Abstract
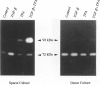
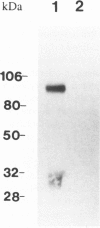
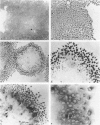
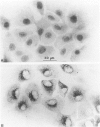
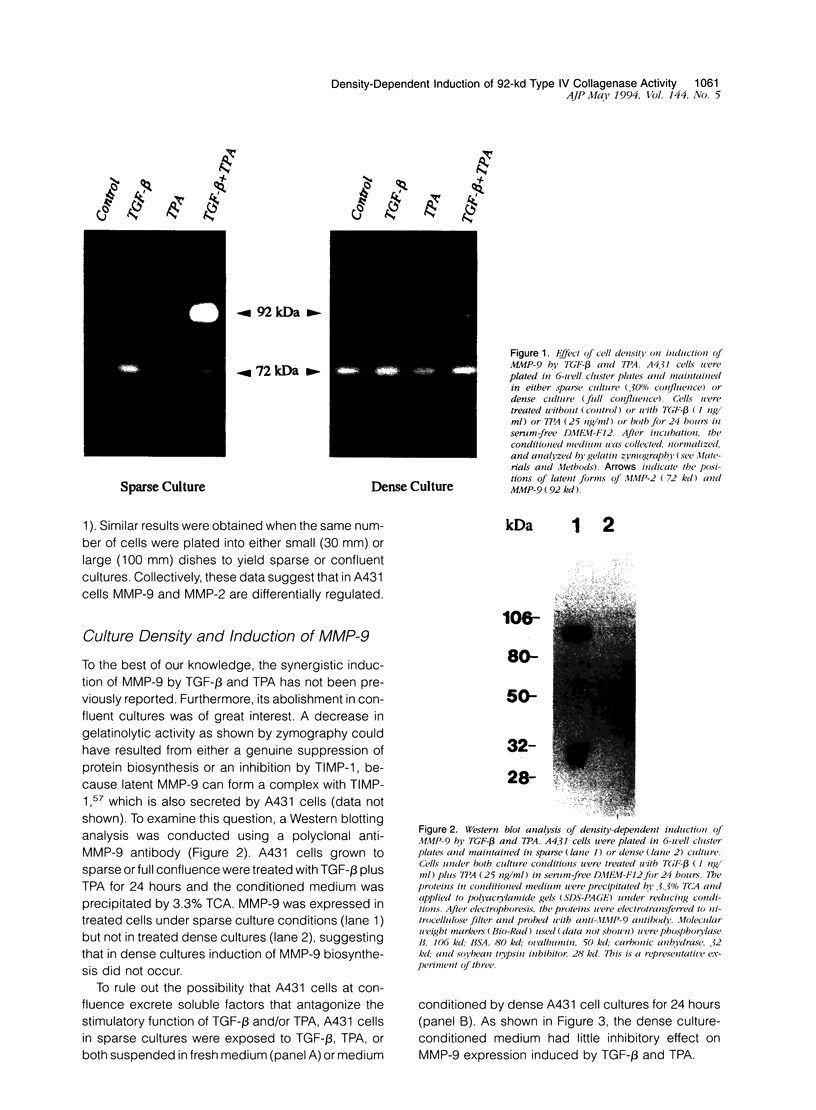
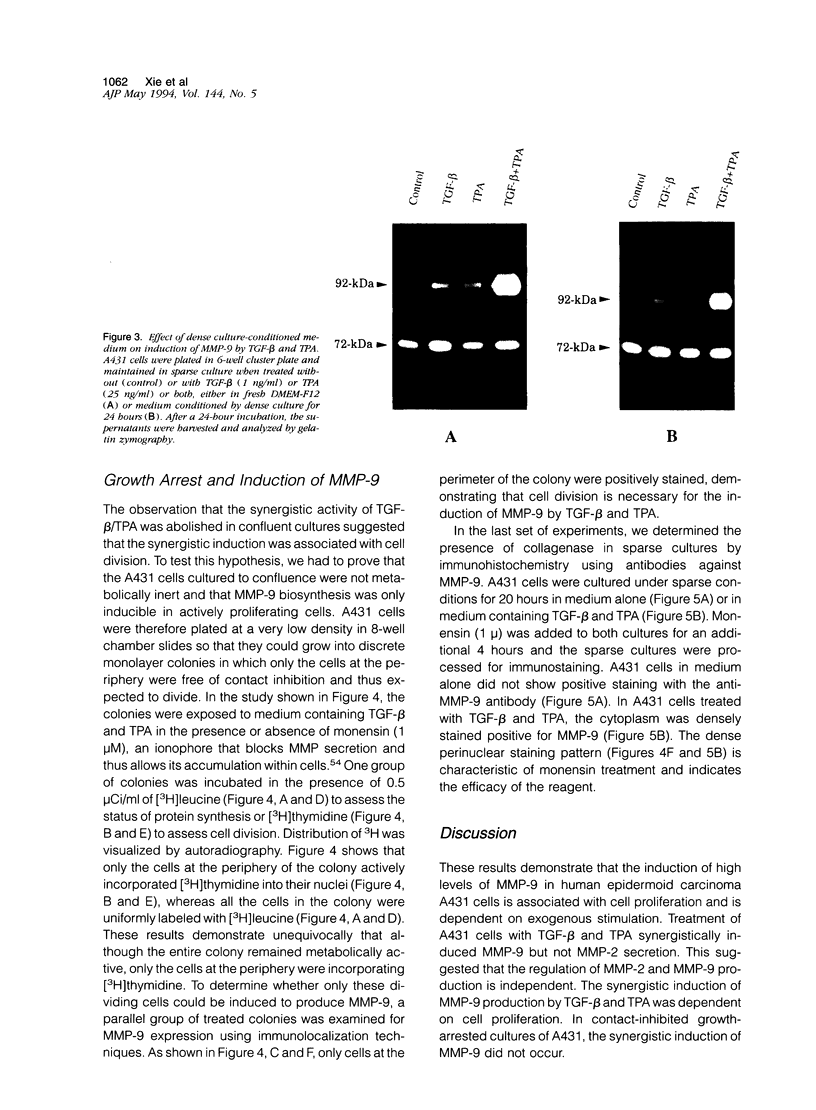
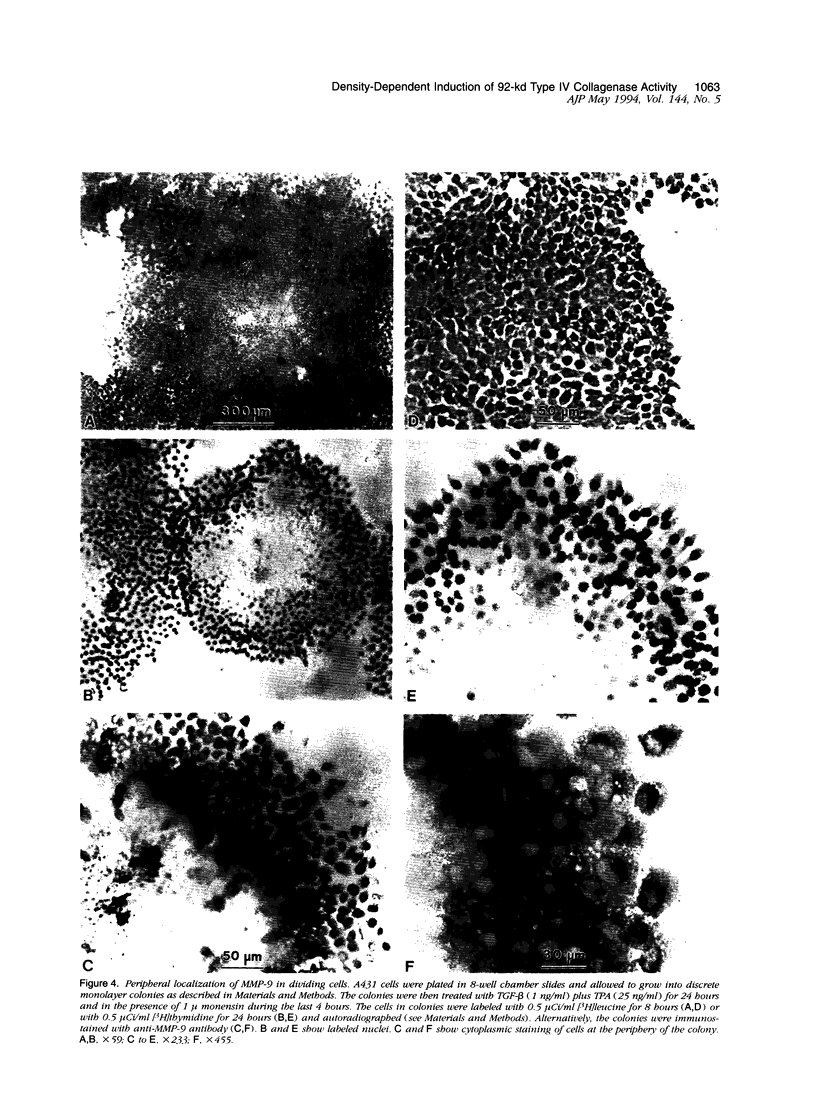
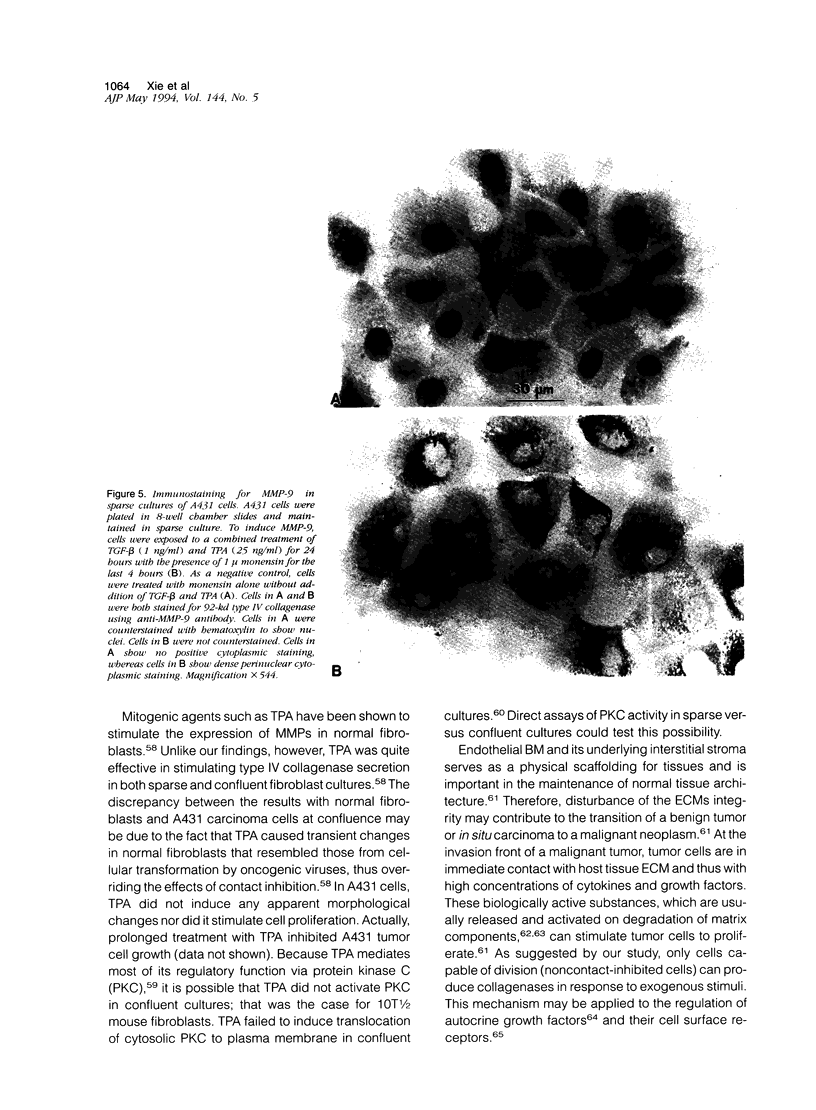
We examined the in vitro regulation of the production of two type IV collagenases, MMP-2 and MMP-9, by A431 human epidermoid carcinoma cells. The A431 cells were cultured under sparse or confluent conditions. The addition of transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-beta) or phorbolester-TPA to sparse cultures induced low levels of MMP-9 secretion, whereas in confluent cultures only TGF-beta produced this effect. Neither treatment altered the level of constitutive secretion of MMP-2. Treatment of sparse, actively growing cultures but not confluent stationary cultures with both TGF-beta and TPA produced synergistic induction of MMP-9 but did not affect MMP-2. A431 cells were grown as discrete large monolayer colonies. Radiolabeling with [3H]leucine or [3H]thymidine followed by autoradiography revealed that all the A431 cells in the colonies were metabolically active and only those on the periphery were dividing. Only these dividing A431 cells stained positive by anti-MMP-9 antibodies. Our results demonstrate that the synergistic induction of MMP-9 secretion in A431 cells occurs subsequent to stimulation by external signals in only noncontact-inhibited dividing tumor cells. These regulatory mechanisms may account for the in vivo finding that many proteinases are localized at the invasion front of a neoplasm where tumor cells are dividing and accessible to various environmental signals.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albini A., Melchiori A., Santi L., Liotta L. A., Brown P. D., Stetler-Stevenson W. G. Tumor cell invasion inhibited by TIMP-2. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1991 Jun 5;83(11):775–779. doi: 10.1093/jnci/83.11.775. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andres J. L., Stanley K., Cheifetz S., Massagué J. Membrane-anchored and soluble forms of betaglycan, a polymorphic proteoglycan that binds transforming growth factor-beta. J Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;109(6 Pt 1):3137–3145. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.6.3137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baird A., Ling N. Fibroblast growth factors are present in the extracellular matrix produced by endothelial cells in vitro: implications for a role of heparinase-like enzymes in the neovascular response. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Jan 30;142(2):428–435. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)90292-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballin M., Gomez D. E., Sinha C. C., Thorgeirsson U. P. Ras oncogene mediated induction of a 92 kDa metalloproteinase; strong correlation with the malignant phenotype. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Aug 15;154(3):832–838. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(88)90215-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barsky S. H., Grossman D. A., Bhuta S. Desmoplastic basal cell carcinomas possess unique basement membrane-degrading properties. J Invest Dermatol. 1987 Mar;88(3):324–329. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12466209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barsky S. H., Siegal G. P., Jannotta F., Liotta L. A. Loss of basement membrane components by invasive tumors but not by their benign counterparts. Lab Invest. 1983 Aug;49(2):140–147. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barsky S. H., Togo S., Garbisa S., Liotta L. A. Type IV collagenase immunoreactivity in invasive breast carcinoma. Lancet. 1983 Feb 5;1(8319):296–297. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)91708-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Basset P., Bellocq J. P., Wolf C., Stoll I., Hutin P., Limacher J. M., Podhajcer O. L., Chenard M. P., Rio M. C., Chambon P. A novel metalloproteinase gene specifically expressed in stromal cells of breast carcinomas. Nature. 1990 Dec 20;348(6303):699–704. doi: 10.1038/348699a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernhard E. J., Muschel R. J., Hughes E. N. Mr 92,000 gelatinase release correlates with the metastatic phenotype in transformed rat embryo cells. Cancer Res. 1990 Jul 1;50(13):3872–3877. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birkedal-Hansen H., Taylor R. E. Detergent-activation of latent collagenase and resolution of its component molecules. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Aug 31;107(4):1173–1178. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(82)80120-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blake M. S., Johnston K. H., Russell-Jones G. J., Gotschlich E. C. A rapid, sensitive method for detection of alkaline phosphatase-conjugated anti-antibody on Western blots. Anal Biochem. 1984 Jan;136(1):175–179. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90320-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnette W. N. "Western blotting": electrophoretic transfer of proteins from sodium dodecyl sulfate--polyacrylamide gels to unmodified nitrocellulose and radiographic detection with antibody and radioiodinated protein A. Anal Biochem. 1981 Apr;112(2):195–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90281-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Childers J. W., Hernandez A. D., Kim J. H., Stricklin G. P. Immunolocalization of collagenase inhibitor in normal skin and basal cell carcinoma. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1987 Dec;17(6):1025–1032. doi: 10.1016/s0190-9622(87)70293-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collier I. E., Wilhelm S. M., Eisen A. Z., Marmer B. L., Grant G. A., Seltzer J. L., Kronberger A., He C. S., Bauer E. A., Goldberg G. I. H-ras oncogene-transformed human bronchial epithelial cells (TBE-1) secrete a single metalloprotease capable of degrading basement membrane collagen. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 15;263(14):6579–6587. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Errico A., Garbisa S., Liotta L. A., Castronovo V., Stetler-Stevenson W. G., Grigioni W. F. Augmentation of type IV collagenase, laminin receptor, and Ki67 proliferation antigen associated with human colon, gastric, and breast carcinoma progression. Mod Pathol. 1991 Mar;4(2):239–246. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Docherty A. J., Lyons A., Smith B. J., Wright E. M., Stephens P. E., Harris T. J., Murphy G., Reynolds J. J. Sequence of human tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases and its identity to erythroid-potentiating activity. Nature. 1985 Nov 7;318(6041):66–69. doi: 10.1038/318066a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fessler L. I., Duncan K. G., Fessler J. H., Salo T., Tryggvason K. Characterization of the procollagen IV cleavage products produced by a specific tumor collagenase. J Biol Chem. 1984 Aug 10;259(15):9783–9789. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fidler I. J. Critical factors in the biology of human cancer metastasis: twenty-eighth G.H.A. Clowes memorial award lecture. Cancer Res. 1990 Oct 1;50(19):6130–6138. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garbisa S., Pozzatti R., Muschel R. J., Saffiotti U., Ballin M., Goldfarb R. H., Khoury G., Liotta L. A. Secretion of type IV collagenolytic protease and metastatic phenotype: induction by transfection with c-Ha-ras but not c-Ha-ras plus Ad2-E1a. Cancer Res. 1987 Mar 15;47(6):1523–1528. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giard D. J., Aaronson S. A., Todaro G. J., Arnstein P., Kersey J. H., Dosik H., Parks W. P. In vitro cultivation of human tumors: establishment of cell lines derived from a series of solid tumors. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1973 Nov;51(5):1417–1423. doi: 10.1093/jnci/51.5.1417. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg G. I., Marmer B. L., Grant G. A., Eisen A. Z., Wilhelm S., He C. S. Human 72-kilodalton type IV collagenase forms a complex with a tissue inhibitor of metalloproteases designated TIMP-2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(21):8207–8211. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.21.8207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg G. I., Wilhelm S. M., Kronberger A., Bauer E. A., Grant G. A., Eisen A. Z. Human fibroblast collagenase. Complete primary structure and homology to an oncogene transformation-induced rat protein. J Biol Chem. 1986 May 15;261(14):6600–6605. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graf M., Baici A., Sträuli P. Histochemical localization of cathepsin B at the invasion front of the rabbit V2 carcinoma. Lab Invest. 1981 Dec;45(6):587–596. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HE C. S., Wilhelm S. M., Pentland A. P., Marmer B. L., Grant G. A., Eisen A. Z., Goldberg G. I. Tissue cooperation in a proteolytic cascade activating human interstitial collagenase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(8):2632–2636. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.8.2632. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hernandez A. D., Hibbs M. S., Postlethwaite A. E. Establishment of basal cell carcinoma in culture: evidence for a basal cell carcinoma-derived factor(s) which stimulates fibroblasts to proliferate and release collagenase. J Invest Dermatol. 