Abstract
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the vasoformative response of isolated vascular explants to a variety of growth factors that have been shown to stimulate angiogenesis. Rings of rat aorta were cultured in collagen gels under serum-free conditions in the presence or absence of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), natural platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF), PDGF-AA, PDGF-BB, insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1), transforming growth factor-alpha (TGF-alpha), transforming growth factor-beta 1 (TGF-beta 1), epidermal growth factor (EGF), interleukin-1 alpha (IL-1 alpha), or hepatocyte growth factor (HGF). The angiogenic response of the rat aorta was stimulated by VEGF, PDGF, PDGF-AA, PDGF-BB, and IGF-1. Maximum stimulatory effects were obtained with VEGF and PDGF-BB. By contrast, TGF-beta 1 and IL-1 alpha had inhibitory activity. No significant effects were observed with TGF-alpha, EGF, or HGF. The vascular outgrowth of VEGF-stimulated cultures was primarily composed of microvessels, whereas that of PDGF- and IGF-1-stimulated cultures contained an increased number of fibroblast-like cells. The inability of TGF-alpha, TGF-beta 1, IL-1 alpha, EGF, and HGF to stimulate rat aortic angiogenesis in serum-free culture suggests that either these factors require the mediatory activity of accessory cells that are not present in the rat aorta model or that blood vessels are heterogeneous in their capacity to respond to different angiogenic factors.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Antoniades H. N., Galanopoulos T., Neville-Golden J., Kiritsy C. P., Lynch S. E. Injury induces in vivo expression of platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) and PDGF receptor mRNAs in skin epithelial cells and PDGF mRNA in connective tissue fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jan 15;88(2):565–569. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.2.565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Auerbach R., Auerbach W., Polakowski I. Assays for angiogenesis: a review. Pharmacol Ther. 1991;51(1):1–11. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(91)90038-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Auerbach R. Vascular endothelial cell differentiation: organ-specificity and selective affinities as the basis for developing anti-cancer strategies. Int J Radiat Biol. 1991 Jul-Aug;60(1-2):1–10. doi: 10.1080/09553009114551401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bar R. S., Boes M., Booth B. A., Dake B. L., Henley S., Hart M. N. The effects of platelet-derived growth factor in cultured microvessel endothelial cells. Endocrinology. 1989 Apr;124(4):1841–1848. doi: 10.1210/endo-124-4-1841. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beitz J. G., Kim I. S., Calabresi P., Frackelton A. R., Jr Receptors for platelet-derived growth factor on microvascular endothelial cells. EXS. 1992;61:85–90. doi: 10.1007/978-3-0348-7001-6_15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BenEzra D., Hemo I., Maftzir G. In vivo angiogenic activity of interleukins. Arch Ophthalmol. 1990 Apr;108(4):573–576. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1990.01070060121061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk B. C., Alexander R. W., Brock T. A., Gimbrone M. A., Jr, Webb R. C. Vasoconstriction: a new activity for platelet-derived growth factor. Science. 1986 Apr 4;232(4746):87–90. doi: 10.1126/science.3485309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bobik A., Campbell J. H. Vascular derived growth factors: cell biology, pathophysiology, and pharmacology. Pharmacol Rev. 1993 Mar;45(1):1–42. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bronzert D. A., Pantazis P., Antoniades H. N., Kasid A., Davidson N., Dickson R. B., Lippman M. E. Synthesis and secretion of platelet-derived growth factor by human breast cancer cell lines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(16):5763–5767. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.16.5763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown L. F., Berse B., Jackman R. W., Tognazzi K., Manseau E. J., Dvorak H. F., Senger D. R. Increased expression of vascular permeability factor (vascular endothelial growth factor) and its receptors in kidney and bladder carcinomas. Am J Pathol. 1993 Nov;143(5):1255–1262. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bussolino F., Di Renzo M. F., Ziche M., Bocchietto E., Olivero M., Naldini L., Gaudino G., Tamagnone L., Coffer A., Comoglio P. M. Hepatocyte growth factor is a potent angiogenic factor which stimulates endothelial cell motility and growth. J Cell Biol. 1992 Nov;119(3):629–641. doi: 10.1083/jcb.119.3.629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clemmons D. R. IGF binding proteins: regulation of cellular actions. Growth Regul. 