Abstract
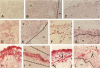
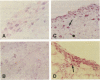
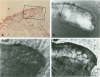
Tissue injury is followed by formation of a provisional, fibrin-containing matrix. It is later on replaced by granulation tissue. Replacement involves extracellular proteolysis by fibrinolytic enzymes. Plasmin is a fibrinolytic proteinase and is generated from ubiquitous plasminogen by cell-derived urokinase-type (uPA) or tissue-type (tPA) plasminogen activator. To explore the cells and components involved in plasminogen activation, we have performed a combined immunohistological and zymographic study on human skin wounds produced iatrogenically by debridement. The fibrin(ogen)-specific staining indicated the progressive removal of a fibrin-containing provisional matrix. Plasmin(ogen) was present over the entire observation period. It was diffusely distributed and also displayed a conspicuous association with cells of the granulation tissue, in particular with monocytes/macrophages and fibroblasts. Also, uPA was associated with monocytes/macrophages and fibroblasts, whereas the uPA-receptor (uPA-R) was stained in monocytes/macrophages only. The uPA was potentially active as indicated by zymography. No tPA-specific staining was found. The findings point at the importance of monocytes/macrophages and fibroblasts in uPA-mediated plasminogen activation in healing human skin wounds.
Full text
PDF











Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andreasen P. A., Georg B., Lund L. R., Riccio A., Stacey S. N. Plasminogen activator inhibitors: hormonally regulated serpins. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1990 Jan 2;68(1):1–19. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(90)90164-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bajpai A., Baker J. B. Cryptic urokinase binding sites on human foreskin fibroblasts. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Dec 17;133(2):475–482. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)90931-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bajpai A., Baker J. B. Urokinase binding sites on human foreskin cells. Evidence for occupancy with endogenous urokinase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Dec 31;133(3):994–1000. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)91234-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blasi F., Stoppelli M. P., Cubellis M. V. The receptor for urokinase-plasminogen activator. J Cell Biochem. 1986;32(3):179–186. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240320303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blasi F., Vassalli J. D., Danø K. Urokinase-type plasminogen activator: proenzyme, receptor, and inhibitors. J Cell Biol. 1987 Apr;104(4):801–804. doi: 10.1083/jcb.104.4.801. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown L. F., Lanir N., McDonagh J., Tognazzi K., Dvorak A. M., Dvorak H. F. Fibroblast migration in fibrin gel matrices. Am J Pathol. 1993 Jan;142(1):273–283. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman H. A., Jr, Vavrin Z., Hibbs J. B., Jr Macrophage fibrinolytic activity: identification of two pathways of plasmin formation by intact cells and of a plasminogen activator inhibitor. Cell. 1982 Mar;28(3):653–662. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90220-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen W. Y., Rogers A. A., Lydon M. J. Characterization of biologic properties of wound fluid collected during early stages of wound healing. J Invest Dermatol. 1992 Nov;99(5):559–564. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12667378. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collen D. Molecular mechanisms of fibrinolysis and their application to fibrin-specific thrombolytic therapy. J Cell Biochem. 1987 Feb;33(2):77–86. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240330202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danø K., Andreasen P. A., Grøndahl-Hansen J., Kristensen P., Nielsen L. S., Skriver L. Plasminogen activators, tissue degradation, and cancer. Adv Cancer Res. 1985;44:139–266. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60028-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dvorak H. F. Tumors: wounds that do not heal. Similarities between tumor stroma generation and wound healing. N Engl J Med. 1986 Dec 25;315(26):1650–1659. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198612253152606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis V., Behrendt N., Danø K. Plasminogen activation by receptor-bound urokinase. A kinetic study with both cell-associated and isolated receptor. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jul 5;266(19):12752–12758. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Estreicher A., Mühlhauser J., Carpentier J. L., Orci L., Vassalli J. D. The receptor for urokinase type plasminogen activator polarizes expression of the protease to the leading edge of migrating monocytes and promotes degradation of enzyme inhibitor complexes. J Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;111(2):783–792. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.2.783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felez J., Miles L. A., Plescia J., Plow E. F. Regulation of plasminogen receptor expression on human monocytes and monocytoid cell lines. J Cell Biol. 1990 Oct;111(4):1673–1683. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.4.1673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fibbi G., Ziche M., Morbidelli L., Magnelli L., Del Rosso M. Interaction of urokinase with specific receptors stimulates mobilization of bovine adrenal capillary endothelial cells. Exp Cell Res. 1988 Dec;179(2):385–395. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(88)90277-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gissler H. M., Frank R., Kramer M. D. Immunohistochemical characterization of the plasminogen activator system in psoriatic epidermis. Br J Dermatol. 1993 Jun;128(6):612–618. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.1993.tb00254.