Abstract
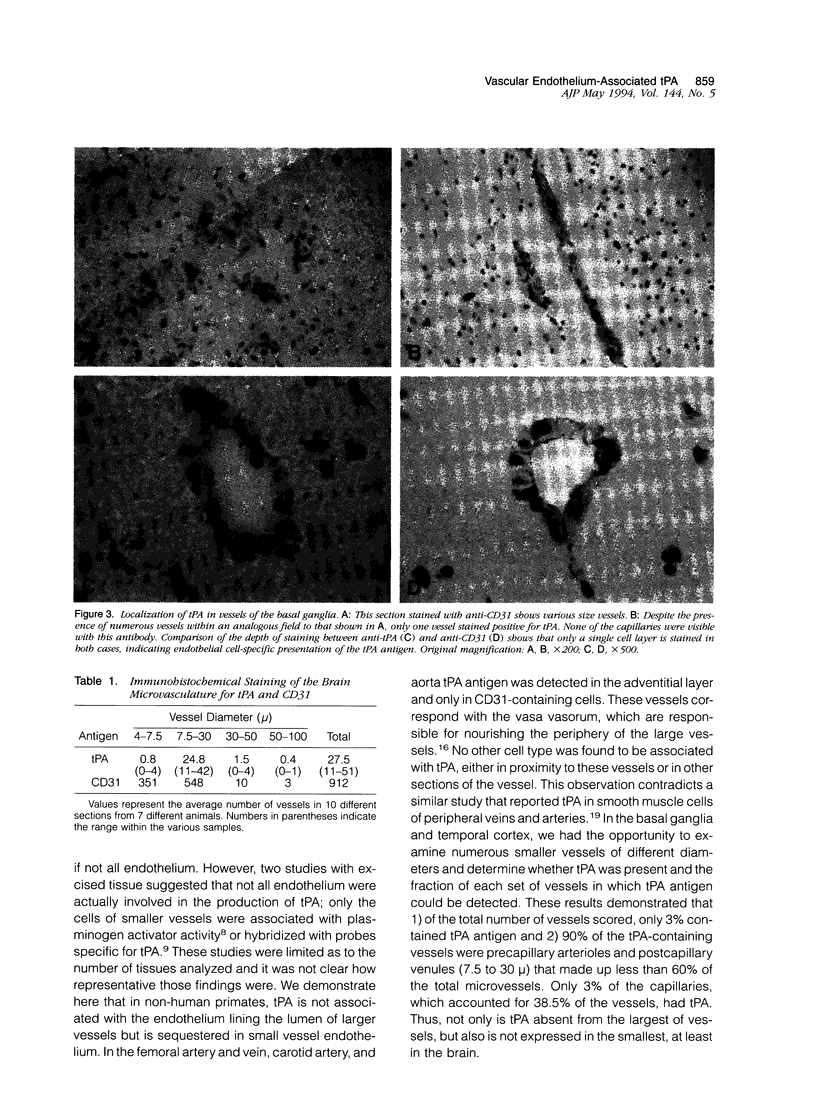
The immunolocalization of tissue plasminogen activator (tPA) was assessed in vessels of various sizes from baboons. Femoral artery and vein, carotid artery, aorta, and sections from basal ganglia and cerebral cortex were stained for tPA and CD31, an endothelial cell-specific surface antigen. In each case, the endothelium of the large vessel stained positively for anti-CD31 but not for tPA. However, vascular structures in the adventitia corresponding to the vasa vasorum were found to be associated with tPA antigen. In situ hybridization of femoral artery with 35S-labeled cRNA probes detected tPA mRNA in the vasa vasorum but not the large vessel endothelium. Analysis of the microvasculature of the basal ganglia and cerebral cortex showed limited immunohistochemical staining for tPA; only 3% of the vessels measuring 4 to 100 mu were positive. Even so, tPA was mostly distributed within a narrow range of vessel size; 90% of the positive vessels were classified as precapillary arterioles and postcapillary venules (7.5 to 30.0 mu), whereas only 3% of the capillaries were positive, despite accounting for 40% of all vessels. Thus, tPA-containing endothelium are distributed mainly in smaller vessels, excluding the capillaries.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albelda S. M., Muller W. A., Buck C. A., Newman P. J. Molecular and cellular properties of PECAM-1 (endoCAM/CD31): a novel vascular cell-cell adhesion molecule. J Cell Biol. 1991 Sep;114(5):1059–1068. doi: 10.1083/jcb.114.5.1059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collen D. On the regulation and control of fibrinolysis. Edward Kowalski Memorial Lecture. Thromb Haemost. 1980 Jun 18;43(2):77–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond S. L., Sharefkin J. B., Dieffenbach C., Frasier-Scott K., McIntire L. V., Eskin S. G. Tissue plasminogen activator messenger RNA levels increase in cultured human endothelial cells exposed to laminar shear stress. J Cell Physiol. 1990 May;143(2):364–371. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041430222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iba T., Shin T., Sonoda T., Rosales O., Sumpio B. E. Stimulation of endothelial secretion of tissue-type plasminogen activator by repetitive stretch. J Surg Res. 1991 May;50(5):457–460. doi: 10.1016/0022-4804(91)90024-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keeton M., Eguchi Y., Sawdey M., Ahn C., Loskutoff D. J. Cellular localization of type 1 plasminogen activator inhibitor messenger RNA and protein in murine renal tissue. Am J Pathol. 1993 Jan;142(1):59–70. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsson A., Astedt B. Immunohistochemical localisation of tissue plasminogen activator and urokinase in the vessel wall. J Clin Pathol. 1985 Feb;38(2):140–145. doi: 10.1136/jcp.38.2.140. