Abstract
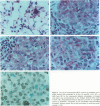
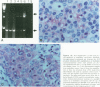
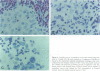
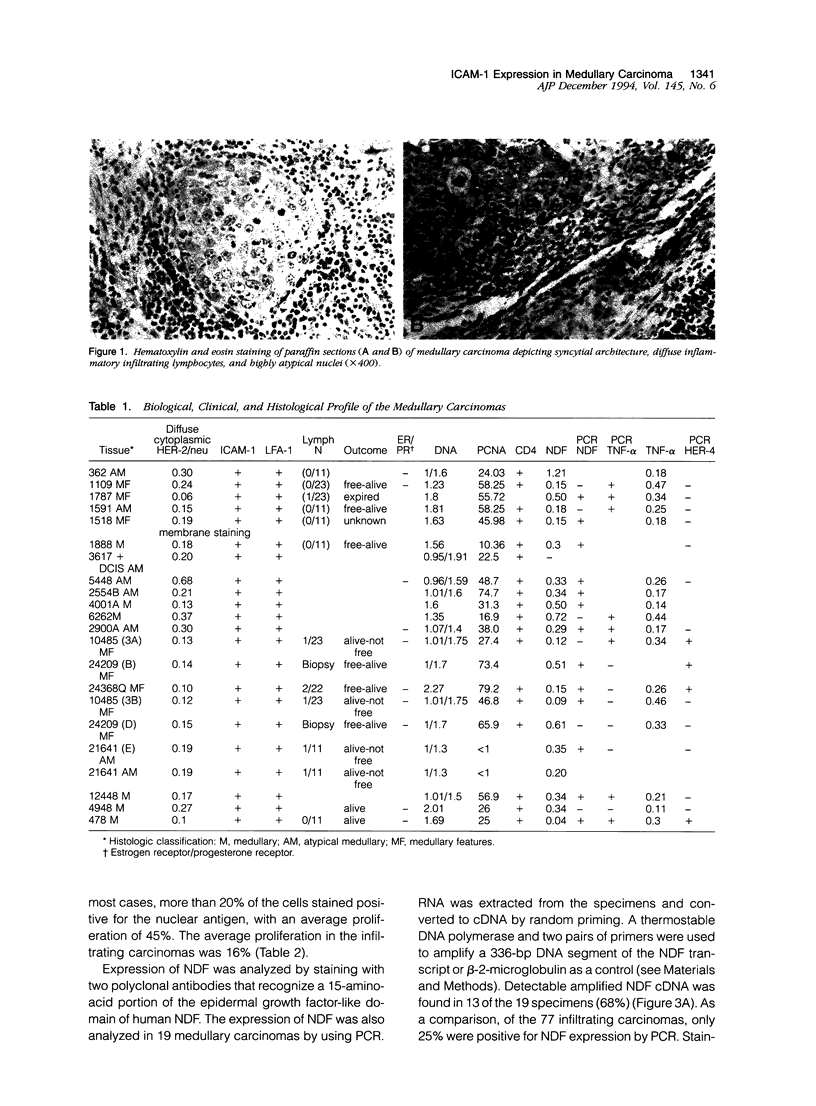
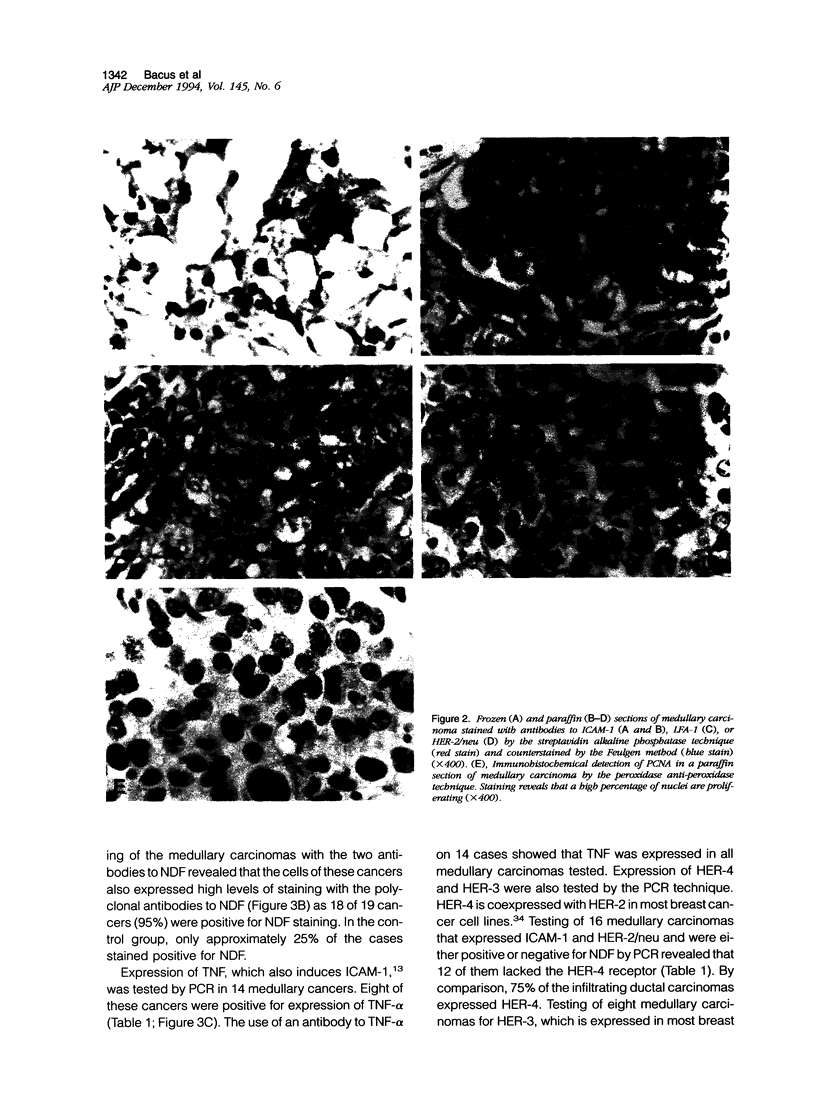
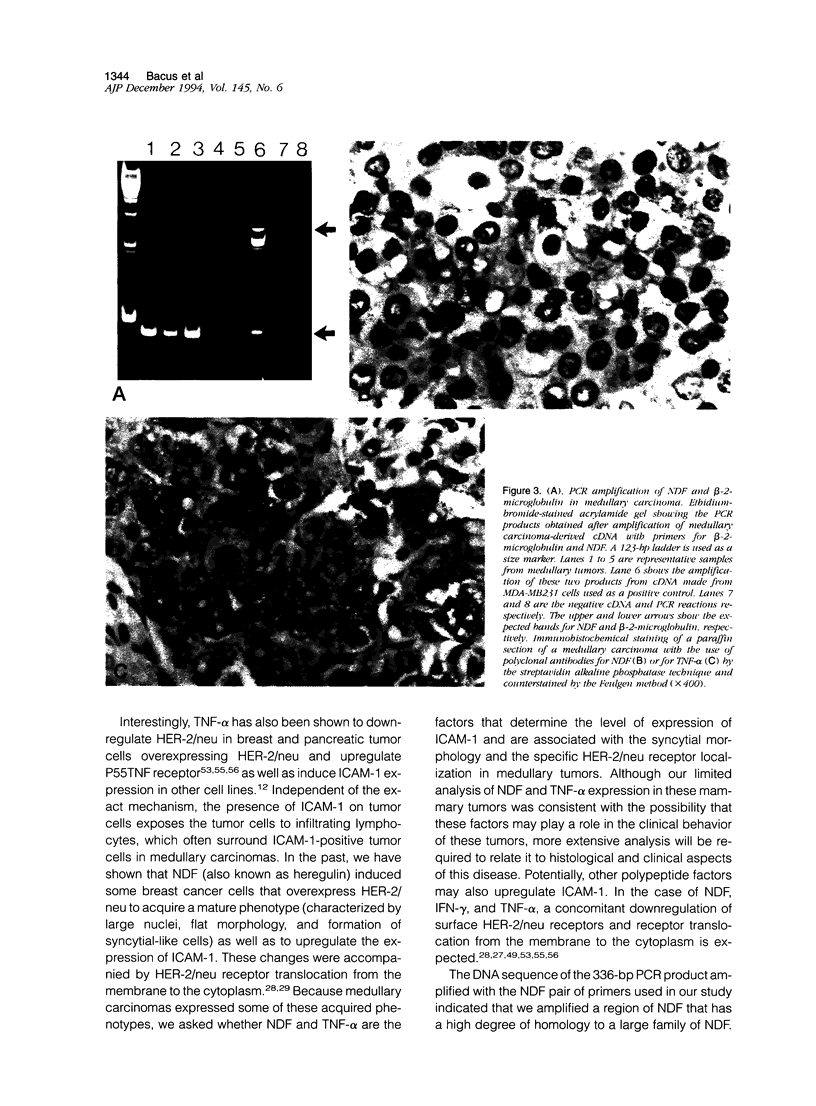
The histological hallmarks for the diagnosis of medullary breast cancer are circumscription, syncytial architecture, diffuse inflammatory infiltrate, and highly atypical nuclei. The biological and prognostic implication is a lower propensity to metastasize. We studied 19 medullary carcinomas for expression of the intercellular adhesion molecule-1 and lymphocyte-function-associated antigen-1, Neu differentiation factor, tumor necrosis factor-alpha, and the expression of HER-2/neu, HER-4, and HER-3 receptors. Our study revealed that all of the 19 medullary carcinomas expressed the intercellular adhesion molecule-1 and lymphocyte function associated antigen. Eighteen of 19 cancers expressed Neu differentiation factor and tumor necrosis factor-alpha. All medullary cancers expressed the HER-2/neu receptor, however, in the majority of the cases, the staining was confined to the cytoplasm. Only 4 of 12 cancers expressed HER-4 and none of the eight medullary cancers tested expressed HER-3. By comparison, in a control group of infiltrating ductal carcinomas, expression of intercellular adhesion molecule-1, lymphocyte function associated antigen-1, and Neu differentiation factor was positive in about 25 to 30% of the cases, HER-4 was expressed in 75% and HER-3 in 95% of the cases. Taken together, our observations suggest that the expression of intercellular adhesion molecule-1, lymphocyte function associated antigen, Neu differentiation factor, and tumor necrosis factor-alpha as factors that may affect the special morphology and the biological behavior that characterizes medullary carcinomas.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bacus S. S., Gudkov A. V., Zelnick C. R., Chin D., Stern R., Stancovski I., Peles E., Ben-Baruch N., Farbstein H., Lupu R. Neu differentiation factor (heregulin) induces expression of intercellular adhesion molecule 1: implications for mammary tumors. Cancer Res. 1993 Nov 1;53(21):5251–5261. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bacus S. S., Kiguchi K., Chin D., King C. R., Huberman E. Differentiation of cultured human breast cancer cells (AU-565 and MCF-7) associated with loss of cell surface HER-2/neu antigen. Mol Carcinog. 1990;3(6):350–362. doi: 10.1002/mc.2940030607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bacus S. S., Ruby S. G. Application of image analysis to the evaluation of cellular prognostic factors in breast carcinoma. Pathol Annu. 1993;28(Pt 1):179–204. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bacus S. S., Ruby S. G., Weinberg D. S., Chin D., Ortiz R., Bacus J. W. HER-2/neu oncogene expression and proliferation in breast cancers. Am J Pathol. 1990 Jul;137(1):103–111. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bacus S. S., Stancovski I., Huberman E., Chin D., Hurwitz E., Mills G. B., Ullrich A., Sela M., Yarden Y. Tumor-inhibitory monoclonal antibodies to the HER-2/Neu receptor induce differentiation of human breast cancer cells. Cancer Res. 1992 May 1;52(9):2580–2589. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bacus S., Flowers J. L., Press M. F., Bacus J. W., McCarty K. S., Jr The evaluation of estrogen receptor in primary breast carcinoma by computer-assisted image analysis. Am J Clin Pathol. 1988 Sep;90(3):233–239. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/90.3.233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bargmann C. I., Hung M. C., Weinberg R. A. Multiple independent activations of the neu oncogene by a point mutation altering the transmembrane domain of p185. Cell. 1986 Jun 6;45(5):649–657. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90779-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Ezra J., Sheibani K. Antigenic phenotype of the lymphocytic component of medullary carcinoma of the breast. Cancer. 1987 Jun 15;59(12):2037–2041. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19870615)59:12<2037::aid-cncr2820591212>3.0.co;2-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger M. S., Greenfield C., Gullick W. J., Haley J., Downward J., Neal D. E., Harris A. L., Waterfield M. D. Evaluation of epidermal growth factor receptors in bladder tumours. Br J Cancer. 1987 Nov;56(5):533–537. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1987.238. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom H. J., Richardson W. W., Field J. R. Host resistance and survival in carcinoma of breast: a study of 104 cases of medullary carcinoma in a series of 1,411 cases of breast cancer followed for 20 years. Br Med J. 1970 Jul 25;3(5716):181–188. doi: 10.1136/bmj.3.5716.181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braakman E., Goedegebuure P. S., Vreugdenhil R. J., Segal D. M., Shaw S., Bolhuis R. L. ICAM- melanoma cells are relatively resistant to CD3-mediated T-cell lysis. Int J Cancer. 1990 Sep 15;46(3):475–480. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910460325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bravo R. Synthesis of the nuclear protein cyclin (PCNA) and its relationship with DNA replication. Exp Cell Res. 1986 Apr;163(2):287–293. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(86)90059-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coussens L., Yang-Feng T. L., Liao Y. C., Chen E., Gray A., McGrath J., Seeburg P. H., Libermann T. A., Schlessinger J., Francke U. Tyrosine kinase receptor with extensive homology to EGF receptor shares chromosomal location with neu oncogene. Science. 1985 Dec 6;230(4730):1132–1139. doi: 10.1126/science.2999974. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Culouscou J. M., Plowman G. D., Carlton G. W., Green J. M., Shoyab M. Characterization of a breast cancer cell differentiation factor that specifically activates the HER4/p180erbB4 receptor. J Biol Chem. 1993 Sep 5;268(25):18407–18410. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fady C., Gardner A. M., Gera J. F., Lichtenstein A. Interferon-induced increase in sensitivity of ovarian cancer targets to lysis by lymphokine-activated killer cells: selective effects on HER2/neu-overexpressing cells. Cancer Res. 1992 Feb 15;52(4):764–769. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falls D. L., Rosen K. M., Corfas G., Lane W. S., Fischbach G. D. ARIA, a protein that stimulates acetylcholine receptor synthesis, is a member of the neu ligand family. Cell. 1993 Mar 12;72(5):801–815. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90407-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaffey M. J., Frierson H. F., Jr, Mills S. E., Boyd J. C., Zarbo R. J., Simpson J. F., Gross L. K., Weiss L. M. Medullary carcinoma of the breast. Identification of lymphocyte subpopulations and their significance. Mod Pathol. 1993 Nov;6(6):721–728. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gong Y. Z., Zwarych P. P., Jr, Lin M. C., Wilson F. A. Effect of antiserum to a 99 kDa polypeptide on the uptake of taurocholic acid by rat ileal brush border membrane vesicles. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Aug 30;179(1):204–209. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)91355-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes W. E., Sliwkowski M. X., Akita R. W., Henzel W. J., Lee J., Park J. W., Yansura D., Abadi N., Raab H., Lewis G. D. Identification of heregulin, a specific activator of p185erbB2. Science. 1992 May 22;256(5060):1205–1210. doi: 10.1126/science.256.5060.1205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hudziak R. M., Lewis G. D., Shalaby M. R., Eessalu T. E., Aggarwal B. B., Ullrich A., Shepard H. M. Amplified expression of the HER2/ERBB2 oncogene induces resistance to tumor necrosis factor alpha in NIH 3T3 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(14):5102–5106. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.14.5102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson J. P., Stade B. G., Holzmann B., Schwäble W., Riethmüller G. De novo expression of intercellular-adhesion molecule 1 in melanoma correlates with increased risk of metastasis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jan;86(2):641–644. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.2.641. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalthoff H., Roeder C., Gieseking J., Humburg I., Schmiegel W. Inverse regulation of human ERBB2 and epidermal growth factor receptors by tumor necrosis factor alpha. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Oct 1;90(19):8972–8976. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.19.8972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kokai Y., Myers J. N., Wada T., Brown V. I., LeVea C. M., Davis J. G., Dobashi K., Greene M. I. Synergistic interaction of p185c-neu and the EGF receptor leads to transformation of rodent fibroblasts. Cell. 1989 Jul 28;58(2):287–292. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90843-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraus M. H., Issing W., Miki T., Popescu N. C., Aaronson S. A. Isolation and characterization of ERBB3, a third member of the ERBB/epidermal growth factor receptor family: evidence for overexpression in a subset of human mammary tumors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(23):9193–9197. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.23.9193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraus M. H., Popescu N. C., Amsbaugh S. C., King C. R. Overexpression of the EGF receptor-related proto-oncogene erbB-2 in human mammary tumor cell lines by different molecular mechanisms. EMBO J. 1987 Mar;6(3):605–610. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04797.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurki P., Ogata K., Tan E. M. Monoclonal antibodies to proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA)/cyclin as probes for proliferating cells by immunofluorescence microscopy and flow cytometry. J Immunol Methods. 1988 Apr 22;109(1):49–59. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(88)90441-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makgoba M. W., Sanders M. E., Ginther Luce G. E., Dustin M. L., Springer T. A., Clark E. A., Mannoni P., Shaw S. ICAM-1 a ligand for LFA-1-dependent adhesion of B, T and myeloid cells. Nature. 1988 Jan 7;331(6151):86–88. doi: 10.1038/331086a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marth C., Cronauer M. V., Doppler W., Ofner D., Ullrich A., Daxenbichler G. Effects of interferons on the expression of the proto-oncogene HER-2 in human ovarian carcinoma cells. Int J Cancer. 1992 Jan 2;50(1):64–68. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910500114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naganuma H., Kiessling R., Patarroyo M., Hansson M., Handgretinger R., Grönberg A. Increased susceptibility of IFN-gamma-treated neuroblastoma cells to lysis by lymphokine-activated killer cells: participation of ICAM-1 induction on target cells. Int J Cancer. 1991 Feb 20;47(4):527–532. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910470410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noonan K. E., Beck C., Holzmayer T. A., Chin J. E., Wunder J. S., Andrulis I. L., Gazdar A. F., Willman C. L., Griffith B., Von Hoff D. D. Quantitative analysis of MDR1 (multidrug resistance) gene expression in human tumors by polymerase chain reaction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Sep;87(18):7160–7164. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.18.7160. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peles E., Bacus S. S., Koski R. A., Lu H. S., Wen D., Ogden S. G., Levy R. B., Yarden Y. Isolation of the neu/HER-2 stimulatory ligand: a 44 kd glycoprotein that induces differentiation of mammary tumor cells. Cell. 1992 Apr 3;69(1):205–216. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90131-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peles E., Ben-Levy R., Tzahar E., Liu N., Wen D., Yarden Y. Cell-type specific interaction of Neu differentiation factor (NDF/heregulin) with Neu/HER-2 suggests complex ligand-receptor relationships. EMBO J. 1993 Mar;12(3):961–971. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05737.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plowman G. D., Culouscou J. M., Whitney G. S., Green J. M., Carlton G. W., Foy L., Neubauer M. G., Shoyab M. Ligand-specific activation of HER4/p180erbB4, a fourth member of the epidermal growth factor receptor family. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Mar 1;90(5):1746–1750. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.5.1746. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plowman G. D., Green J. M., Culouscou J. M., Carlton G. W., Rothwell V. M., Buckley S. Heregulin induces tyrosine phosphorylation of HER4/p180erbB4. Nature. 1993 Dec 2;366(6454):473–475. doi: 10.1038/366473a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RICHARDSON W. W. Medullary carcinoma of the breast; a distinctive tumour type with a relatively good prognosis following radical mastectomy. Br J Cancer. 1956 Sep;10(3):415–423. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1956.48. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapin V., Contesso G., Mouriesse H., Bertin F., Lacombe M. J., Piekarski J. D., Travagli J. P., Gadenne C., Friedman S. Medullary breast carcinoma. A reevaluation of 95 cases of breast cancer with inflammatory stroma. Cancer. 1988 Jun 15;61(12):2503–2510. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19880615)61:12<2503::aid-cncr2820611219>3.0.co;2-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ridolfi R. L., Rosen P. P., Port A., Kinne D., Miké V. Medullary carcinoma of the breast: a clinicopathologic study with 10 year follow-up. Cancer. 1977 Oct;40(4):1365–1385. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197710)40:4<1365::aid-cncr2820400402>3.0.co;2-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothlein R., Czajkowski M., O'Neill M. M., Marlin S. D., Mainolfi E., Merluzzi V. J. Induction of intercellular adhesion molecule 1 on primary and continuous cell lines by pro-inflammatory cytokines. Regulation by pharmacologic agents and neutralizing antibodies. J Immunol. 1988 Sep 1;141(5):1665–1669. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shah N. M., Marchionni M. A., Isaacs I., Stroobant P., Anderson D. J. Glial growth factor restricts mammalian neural crest stem cells to a glial fate. Cell. 1994 May 6;77(3):349–360. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90150-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmons D., Makgoba M. W., Seed B. ICAM, an adhesion ligand of LFA-1, is homologous to the neural cell adhesion molecule NCAM. Nature. 1988 Feb 18;331(6157):624–627. doi: 10.1038/331624a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slamon D. J., Clark G. M., Wong S. G., Levin W. J., Ullrich A., McGuire W. L. Human breast cancer: correlation of relapse and survival with amplification of the HER-2/neu oncogene. Science. 