Abstract
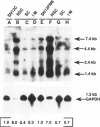
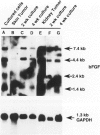
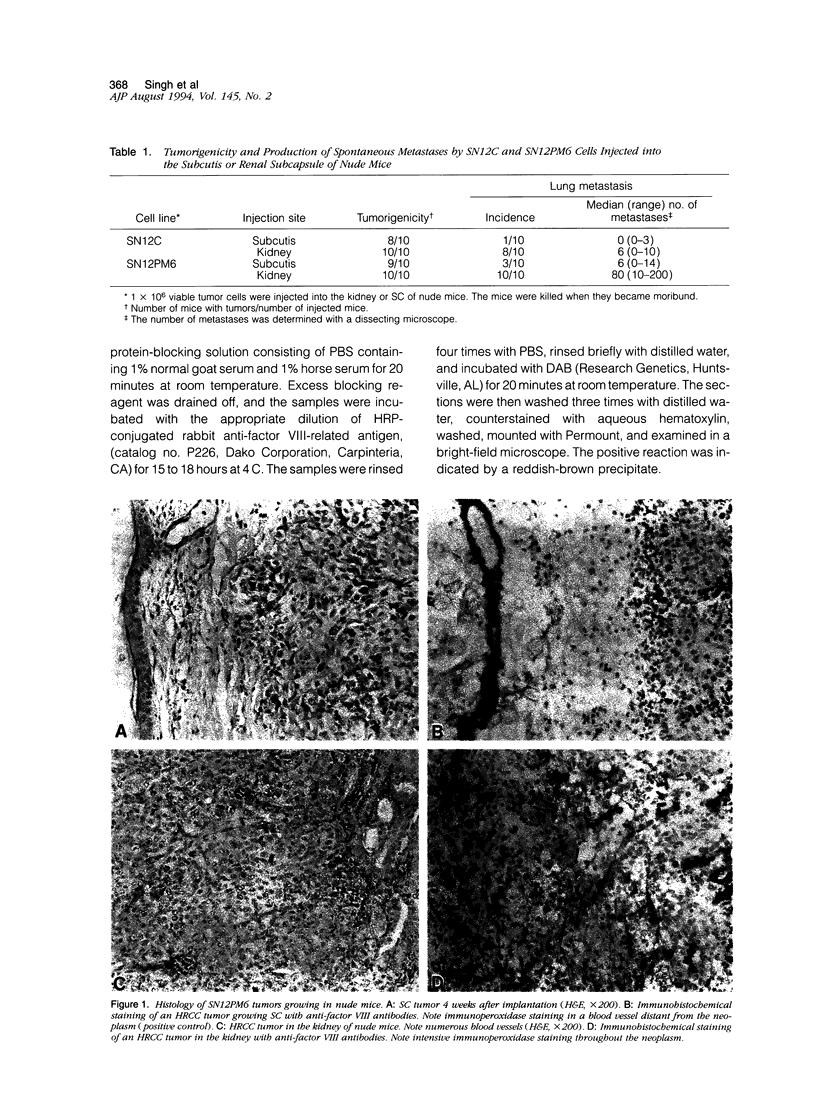
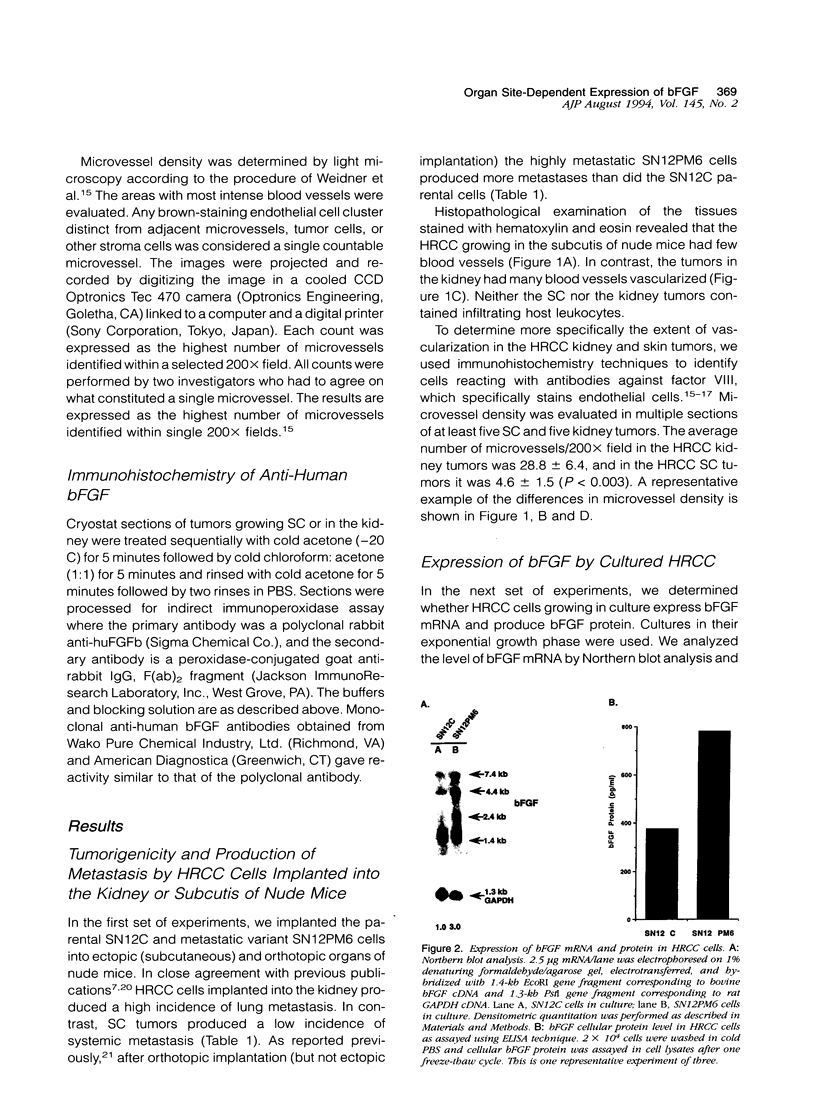
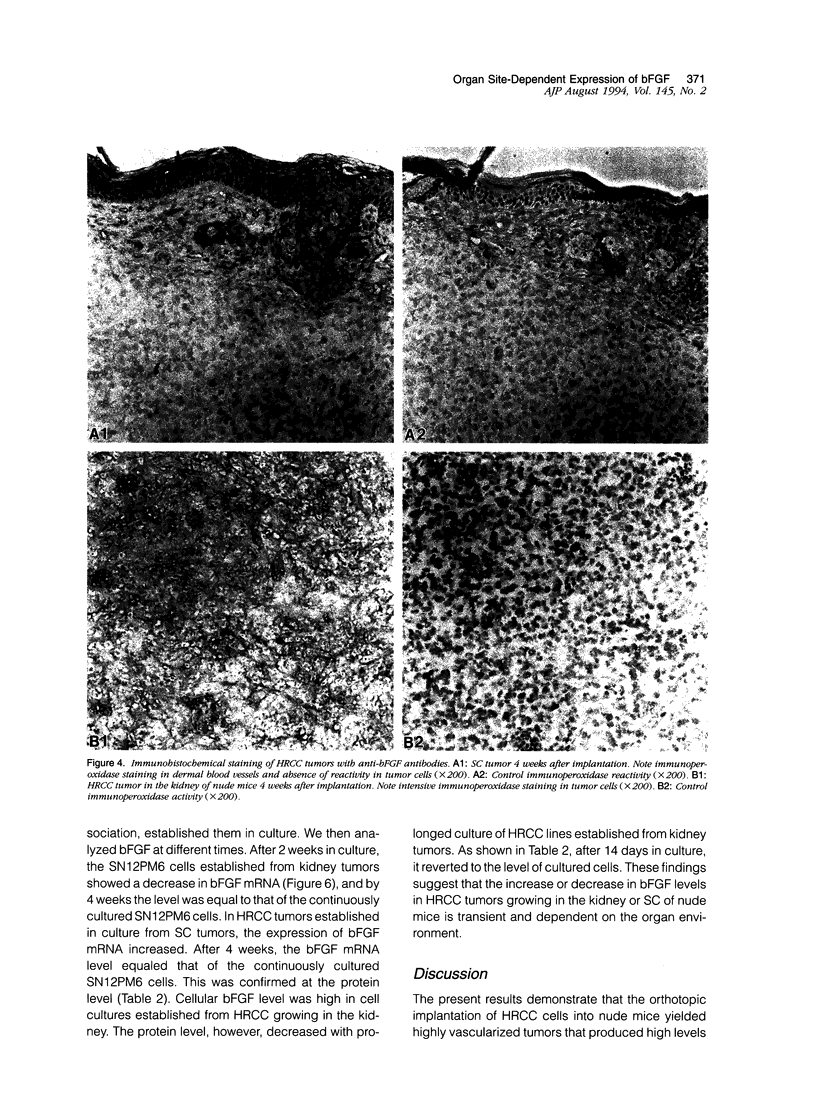
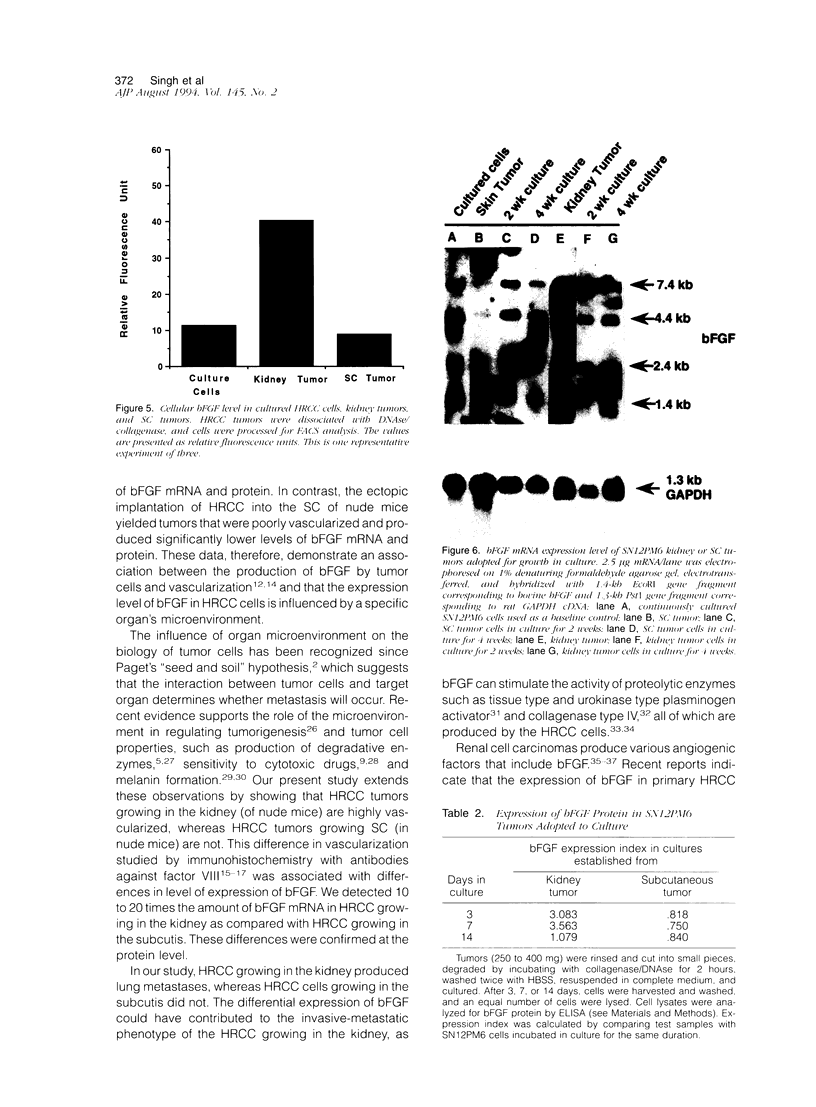
We investigated the influence of organ microenvironment on the angiogenic phenotype in human renal cell carcinoma (HRCC) cells. HRCC line SN12C was established in vitro from a surgical specimen, and metastatic line SN12PM6 was isolated from a lung metastasis produced by parental cells implanted into the kidney of nude mice. SN12C (low metastasis) and SN12PM6 (high metastasis) cells were injected into the kidney or subcutis of nude mice. The kidney tumors were highly vascularized (as revealed by immunohistochemistry using antibodies against factor VIII), and metastatic, whereas the subcutaneous tumors were not. The expression of mRNA for basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF) in kidney tumors was 10 to 20 times that found in subcutaneous tumors. Similar data were obtained at the protein level by using fluorescence activated cell sorting, immunohistochemistry, and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. bFGF was detected in the urine of mice with tumors in the kidney but not subcutaneous tumors. The level of bFGF in the serum of mice with kidney tumors was two to three times that in mice with subcutaneous tumors. The changes in bFGF expression in the tumors was transient. Collectively, these data indicate that the organ microenvironment can influence the expression level of bFGF in HRCC.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bouck N. Tumor angiogenesis: the role of oncogenes and tumor suppressor genes. Cancer Cells. 1990 Jun;2(6):179–185. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckley-Sturrock A., Woodward S. C., Senior R. M., Griffin G. L., Klagsbrun M., Davidson J. M. Differential stimulation of collagenase and chemotactic activity in fibroblasts derived from rat wound repair tissue and human skin by growth factors. J Cell Physiol. 1989 Jan;138(1):70–78. