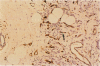
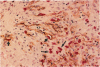
Abstract
Tumor angiogenesis is essential for tumor growth and metastasis, and intratumoral microvessel density correlates with prognosis in breast carcinoma. Yet, how intratumoral microvessel density correlates with tumor cell and intratumoral endothelial cell proliferation remains incompletely understood. To this end, we stained 57 formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded breast carcinomas with antibody MIB1 to determine tumor cell Ki67 labeling index and with anti-CD34 to observe microvessels. We correlated the tumor cell Ki67 labeling index and mitotic figure index with intratumoral microvessel density. Using a double labeling technique combining antibody MIB1 and anti-CD34, we measured intratumoral endothelial cell proliferation in 20 of these cases and correlated these findings with tumor cell Ki67 labeling index, mitotic figure index, and intratumoral microvessel density. The intratumoral Ki67-labeling index was 45-fold greater (P < 0.000001) than that of microvessels in adjacent benign breast. Yet, endothelial cell Ki67 labeling index did not correlate with intratumoral microvessel density, tumor cell Ki67 labeling index, or mitotic figure index nor did intratumoral microvessel density correlate with tumor cell Ki67 labeling index or mitotic figure index. These findings suggest that, although endothelial cells are actively proliferating within the tumor, intratumoral microvessel density and intratumoral endothelial cell proliferation are independent of each other and of tumor cell proliferation. Thus, intratumoral microvessel density, endothelial cell proliferation, and tumor cell proliferation may be regulated by separate mechanisms.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Auerbach R., Arensman R., Kubai L., Folkman J. Tumor-induced angiogenesis: lack of inhibition by irradiation. Int J Cancer. 1975 Feb 15;15(2):241–245. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910150209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aznavoorian S., Murphy A. N., Stetler-Stevenson W. G., Liotta L. A. Molecular aspects of tumor cell invasion and metastasis. Cancer. 1993 Feb 15;71(4):1368–1383. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19930215)71:4<1368::aid-cncr2820710432>3.0.co;2-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bosari S., Lee A. K., DeLellis R. A., Wiley B. D., Heatley G. J., Silverman M. L. Microvessel quantitation and prognosis in invasive breast carcinoma. Hum Pathol. 1992 Jul;23(7):755–761. doi: 10.1016/0046-8177(92)90344-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brien S. E., Zagzag D., Brem S. Rapid in situ cellular kinetics of intracerebral tumor angiogenesis using a monoclonal antibody to bromodeoxyuridine. Neurosurgery. 1989 Nov;25(5):715–719. doi: 10.1097/00006123-198911000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cattoretti G., Becker M. H., Key G., Duchrow M., Schlüter C., Galle J., Gerdes J. Monoclonal antibodies against recombinant parts of the Ki-67 antigen (MIB 1 and MIB 3) detect proliferating cells in microwave-processed formalin-fixed paraffin sections. J Pathol. 1992 Dec;168(4):357–363. doi: 10.1002/path.1711680404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denekamp J., Hobson B. Endothelial-cell proliferation in experimental tumours. Br J Cancer. 1982 Nov;46(5):711–720. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1982.263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denekamp J. Review article: angiogenesis, neovascular proliferation and vascular pathophysiology as targets for cancer therapy. Br J Radiol. 1993 Mar;66(783):181–196. doi: 10.1259/0007-1285-66-783-181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folkman J., Klagsbrun M. Angiogenic factors. Science. 1987 Jan 23;235(4787):442–447. doi: 10.1126/science.2432664. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folkman J. Tumor angiogenesis: therapeutic implications. N Engl J Med. 1971 Nov 18;285(21):1182–1186. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197111182852108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folkman J., Watson K., Ingber D., Hanahan D. Induction of angiogenesis during the transition from hyperplasia to neoplasia. Nature. 1989 May 4;339(6219):58–61. doi: 10.1038/339058a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folkman J. What is the evidence that tumors are angiogenesis dependent? J Natl Cancer Inst. 1990 Jan 3;82(1):4–6. doi: 10.1093/jnci/82.1.4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox S. B., Gatter K. C., Bicknell R., Going J. J., Stanton P., Cooke T. G., Harris A. L. Relationship of endothelial cell proliferation to tumor vascularity in human breast cancer. Cancer Res. 1993 Sep 15;53(18):4161–4163. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furcht L. T. Critical factors controlling angiogenesis: cell products, cell matrix, and growth factors. Lab Invest. 1986 Nov;55(5):505–509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunduz N. Cytokinetics of tumour and endothelial cells and vascularization of lung metastases in C3H/He mice. Cell Tissue Kinet. 