Abstract
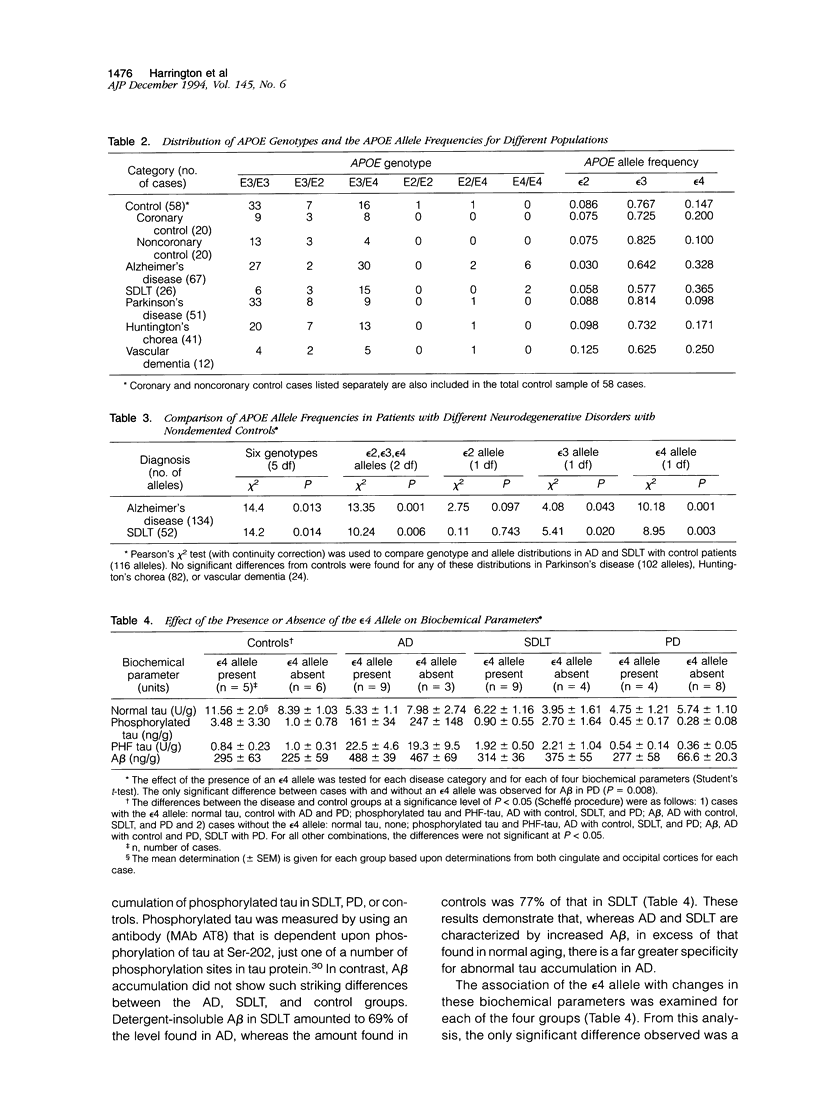
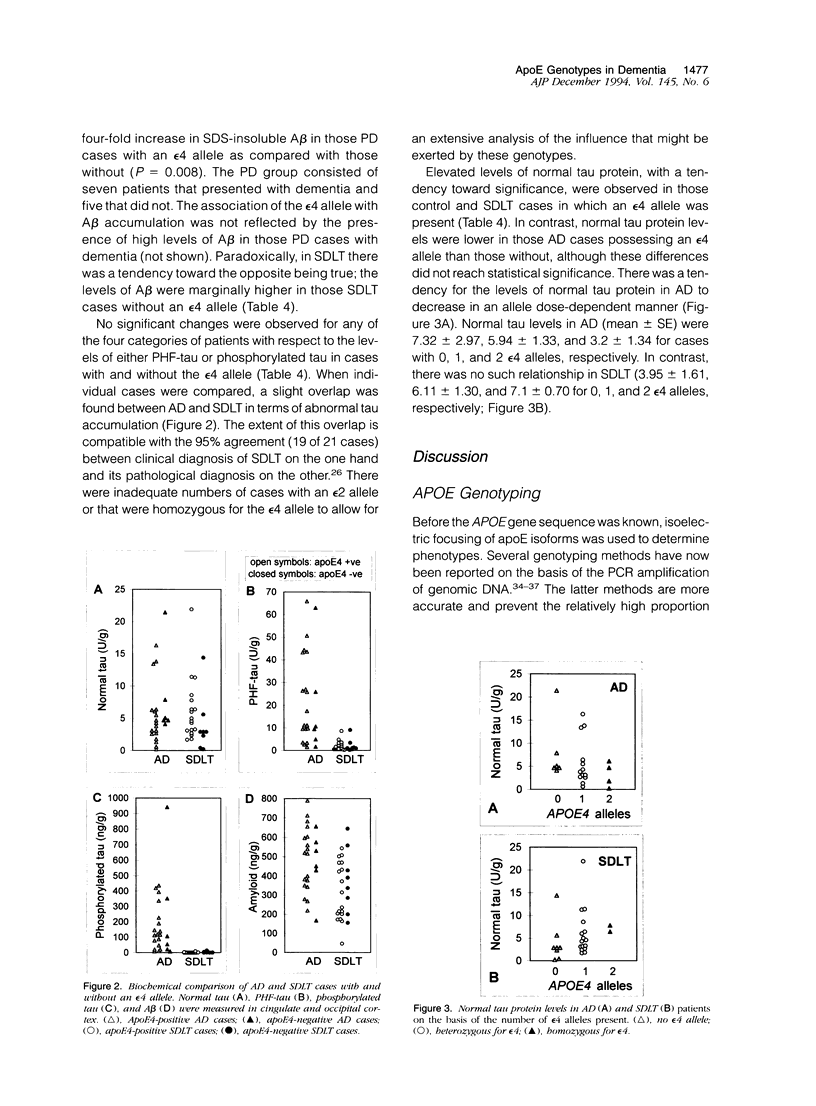
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is associated with an increased frequency of the apolipoprotein E type epsilon 4 allele. To address both the disease and the allele specificity of this association, we have examined the apolipoprotein E allele distribution in 255 elderly persons including those with autopsy-confirmed AD, senile dementia of the Lewy body type (SDLT), vascular dementia, Parkinson's disease (PD) or Huntington's disease and in nondemented controls either with or without coronary complications. The epsilon 4 allele frequency was increased in SDLT (0.365) and AD (0.328) as compared with controls (0.147), PD (0.098), or Huntington's chorea (0.171). Coronary disease and vascular dementia were associated with marginally higher epsilon 4 allele frequencies than in controls. In PD, amyloid beta-protein accumulated to a greater extent in those cases possessing an epsilon 4 allele than in those without. Those PD cases with dementia were not distinguished from either controls or PD cases without dementia, whether tested biochemically or by apolipoprotein E genotype. It is the comparison of the results in AD and SDLT that yielded the most significant findings. There was a 1.8-fold excess of amyloid beta-protein in AD as compared with controls, and the levels in SDLT were intermediate between those in AD and controls. In contrast, AD was discriminated from both controls and SDLT by the substantial accumulation of paired helical filament tau and phosphorylated tau (both increased more than 20-fold as compared with controls). SDLT was nevertheless characterized by an increased epsilon 4 allele frequency in the absence of significant tau pathology (at least 10-fold less than that in AD). These findings indicate that tau processing is more specifically associated with AD than is amyloid beta-protein accumulation and that presence of the epsilon 4 allele is not an etiological factor that accounts for tau pathology.