1985 Nov;85(5):470–475. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12277201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hewitt R. E., Leach I. H., Powe D. G., Clark I. M., Cawston T. E., Turner D. R. Distribution of collagenase and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases (TIMP) in colorectal tumours. Int J Cancer. 1991 Nov 11;49(5):666–672. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910490507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hibbs M. S., Hasty K. A., Seyer J. M., Kang A. H., Mainardi C. L. Biochemical and immunological characterization of the secreted forms of human neutrophil gelatinase. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 25;260(4):2493–2500. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson-Wint B. Regulation of stromal cell collagenase production in adult rabbit cornea: in vitro stimulation and inhibition by epithelial cell products. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5331–5335. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karelina T. V., Hruza G. J., Goldberg G. I., Eisen A. Z. Localization of 92-kDa type IV collagenase in human skin tumors: comparison with normal human fetal and adult skin. J Invest Dermatol. 1993 Feb;100(2):159–165. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12462791. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khokha R., Waterhouse P., Yagel S., Lala P. K., Overall C. M., Norton G., Denhardt D. T. Antisense RNA-induced reduction in murine TIMP levels confers oncogenicity on Swiss 3T3 cells. Science. 1989 Feb 17;243(4893):947–950. doi: 10.1126/science.2465572. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy A. T., Cioce V., Sobel M. E., Garbisa S., Grigioni W. F., Liotta L. A., Stetler-Stevenson W. G. Increased expression of the Mr 72,000 type IV collagenase in human colonic adenocarcinoma. Cancer Res. 1991 Jan 1;51(1):439–444. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liotta L. A., Rao C. N., Barsky S. H. Tumor invasion and the extracellular matrix. Lab Invest. 1983 Dec;49(6):636–649. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liotta L. A., Rao C. N., Wewer U. M. Biochemical interactions of tumor cells with the basement membrane. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:1037–1057. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.005133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liotta L. A., Tryggvason K., Garbisa S., Hart I., Foltz C. M., Shafie S. Metastatic potential correlates with enzymatic degradation of basement membrane collagen. Nature. 1980 Mar 6;284(5751):67–68. doi: 10.1038/284067a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matrisian L. M. The matrix-degrading metalloproteinases. Bioessays. 1992 Jul;14(7):455–463. doi: 10.1002/bies.950140705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miłoszewska J., Trawicki W., Janik P., Moraczewski J., Przybyszewska M., Szaniawska B. Protein kinase C translocation in relation to proliferative state of C3H 10T1/2 cells. FEBS Lett. 1986 Oct 6;206(2):283–286. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80997-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monteagudo C., Merino M. J., San-Juan J., Liotta L. A., Stetler-Stevenson W. G. Immunohistochemical distribution of type IV collagenase in normal, benign, and malignant breast tissue. Am J Pathol. 1990 Mar;136(3):585–592. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulder K. M. Differential regulation of c-myc and transforming growth factor-alpha messenger RNA expression in poorly differentiated and well-differentiated colon carcinoma cells during the establishment of a quiescent state. Cancer Res. 1991 May 1;51(9):2256–2262. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy G., Cockett M. I., Stephens P. E., Smith B. J., Docherty A. J. Stromelysin is an activator of procollagenase. A study with natural and recombinant enzymes. Biochem J. 1987 Nov 15;248(1):265–268. doi: 10.1042/bj2480265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy G., Ward R., Hembry R. M., Reynolds J. J., Kühn K., Tryggvason K. Characterization of gelatinase from pig polymorphonuclear leucocytes. A metalloproteinase resembling tumour type IV collagenase. Biochem J. 1989 Mar 1;258(2):463–472. doi: 10.1042/bj2580463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagase H., Brinckerhoff C. E., Vater C. A., Harris E. D., Jr Biosynthesis and secretion of procollagenase by rabbit synovial fibroblasts. Inhibition of procollagenase secretion by monensin and evidence for glycosylation of procollagenase. Biochem J. 1983 Aug 15;214(2):281–288. doi: 10.1042/bj2140281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakajima M., Morikawa K., Fabra A., Bucana C. D., Fidler I. J. Influence of organ environment on extracellular matrix degradative activity and metastasis of human colon carcinoma cells. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1990 Dec 19;82(24):1890–1898. doi: 10.1093/jnci/82.24.1890. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakajima M., Welch D. R., Belloni P. N., Nicolson G. L. Degradation of basement membrane type IV collagen and lung subendothelial matrix by rat mammary adenocarcinoma cell clones of differing metastatic potentials. Cancer Res. 1987 Sep 15;47(18):4869–4876. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brian C. A., Ward N. E. Biology of the protein kinase C family. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 1989 Dec;8(3):199–214. doi: 10.1007/BF00047337. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogata Y., Enghild J. J., Nagase H. Matrix metalloproteinase 3 (stromelysin) activates the precursor for the human matrix metalloproteinase 9. J Biol Chem. 1992 Feb 25;267(6):3581–3584. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okada Y., Morodomi T., Enghild J. J., Suzuki K., Yasui A., Nakanishi I., Salvesen G., Nagase H. Matrix metalloproteinase 2 from human rheumatoid synovial fibroblasts. Purification and activation of the precursor and enzymic properties. Eur J Biochem. 1990 Dec 27;194(3):721–730. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb19462.