Abstract
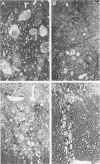
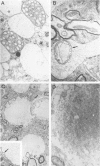
Transgenic mice expressing mutant Cu,Zn superoxide dismutase (SOD), containing a substitution of glycine at position 93 by alanine, develop disease prevalently affecting motor neurons. Light microscopical and ultrastructural studies reveal that the earliest pathological features are microvesiculation of large neurons of the anterior horns of the spinal cord. These vacuoles originate from dilation of rough endoplasmic reticulum and from degenerating mitochondria. At the end stage of the disease, the microvesicular pattern gives way to atrophic anterior horns showing severe neuronal depletion and hyaline, filamentous inclusions in some of the surviving neurons. Posterior horn neurons and dorsal root ganglia are not affected. With disease progression, moderate degeneration of anterior and lateral columns, severe degeneration of anterior roots, and mild degeneration in posterior columns and roots become apparent. This study shows that a mutation in SOD, known to occur in a percentage of familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis patients, may affect only selective neuronal populations, although SOD is a ubiquitous enzyme.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Avraham K. B., Schickler M., Sapoznikov D., Yarom R., Groner Y. Down's syndrome: abnormal neuromuscular junction in tongue of transgenic mice with elevated levels of human Cu/Zn-superoxide dismutase. Cell. 1988 Sep 9;54(6):823–829. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)91153-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Avraham K. B., Sugarman H., Rotshenker S., Groner Y. Down's syndrome: morphological remodelling and increased complexity in the neuromuscular junction of transgenic CuZn-superoxide dismutase mice. J Neurocytol. 1991 Mar;20(3):208–215. doi: 10.1007/BF01186993. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beckman J. S., Beckman T. W., Chen J., Marshall P. A., Freeman B. A. Apparent hydroxyl radical production by peroxynitrite: implications for endothelial injury from nitric oxide and superoxide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(4):1620–1624. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.4.1620. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beckman J. S., Carson M., Smith C. D., Koppenol W. H. ALS, SOD and peroxynitrite. Nature. 1993 Aug 12;364(6438):584–584. doi: 10.1038/364584a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowling A. C., Schulz J. B., Brown R. H., Jr, Beal M. F. Superoxide dismutase activity, oxidative damage, and mitochondrial energy metabolism in familial and sporadic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J Neurochem. 1993 Dec;61(6):2322–2325. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1993.tb07478.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deng H. X., Hentati A., Tainer J. A., Iqbal Z., Cayabyab A., Hung W. Y., Getzoff E. D., Hu P., Herzfeldt B., Roos R. P. Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and structural defects in Cu,Zn superoxide dismutase. Science. 1993 Aug 20;261(5124):1047–1051. doi: 10.1126/science.8351519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elroy-Stein O., Bernstein Y., Groner Y. Overproduction of human Cu/Zn-superoxide dismutase in transfected cells: extenuation of paraquat-mediated cytotoxicity and enhancement of lipid peroxidation. EMBO J. 1986 Mar;5(3):615–622. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04255.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein C. J., Avraham K. B., Lovett M., Smith S., Elroy-Stein O., Rotman G., Bry C., Groner Y. Transgenic mice with increased Cu/Zn-superoxide dismutase activity: animal model of dosage effects in Down syndrome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(22):8044–8048. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.22.8044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gavrieli Y., Sherman Y., Ben-Sasson S. A. Identification of programmed cell death in situ via specific labeling of nuclear DNA fragmentation. J Cell Biol. 1992 Nov;119(3):493–501. doi: 10.1083/jcb.119.3.493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gurney M. E., Pu H., Chiu A. Y., Dal Canto M. C., Polchow C. Y., Alexander D. D., Caliendo J., Hentati A., Kwon Y. W., Deng H. X. Motor neuron degeneration in mice that express a human Cu,Zn superoxide dismutase mutation. Science. 1994 Jun 17;264(5166):1772–1775. doi: 10.1126/science.8209258. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirano A., Kurland L. T., Sayre G. P. Familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. A subgroup characterized by posterior and spinocerebellar tract involvement and hyaline inclusions in the anterior horn cells. Arch Neurol. 1967 Mar;16(3):232–243. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1967.00470210008002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirano A., Nakano I., Kurland L. T., Mulder D. W., Holley P. W., Saccomanno G. Fine structural study of neurofibrillary changes in a family with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1984 Sep;43(5):471–480. doi: 10.1097/00005072-198409000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ischiropoulos H., Zhu L., Chen J., Tsai M., Martin J. C., Smith C. D., Beckman J. S. Peroxynitrite-mediated tyrosine nitration catalyzed by superoxide dismutase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1992 Nov 1;298(2):431–437. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(92)90431-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linnik M. D., Zobrist R. H., Hatfield M. D. Evidence supporting a role for programmed cell death in focal cerebral ischemia in rats. Stroke. 1993 Dec;24(12):2002–2009. doi: 10.1161/01.str.24.12.2002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milde L. N. Pathophysiology of ischemic brain injury. Crit Care Clin. 1989 Oct;5(4):729–753. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowicki J. P., Duval D., Poignet H., Scatton B. Nitric oxide mediates neuronal death after focal cerebral ischemia in the mouse. Eur J Pharmacol. 1991 Nov 12;204(3):339–340. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(91)90862-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scozzafava A., Viezzoli M. S. The role of the active site amino acid residues on the catalytic activity of Cu2Zn2SOD. Mol Chem Neuropathol. 1993 May-Jun;19(1-2):193–204. doi: 10.1007/BF03160179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siddique T. Molecular genetics of familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Adv Neurol. 1991;56:227–231. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tainer J. A., Getzoff E. D., Beem K. M., Richardson J. S., Richardson D. C. Determination and analysis of the 2 A-structure of copper, zinc superoxide dismutase. J Mol Biol. 1982 Sep 15;160(2):181–217. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90174-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyllie A. H., Kerr J. F., Currie A. R. Cell death: the significance of apoptosis. Int Rev Cytol. 1980;68:251–306. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)62312-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]