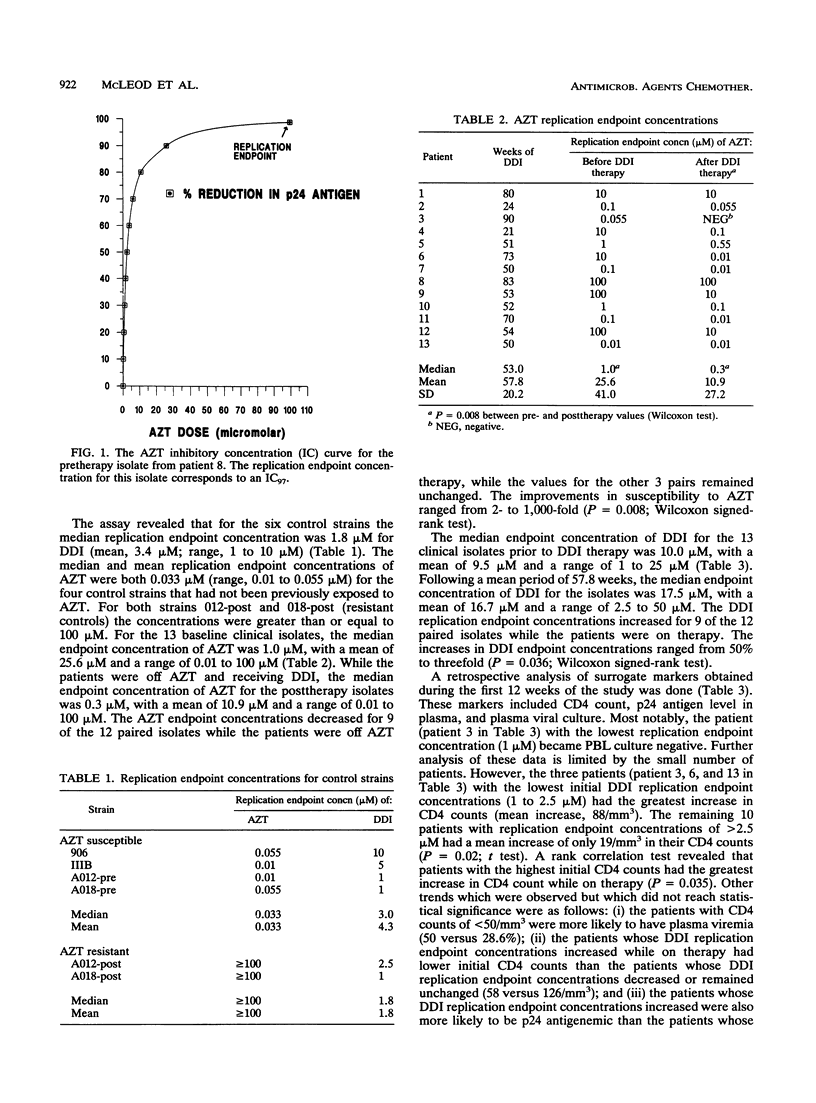
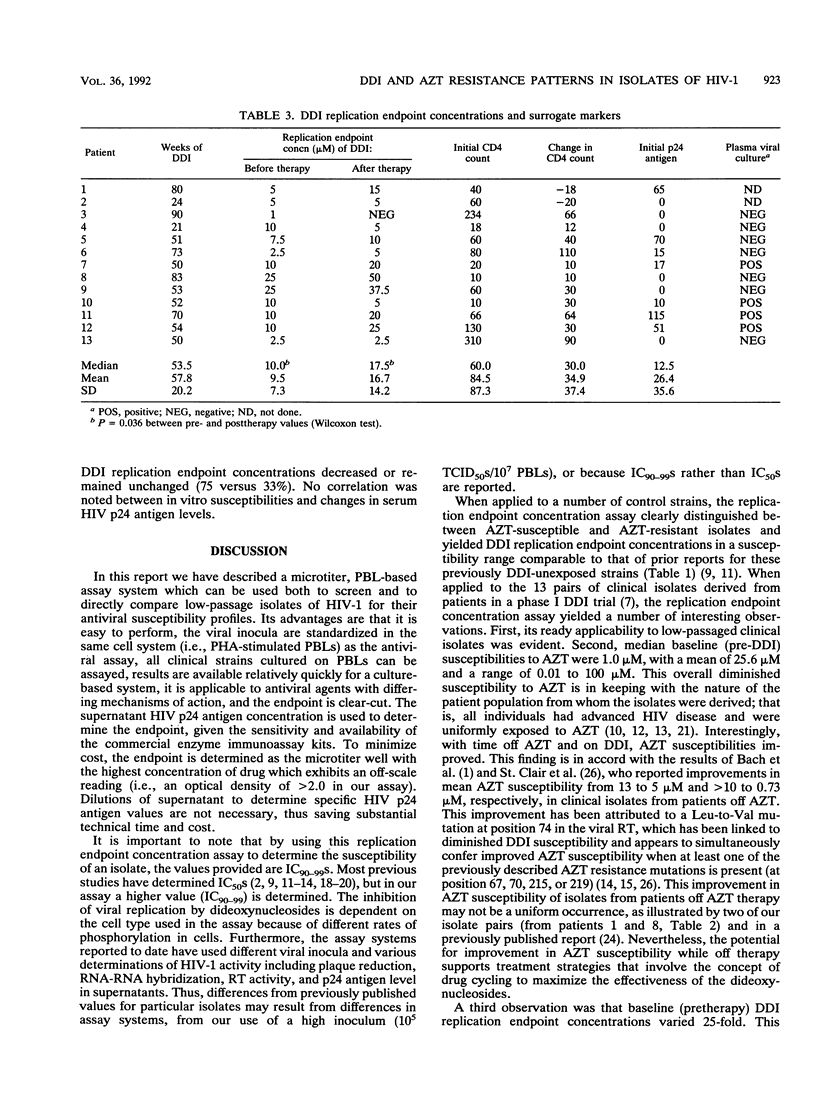
Abstract
Reports of in vitro resistance of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) to zidovudine (AZT) have raised concerns about the development of resistance to other dideoxynucleosides in clinical use. To address this, we have developed a screening assay which supports the growth of clinical isolates and have applied this to a series of paired isolates from patients entered into a phase I trial of didanosine (DDI). Thirteen patients (10 with AIDS, 3 with AIDS-related complex) who had been exposed to AZT for a mean of 6.5 months (range, 1 to 13 months) were treated with DDI at 750 mg/day. Paired isolates were obtained pretherapy and after a mean of 58 weeks (range, 21 to 90) of DDI therapy by coculture of peripheral blood mononuclear leukocytes (PBLs) with phytohemagglutinin-stimulated donor PBLs. Isolates were passaged only one additional time in PBLs and then tested in parallel in a microtiter assay with phytohemagglutinin-stimulated donor PBLs as targets. PBLs were infected with 10(5) 50% tissue culture infectious doses per 10(7) cells and exposed to DDI (1 to 50 microM) or AZT (0.01 to 100 microM), and supernatants were assayed for the HIV p24 antigen at 7 days postinfection. Control AZT-susceptible and resistant isolates were included. The median pre- and posttherapy DDI susceptibilities of the 13 pairs of isolates were 10.0 microM (range, 1 to 25 microM) and 17.5 microM (range, 2.5 to 50 microM), respectively (P = 0.036; Wilcoxon signed-rank test). These studies thus indicated that (i) the susceptibility to DDI tends to mildly decrease with drug exposure; (ii) the susceptibility to AZT improves with time off AZT; (iii) baseline susceptibilities to DDI have a wide range, and the CD4 response may correlate with the initial susceptibility; and (iv) a PBL-based microtiter assay is useful for screening clinical isolated for dideoxynucleoside susceptibility profiles.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boucher C. A., Tersmette M., Lange J. M., Kellam P., de Goede R. E., Mulder J. W., Darby G., Goudsmit J., Larder B. A. Zidovudine sensitivity of human immunodeficiency viruses from high-risk, symptom-free individuals during therapy. Lancet. 1990 Sep 8;336(8715):585–590. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)93391-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler K. M., Husson R. N., Balis F. M., Brouwers P., Eddy J., el-Amin D., Gress J., Hawkins M., Jarosinski P., Moss H. Dideoxyinosine in children with symptomatic human immunodeficiency virus infection. N Engl J Med. 1991 Jan 17;324(3):137–144. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199101173240301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chesebro B., Wehrly K. Development of a sensitive quantitative focal assay for human immunodeficiency virus infectivity. J Virol. 1988 Oct;62(10):3779–3788. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.10.3779-3788.