Abstract
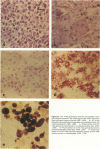
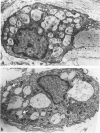
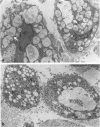
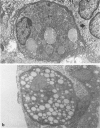
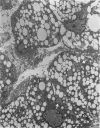
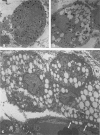
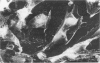
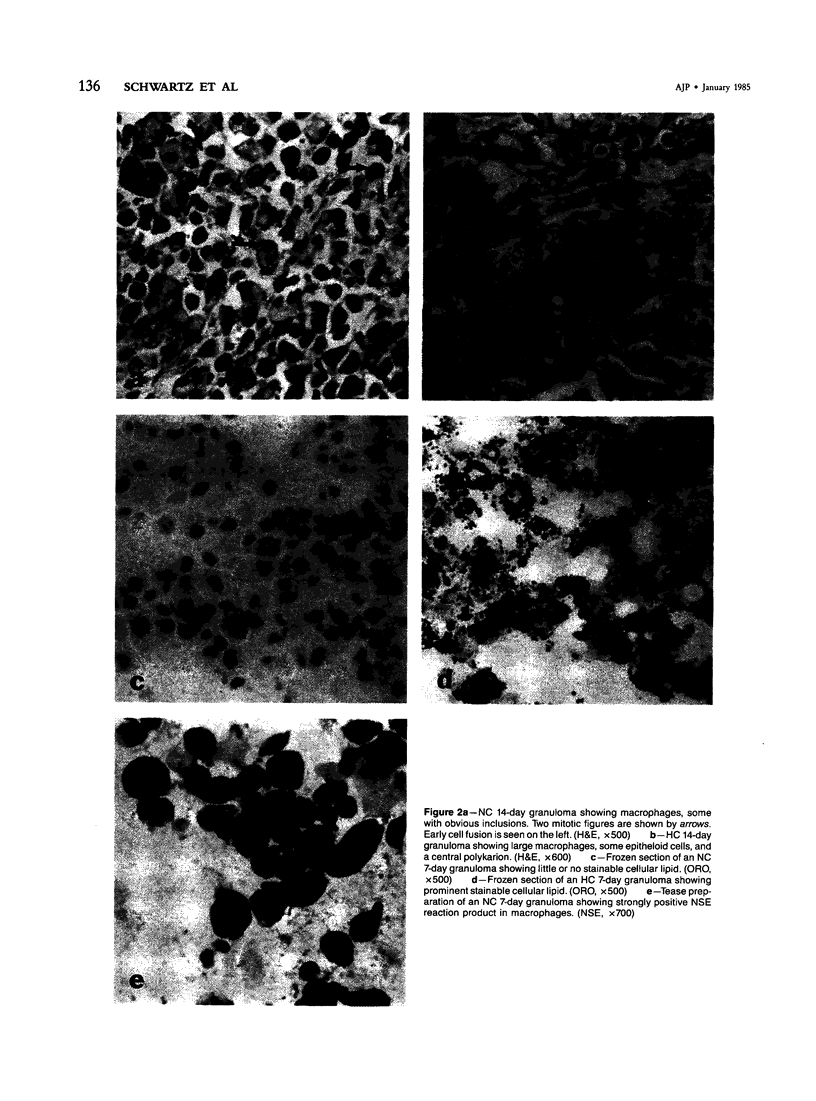
With an increasing interest in the role of the monocyte-macrophage in the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis and as a progenitor of plaque intimal foam cells, a model for the study of foam-cell differentiation in an extravascular environment has been developed. Granulomas were induced in 25 normocholesterolemic (NC) and 28 hypercholesterolemic (HC) rabbits by the subcutaneous injection of 15 ml of 1% carrageenan. Granuloma tissue was harvested at 4, 7, 14, and 28 days and studied by light and transmission electron microscopy. Macrophages and foam cells were isolated by enzymic dispersion with collagenase and cultured for further characterization by scanning electron microscopy, nonspecific esterase (NSE), and oil red O (ORO) staining. Granuloma macrophages from NC rabbits were consistently ORO-negative, contrasting with those from HC rabbits which were strongly ORO-positive, even at 4 and 7 days. With an increasing duration of exposure to hypercholesterolemia, macrophages accumulated increasing amounts of stainable lipid, and in the 28-day HC granulomas, large foam cells distended by lipid inclusions accounted for 70% of the cells present. This model has established that NSE-positive macrophages in HC granulomas accumulate lipid and assume the morphologic characteristics of atheromatous intimal foam cells.