Full text
PDF










Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adlercreutz H., Markkanen H., Watanabe S. Plasma concentrations of phyto-oestrogens in Japanese men. Lancet. 1993 Nov 13;342(8881):1209–1210. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(93)92188-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashall F., Goate A. M. Role of the beta-amyloid precursor protein in Alzheimer's disease. Trends Biochem Sci. 1994 Jan;19(1):42–46. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(94)90173-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brousseau T., Legrain S., Berr C., Gourlet V., Vidal O., Amouyel P. Confirmation of the epsilon 4 allele of the apolipoprotein E gene as a risk factor for late-onset Alzheimer's disease. Neurology. 1994 Feb;44(2):342–344. doi: 10.1212/wnl.44.2.342. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cauley J. A., Eichner J. E., Kamboh M. I., Ferrell R. E., Kuller L. H. Apo E allele frequencies in younger (age 42-50) vs older (age 65-90) women. Genet Epidemiol. 1993;10(1):27–34. doi: 10.1002/gepi.1370100104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chartier-Harlin M. C., Parfitt M., Legrain S., Pérez-Tur J., Brousseau T., Evans A., Berr C., Vidal O., Roques P., Gourlet V. Apolipoprotein E, epsilon 4 allele as a major risk factor for sporadic early and late-onset forms of Alzheimer's disease: analysis of the 19q13.2 chromosomal region. Hum Mol Genet. 1994 Apr;3(4):569–574. doi: 10.1093/hmg/3.4.569. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corder E. H., Saunders A. M., Risch N. J., Strittmatter W. J., Schmechel D. E., Gaskell P. C., Jr, Rimmler J. B., Locke P. A., Conneally P. M., Schmader K. E. Protective effect of apolipoprotein E type 2 allele for late onset Alzheimer disease. Nat Genet. 1994 Jun;7(2):180–184. doi: 10.1038/ng0694-180. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corder E. H., Saunders A. M., Strittmatter W. J., Schmechel D. E., Gaskell P. C., Small G. W., Roses A. D., Haines J. L., Pericak-Vance M. A. Gene dose of apolipoprotein E type 4 allele and the risk of Alzheimer's disease in late onset families. Science. 1993 Aug 13;261(5123):921–923. doi: 10.1126/science.8346443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cumming A. M., Robertson F. W. Polymorphism at the apoprotein-E locus in relation to risk of coronary disease. Clin Genet. 1984 Apr;25(4):310–313. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1984.tb01995.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czech C., Mönning V., Tienari P. J., Hartmann T., Masters C., Beyreuther K., Förstl H. Apolipoprotein E-epsilon 4 allele and Alzheimer's disease. Lancet. 1993 Nov 20;342(8882):1309–1309. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davignon J., Gregg R. E., Sing C. F. Apolipoprotein E polymorphism and atherosclerosis. Arteriosclerosis. 1988 Jan-Feb;8(1):1–21. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.8.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickson D. W., Crystal H., Mattiace L. A., Kress Y., Schwagerl A., Ksiezak-Reding H., Davies P., Yen S. H. Diffuse Lewy body disease: light and electron microscopic immunocytochemistry of senile plaques. Acta Neuropathol. 1989;78(6):572–584. doi: 10.1007/BF00691284. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diedrich J. F., Minnigan H., Carp R. I., Whitaker J. N., Race R., Frey W., 2nd, Haase A. T. Neuropathological changes in scrapie and Alzheimer's disease are associated with increased expression of apolipoprotein E and cathepsin D in astrocytes. J Virol. 1991 Sep;65(9):4759–4768. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.9.4759-4768.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eichner J. E., Kuller L. H., Orchard T. J., Grandits G. A., McCallum L. M., Ferrell R. E., Neaton J. D. Relation of apolipoprotein E phenotype to myocardial infarction and mortality from coronary artery disease. Am J Cardiol. 1993 Jan 15;71(2):160–165. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(93)90732-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emi M., Wu L. L., Robertson M. A., Myers R. L., Hegele R. A., Williams R. R., White R., Lalouel J. M. Genotyping and sequence analysis of apolipoprotein E isoforms. Genomics. 1988 Nov;3(4):373–379. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(88)90130-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eto M., Watanabe K., Makino I. Increased frequencies of apolipoprotein epsilon 2 and epsilon 4 alleles in patients with ischemic heart disease. Clin Genet. 1989 Sep;36(3):183–188. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1989.tb03186.