Abstract
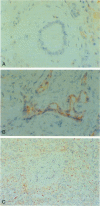
The expression of the inflammatory adhesion molecules intercellular adhesion molecule-1, vascular cell adhesion molecule-1, and endothelial leukocyte adhesion molecule-1, was studied in six infants with biliary atresia using an immunoperoxidase technique on frozen sections. Controls consisted of five patients with various conditions including total parenteral nutrition-induced cholestasis, choledochal cyst, viral hepatitis, metastatic carcinoma, and thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. None of the patients were in liver failure. Bile ducts from the control subjects did not express any of the inflammatory adhesion molecules on ductal epithelium. In marked contrast, all of the biliary atresia specimens demonstrated strong intercellular adhesion molecule-1 expression and occasional vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 staining on epithelial cell membranes of both intra- and extrahepatic ductal structures. Hepatocytes and sinusoidal lining cells including Kupffer cells showed a pattern of intense intercellular adhesion molecule-1 and vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 expression in all specimens with active inflammation that could not differentiate the biliary atresia cases from the control group. Lymphocyte function-associated antigen-1 intensely stained the inflammatory cell infiltrate in the biliary atresia and inflamed control specimens. The strong expression of intercellular adhesion molecule-1 on biliary ductal epithelium in patients with biliary atresia suggests a potential role for this adhesion molecule in the pathogenesis of this devastating neonatal hepatic disorder.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams D. H., Hubscher S. G., Shaw J., Johnson G. D., Babbs C., Rothlein R., Neuberger J. M. Increased expression of intercellular adhesion molecule 1 on bile ducts in primary biliary cirrhosis and primary sclerosing cholangitis. Hepatology. 1991 Sep;14(3):426–431. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adams D. H., Hubscher S. G., Shaw J., Rothlein R., Neuberger J. M. Intercellular adhesion molecule 1 on liver allografts during rejection. Lancet. 1989 Nov 11;2(8672):1122–1125. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)91489-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broomé U., Hultcrantz R., Scheynius A. Lack of concomitant expression of ICAM-1 and HLA-DR on bile duct cells from patients with primary sclerosing cholangitis and primary biliary cirrhosis. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1993 Feb;28(2):126–130. doi: 10.3109/00365529309096058. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morecki R., Glaser J. H., Cho S., Balistreri W. F., Horwitz M. S. Biliary atresia and reovirus type 3 infection. N Engl J Med. 1984 Jun 14;310(24):1610–1610. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198406143102418. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmeling D. J., Oldham K. T., Guice K. S., Kunkel R. G., Johnson K. J. Experimental obliterative cholangitis. A model for the study of biliary atresia. Ann Surg. 1991 Apr;213(4):350–355. doi: 10.1097/00000658-199104000-00010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Springer T. A. Adhesion receptors of the immune system. Nature. 1990 Aug 2;346(6283):425–434. doi: 10.1038/346425a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volpes R., Van Den Oord J. J., Desmet V. J. Vascular adhesion molecules in acute and chronic liver inflammation. Hepatology. 1992 Feb;15(2):269–275. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840150216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volpes R., van den Oord J. J., Desmet V. J. Hepatic expression of intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1) in viral hepatitis B. Hepatology. 1990 Jul;12(1):148–154. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840120123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volpes R., van den Oord J. J., Desmet V. J. Immunohistochemical study of adhesion molecules in liver inflammation. Hepatology. 1990 Jul;12(1):59–65. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840120110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wee S. L., Cosimi A. B., Preffer F. I., Rothlein R., Faanes R., Conti D., Colvin R. B. Functional consequences of anti-ICAM-1 (CD54) in cynomolgus monkeys with renal allografts. Transplant Proc. 1991 Feb;23(1 Pt 1):279–280. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]