Abstract
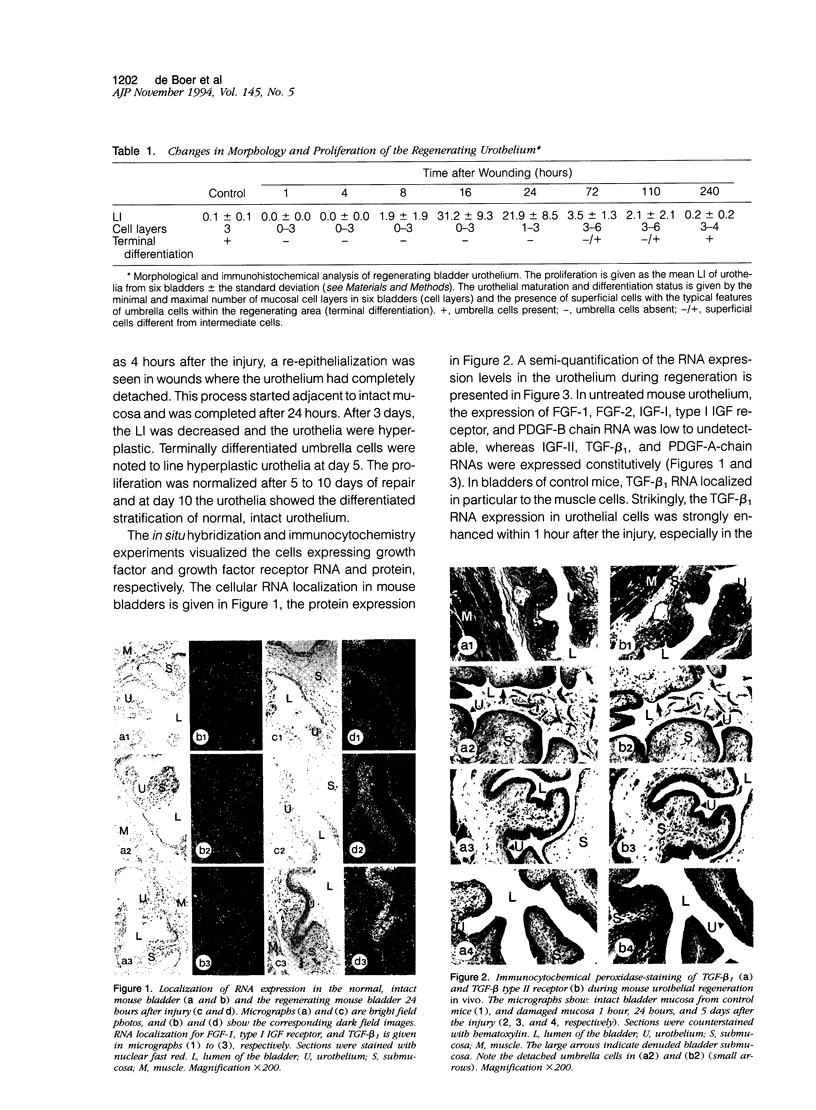
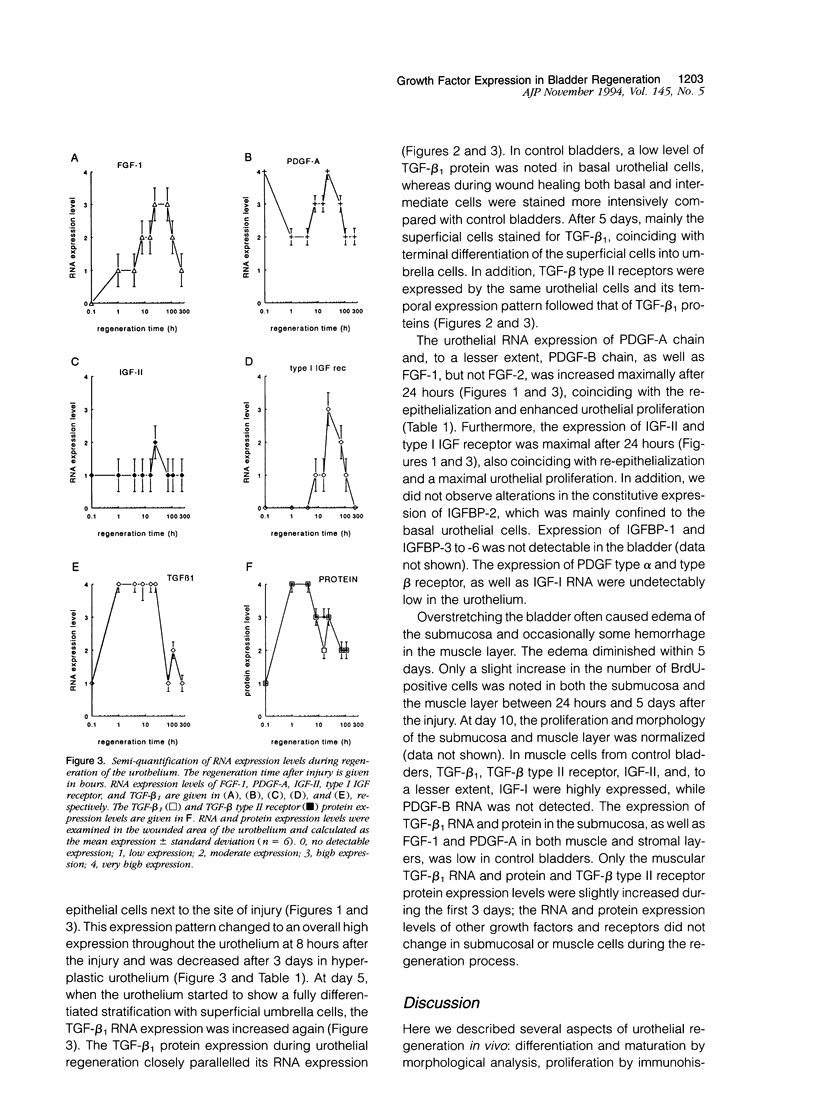
We investigated the spatio-temporal changes in RNA and protein expression of growth factors and their receptors by in situ hybridization and immunocytochemistry during regeneration after acute injury of mouse urothelium in vivo. These data were correlated with changes in morphology and proliferation during regeneration. Except for an enhanced muscular transforming growth factor-beta 1 (TGF-beta 1) and TGF-beta type II receptor expression, changes in expression patterns of growth factors or receptors were confined to the urothelium. Increased mucosal RNA expression of insulin-like growth factor-II (IGF-II) and particularly of type I IGF receptor, as well as fibroblast growth factor-1 (FGF-1) but not of FGF-2, coincided with re-epithelialization and urothelial proliferation. Both high levels of urothelial TGF-beta 1 RNA and protein expression were associated with re-epithelialization and differentiation. In addition, TGF beta type II receptor protein expression was similarly enhanced in the same urothelial cells. Platelet-derived growth factor-A (PDGF-A) RNA was expressed constitutively in the mucosa but decreased in the reepithelialization phase. The data are consistent with the notion that urothelial regeneration can be achieved by paracrine or autocrine acting, urothelium-derived growth factors. Since analogous growth factor RNA expression patterns in regenerating skin epidermis have been found, a more general growth factor-regulated mechanism for epithelial regeneration may be suggested.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aaronson S. A. Growth factors and cancer. Science. 1991 Nov 22;254(5035):1146–1153. doi: 10.1126/science.1659742. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Antoniades H. N., Galanopoulos T., Neville-Golden J., Kiritsy C. P., Lynch S. E. Expression of growth factor and receptor mRNAs in skin epithelial cells following acute cutaneous injury. Am J Pathol. 1993 Apr;142(4):1099–1110. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Antoniades H. N., Galanopoulos T., Neville-Golden J., Kiritsy C. P., Lynch S. E. Injury induces in vivo expression of platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) and PDGF receptor mRNAs in skin epithelial cells and PDGF mRNA in connective tissue fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jan 15;88(2):565–569. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.2.565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brewitt B., Clark J. I. Growth and transparency in the lens, an epithelial tissue, stimulated by pulses of PDGF. Science. 1988 Nov 4;242(4879):777–779. doi: 10.1126/science.3187521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campochiaro P. A., Glaser B. M. Platelet-derived growth factor is chemotactic for human retinal pigment epithelial cells. Arch Ophthalmol. 1985 Apr;103(4):576–579. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1985.01050040118034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter G. Epidermal growth factor: biology and receptor metabolism. J Cell Sci Suppl. 