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gentleman S. M., Williams B., Royston M. C., Jagoe R., Clinton J., Perry R. H., Ince P. G., Allsop D., Polak J. M., Roberts G. W. Quantification of beta A4 protein deposition in the medial temporal lobe: a comparison of Alzheimer's disease and senile dementia of the Lewy body type. Neurosci Lett. 1992 Aug 3;142(1):9–12. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(92)90608-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goedert M., Jakes R., Crowther R. A., Six J., Lübke U., Vandermeeren M., Cras P., Trojanowski J. Q., Lee V. M. The abnormal phosphorylation of tau protein at Ser-202 in Alzheimer disease recapitulates phosphorylation during development. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jun 1;90(11):5066–5070. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.11.5066. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hallman D. M., Boerwinkle E., Saha N., Sandholzer C., Menzel H. J., Csázár A., Utermann G. The apolipoprotein E polymorphism: a comparison of allele frequencies and effects in nine populations. Am J Hum Genet. 1991 Aug;49(2):338–349. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handelmann G. E., Boyles J. K., Weisgraber K. H., Mahley R. W., Pitas R. E. Effects of apolipoprotein E, beta-very low density lipoproteins, and cholesterol on the extension of neurites by rabbit dorsal root ganglion neurons in vitro. J Lipid Res. 1992 Nov;33(11):1677–1688. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen L., Salmon D., Galasko D., Masliah E., Katzman R., DeTeresa R., Thal L., Pay M. M., Hofstetter R., Klauber M. The Lewy body variant of Alzheimer's disease: a clinical and pathologic entity. Neurology. 1990 Jan;40(1):1–8. doi: 10.1212/wnl.40.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardy J., Crook R., Perry R., Raghavan R., Roberts G. ApoE genotype and Down's syndrome. Lancet. 1994 Apr 16;343(8903):979–980. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(94)90106-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrington C. R., Mukaetova-Ladinska E. B., Hills R., Edwards P. C., Montejo de Garcini E., Novak M., Wischik C. M. Measurement of distinct immunochemical presentations of tau protein in Alzheimer disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 1;88(13):5842–5846. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.13.5842. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrington C. R., Perry R. H., Perry E. K., Hurt J., McKeith I. G., Roth M., Wischik C. M. Senile dementia of Lewy body type and Alzheimer type are biochemically distinct in terms of paired helical filaments and hyperphosphorylated tau protein. Dementia. 1994 Sep-Oct;5(5):215–228. doi: 10.1159/000106727. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hixson J. E., Vernier D. T. Restriction isotyping of human apolipoprotein E by gene amplification and cleavage with HhaI. J Lipid Res. 1990 Mar;31(3):545–548. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes A. J., Daniel S. E., Kilford L., Lees A. J. Accuracy of clinical diagnosis of idiopathic Parkinson's disease: a clinico-pathological study of 100 cases. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1992 Mar;55(3):181–184. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.55.3.181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kida E., Golabek A. A., Wisniewski T., Wisniewski K. E. Regional differences in apolipoprotein E immunoreactivity in diffuse plaques in Alzheimer's disease brain. Neurosci Lett. 1994 Feb 14;167(1-2):73–76. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(94)91030-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kontula K., Aalto-Setälä K., Kuusi T., Hämäläinen L., Syvänen A. C. Apolipoprotein E polymorphism determined by restriction enzyme analysis of DNA amplified by polymerase chain reaction: convenient alternative to phenotyping by isoelectric focusing. Clin Chem. 1990 Dec;36(12):2087–2092. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuusi T., Nieminen M. S., Ehnholm C., Yki-Järvinen H., Valle M., Nikkilä E. A., Taskinen M. R. Apoprotein E polymorphism and coronary artery disease. Increased prevalence of apolipoprotein E-4 in angiographically verified coronary patients. Arteriosclerosis. 1989 Mar-Apr;9(2):237–241. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.9.2.237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lannfelt L., Lilius L., Nastase M., Viitanen M., Fratiglioni L., Eggertsen G., Berglund L., Angelin B., Linder J., Winblad B. Lack of association between apolipoprotein E allele epsilon 4 and sporadic Alzheimer's disease. Neurosci Lett. 1994 Mar 14;169(1-2):175–178. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(94)90384-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lennox G., Lowe J., Morrell K., Landon M., Mayer R. J. Anti-ubiquitin immunocytochemistry is more sensitive than conventional techniques in the detection of diffuse Lewy body disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1989 Jan;52(1):67–71. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.52.1.67. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liddell M., Williams J., Bayer A., Kaiser F., Owen M. Confirmation of association between the e4 allele of apolipoprotein E and Alzheimer's disease. J Med Genet. 1994 Mar;31(3):197–200. doi: 10.1136/jmg.31.3.197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahley R. W. Apolipoprotein E: cholesterol transport protein with expanding role in cell biology. Science. 1988 Apr 29;240(4852):622–630. doi: 10.1126/science.3283935. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayeux R., Stern Y., Ottman R., Tatemichi T. K., Tang M. X., Maestre G., Ngai C., Tycko B., Ginsberg H. The apolipoprotein epsilon 4 allele in patients with Alzheimer's disease. Ann Neurol. 1993 Nov;34(5):752–754. doi: 10.1002/ana.410340527. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKeith I. G., Perry R. H., Fairbairn A. F., Jabeen S., Perry E. K. Operational criteria for senile dementia of Lewy body type (SDLT). Psychol Med. 1992 Nov;22(4):911–922. doi: 10.1017/s0033291700038484. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKhann G., Drachman D., Folstein M., Katzman R., Price D., Stadlan E. M. Clinical diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease: report of the NINCDS-ADRDA Work Group under the auspices of Department of Health and Human Services Task Force on Alzheimer's Disease. Neurology. 1984 Jul;34(7):939–944. doi: 10.1212/wnl.34.7.939. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menzel H. J., Kladetzky R. G., Assmann G. Apolipoprotein E polymorphism and coronary artery disease. Arteriosclerosis. 1983 Jul-Aug;3(4):310–315. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.3.4.310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mukaetova-Ladinska E. B., Harrington C. R., Roth M., Wischik C. M. Biochemical and anatomical redistribution of tau protein in Alzheimer's disease. Am J Pathol. 1993 Aug;143(2):565–578. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Namba Y., Tomonaga M., Kawasaki H., Otomo E., Ikeda K. Apolipoprotein E immunoreactivity in cerebral amyloid deposits and neurofibrillary tangles in Alzheimer's disease and kuru plaque amyloid in Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Brain Res. 1991 Feb 8;541(1):163–166. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(91)91092-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan B. P., Bellosta S., Sanan D. A., Weisgraber K. H., Mahley R. W., Pitas R. E. Differential effects of apolipoproteins E3 and E4 on neuronal growth in vitro. Science. 1994 May 6;264(5160):850–852. doi: 10.1126/science.8171342. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noguchi S., Murakami K., Yamada N. Apolipoprotein E genotype and Alzheimer's disease. Lancet. 1993 Sep 18;342(8873):737–737. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(93)91728-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novak M., Kabat J., Wischik C. M. Molecular characterization of the minimal protease resistant tau unit of the Alzheimer's disease paired helical filament. EMBO J. 1993 Jan;12(1):365–370. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05665.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peacock M. L., Fink J. K. ApoE epsilon 4 allelic association with Alzheimer's disease: independent confirmation using denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis. Neurology. 1994 Feb;44(2):339–341. doi: 10.1212/wnl.44.2.339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry R. H., Irving D., Blessed G., Fairbairn A., Perry E. K. Senile dementia of Lewy body type. A clinically and neuropathologically distinct form of Lewy body dementia in the elderly. J Neurol Sci. 1990 Feb;95(2):119–139. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(90)90236-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pickering-Brown S. M., Mann D. M., Bourke J. P., Roberts D. A., Balderson D., Burns A., Byrne J., Owen F. Apolipoprotein E4 and Alzheimer's disease pathology in Lewy body disease and in other beta-amyloid-forming diseases. Lancet. 1994 May 7;343(8906):1155–1155. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(94)90257-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poirier J., Davignon J., Bouthillier D., Kogan S., Bertrand P., Gauthier S. Apolipoprotein E polymorphism and Alzheimer's disease. Lancet. 