1981 Jul;14(4):343–363. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2184.1981.tb00542.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hobson B., Denekamp J. Endothelial proliferation in tumours and normal tissues: continuous labelling studies. Br J Cancer. 1984 Apr;49(4):405–413. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1984.66. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horak E. R., Leek R., Klenk N., LeJeune S., Smith K., Stuart N., Greenall M., Stepniewska K., Harris A. L. Angiogenesis, assessed by platelet/endothelial cell adhesion molecule antibodies, as indicator of node metastases and survival in breast cancer. Lancet. 1992 Nov 7;340(8828):1120–1124. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(92)93150-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu S. M., Raine L., Fanger H. Use of avidin-biotin-peroxidase complex (ABC) in immunoperoxidase techniques: a comparison between ABC and unlabeled antibody (PAP) procedures. J Histochem Cytochem. 1981 Apr;29(4):577–580. doi: 10.1177/29.4.6166661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macchiarini P., Fontanini G., Hardin M. J., Squartini F., Angeletti C. A. Relation of neovascularisation to metastasis of non-small-cell lung cancer. Lancet. 1992 Jul 18;340(8812):145–146. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(92)93217-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahadevan V., Hart I. R. Metastasis and angiogenesis. Acta Oncol. 1990;29(1):97–103. doi: 10.3109/02841869009089997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarthy S. A., Kuzu I., Gatter K. C., Bicknell R. Heterogeneity of the endothelial cell and its role in organ preference of tumour metastasis. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1991 Dec;12(12):462–467. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(91)90637-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormick D., Chong H., Hobbs C., Datta C., Hall P. A. Detection of the Ki-67 antigen in fixed and wax-embedded sections with the monoclonal antibody MIB1. Histopathology. 1993 Apr;22(4):355–360. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2559.1993.tb00135.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormick D., Yu C., Hobbs C., Hall P. A. The relevance of antibody concentration to the immunohistological quantification of cell proliferation-associated antigens. Histopathology. 1993 Jun;22(6):543–547. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2559.1993.tb00174.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sholley M. M., Ferguson G. P., Seibel H. R., Montour J. L., Wilson J. D. Mechanisms of neovascularization. Vascular sprouting can occur without proliferation of endothelial cells. Lab Invest. 1984 Dec;51(6):624–634. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tannock I. F. Population kinetics of carcinoma cells, capillary endothelial cells, and fibroblasts in a transplanted mouse mammary tumor. Cancer Res. 1970 Oct;30(10):2470–2476. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tannock I. F. The relation between cell proliferation and the vascular system in a transplanted mouse mammary tumour. Br J Cancer. 1968 Jun;22(2):258–273. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1968.34. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weidner N., Carroll P. R., Flax J., Blumenfeld W., Folkman J. Tumor angiogenesis correlates with metastasis in invasive prostate carcinoma. Am J Pathol. 1993 Aug;143(2):401–409. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weidner N., Folkman J., Pozza F., Bevilacqua P., Allred E. N., Moore D. H., Meli S., Gasparini G. Tumor angiogenesis: a new significant and independent prognostic indicator in early-stage breast carcinoma. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1992 Dec 16;84(24):1875–1887. doi: 10.1093/jnci/84.24.1875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weidner N., Semple J. P., Welch W. R., Folkman J. Tumor angiogenesis and metastasis--correlation in invasive breast carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 1991 Jan 3;324(1):1–8. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199101033240101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weidner N. Tumor angiogenesis: review of current applications in tumor prognostication. Semin Diagn Pathol. 1993 Nov;10(4):302–313. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshii Y., Sugiyama K. Intercapillary distance in the proliferating area of human glioma. Cancer Res. 1988 May 15;48(10):2938–2941. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Diest P. J., Baak J. P., Matze-Cok P., Wisse-Brekelmans E. C., van Galen C. M., Kurver P. H., Bellot S. M., Fijnheer J., van Gorp L. H., Kwee W. S. Reproducibility of mitosis counting in 2,469 breast cancer specimens: results from the Multicenter Morphometric Mammary Carcinoma Project. Hum Pathol. 1992 Jun;23(6):603–607. doi: 10.1016/0046-8177(92)90313-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]