1985;3:1–9. doi: 10.1242/jcs.1985.supplement_3.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clemmons D. R. IGF binding proteins: regulation of cellular actions. Growth Regul. 1992 Jun;2(2):80–87. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S. M. Toxic and nontoxic changes induced in the urothelium by xenobiotics. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1989 Dec;101(3):484–498. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(89)90197-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coombs L. M., Pigott D. A., Eydmann M. E., Proctor A. J., Knowles M. A. Reduced expression of TGF beta is associated with advanced disease in transitional cell carcinoma. Br J Cancer. 1993 Mar;67(3):578–584. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1993.106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Boer W. I., Rebel J. M., Foekens J. A., Vermey M., Van der Kwast T. H. Characterization of mouse urothelial cell lines in different phases of transitional-cell carcinogenesis. Int J Cancer. 1993 Jul 30;54(6):1022–1027. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910540627. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzpatrick L. R., Jakubowska A., Martin G. E., Davis M., Jaye M. C., Dionne C. A. Acidic fibroblast growth factor accelerates the healing of acetic-acid-induced gastric ulcers in rats. Digestion. 1992;53(1-2):17–27. doi: 10.1159/000200967. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glick A. B., Danielpour D., Morgan D., Sporn M. B., Yuspa S. H. Induction and autocrine receptor binding of transforming growth factor-beta 2 during terminal differentiation of primary mouse keratinocytes. Mol Endocrinol. 1990 Jan;4(1):46–52. doi: 10.1210/mend-4-1-46. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gospodarowicz D., Plouët J., Malerstein B. Comparison of the ability of basic and acidic fibroblast growth factor to stimulate the proliferation of an established keratinocyte cell line: modulation of their biological effects by heparin, transforming growth factor beta (TGF beta), and epidermal growth factor (EGF). J Cell Physiol. 1990 Feb;142(2):325–333. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041420215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hebda P. A. Stimulatory effects of transforming growth factor-beta and epidermal growth factor on epidermal cell outgrowth from porcine skin explant cultures. J Invest Dermatol. 1988 Nov;91(5):440–445. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12476480. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hicks R. M. The mammalian urinary bladder: an accommodating organ. Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc. 1975 May;50(2):215–246. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-185x.1975.tb01057.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hudspeth A. J. Establishment of tight junctions between epithelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jul;72(7):2711–2713. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.7.2711. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jennische E., Skottner A., Hansson H. A. Dynamic changes in insulin-like growth factor I immunoreactivity correlate to repair events in rat ear after freeze-thaw injury. Exp Mol Pathol. 