1993 Sep 18;342(8873):697–699. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(93)91705-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poirier J., Hess M., May P. C., Finch C. E. Astrocytic apolipoprotein E mRNA and GFAP mRNA in hippocampus after entorhinal cortex lesioning. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 1991 Sep;11(2):97–106. doi: 10.1016/0169-328x(91)90111-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollanen M. S., Dickson D. W., Bergeron C. Pathology and biology of the Lewy body. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1993 May;52(3):183–191. doi: 10.1097/00005072-199305000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rebeck G. W., Reiter J. S., Strickland D. K., Hyman B. T. Apolipoprotein E in sporadic Alzheimer's disease: allelic variation and receptor interactions. Neuron. 1993 Oct;11(4):575–580. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(93)90070-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saunders A. M., Schmader K., Breitner J. C., Benson M. D., Brown W. T., Goldfarb L., Goldgaber D., Manwaring M. G., Szymanski M. H., McCown N. Apolipoprotein E epsilon 4 allele distributions in late-onset Alzheimer's disease and in other amyloid-forming diseases. Lancet. 1993 Sep 18;342(8873):710–711. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(93)91709-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saunders A. M., Strittmatter W. J., Schmechel D., George-Hyslop P. H., Pericak-Vance M. A., Joo S. H., Rosi B. L., Gusella J. F., Crapper-MacLachlan D. R., Alberts M. J. Association of apolipoprotein E allele epsilon 4 with late-onset familial and sporadic Alzheimer's disease. Neurology. 1993 Aug;43(8):1467–1472. doi: 10.1212/wnl.43.8.1467. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmechel D. E., Saunders A. M., Strittmatter W. J., Crain B. J., Hulette C. M., Joo S. H., Pericak-Vance M. A., Goldgaber D., Roses A. D. Increased amyloid beta-peptide deposition in cerebral cortex as a consequence of apolipoprotein E genotype in late-onset Alzheimer disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Oct 15;90(20):9649–9653. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.20.9649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schächter F., Faure-Delanef L., Guénot F., Rouger H., Froguel P., Lesueur-Ginot L., Cohen D. Genetic associations with human longevity at the APOE and ACE loci. Nat Genet. 1994 Jan;6(1):29–32. doi: 10.1038/ng0194-29. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selkoe D. J. Normal and abnormal biology of the beta-amyloid precursor protein. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1994;17:489–517. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.17.030194.002421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- St George-Hyslop P., McLachlan D. C., Tsuda T., Rogaev E., Karlinsky H., Lippa C. F., Pollen D., Tuda T. Alzheimer's disease and possible gene interaction. Science. 1994 Jan 28;263(5146):537–537. doi: 10.1126/science.8290965. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strittmatter W. J., Saunders A. M., Schmechel D., Pericak-Vance M., Enghild J., Salvesen G. S., Roses A. D. Apolipoprotein E: high-avidity binding to beta-amyloid and increased frequency of type 4 allele in late-onset familial Alzheimer disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Mar 1;90(5):1977–1981. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.5.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strittmatter W. J., Weisgraber K. H., Goedert M., Saunders A. M., Huang D., Corder E. H., Dong L. M., Jakes R., Alberts M. J., Gilbert J. R. Hypothesis: microtubule instability and paired helical filament formation in the Alzheimer disease brain are related to apolipoprotein E genotype. Exp Neurol. 1994 Feb;125(2):163–174. doi: 10.1006/exnr.1994.1019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strittmatter W. J., Weisgraber K. H., Huang D. Y., Dong L. M., Salvesen G. S., Pericak-Vance M., Schmechel D., Saunders A. M., Goldgaber D., Roses A. D. Binding of human apolipoprotein E to synthetic amyloid beta peptide: isoform-specific effects and implications for late-onset Alzheimer disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Sep 1;90(17):8098–8102. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.17.8098. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talbot C., Lendon C., Craddock N., Shears S., Morris J. C., Goate A. Protection against Alzheimer's disease with apoE epsilon 2. Lancet. 