Full text
PDF






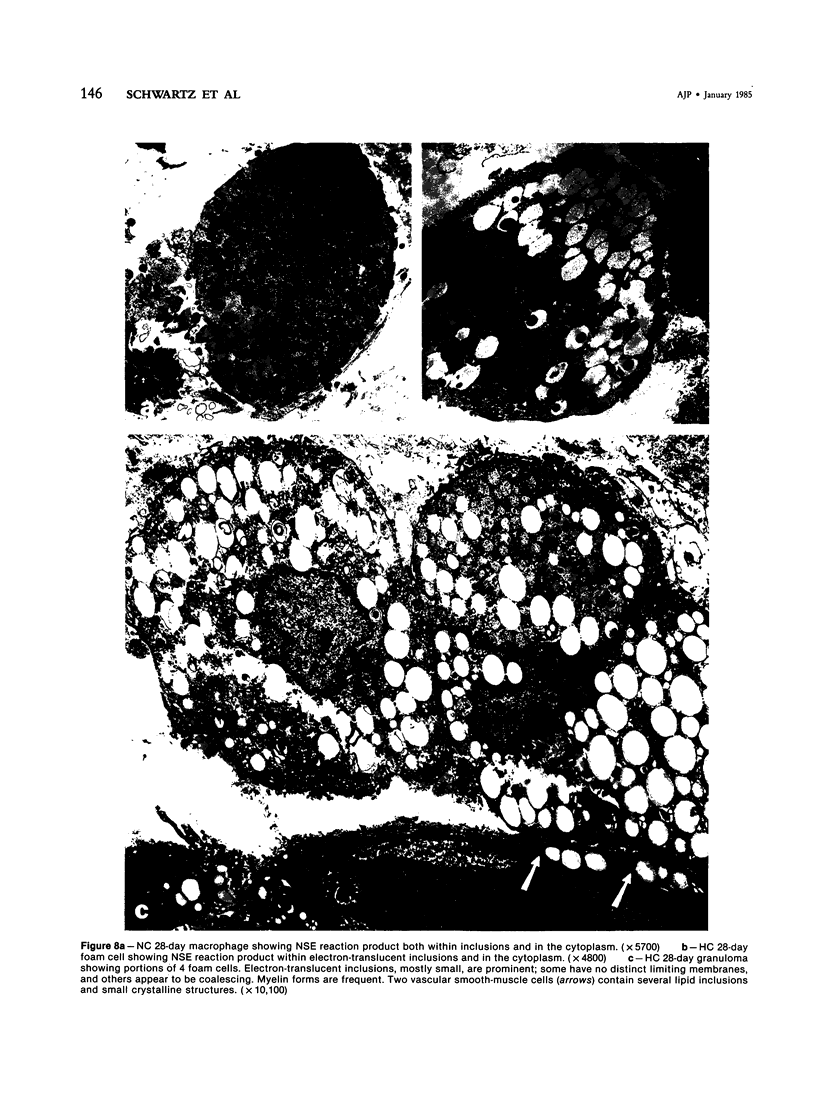
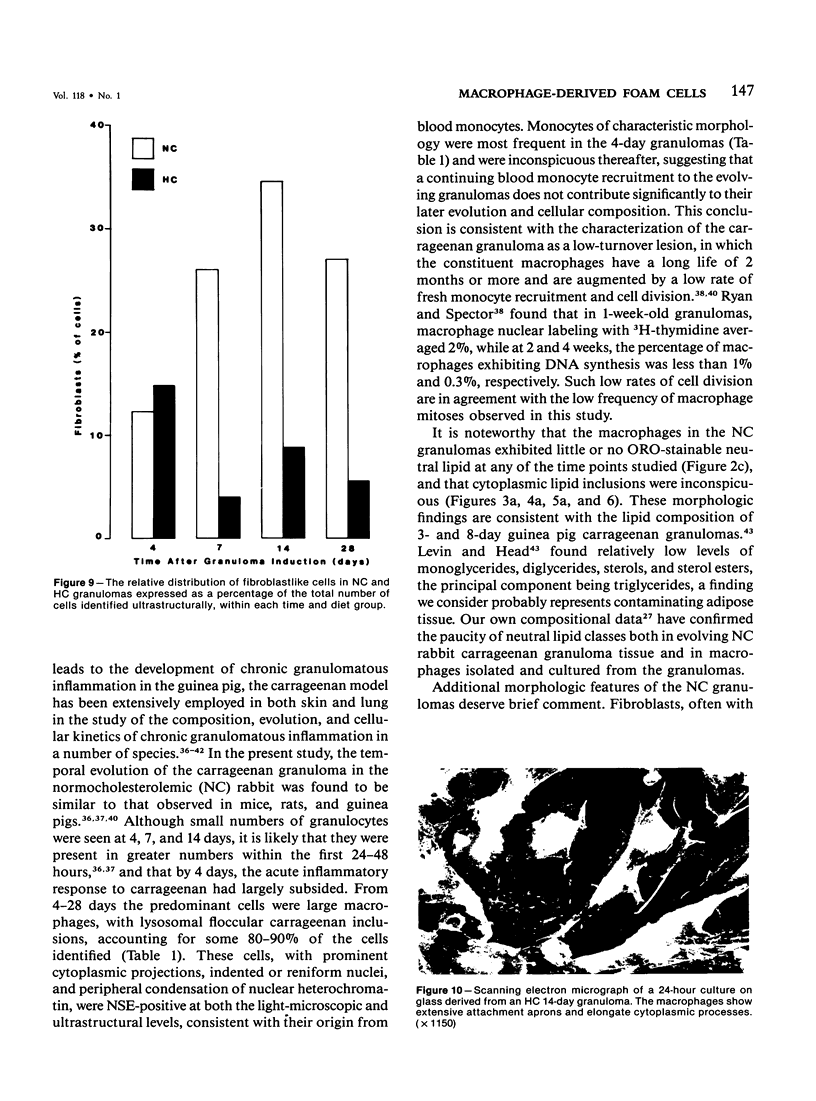



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ATKINSON R. M., JENKINS L., TOMICH E. G., WOOLLETT E. A. The effects of some anti-inflammatory substances on carrageenin-induced granulomata. J Endocrinol. 1962 Sep;25:87–93. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0250087. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Albert D. H., Traber M. G., Kayden H. J. Cholesterol metabolism in human monocyte-derived macrophages: stimulation of cholesteryl ester formation and cholesterol excretion by serum lipoproteins. Lipids. 1982 Oct;17(10):709–715. doi: 10.1007/BF02534656. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allain C. C., Poon L. S., Chan C. S., Richmond W., Fu P. C. Enzymatic determination of total serum cholesterol. Clin Chem. 1974 Apr;20(4):470–475. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbolini G., Scilabra G. A., Botticelli A., Botticelli S. On the origin of foam cells in cholesterol-induced atherosclerosis of the rabbit. Virchows Arch B Cell Pathol. 1969;3(1):24–32. doi: 10.1007/BF02901924. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowers R. R., Stapleton M. E., Lew P. D. An ultrastructural study of the macrophages of the carrageenan-induced granuloma in the rat lung. J Pathol. 1983 May;140(1):29–40. doi: 10.1002/path.1711400105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L., Krieger M., Ho Y. K., Anderson R. G. Reversible accumulation of cholesteryl esters in macrophages incubated with acetylated lipoproteins. J Cell Biol. 1979 Sep;82(3):597–613. doi: 10.1083/jcb.82.3.597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUFF G. L., McMILLAN G. C., RITCHIE A. C. The morphology of early atherosclerotic lesions of the aorta demonstrated by the surface technique in rabbits fed cholesterol; together with a description of the anatomy of the intima of the rabbit's aorta and the spontaneous lesions which occur in it. Am J Pathol. 1957 Sep-Oct;33(5):845–873. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Del Arenal P., Pérez-Tamayo R. The nature of collagen in the carrageenin granuloma. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1973 Mar;142(3):1031–1035. doi: 10.3181/00379727-142-37169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fogelman A. M., Shechter I., Seager J., Hokom M., Child J. S., Edwards P. A. Malondialdehyde alteration of low density lipoproteins leads to cholesteryl ester accumulation in human monocyte-macrophages. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Apr;77(4):2214–2218. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.4.2214. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerrity R. G., Naito H. K., Richardson M., Schwartz C. J. Dietary induced atherogenesis in swine. Morphology of the intima in prelesion stages. Am J Pathol. 1979 Jun;95(3):775–792. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerrity R. G., Schwartz C. J. Endothelial cell injury in early mild hypercholesterolemia. Prog Biochem Pharmacol. 1977;13:213–219. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerrity R. G. The role of the monocyte in atherogenesis: I. Transition of blood-borne monocytes into foam cells in fatty lesions. Am J Pathol. 1981 May;103(2):181–190. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gianturco S. H., Bradley W. A., Gotto A. M., Jr, Morrisett J. D., Peavy D. L. Hypertriglyceridemic very low density lipoproteins induce triglyceride synthesis and accumulation in mouse peritoneal macrophages. J Clin Invest. 1982 Jul;70(1):168–178. doi: 10.1172/JCI110590. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenburg G. B., Hunt T. K. The proliferative response in vitro of vascular endothelial and smooth muscle cells exposed to wound fluids and macrophages. J Cell Physiol. 1978 Dec;97(3 Pt 1):353–360. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040970310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joris I., Zand T., Nunnari J. J., Krolikowski F. J., Majno G. Studies on the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis. I. Adhesion and emigration of mononuclear cells in the aorta of hypercholesterolemic rats. Am J Pathol. 1983 Dec;113(3):341–358. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn A. J., Stewart C. C., Teitelbaum S. L. Contact-mediated bone resorption by human monocytes in vitro. Science. 1978 Mar 3;199(4332):988–990. doi: 10.1126/science.622581. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim H., Pangalis G. A., Payne B. C., Kadin M. E., Rappaport H. Ultrastructural identification of neoplastic histiocytes--monocytes: an application of a newly developed cytochemical technique. Am J Pathol. 1982 Feb;106(2):204–223. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin E., Head C. Lipids of connective tissue. I. The in vitro incorporation of acetate-1-C-14 into the neutral lipids of the carrageenin granuloma. J Lab Clin Med. 1965 Nov;66(5):750–757. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis J. C., Taylor R. G., Jones N. D., St Clair R. W., Cornhill J. F. Endothelial surface characteristics in pigeon coronary artery atherosclerosis. I. Cellular alterations during the initial stages of dietary cholesterol challenge. Lab Invest. 1982 Feb;46(2):123–138. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li C. Y., Yam L. T., Crosby W. H. Histochemical characterization of cellular and structural elements of the human spleen. J Histochem Cytochem. 