Abstract
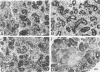
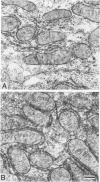
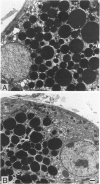
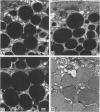
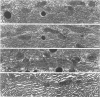
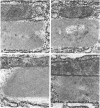
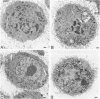
We have demonstrated that microwave energy (MW) can be used in conjunction with chemical cross-linking agents in order to rapidly fix cell suspensions and tissue blocks for electron microscopy in 7-9 seconds. The optimal MW fixation method involved immersing tissues up to 1 cu cm in dilute aldehyde fixation and immediately irradiating the specimens in a conventional microwave oven for 9 seconds to 50 C. Ultrastructural preservation of samples irradiated by MW energy was comparable to that of the control samples immersed in aldehyde fixative for 2 hours at 25 C. Stereologic analysis showed that tissue blocks fixed by the MW fixation method did not cause organelles such as liver mitochondria and salivary gland granules to shrink or to swell. Potential applications for this new fixation technology include the investigation of rapid intracellular processes (eg, vesicular transport) and preservation of proteins that are difficult to demonstrate with routine fixation methods (eg, antigens and enzymes).
Full text
PDF













Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alam M. T., Barthakur N., Lambert N. G., Kasatiya S. S. Cytological effects of microwave radiation in Chinese hamster cells in vitro. Can J Genet Cytol. 1978 Mar;20(1):23–30. doi: 10.1139/g78-004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernard G. R. Microwave irradiation as a generator of heat for histological fixation. Stain Technol. 1974 Jul;49(4):215–224. doi: 10.3109/10520297409116981. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolender R. P. Stereological analysis of the guinea pig pancreas. I. Analytical model and quantitative description of nonstimulated pancreatic exocrine cells. J Cell Biol. 1974 May;61(2):269–287. doi: 10.1083/jcb.61.2.269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dudek R. W., Childs G. V., Boyne A. F. Quick-freezing and freeze-drying in preparation for high quality morphology and immunocytochemistry at the ultrastructural level: application to pancreatic beta cell. J Histochem Cytochem. 1982 Feb;30(2):129–138. doi: 10.1177/30.2.7037935. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dvorak A. M., Hammond M. E., Dvorak H. F., Karnovsky M. J. Loss of cell surface material from peritoneal exudate cells associated with lymphocyte-mediated inhibition of macrophage migration from capillary tubes. Lab Invest. 1972 Dec;27(6):561–574. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dvorak H. F., Mihm M. C., Jr, Dvorak A. M., Johnson R. A., Manseau E. J., Morgan E., Colvin R. B. Morphology of delayed type hypersensitivity reactions in man. I. Quantitative description of the inflammatory response. Lab Invest. 1974 Aug;31(2):111–130. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elder J. A., Ali J. S. The effect of microwaves (2450 MHz) on isolated rat liver mitochondria. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1975 Feb 28;247:251–262. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1975.tb36000.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellar D. J., Muñoz E., Salton M. R. The effect of low concentrations of glutaraldehyde on Micrococcus lysodeikticus membranes: changes in the release of membrane-associated enzymes and membrane structure. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Jan 5;225(1):140–150. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(71)90292-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farquhar M. G., Palade G. E. Cell junctions in amphibian skin. J Cell Biol. 1965 Jul;26(1):263–291. doi: 10.1083/jcb.26.1.263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galvin M. J., Hall C. A., McRee D. I. Microwave radiation effects on cardiac muscle cells in vitro. Radiat Res. 1981 May;86(2):358–367. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon H. W., Daniel E. J. Preliminary report: microwave fixation of human tissues. Am J Med Technol. 1974 Oct;40(10):441–442. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grillo T. A., Ogunnaike P. O., Faoye S. Effects of histological and electron microscopical fixatives on the insulin content of the rat pancreas. J Endocrinol. 1971 Dec;51(4):645–649. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0510645. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hand J. W. Microwave heating patterns in simple tissue models. Phys Med Biol. 1977 Sep;22(5):981–987. doi: 10.1088/0031-9155/22/5/018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hassell J., Hand A. R. Tissue fixation with diimidoesters as an alternative to aldehydes. I. Comparison of cross-linking and ultrastructure obtained with dimethylsuberimidate and glutaraldehyde. J Histochem Cytochem. 1974 Apr;22(4):223–229. doi: 10.1177/22.4.223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heuser J. E., Reese T. S., Dennis M. J., Jan Y., Jan L., Evans L. Synaptic vesicle exocytosis captured by quick freezing and correlated with quantal transmitter release. J Cell Biol. 1979 May;81(2):275–300. doi: 10.1083/jcb.81.2.275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopwood D. Some aspects of fixation with glutaraldehyde. A biochemical and histochemical comparison of the effects of formaldehyde and glutaraldehyde fixation on various enzymes and glycogen, with a note on penetration of glutaraldehyde into liver. J Anat. 1967 Jan;101(Pt 1):83–92. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopwood D. Theoretical and practical aspects of glutaraldehyde fixation. Histochem J. 1972 Jul;4(4):267–303. doi: 10.1007/BF01005005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karnovsky M. J. The ultrastructural basis of capillary permeability studied with peroxidase as a tracer. J Cell Biol. 1967 Oct;35(1):213–236. doi: 10.1083/jcb.35.1.213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenard J., Singer S. J. Alteration of the conformation of proteins in red blood cell membranes and in solution by fixatives used in electron microscopy. J Cell Biol. 1968 Apr;37(1):117–121. doi: 10.1083/jcb.37.1.117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Login G. R. Microwave fixation versus formalin fixation of surgical and autopsy tissue. Am J Med Technol. 1978 May;44(5):435–437. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lust W. D., Passonneau J. V., Veech R. L. Cyclic adenosine monphosphate, metabolites, and phosphorylase in neural tissue: a comparison a methods of fixation. Science. 1973 Jul 20;181(4096):280–282. doi: 10.1126/science.181.4096.280. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayers C. P. Histological fixation by microwave heating. J Clin Pathol. 1970 Apr;23(3):273–275. doi: 10.1136/jcp.23.3.273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medina M. A., Jones D. J., Stavinoha W. B., Ross D. H. The levels of labile intermediary metabolites in mouse brain following rapid tissue fixation with microwave irradiation. J Neurochem. 1975 Feb;24(2):223–227. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1975.tb11868.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merritt J. H., Frazer J. W. Microwave fixation of brain tissue as a neurochemical technique- a review. J Microw Power. 1977 Jun;12(2):133–139. doi: 10.1080/16070658.1977.11689039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyerhoff J. L., Kant G. J., Lenox R. H. Increase in dopamine in cerebral cortex and other regions of rat brain after microwave fixation: possible diffusion artifact. Brain Res. 1978 Aug 18;152(1):161–169. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(78)90143-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Modak A. T., Weintraub S. T., McCoy T. H., Stavinoha W. B. Use of 300-msec microwave irradiation for enzyme inactivation: a study of effects of sodium pentobarbital on acetylcholine concentration in mouse brain regions. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1976 May;197(2):245–252. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ortner M. J., Galvin M. J., Chignell C. F., McRee D. I. A circular dichroism study of human erythrocyte ghost proteins during exposure to 2450 MHz microwave radiation. Cell Biophys. 1981 Dec;3(4):335–347. doi: 10.1007/BF02785118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PALADE G. E. A study of fixation for electron microscopy. J Exp Med. 1952 Mar;95(3):285–298. doi: 10.1084/jem.95.3.285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Packer L., Wrigglesworth J. M., Fortes P. A., Pressman B. C. Expansion of the inner membrane compartment and its relation to mitochondrial volume and ion transport. J Cell Biol. 1968 Nov;39(2):382–391. doi: 10.1083/jcb.39.2.382. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petrere J. A., Schardein J. L. Microwave fixation of fetal specimens. Stain Technol. 1977 Mar;52(2):113–114. doi: 10.3109/10520297709116757. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reese T. S., Karnovsky M. J. Fine structural localization of a blood-brain barrier to exogenous peroxidase. J Cell Biol. 1967 Jul;34(1):207–217. doi: 10.1083/jcb.34.1.207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruoff H. J. Cyclic AMP and cyclic GMP in the rat gastric mucosa. The significance of post mortem changes and tissue fixation on the estimation of the in vivo level. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1977 Jun;298(2):167–173. doi: 10.1007/BF00508625. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SABATINI D. D., BENSCH K., BARRNETT R. J. Cytochemistry and electron microscopy. The preservation of cellular ultrastructure and enzymatic activity by aldehyde fixation. J Cell Biol. 1963 Apr;17:19–58. doi: 10.1083/jcb.17.1.19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt M. J., Schmidt D. E., Robison G. A. Cyclic adenosine monophosphate in brain areas: microwave irradiation as a means of tissue fixation. Science. 1971 Sep 17;173(4002):1142–1143. doi: 10.1126/science.173.4002.1142. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stensaas L. J., Partlow L. M., Bush L. G., Iversen P. L., Hill D. W., Hagmann M. J., Gandhi O. P. Effects of millimeter-wave radiation on monolayer cell cultures. II. Scanning and transmission electron microscopy. Bioelectromagnetics. 1981;2(2):141–150. doi: 10.1002/bem.2250020205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternlieb I., Feldmann G. Effects of anticopper therapy on hepatocellular mitochondria in patients with Wilson's disease: an ultrastructural and stereological study. Gastroenterology. 1976 Sep;71(3):457–461. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valtonen E. J. Giant mast cells--a special degenerative form produced by microwave radiation. Exp Cell Res. 1966 Aug;43(1):221–224. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(66)90396-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webber M. M., Barnes F. S., Seltzer L. A., Bouldin T. R., Prasad K. N. Short microwave pulses cause ultrastructural membrane damage in neuroblastoma cells. J Ultrastruct Res. 1980 Jun;71(3):321–330. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(80)90083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]