1987 Oct;47(2):193–201. doi: 10.1016/0014-4800(87)90074-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jouanneau J., Gavrilovic J., Caruelle D., Jaye M., Moens G., Caruelle J. P., Thiery J. P. Secreted or nonsecreted forms of acidic fibroblast growth factor produced by transfected epithelial cells influence cell morphology, motility, and invasive potential. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Apr 1;88(7):2893–2897. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.7.2893. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kagami S., Border W. A., Ruoslahti E., Noble N. A. Coordinated expression of beta 1 integrins and transforming growth factor-beta-induced matrix proteins in glomerulonephritis. Lab Invest. 1993 Jul;69(1):68–76. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamalati T., Howard M., Brooks R. F. IGF I induces differentiation in a transformed human keratinocyte line. Development. 1989 Jun;106(2):283–293. doi: 10.1242/dev.106.2.283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kane C. J., Hebda P. A., Mansbridge J. N., Hanawalt P. C. Direct evidence for spatial and temporal regulation of transforming growth factor beta 1 expression during cutaneous wound healing. J Cell Physiol. 1991 Jul;148(1):157–173. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041480119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawamata H., Azuma M., Kameyama S., Nan L., Oyasu R. Effect of epidermal growth factor/transforming growth factor alpha and transforming growth factor beta 1 on growth in vitro of rat urinary bladder carcinoma cells. Cell Growth Differ. 1992 Nov;3(11):819–825. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimball E. S., Bohn W. H., Cockley K. D., Warren T. C., Sherwin S. A. Distinct high-performance liquid chromatography pattern of transforming growth factor activity in urine of cancer patients as compared with that of normal individuals. Cancer Res. 1984 Aug;44(8):3613–3619. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee K. H., Bowen-Pope D. F., Reed R. R. Isolation and characterization of the alpha platelet-derived growth factor receptor from rat olfactory epithelium. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 May;10(5):2237–2246. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.5.2237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine J. H., Moses H. L., Gold L. I., Nanney L. B. Spatial and temporal patterns of immunoreactive transforming growth factor beta 1, beta 2, and beta 3 during excisional wound repair. Am J Pathol. 1993 Aug;143(2):368–380. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lynch S. E., Colvin R. B., Antoniades H. N. Growth factors in wound healing. Single and synergistic effects on partial thickness porcine skin wounds. J Clin Invest. 1989 Aug;84(2):640–646. doi: 10.1172/JCI114210. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matejka G. L., Jennische E. IGF-I binding and IGF-I mRNA expression in the post-ischemic regenerating rat kidney. Kidney Int. 1992 Nov;42(5):1113–1123. doi: 10.1038/ki.1992.395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellin T. N., Mennie R. J., Cashen D. E., Ronan J. J., Capparella J., James M. L., Disalvo J., Frank J., Linemeyer D., Gimenez-Gallego G. Acidic fibroblast growth factor accelerates dermal wound healing. Growth Factors. 1992;7(1):1–14. doi: 10.3109/08977199209023933. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing E. M., Hanson P., Ulrich P., Erturk E. Epidermal growth factor--interactions with normal and malignant urothelium: in vivo and in situ studies. J Urol. 1987 Nov;138(5):1329–1335. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5347(17)43593-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mustoe T. A., Pierce G. F., Morishima C., Deuel T. F. Growth factor-induced acceleration of tissue repair through direct and inductive activities in a rabbit dermal ulcer model. J Clin Invest. 1991 Feb;87(2):694–703. doi: 10.1172/JCI115048. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nickoloff B. J., Mitra R. S., Riser B. L., Dixit V. M., Varani J. Modulation of keratinocyte motility. Correlation with production of extracellular matrix molecules in response to growth promoting and antiproliferative factors. Am J Pathol. 1988 Sep;132(3):543–551. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odland G., Ross R. Human wound repair. I. Epidermal regeneration. J Cell Biol. 1968 Oct;39(1):135–151. doi: 10.1083/jcb.39.1.135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Post J. G., te Poele J. A., Oussoren Y., Stewart F. A. Bladder damage in mice after single and repeated intravesical instillations of mitomycin C or doxorubicin. J Urol. 1993 Dec;150(6):1965–1969. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5347(17)35947-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ristow H. J., Messmer T. O. Basic fibroblast growth factor and insulin-like growth factor I are strong mitogens for cultured mouse keratinocytes. J Cell Physiol. 1988 Nov;137(2):277–284. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041370210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sacco O., Romberger D., Rizzino A., Beckmann J. D., Rennard S. I., Spurzem J. R. Spontaneous production of transforming growth factor-beta 2 by primary cultures of bronchial epithelial cells. Effects on cell behavior in vitro. J Clin Invest. 1992 Oct;90(4):1379–1385. doi: 10.1172/JCI116004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scharffetter-Kochanek K., Klein C. E., Heinen G., Mauch C., Schaefer T., Adelmann-Grill B. C., Goerz G., Fusenig N. E., Krieg T. M., Plewig G. Migration of a human keratinocyte cell line (HACAT) to interstitial collagen type I is mediated by the alpha 2 beta 1-integrin receptor. J Invest Dermatol. 1992 Jan;98(1):3–11. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12493266. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid P., Cox D., Bilbe G., McMaster G., Morrison C., Stähelin H., Lüscher N., Seiler W. TGF-beta s and TGF-beta type II receptor in human epidermis: differential expression in acute and chronic skin wounds. J Pathol. 