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin E. G., Santell L., Saljooque F. Hyperosmotic stress stimulates tissue plasminogen activator expression by a PKC-independent pathway. Am J Physiol. 1993 Aug;265(2 Pt 1):C387–C396. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1993.265.2.C387. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mannucci P. M., Aberg M., Nilsson I. M., Robertson B. Mechanism of plasminogen activator and factor VIII increase after vasoactive drugs. Br J Haematol. 1975 May;30(1):81–93. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1975.tb00521.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pandolfi M., Robertson B., Isacson S., Nilsson I. M. Fibrinolytic activity of human veins in arms and legs. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1968 Nov 15;20(1):247–256. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rijken D. C., Wijngaards G., Welbergen J. Immunological characterization of plasminogen activator activities in human tissues and body fluids. J Lab Clin Med. 1981 Apr;97(4):477–486. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rijken D. C., Wijngaards G., Welbergen J. Relationship between tissue plasminogen activator and the activators in blood and vascular wall. Thromb Res. 1980 Jun 15;18(6):815–830. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(80)90204-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHERRY S., LINDEMEYER R. I., FLETCHER A. P., ALKJAERSIG N. Studies on enhanced fibrinolytic activity in man. J Clin Invest. 1959 May;38(5):810–822. doi: 10.1172/JCI103863. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TODD A. S. The histological localisation of fibrinolysin activator. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1959 Jul;78:281–283. doi: 10.1002/path.1700780131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- del Zoppo G. J., Schmid-Schönbein G. W., Mori E., Copeland B. R., Chang C. M. Polymorphonuclear leukocytes occlude capillaries following middle cerebral artery occlusion and reperfusion in baboons. Stroke. 1991 Oct;22(10):1276–1283. doi: 10.1161/01.str.22.10.1276. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- del Zoppo G. J., Yu J. Q., Copeland B. R., Thomas W. S., Schneiderman J., Morrissey J. H. Tissue factor localization in non-human primate cerebral tissue. Thromb Haemost. 1992 Dec 7;68(6):642–647. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Hinsbergh V. W., Kooistra T., Emeis J. J., Koolwijk P. Regulation of plasminogen activator production by endothelial cells: role in fibrinolysis and local proteolysis. Int J Radiat Biol. 1991 Jul-Aug;60(1-2):261–272. doi: 10.1080/09553009114551981. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Mourik J. A., Leeksma O. C., Reinders J. H., de Groot P. G., Zandbergen-Spaargaren J. Vascular endothelial cells synthesize a plasma membrane protein indistinguishable from the platelet membrane glycoprotein IIa. J Biol Chem. 1985 Sep 15;260(20):11300–11306. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]