1992 Jun;2(2):80–87. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cozzolino F., Torcia M., Aldinucci D., Ziche M., Almerigogna F., Bani D., Stern D. M. Interleukin 1 is an autocrine regulator of human endothelial cell growth. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Sep;87(17):6487–6491. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.17.6487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrara N., Winer J., Burton T. Aortic smooth muscle cells express and secrete vascular endothelial growth factor. Growth Factors. 1991;5(2):141–148. doi: 10.3109/08977199109000278. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finkenzeller G., Marmé D., Weich H. A., Hug H. Platelet-derived growth factor-induced transcription of the vascular endothelial growth factor gene is mediated by protein kinase C. Cancer Res. 1992 Sep 1;52(17):4821–4823. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folkman J., Shing Y. Angiogenesis. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jun 5;267(16):10931–10934. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grant M. B., Mames R. N., Fitzgerald C., Ellis E. A., Caballero S., Chegini N., Guy J. Insulin-like growth factor I as an angiogenic agent. In vivo and in vitro studies. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1993 Aug 27;692:230–242. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1993.tb26221.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoover G. A., McCormick S., Kalant N. Effects of porcine aortic smooth muscle cell conditioned medium on endothelial cell replication. Arteriosclerosis. 1989 Jan-Feb;9(1):76–83. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.9.1.76. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingber D. E., Folkman J. How does extracellular matrix control capillary morphogenesis? Cell. 1989 Sep 8;58(5):803–805. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90928-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kazlauskas A., DiCorleto P. E. Cultured endothelial cells do not respond to a platelet-derived growth-factor-like protein in an autocrine manner. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Sep 30;846(3):405–412. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(85)90013-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khorsandi M. J., Fagin J. A., Giannella-Neto D., Forrester J. S., Cercek B. Regulation of insulin-like growth factor-I and its receptor in rat aorta after balloon denudation. Evidence for local bioactivity. J Clin Invest. 1992 Nov;90(5):1926–1931. doi: 10.1172/JCI116070. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kulkarni A. B., Huh C. G., Becker D., Geiser A., Lyght M., Flanders K. C., Roberts A. B., Sporn M. B., Ward J. M., Karlsson S. Transforming growth factor beta 1 null mutation in mice causes excessive inflammatory response and early death. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jan 15;90(2):770–774. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.2.770. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leung D. W., Cachianes G., Kuang W. J., Goeddel D. V., Ferrara N. Vascular endothelial growth factor is a secreted angiogenic mitogen. Science. 1989 Dec 8;246(4935):1306–1309. doi: 10.1126/science.2479986. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu J. P., Baker J., Perkins A. S., Robertson E. J., Efstratiadis A. Mice carrying null mutations of the genes encoding insulin-like growth factor I (Igf-1) and type 1 IGF receptor (Igf1r). Cell. 1993 Oct 8;75(1):59–72. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majack R. A., Cook S. C., Bornstein P. Platelet-derived growth factor and heparin-like glycosaminoglycans regulate thrombospondin synthesis and deposition in the matrix by smooth muscle cells. J Cell Biol. 1985 Sep;101(3):1059–1070. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.3.1059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majesky M. W., Reidy M. A., Bowen-Pope D. F., Hart C. E., Wilcox J. N., Schwartz S. M. PDGF ligand and receptor gene expression during repair of arterial injury. J Cell Biol. 1990 Nov;111(5 Pt 1):2149–2158. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.5.2149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marx M., Perlmutter R. A., Madri J. A. Modulation of platelet-derived growth factor receptor expression in microvascular endothelial cells during in vitro angiogenesis. J Clin Invest. 1994 Jan;93(1):131–139. doi: 10.1172/JCI116936. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merwin J. R., Anderson J. M., Kocher O., Van Itallie C. M., Madri J. A. Transforming growth factor beta 1 modulates extracellular matrix organization and cell-cell junctional complex formation during in vitro angiogenesis. J Cell Physiol. 1990 Jan;142(1):117–128. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041420115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicosia R. F., Bonanno E., Smith M. Fibronectin promotes the elongation of microvessels during angiogenesis in vitro. J Cell Physiol. 1993 Mar;154(3):654–661. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041540325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicosia R. F., Bonanno E., Villaschi S. Large-vessel endothelium switches to a microvascular phenotype during angiogenesis in collagen gel culture of rat aorta. Atherosclerosis. 1992 Aug;95(2-3):191–199. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(92)90022-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
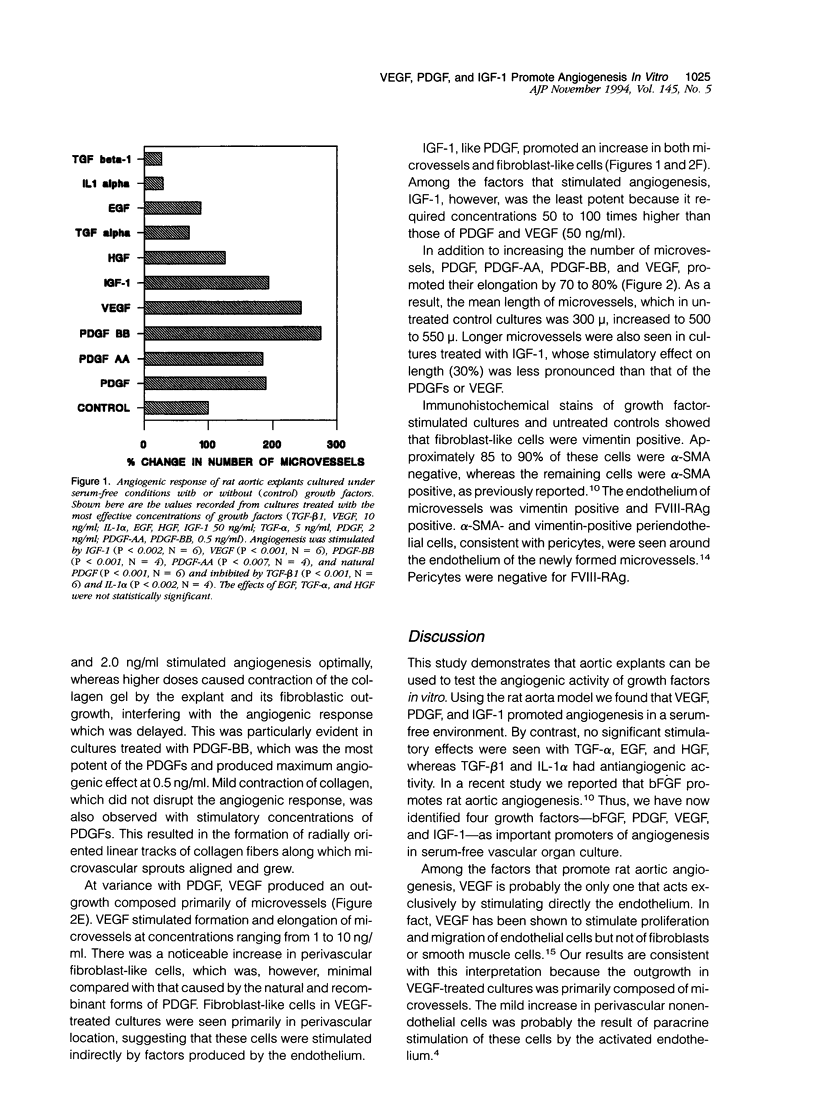
- Nicosia R. F., Ottinetti A. Growth of microvessels in serum-free matrix culture of rat aorta. A quantitative assay of angiogenesis in vitro. Lab Invest. 1990 Jul;63(1):115–122. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicosia R. F., Tuszynski G. P. Matrix-bound thrombospondin promotes angiogenesis in vitro. J Cell Biol. 1994 Jan;124(1-2):183–193. doi: 10.1083/jcb.124.1.183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pepper M. S., Ferrara N., Orci L., Montesano R. Potent synergism between vascular endothelial growth factor and basic fibroblast growth factor in the induction of angiogenesis in vitro. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Dec 15;189(2):824–831. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(92)92277-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips G. D., Whitehead R. A., Knighton D. R. Inhibition by methylprednisolone acetate suggests an indirect mechanism for TGF-B induced angiogenesis. Growth Factors. 1992;6(1):77–84. doi: 10.3109/08977199209008873. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plate K. H., Breier G., Millauer B., Ullrich A., Risau W. Up-regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor and its cognate receptors in a rat glioma model of tumor angiogenesis. Cancer Res. 1993 Dec 1;53(23):5822–5827. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RayChaudhury A., D'Amore P. A. Endothelial cell regulation by transforming growth factor-beta. J Cell Biochem. 1991 Nov;47(3):224–229. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240470307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarzani R., Brecher P., Chobanian A. V. Growth factor expression in aorta of normotensive and hypertensive rats. J Clin Invest. 1989 Apr;83(4):1404–1408. doi: 10.1172/JCI114029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato N., Beitz J. G., Kato J., Yamamoto M., Clark J. W., Calabresi P., Raymond A., Frackelton A. R., Jr Platelet-derived growth factor indirectly stimulates angiogenesis in vitro. Am J Pathol. 1993 Apr;142(4):1119–1130. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato N., Tsuruoka N., Yamamoto M., Nishihara T., Goto T. Identification of non heparin-binding endothelial cell growth factor from rat myofibroblasts. EXS. 1992;61:179–187. doi: 10.1007/978-3-0348-7001-6_27. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreiber A. B., Winkler M. E., Derynck R. Transforming growth factor-alpha: a more potent angiogenic mediator than epidermal growth factor. Science. 1986 Jun 6;232(4755):1250–1253. doi: 10.1126/science.2422759. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vernon R. B., Angello J. C., Iruela-Arispe M. L., Lane T. F., Sage E. H. Reorganization of basement membrane matrices by cellular traction promotes the formation of cellular networks in vitro. Lab Invest. 1992 May;66(5):536–547. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Villaschi S., Nicosia R. F. Angiogenic role of endogenous basic fibroblast growth factor released by rat aorta after injury. Am J Pathol. 1993 Jul;143(1):181–190. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Villaschi S., Nicosia R. F. Paracrine interactions between fibroblasts and endothelial cells in a serum-free coculture model. Modulation of angiogenesis and collagen gel contraction. Lab Invest. 1994 Aug;71(2):291–299. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Villaschi S., Nicosia R. F., Smith M. R. Isolation of a morphologically and functionally distinct smooth muscle cell type from the intimal aspect of the normal rat aorta. Evidence for smooth muscle cell heterogeneity. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 1994 Sep;30A(9):589–595. doi: 10.1007/BF02631257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]