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chesebro B., Wehrly K., Metcalf J., Griffin D. E. Use of a new CD4-positive HeLa cell clone for direct quantitation of infectious human immunodeficiency virus from blood cells of AIDS patients. J Infect Dis. 1991 Jan;163(1):64–70. doi: 10.1093/infdis/163.1.64. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou T. C., Talalay P. Quantitative analysis of dose-effect relationships: the combined effects of multiple drugs or enzyme inhibitors. Adv Enzyme Regul. 1984;22:27–55. doi: 10.1016/0065-2571(84)90007-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connolly K. J., Allan J. D., Fitch H., Jackson-Pope L., McLaren C., Canetta R., Groopman J. E. Phase I study of 2'-3'-dideoxyinosine administered orally twice daily to patients with AIDS or AIDS-related complex and hematologic intolerance to zidovudine. Am J Med. 1991 Nov;91(5):471–478. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(91)90182-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho D. D., Moudgil T., Alam M. Quantitation of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 in the blood of infected persons. N Engl J Med. 1989 Dec 14;321(24):1621–1625. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198912143212401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Japour A. J., Chatis P. A., Eigenrauch H. A., Crumpacker C. S. Detection of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 clinical isolates with reduced sensitivity to zidovudine and dideoxyinosine by RNA.RNA hybridization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Apr 15;88(8):3092–3096. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.8.3092. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Land S., Terloar G., McPhee D., Birch C., Doherty R., Cooper D., Gust I. Decreased in vitro susceptibility to zidovudine of HIV isolates obtained from patients with AIDS. J Infect Dis. 1990 Feb;161(2):326–329. doi: 10.1093/infdis/161.2.326. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larder B. A., Chesebro B., Richman D. D. Susceptibilities of zidovudine-susceptible and -resistant human immunodeficiency virus isolates to antiviral agents determined by using a quantitative plaque reduction assay. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Mar;34(3):436–441. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.3.436. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larder B. A., Darby G., Richman D. D. HIV with reduced sensitivity to zidovudine (AZT) isolated during prolonged therapy. Science. 1989 Mar 31;243(4899):1731–1734. doi: 10.1126/science.2467383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larder B. A., Kellam P., Kemp S. D. Zidovudine resistance predicted by direct detection of mutations in DNA from HIV-infected lymphocytes. AIDS. 1991 Feb;5(2):137–144. doi: 10.1097/00002030-199102000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larder B. A., Kemp S. D. Multiple mutations in HIV-1 reverse transcriptase confer high-level resistance to zidovudine (AZT). Science. 