y. Absence of immature mast cells in the skin of Ws/Ws rats with a small deletion at tyrosine kinase domain of the c-kit gene. Am J Pathol. 1993 Apr;142(4):1001–1007. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orr-Urtreger A., Avivi A., Zimmer Y., Givol D., Yarden Y., Lonai P. Developmental expression of c-kit, a proto-oncogene encoded by the W locus. Development. 1990 Aug;109(4):911–923. doi: 10.1242/dev.109.4.911. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qiu F. H., Ray P., Brown K., Barker P. E., Jhanwar S., Ruddle F. H., Besmer P. Primary structure of c-kit: relationship with the CSF-1/PDGF receptor kinase family--oncogenic activation of v-kit involves deletion of extracellular domain and C terminus. EMBO J. 1988 Apr;7(4):1003–1011. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02907.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reith A. D., Rottapel R., Giddens E., Brady C., Forrester L., Bernstein A. W mutant mice with mild or severe developmental defects contain distinct point mutations in the kinase domain of the c-kit receptor. Genes Dev. 1990 Mar;4(3):390–400. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.3.390. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds D. S., Stevens R. L., Gurley D. S., Lane W. S., Austen K. F., Serafin W. E. Isolation and molecular cloning of mast cell carboxypeptidase A. A novel member of the carboxypeptidase gene family. J Biol Chem. 1989 Nov 25;264(33):20094–20099. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell E. S. Hereditary anemias of the mouse: a review for geneticists. Adv Genet. 1979;20:357–459. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonoda T., Kitamura Y., Haku Y., Hara H., Mori K. J. Mast-cell precursors in various haematopoietic colonies of mice produced in vivo and in vitro. Br J Haematol. 1983 Apr;53(4):611–620. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1983.tb07312.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stechschulte D. J., Sharma R., Dileepan K. N., Simpson K. M., Aggarwal N., Clancy J., Jr, Jilka R. L. Effect of the mi allele on mast cells, basophils, natural killer cells, and osteoclasts in C57Bl/6J mice. J Cell Physiol. 1987 Sep;132(3):565–570. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041320321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens J., Loutit J. F. Mast cells in spotted mutant mice (W Ph mi). Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1982 Jun 22;215(1200):405–409. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1982.0050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan J. C., Nocka K., Ray P., Traktman P., Besmer P. The dominant W42 spotting phenotype results from a missense mutation in the c-kit receptor kinase. Science. 1990 Jan 12;247(4939):209–212. doi: 10.1126/science.1688471. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsujimura T., Koshimizu U., Katoh H., Isozaki K., Kanakura Y., Tono T., Adachi S., Kasugai T., Tei H., Nishimune Y. Mast cell number in the skin of heterozygotes reflects the molecular nature of c-kit mutation. Blood. 1993 May 15;81(10):2530–2538. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weston J. A. The migration and differentiation of neural crest cells. Adv Morphog. 1970;8:41–114. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-028608-9.50006-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams D. E., Eisenman J., Baird A., Rauch C., Van Ness K., March C. J., Park L. S., Martin U., Mochizuki D. Y., Boswell H. S. Identification of a ligand for the c-kit proto-oncogene. Cell. 1990 Oct 5;63(1):167–174. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90297-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshinaga K., Nishikawa S., Ogawa M., Hayashi S., Kunisada T., Fujimoto T., Nishikawa S. Role of c-kit in mouse spermatogenesis: identification of spermatogonia as a specific site of c-kit expression and function. Development. 1991 Oct;113(2):689–699. doi: 10.1242/dev.113.2.689. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zsebo K. M., Williams D. A., Geissler E. N., Broudy V. C., Martin F. H., Atkins H. L., Hsu R. Y., Birkett N. C., Okino K. H., Murdock D. C. Stem cell factor is encoded at the Sl locus of the mouse and is the ligand for the c-kit tyrosine kinase receptor. Cell. 1990 Oct 5;63(1):213–224. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90302-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]