1987 Jan 9;235(4785):177–182. doi: 10.1126/science.3798106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stancovski I., Hurwitz E., Leitner O., Ullrich A., Yarden Y., Sela M. Mechanistic aspects of the opposing effects of monoclonal antibodies to the ERBB2 receptor on tumor growth. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 1;88(19):8691–8695. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.19.8691. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varley J. M., Swallow J. E., Brammar W. J., Whittaker J. L., Walker R. A. Alterations to either c-erbB-2(neu) or c-myc proto-oncogenes in breast carcinomas correlate with poor short-term prognosis. Oncogene. 1987;1(4):423–430. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venter D. J., Tuzi N. L., Kumar S., Gullick W. J. Overexpression of the c-erbB-2 oncoprotein in human breast carcinomas: immunohistological assessment correlates with gene amplification. Lancet. 1987 Jul 11;2(8550):69–72. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)92736-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogetseder W., Feichtinger H., Schulz T. F., Schwaeble W., Tabaczewski P., Mitterer M., Böck G., Marth C., Dapunt O., Mikuz G. Expression of 7F7-antigen, a human adhesion molecule identical to intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1) in human carcinomas and their stromal fibroblasts. Int J Cancer. 1989 May 15;43(5):768–773. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910430504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wen D., Peles E., Cupples R., Suggs S. V., Bacus S. S., Luo Y., Trail G., Hu S., Silbiger S. M., Levy R. B. Neu differentiation factor: a transmembrane glycoprotein containing an EGF domain and an immunoglobulin homology unit. Cell. 1992 May 1;69(3):559–572. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90456-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto T., Ikawa S., Akiyama T., Semba K., Nomura N., Miyajima N., Saito T., Toyoshima K. Similarity of protein encoded by the human c-erb-B-2 gene to epidermal growth factor receptor. Nature. 1986 Jan 16;319(6050):230–234. doi: 10.1038/319230a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yarden Y., Weinberg R. A. Experimental approaches to hypothetical hormones: detection of a candidate ligand of the neu protooncogene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(9):3179–3183. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.9.3179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou D., Battifora H., Yokota J., Yamamoto T., Cline M. J. Association of multiple copies of the c-erbB-2 oncogene with spread of breast cancer. Cancer Res. 1987 Nov 15;47(22):6123–6125. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van de Vijver M., van de Bersselaar R., Devilee P., Cornelisse C., Peterse J., Nusse R. Amplification of the neu (c-erbB-2) oncogene in human mammmary tumors is relatively frequent and is often accompanied by amplification of the linked c-erbA oncogene. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 May;7(5):2019–2023. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.5.2019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]