1989 Dec 1;246(4934):1155–1158. doi: 10.1126/science.2479983. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richman D. D., Grimes J. M., Lagakos S. W. Effect of stage of disease and drug dose on zidovudine susceptibilities of isolates of human immunodeficiency virus. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 1990;3(8):743–746. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richman D. D. Susceptibility to nucleoside analogues of zidovudine-resistant isolates of human immunodeficiency virus. Am J Med. 1990 May 21;88(5B):8S–10S. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(90)90414-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rooke R., Parniak M. A., Tremblay M., Soudeyns H., Li X. G., Gao Q., Yao X. J., Wainberg M. A. Biological comparison of wild-type and zidovudine-resistant isolates of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 from the same subjects: susceptibility and resistance to other drugs. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1991 May;35(5):988–991. doi: 10.1128/aac.35.5.988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rooke R., Tremblay M., Soudeyns H., DeStephano L., Yao X. J., Fanning M., Montaner J. S., O'Shaughnessy M., Gelmon K., Tsoukas C. Isolation of drug-resistant variants of HIV-1 from patients on long-term zidovudine therapy. Canadian Zidovudine Multi-Centre Study Group. AIDS. 1989 Jul;3(7):411–415. doi: 10.1097/00002030-198907000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozencweig M., McLaren C., Beltangady M., Ritter J., Canetta R., Schacter L., Kelley S., Nicaise C., Smaldone L., Dunkle L. Overview of phase I trials of 2',3'-dideoxyinosine (ddI) conducted on adult patients. Rev Infect Dis. 1990 Jul-Aug;12 (Suppl 5):S570–S575. doi: 10.1093/clinids/12.supplement_5.s570. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saag M. S., Crain M. J., Decker W. D., Campbell-Hill S., Robinson S., Brown W. E., Leuther M., Whitley R. J., Hahn B. H., Shaw G. M. High-level viremia in adults and children infected with human immunodeficiency virus: relation to disease stage and CD4+ lymphocyte levels. J Infect Dis. 1991 Jul;164(1):72–80. doi: 10.1093/infdis/164.1.72. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- St Clair M. H., Martin J. L., Tudor-Williams G., Bach M. C., Vavro C. L., King D. M., Kellam P., Kemp S. D., Larder B. A. Resistance to ddI and sensitivity to AZT induced by a mutation in HIV-1 reverse transcriptase. Science. 1991 Sep 27;253(5027):1557–1559. doi: 10.1126/science.1716788. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tudor-Williams G., St Clair M. H., McKinney R. E., Maha M., Walter E., Santacroce S., Mintz M., O'Donnell K., Rudoll T., Vavro C. L. HIV-1 sensitivity to zidovudine and clinical outcome in children. Lancet. 1992 Jan 4;339(8784):15–19. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(92)90140-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