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granelli-Piperno A., Vassalli J. D., Reich E. Secretion of plasminogen activator by human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Modulation by glucocorticoids and other effectors. J Exp Med. 1977 Dec 1;146(6):1693–1706. doi: 10.1084/jem.146.6.1693. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grulich-Henn J., Müller-Berghaus G. The role of vascular endothelial cells in the regulation of fibrinolysis. Z Kardiol. 1989;78 (Suppl 6):25–29. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hajjar K. A., Harpel P. C., Jaffe E. A., Nachman R. L. Binding of plasminogen to cultured human endothelial cells. J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 5;261(25):11656–11662. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heiple J. M., Ossowski L. Human neutrophil plasminogen activator is localized in specific granules and is translocated to the cell surface by exocytosis. J Exp Med. 1986 Sep 1;164(3):826–840. doi: 10.1084/jem.164.3.826. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hekman C. M., Loskutoff D. J. Endothelial cells produce a latent inhibitor of plasminogen activators that can be activated by denaturants. J Biol Chem. 1985 Sep 25;260(21):11581–11587. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer M. D., Müller-Bardorff M., Simon M. M., Tilgen W., Schickel E., Petzoldt D. Measurement of free human leukocyte elastase and human leukocyte elastase/alpha 1 proteinase inhibitor complexes by an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. J Immunol Methods. 1990 Jul 20;131(1):41–48. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(90)90230-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laiho M., Keski-Oja J. Growth factors in the regulation of pericellular proteolysis: a review. Cancer Res. 1989 May 15;49(10):2533–2553. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer M. Biochemical and biological aspects of the plasminogen activation system. Clin Biochem. 1990 Jun;23(3):197–211. doi: 10.1016/0009-9120(90)90601-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meissauer A., Kramer M. D., Hofmann M., Erkell L. J., Jacob E., Schirrmacher V., Brunner G. Urokinase-type and tissue-type plasminogen activators are essential for in vitro invasion of human melanoma cells. Exp Cell Res. 1991 Feb;192(2):453–459. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(91)90064-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miles L. A., Levin E. G., Plescia J., Collen D., Plow E. F. Plasminogen receptors, urokinase receptors, and their modulation on human endothelial cells. Blood. 1988 Aug;72(2):628–635. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Min H. Y., Semnani R., Mizukami I. F., Watt K., Todd R. F., 3rd, Liu D. Y. cDNA for Mo3, a monocyte activation antigen, encodes the human receptor for urokinase plasminogen activator. J Immunol. 1992 Jun 1;148(11):3636–3642. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyashita C., Wenzel E., Heiden M. Plasminogen: a brief introduction into its biochemistry and function. Haemostasis. 1988;18 (Suppl 1):7–13. doi: 10.1159/000215824. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizukami I. F., Vinjamuri S. D., Perini F., Liu D. Y., Todd R. F., 3rd Purification, biochemical composition, and biosynthesis of the Mo3 activation antigen expressed on the plasma membrane of human mononuclear phagocytes. J Immunol. 1991 Aug 15;147(4):1331–1337. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizukami I. F., Vinjamuri S. D., Trochelman R. D., Todd R. F., 3rd A structural characterization of the Mo3 activation antigen expressed on the plasma membrane of human mononuclear phagocytes. J Immunol. 1990 Mar 1;144(5):1841–1848. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nykjaer A., Petersen C. M., Christensen E. I., Davidsen O., Gliemann J. Urokinase receptors in human monocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 May 22;1052(3):399–407. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(90)90149-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plow E. F., Freaney D. E., Plescia J., Miles L. A. The plasminogen system and cell surfaces: evidence for plasminogen and urokinase receptors on the same cell type. J Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;103(6 Pt 1):2411–2420. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.6.2411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rømer J., Lund L. R., Eriksen J., Ralfkiaer E., Zeheb R., Gelehrter T. D., Danø K., Kristensen P. Differential expression of urokinase-type plasminogen activator and its type-1 inhibitor during healing of mouse skin wounds. J Invest Dermatol. 1991 Nov;97(5):803–811. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12486833. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saksela O. Plasminogen activation and regulation of pericellular proteolysis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Nov 12;823(1):35–65. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(85)90014-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sappino A. P., Huarte J., Vassalli J. D., Belin D. Sites of synthesis of urokinase and tissue-type plasminogen activators in the murine kidney. J Clin Invest. 1991 Mar;87(3):962–970. doi: 10.1172/JCI115104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scully M. F. Plasminogen activator-dependent pericellular proteolysis. Br J Haematol. 1991 Dec;79(4):537–543. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1991.tb08078.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens R. W., Pöllänen J., Tapiovaara H., Leung K. C., Sim P. S., Salonen E. M., Rønne E., Behrendt N., Danø K., Vaheri A. Activation of pro-urokinase and plasminogen on human sarcoma cells: a proteolytic system with surface-bound reactants. J Cell Biol. 1989 May;108(5):1987–1995. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.5.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vassalli J. D., Belin D. Amiloride selectively inhibits the urokinase-type plasminogen activator. FEBS Lett. 1987 Apr 6;214(1):187–191. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80039-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vassalli J. D., Sappino A. P., Belin D. The plasminogen activator/plasmin system. J Clin Invest. 1991 Oct;88(4):1067–1072. doi: 10.1172/JCI115405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]