1994 Jun 4;343(8910):1432–1433. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(94)92557-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai M. S., Tangalos E. G., Petersen R. C., Smith G. E., Schaid D. J., Kokmen E., Ivnik R. J., Thibodeau S. N. Apolipoprotein E: risk factor for Alzheimer disease. Am J Hum Genet. 1994 Apr;54(4):643–649. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueki A., Kawano M., Namba Y., Kawakami M., Ikeda K. A high frequency of apolipoprotein E4 isoprotein in Japanese patients with late-onset nonfamilial Alzheimer's disease. Neurosci Lett. 1993 Dec 12;163(2):166–168. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(93)90373-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Broeckhoven C., Backhovens H., Cruts M., Martin J. J., Crook R., Houlden H., Hardy J. APOE genotype does not modulate age of onset in families with chromosome 14 encoded Alzheimer's disease. Neurosci Lett. 1994 Mar 14;169(1-2):179–180. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(94)90385-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace D. C. Mitochondrial genetics: a paradigm for aging and degenerative diseases? Science. 1992 May 1;256(5057):628–632. doi: 10.1126/science.1533953. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waring S. C., O'Brien P. C., Kurland L. T., Thibodeau S. N., Tsai M. S., Petersen R. C., Esteban-Santillan C. E. Apolipoprotein E allele in Chamorros with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis/parkinsonism-dementia complex. Lancet. 1994 Mar 5;343(8897):611–611. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(94)91568-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisgraber K. H. Apolipoprotein E: structure-function relationships. Adv Protein Chem. 1994;45:249–302. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60642-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wenham P. R., Price W. H., Blandell G. Apolipoprotein E genotyping by one-stage PCR. Lancet. 1991 May 11;337(8750):1158–1159. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(91)92823-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wenham P. R., Sedky A., Spooner R. J. Apolipoprotein E phenotyping: a word of caution. Ann Clin Biochem. 1991 Nov;28(Pt 6):599–605. doi: 10.1177/000456329102800610. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitson J. S., Mims M. P., Strittmatter W. J., Yamaki T., Morrisett J. D., Appel S. H. Attenuation of the neurotoxic effect of A beta amyloid peptide by apolipoprotein E. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1994 Feb 28;199(1):163–170. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1994.1209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilcock G. K., Esiri M. M., Bowen D. M., Smith C. C. Alzheimer's disease. Correlation of cortical choline acetyltransferase activity with the severity of dementia and histological abnormalities. J Neurol Sci. 1982 Dec;57(2-3):407–417. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(82)90045-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wisniewski T., Frangione B. Apolipoprotein E: a pathological chaperone protein in patients with cerebral and systemic amyloid. Neurosci Lett. 1992 Feb 3;135(2):235–238. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(92)90444-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wisniewski T., Golabek A., Matsubara E., Ghiso J., Frangione B. Apolipoprotein E: binding to soluble Alzheimer's beta-amyloid. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1993 Apr 30;192(2):359–365. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1993.1423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu C. E., Payami H., Olson J. M., Boehnke M., Wijsman E. M., Orr H. T., Kukull W. A., Goddard K. A., Nemens E., White J. A. The apolipoprotein E/CI/CII gene cluster and late-onset Alzheimer disease. Am J Hum Genet. 1994 Apr;54(4):631–642. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Bockxmeer F. M. ApoE and ACE genes: impact on human longevity. Nat Genet. 1994 Jan;6(1):4–5. doi: 10.1038/ng0194-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Bockxmeer F. M., Mamotte C. D. Apolipoprotein epsilon 4 homozygosity in young men with coronary heart disease. Lancet. 1992 Oct 10;340(8824):879–880. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(92)93288-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Duijn C. M., de Knijff P., Cruts M., Wehnert A., Havekes L. M., Hofman A., Van Broeckhoven C. Apolipoprotein E4 allele in a population-based study of early-onset Alzheimer's disease. Nat Genet. 1994 May;7(1):74–78. doi: 10.1038/ng0594-74. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


