Abstract
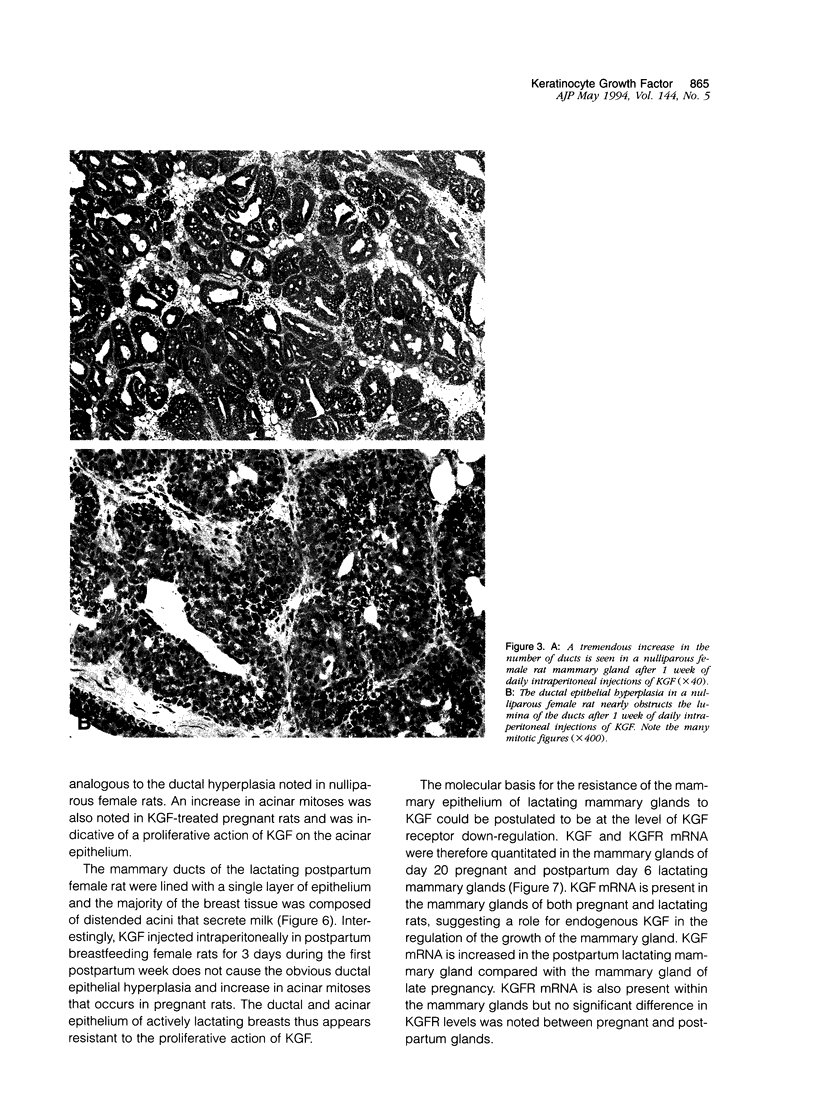
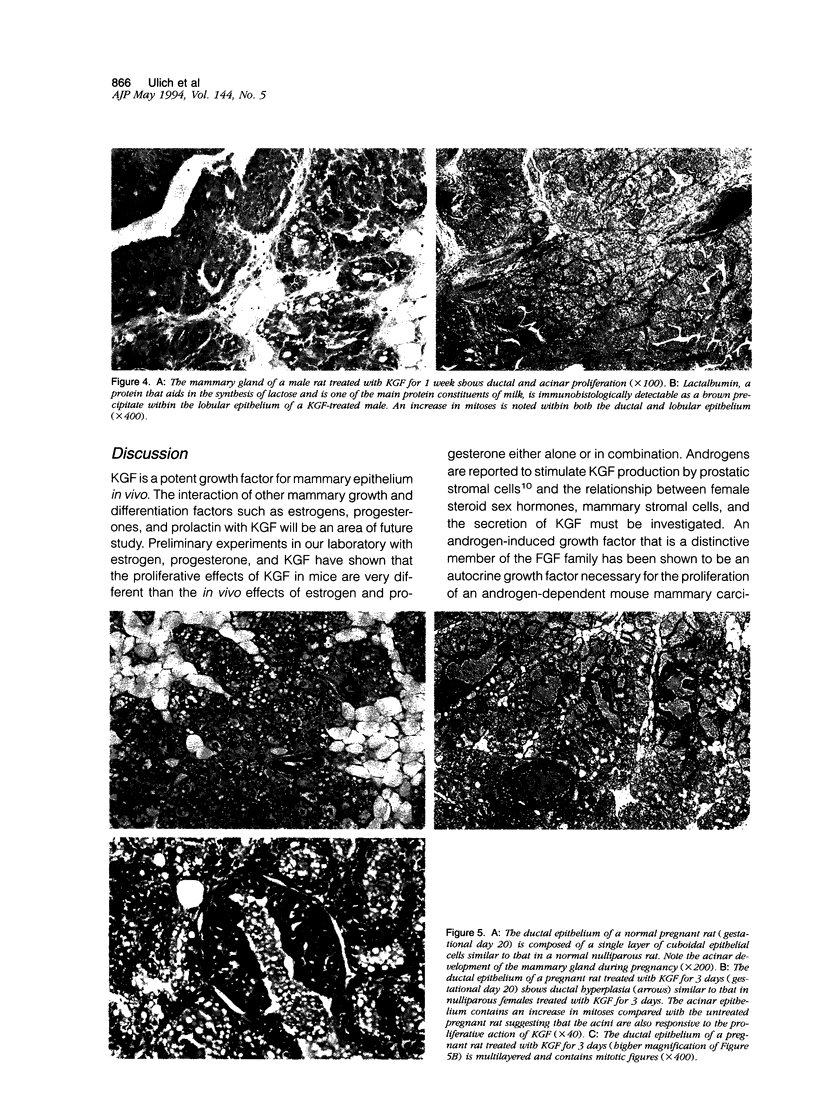
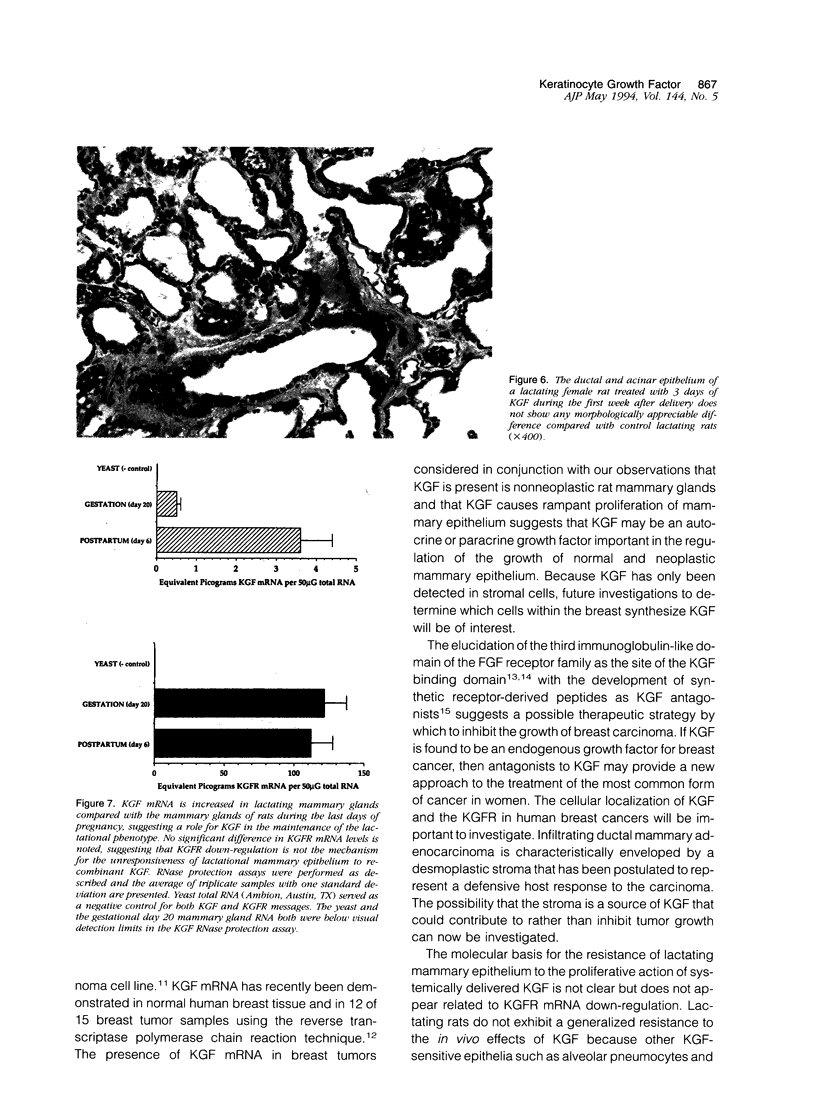
Keratinocyte growth factor (KGF) is a member of the fibroblast growth factor (FGF) family. KGF is secreted by stromal cells and affects epithelial but not mesenchymal cell proliferation. KGF injected intravenously was found to cause dramatic proliferation of mammary epithelium in the mammary glands of rats. KGF causes ductal neogenesis and intraductal epithelial hyperplasia but not lobular differentiation in nulliparous female rats. KGF causes ductal and lobular epithelial hyperplasia in male rats. KGF causes proliferation of ductal and acinar cells in the mammary glands of pregnant rats. On the other hand, the ductal epithelium of lactating postpartum rats is resistant to the proliferative action of KGF. The mammary glands of lactating rats did not express less KGF receptor mRNA than the glands of pregnant rats, suggesting that the resistance of the ductal epithelium to KGF during lactation is not related to KGF receptor mRNA down-regulation. The mammary glands of both pregnant and postpartum lactating rats express KGF mRNA with more KGF present in the glands of lactating rats. In conclusion, the KGF and KGF receptor genes are expressed in rat mammary glands and recombinant KGF is a potent growth factor for mammary epithelium.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bottaro D. P., Fortney E., Rubin J. S., Aaronson S. A. A keratinocyte growth factor receptor-derived peptide antagonist identifies part of the ligand binding site. J Biol Chem. 1993 May 5;268(13):9180–9183. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dell K. R., Williams L. T. A novel form of fibroblast growth factor receptor 2. Alternative splicing of the third immunoglobulin-like domain confers ligand binding specificity. J Biol Chem. 1992 Oct 15;267(29):21225–21229. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finch P. W., Rubin J. S., Miki T., Ron D., Aaronson S. A. Human KGF is FGF-related with properties of a paracrine effector of epithelial cell growth. Science. 1989 Aug 18;245(4919):752–755. doi: 10.1126/science.2475908. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koos R. D., Banks P. K., Inkster S. E., Yue W., Brodie A. M. Detection of aromatase and keratinocyte growth factor expression in breast tumors using reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 1993 Apr;45(4):217–225. doi: 10.1016/0960-0760(93)90335-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miki T., Bottaro D. P., Fleming T. P., Smith C. L., Burgess W. H., Chan A. M., Aaronson S. A. Determination of ligand-binding specificity by alternative splicing: two distinct growth factor receptors encoded by a single gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jan 1;89(1):246–250. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.1.246. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miki T., Fleming T. P., Bottaro D. P., Rubin J. S., Ron D., Aaronson S. A. Expression cDNA cloning of the KGF receptor by creation of a transforming autocrine loop. Science. 1991 Jan 4;251(4989):72–75. doi: 10.1126/science.1846048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miki T., Fleming T. P., Bottaro D. P., Rubin J. S., Ron D., Aaronson S. A. Expression cDNA cloning of the KGF receptor by creation of a transforming autocrine loop. Science. 1991 Jan 4;251(4989):72–75. doi: 10.1126/science.1846048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin J. S., Osada H., Finch P. W., Taylor W. G., Rudikoff S., Aaronson S. A. Purification and characterization of a newly identified growth factor specific for epithelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Feb;86(3):802–806. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.3.802. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka A., Miyamoto K., Minamino N., Takeda M., Sato B., Matsuo H., Matsumoto K. Cloning and characterization of an androgen-induced growth factor essential for the androgen-dependent growth of mouse mammary carcinoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Oct 1;89(19):8928–8932. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.19.8928. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yan G., Fukabori Y., Nikolaropoulos S., Wang F., McKeehan W. L. Heparin-binding keratinocyte growth factor is a candidate stromal-to-epithelial-cell andromedin. Mol Endocrinol. 1992 Dec;6(12):2123–2128. doi: 10.1210/mend.6.12.1491693. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yayon A., Zimmer Y., Shen G. H., Avivi A., Yarden Y., Givol D. A confined variable region confers ligand specificity on fibroblast growth factor receptors: implications for the origin of the immunoglobulin fold. EMBO J. 1992 May;11(5):1885–1890. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05240.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]