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041380111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chodak G. W., Hospelhorn V., Judge S. M., Mayforth R., Koeppen H., Sasse J. Increased levels of fibroblast growth factor-like activity in urine from patients with bladder or kidney cancer. Cancer Res. 1988 Apr 15;48(8):2083–2088. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cozzolino F., Torcia M., Lucibello M., Morbidelli L., Ziche M., Platt J., Fabiani S., Brett J., Stern D. Interferon-alpha and interleukin 2 synergistically enhance basic fibroblast growth factor synthesis and induce release, promoting endothelial cell growth. J Clin Invest. 1993 Jun;91(6):2504–2512. doi: 10.1172/JCI116486. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabra A., Nakajima M., Bucana C. D., Fidler I. J. Modulation of the invasive phenotype of human colon carcinoma cells by organ specific fibroblasts of nude mice. Differentiation. 1992 Dec;52(1):101–110. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.1992.tb00504.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fidler I. J. Critical factors in the biology of human cancer metastasis: twenty-eighth G.H.A. Clowes memorial award lecture. Cancer Res. 1990 Oct 1;50(19):6130–6138. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fidler I. J. Orthotopic implantation of human colon carcinomas into nude mice provides a valuable model for the biology and therapy of metastasis. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 1991 Oct;10(3):229–243. doi: 10.1007/BF00050794. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folkman J., Cotran R. Relation of vascular proliferation to tumor growth. Int Rev Exp Pathol. 1976;16:207–248. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folkman J. How is blood vessel growth regulated in normal and neoplastic tissue? G.H.A. Clowes memorial Award lecture. Cancer Res. 1986 Feb;46(2):467–473. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folkman J., Klagsbrun M. Angiogenic factors. Science. 1987 Jan 23;235(4787):442–447. doi: 10.1126/science.2432664. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folkman J. The role of angiogenesis in tumor growth. Semin Cancer Biol. 1992 Apr;3(2):65–71. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folkman J. What is the evidence that tumors are angiogenesis dependent? J Natl Cancer Inst. 1990 Jan 3;82(1):4–6. doi: 10.1093/jnci/82.1.4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fort P., Marty L., Piechaczyk M., el Sabrouty S., Dani C., Jeanteur P., Blanchard J. M. Various rat adult tissues express only one major mRNA species from the glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate-dehydrogenase multigenic family. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Mar 11;13(5):1431–1442. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.5.1431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris E. D., Jr Rheumatoid arthritis. Pathophysiology and implications for therapy. N Engl J Med. 1990 May 3;322(18):1277–1289. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199005033221805. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hart I. R. 'Seed and soil' revisited: mechanisms of site-specific metastasis. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 1982;1(1):5–16. doi: 10.1007/BF00049477. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hart I. R., Fidler I. J. Role of organ selectivity in the determination of metastatic patterns of B16 melanoma. Cancer Res. 1980 Jul;40(7):2281–2287. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hart I. R., Talmadge J. E., Fidler I. J. Metastatic behavior of a murine reticulum cell sarcoma exhibiting organ-specific growth. Cancer Res. 1981 Apr;41(4):1281–1287. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hossain M. Z., Wilkens L. R., Mehta P. P., Loewenstein W., Bertram J. S. Enhancement of gap junctional communication by retinoids correlates with their ability to inhibit neoplastic transformation. Carcinogenesis. 1989 Sep;10(9):1743–1748. doi: 10.1093/carcin/10.9.1743. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morikawa K., Walker S. M., Nakajima M., Pathak S., Jessup J. M., Fidler I. J. Influence of organ environment on the growth, selection, and metastasis of human colon carcinoma cells in nude mice. Cancer Res. 1988 Dec 1;48(23):6863–6871. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murakami Y., Mizuno S., Hori M., Uehara Y. Reversal of transformed phenotypes by herbimycin A in src oncogene expressed rat fibroblasts. Cancer Res. 1988 Mar 15;48(6):1587–1590. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mydlo J. H., Heston W. D., Fair W. R. Characterization of a heparin-binding growth factor from adenocarcinoma of the kidney. J Urol. 1988 Dec;140(6):1575–1579. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5347(17)42130-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naito S., Walker S. M., Fidler I. J. In vivo selection of human renal cell carcinoma cells with high metastatic potential in nude mice. Clin Exp Metastasis. 1989 Jul-Aug;7(4):381–389. doi: 10.1007/BF01753659. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naito S., von Eschenbach A. C., Fidler I. J. Different growth pattern and biologic behavior of human renal cell carcinoma implanted into different organs of nude mice. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1987 Feb;78(2):377–385. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naito S., von Eschenbach A. C., Giavazzi R., Fidler I. J. Growth and metastasis of tumor cells isolated from a human renal cell carcinoma implanted into different organs of nude mice. Cancer Res. 1986 Aug;46(8):4109–4115. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakajima M., Morikawa K., Fabra A., Bucana C. D., Fidler I. J. Influence of organ environment on extracellular matrix degradative activity and metastasis of human colon carcinoma cells. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1990 Dec 19;82(24):1890–1898. doi: 10.1093/jnci/82.24.1890. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nanus D. M., Schmitz-Dräger B. J., Motzer R. J., Lee A. C., Vlamis V., Cordon-Cardo C., Albino A. P., Reuter V. E. Expression of basic fibroblast growth factor in primary human renal tumors: correlation with poor survival. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1993 Oct 6;85(19):1597–1599. doi: 10.1093/jnci/85.19.1597. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen M., Watanabe H., Budson A. E., Richie J. P., Hayes D. F., Folkman J. Elevated levels of an angiogenic peptide, basic fibroblast growth factor, in the urine of patients with a wide spectrum of cancers. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1994 Mar 2;86(5):356–361. doi: 10.1093/jnci/86.5.356. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plouët J., Gospodarowicz D. Transforming growth factor beta-1 positively modulates the bioactivity of fibroblast growth factor on corneal endothelial cells. J Cell Physiol. 1989 Nov;141(2):392–399. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041410221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Presta M., Maier J. A., Ragnotti G. The mitogenic signaling pathway but not the plasminogen activator-inducing pathway of basic fibroblast growth factor is mediated through protein kinase C in fetal bovine aortic endothelial cells. J Cell Biol. 1989 Oct;109(4 Pt 1):1877–1884. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.4.1877. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price J. E., Tarin D., Fidler I. J. Influence of organ microenvironment on pigmentation of a metastatic murine melanoma. Cancer Res. 1988 Apr 15;48(8):2258–2264. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radinsky R., Kraemer P. M., Raines M. A., Kung H. J., Culp L. A. Amplification and rearrangement of the Kirsten ras oncogene in virus-transformed BALB/c 3T3 cells during malignant tumor progression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(15):5143–5147. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.15.5143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogelj S., Weinberg R. A., Fanning P., Klagsbrun M. Basic fibroblast growth factor fused to a signal peptide transforms cells. Nature. 1988 Jan 14;331(6152):173–175. doi: 10.1038/331173a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki I., Naito S., Yoneda J., Azuma I., Price J. E., Fidler I. J. Characterization of the invasive and metastatic phenotype in human renal cell carcinoma. Clin Exp Metastasis. 1991 Nov-Dec;9(6):551–566. doi: 10.1007/BF01768583. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schackert G., Fidler I. J. Site-specific metastasis of mouse melanomas and a fibrosarcoma in the brain or meninges of syngeneic animals. Cancer Res. 1988 Jun 15;48(12):3478–3484. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Senger D. R., Van de Water L., Brown L. F., Nagy J. A., Yeo K. T., Yeo T. K., Berse B., Jackman R. W., Dvorak A. M., Dvorak H. F. Vascular permeability factor (VPF, VEGF) in tumor biology. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 1993 Sep;12(3-4):303–324. doi: 10.1007/BF00665960. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staroselsky A. N., Fan D., O'Brian C. A., Bucana C. D., Gupta K. P., Fidler I. J. Site-dependent differences in response of the UV-2237 murine fibrosarcoma to systemic therapy with adriamycin. Cancer Res. 1990 Dec 15;50(24):7775–7780. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stirling D., Magness R. R., Stone R., Waterman M. R., Simpson E. R. Angiotensin II inhibits luteinizing hormone-stimulated cholesterol side chain cleavage expression and stimulates basic fibroblast growth factor expression in bovine luteal cells in primary culture. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jan 5;265(1):5–8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weidner N., Carroll P. R., Flax J., Blumenfeld W., Folkman J. Tumor angiogenesis correlates with metastasis in invasive prostate carcinoma. Am J Pathol. 1993 Aug;143(2):401–409. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weidner N., Folkman J., Pozza F., Bevilacqua P., Allred E. N., Moore D. H., Meli S., Gasparini G. Tumor angiogenesis: a new significant and independent prognostic indicator in early-stage breast carcinoma. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1992 Dec 16;84(24):1875–1887. doi: 10.1093/jnci/84.24.1875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weidner N., Semple J. P., Welch W. R., Folkman J. Tumor angiogenesis and metastasis--correlation in invasive breast carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 1991 Jan 3;324(1):1–8. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199101033240101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilmanns C., Fan D., O'Brian C. A., Bucana C. D., Fidler I. J. Orthotopic and ectopic organ environments differentially influence the sensitivity of murine colon carcinoma cells to doxorubicin and 5-fluorouracil. Int J Cancer. 1992 Aug 19;52(1):98–104. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910520118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]