1993 Nov;171(3):191–197. doi: 10.1002/path.1711710307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuller A. G., Lindenbergh-Kortleve D. J., de Boer W. I., Zwarthoff E. C., Drop S. L. Localization of the epitope of a monoclonal antibody against human insulin-like growth factor binding protein-1, functionally interfering with insulin-like growth factor binding. Growth Regul. 1993 Mar;3(1):32–34. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuller A. G., Zwarthoff E. C., Drop S. L. Gene expression of the six insulin-like growth factor binding proteins in the mouse conceptus during mid- and late gestation. Endocrinology. 1993 Jun;132(6):2544–2550. doi: 10.1210/endo.132.6.7684980. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schutte B., Reynders M. M., van Assche C. L., Hupperets P. S., Bosman F. T., Blijham G. H. An improved method for the immunocytochemical detection of bromodeoxyuridine labeled nuclei using flow cytometry. Cytometry. 1987 Jul;8(4):372–376. doi: 10.1002/cyto.990080405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shipley G. D., Keeble W. W., Hendrickson J. E., Coffey R. J., Jr, Pittelkow M. R. Growth of normal human keratinocytes and fibroblasts in serum-free medium is stimulated by acidic and basic fibroblast growth factor. J Cell Physiol. 1989 Mar;138(3):511–518. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041380310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silen W., Ito S. Mechanisms for rapid re-epithelialization of the gastric mucosal surface. Annu Rev Physiol. 1985;47:217–229. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.47.030185.001245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tong Y. C., Monson F. C., Erika B., Levin R. M. Effects of acute in vitro overdistension of the rabbit urinary bladder on DNA synthesis. J Urol. 1992 Oct;148(4):1347–1350. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5347(17)36906-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuboi R., Sato C., Shi C. M., Ogawa H. Stimulation of keratinocyte migration by growth factors. J Dermatol. 1992 Nov;19(11):652–653. doi: 10.1111/j.1346-8138.1992.tb03751.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tucker G. C., Delouvée A., Jouanneau J., Gavrilovic J., Moens G., Vallés A. M., Thiery J. P. Amplification of invasiveness in organotypic cultures after NBT-II rat bladder carcinoma stimulation with in vitro scattering factors. Invasion Metastasis. 1991;11(6):297–309. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vallés A. M., Boyer B., Badet J., Tucker G. C., Barritault D., Thiery J. P. Acidic fibroblast growth factor is a modulator of epithelial plasticity in a rat bladder carcinoma cell line. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(3):1124–1128. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.3.1124. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werner S., Peters K. G., Longaker M. T., Fuller-Pace F., Banda M. J., Williams L. T. Large induction of keratinocyte growth factor expression in the dermis during wound healing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 1;89(15):6896–6900. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.15.6896. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]