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okada Y., Nagase H., Harris E. D., Jr A metalloproteinase from human rheumatoid synovial fibroblasts that digests connective tissue matrix components. Purification and characterization. J Biol Chem. 1986 Oct 25;261(30):14245–14255. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Overall C. M., Wrana J. L., Sodek J. Transcriptional and post-transcriptional regulation of 72-kDa gelatinase/type IV collagenase by transforming growth factor-beta 1 in human fibroblasts. Comparisons with collagenase and tissue inhibitor of matrix metalloproteinase gene expression. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jul 25;266(21):14064–14071. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poulsom R., Pignatelli M., Stetler-Stevenson W. G., Liotta L. A., Wright P. A., Jeffery R. E., Longcroft J. M., Rogers L., Stamp G. W. Stromal expression of 72 kda type IV collagenase (MMP-2) and TIMP-2 mRNAs in colorectal neoplasia. Am J Pathol. 1992 Aug;141(2):389–396. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pyke C., Ralfkiaer E., Huhtala P., Hurskainen T., Danø K., Tryggvason K. Localization of messenger RNA for Mr 72,000 and 92,000 type IV collagenases in human skin cancers by in situ hybridization. Cancer Res. 1992 Mar 1;52(5):1336–1341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pyke C., Ralfkiaer E., Tryggvason K., Danø K. Messenger RNA for two type IV collagenases is located in stromal cells in human colon cancer. Am J Pathol. 1993 Feb;142(2):359–365. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rizzino A., Kazakoff P., Nebelsick J. Density-induced down regulation of epidermal growth factor receptors. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol. 1990 May;26(5):537–542. doi: 10.1007/BF02624098. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salo T., Lyons J. G., Rahemtulla F., Birkedal-Hansen H., Larjava H. Transforming growth factor-beta 1 up-regulates type IV collagenase expression in cultured human keratinocytes. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jun 25;266(18):11436–11441. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salo T., Turpeenniemi-Hujanen T., Tryggvason K. Tumor-promoting phorbol esters and cell proliferation stimulate secretion of basement membrane (type IV) collagen-degrading metalloproteinase by human fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jul 15;260(14):8526–8531. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato H., Kida Y., Mai M., Endo Y., Sasaki T., Tanaka J., Seiki M. Expression of genes encoding type IV collagen-degrading metalloproteinases and tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases in various human tumor cells. Oncogene. 1992 Jan;7(1):77–83. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz R. M., Silberman S., Persky B., Bajkowski A. S., Carmichael D. F. Inhibition by human recombinant tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases of human amnion invasion and lung colonization by murine B16-F10 melanoma cells. Cancer Res. 1988 Oct 1;48(19):5539–5545. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skriver L., Larsson L. I., Kielberg V., Nielsen L. S., Andresen P. B., Kristensen P., Danø K. Immunocytochemical localization of urokinase-type plasminogen activator in Lewis lung carcinoma. J Cell Biol. 1984 Aug;99(2):753–757. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.2.753. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stearns M. E., Wang M. Type IV collagenase (M(r) 72,000) expression in human prostate: benign and malignant tissue. Cancer Res. 1993 Feb 15;53(4):878–883. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stetler-Stevenson W. G., Krutzsch H. C., Liotta L. A. Tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase (TIMP-2). A new member of the metalloproteinase inhibitor family. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 15;264(29):17374–17378. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stetler-Stevenson W. G., Krutzsch H. C., Wacher M. P., Margulies I. M., Liotta L. A. The activation of human type IV collagenase proenzyme. Sequence identification of the major conversion product following organomercurial activation. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 25;264(3):1353–1356. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tryggvason K., Höyhtyä M., Pyke C. Type IV collagenases in invasive tumors. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 1993;24(3):209–218. doi: 10.1007/BF01833261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turpeenniemi-Hujanen T., Thorgeirsson U. P., Hart I. R., Grant S. S., Liotta L. A. Expression of collagenase IV (basement membrane collagenase) activity in murine tumor cell hybrids that differ in metastatic potential. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1985 Jul;75(1):99–103. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ura H., Bonfil R. D., Reich R., Reddel R., Pfeifer A., Harris C. C., Klein-Szanto A. J. Expression of type IV collagenase and procollagen genes and its correlation with the tumorigenic, invasive, and metastatic abilities of oncogene-transformed human bronchial epithelial cells. Cancer Res. 1989 Aug 15;49(16):4615–4621. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilhelm S. M., Collier I. E., Marmer B. L., Eisen A. Z., Grant G. A., Goldberg G. I. SV40-transformed human lung fibroblasts secrete a 92-kDa type IV collagenase which is identical to that secreted by normal human macrophages. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 15;264(29):17213–17221. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams G. M., Stromberg K., Krodes R. Cytochemical and ultrastructural alterations associated with confluent growth in cell cultures of epithelial-like cells from rat liver. Lab Invest. 1973 Sep;29(3):293–303. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woolley D. E. Collagenolytic mechanisms in tumor cell invasion. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 1984;3(4):361–372. doi: 10.1007/BF00051460. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamagata S., Tanaka R., Ito Y., Shimizu S. Gelatinases of murine metastatic tumor cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Jan 16;158(1):228–234. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(89)80202-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]