1972 Dec;20(12):1049–1058. doi: 10.1177/20.12.1049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahley R. W., Innerarity T. L., Brown M. S., Ho Y. K., Goldstein J. L. Cholesteryl ester synthesis in macrophages: stimulation by beta-very low density lipoproteins from cholesterol-fed animals of several species. J Lipid Res. 1980 Nov;21(8):970–980. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin B. M., Gimbrone M. A., Jr, Unanue E. R., Cotran R. S. Stimulation of nonlymphoid mesenchymal cell proliferation by a macrophage-derived growth factor. J Immunol. 1981 Apr;126(4):1510–1515. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCandless E. L. Chemical structural requirements for stimulation of connective tissue growth by polysaccharides. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1965 May 28;118(22):869–881. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1965.tb40156.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papadimitriou J. M., Spector W. G. The ultrastructure of high- and low-turnover inflammatory granulomata. J Pathol. 1972 Jan;106(1):37–43. doi: 10.1002/path.1711060104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierce C. W. Macrophages: modulators of immunity. Parke-Davis Award Lecture. Am J Pathol. 1980 Jan;98(1):10–28. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polverini P. J., Cotran R. S., Sholley M. M. Endothelial proliferation in the delayed hypersensitivity reaction: an autoradiographic study. J Immunol. 1977 Feb;118(2):529–532. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pérez-Tamayo R. Collagen resorption in carrageenin granulomas. I. Collagenolytic activity in in vitro explants. Lab Invest. 1970 Feb;22(2):137–141. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raymond T. L., Reynolds S. A. Lipoproteins of the extravascular space: alterations in low density lipoproteins of interstitial inflammatory fluid. J Lipid Res. 1983 Feb;24(2):113–119. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan G. B., Spector W. G. Natural selection of long-lived macrophages in experimental granulomata. J Pathol. 1969 Oct;99(2):139–151. doi: 10.1002/path.1710990208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHWARTZ C. J., MITCHELL J. R. Cellular infiltration of the human arterial adventitia associated with atheromatous plaques. Circulation. 1962 Jul;26:73–78. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.26.1.73. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHWARTZ C. J., MITCHELL J. R. The morphology, terminology and pathogenesis of arterial plaques. Postgrad Med J. 1962 Jan;38:25–34. doi: 10.1136/pgmj.38.435.25. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SIMON R. C., STILL W. J., O'NEAL R. M. The circulating lipophage and experimental atherosclerosis. J Atheroscler Res. 1961 Sep-Dec;1:395–400. doi: 10.1016/s0368-1319(61)80016-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITH D. B., COOK W. H. Fractionation of carrageenin. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1953 Jul;45(1):232–233. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(53)90421-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STILL W. J., O'NEAL R. M. Electron microscopic study of experimental atherosclerosis in the rat. Am J Pathol. 1962 Jan;40:21–35. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaffner T., Taylor K., Bartucci E. J., Fischer-Dzoga K., Beeson J. H., Glagov S., Wissler R. W. Arterial foam cells with distinctive immunomorphologic and histochemical features of macrophages. Am J Pathol. 1980 Jul;100(1):57–80. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shio H., Haley N. J., Fowler S. Characterization of lipid-laden aortic cells from cholesterol-fed rabbits. II. Morphometric analysis of lipid-filled lysosomes and lipid droplets in aortic cell populations. Lab Invest. 1978 Oct;39(4):390–397. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shio H., Haley N. J., Fowler S. Characterization of lipid-laden aortic cells from cholesterol-fed rabbits. III. Intracellular localization of cholesterol and cholesteryl ester. Lab Invest. 1979 Aug;41(2):160–167. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sprague E. A., Kelley J. L., Schwartz C. J. Growth, structure and function of baboon aortic smooth muscle cells in culture. Exp Mol Pathol. 1982 Aug;37(1):48–66. doi: 10.1016/0014-4800(82)90021-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stary H. C. The intimal macrophage in atherosclerosis. Artery. 1980;8(3):205–207. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stossel T. P. Phagocytosis (third of three parts). N Engl J Med. 1974 Apr 11;290(15):833–839. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197404112901506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutton J. S., Weiss L. Transformation of monocytes in tissue culture into macrophages, epithelioid cells, and multinucleated giant cells. An electron microscope study. J Cell Biol. 1966 Feb;28(2):303–332. doi: 10.1083/jcb.28.2.303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki M., O'Neal R. M. Circulating lipophages, serum lipids, and atherosclerosis in rats. Arch Pathol. 1967 Feb;83(2):169–174. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thakral K. K., Goodson W. H., 3rd, Hunt T. K. Stimulation of wound blood vessel growth by wound macrophages. J Surg Res. 1979 Apr;26(4):430–436. doi: 10.1016/0022-4804(79)90031-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unanue E. R. Secretory function of mononuclear phagocytes: a review. Am J Pathol. 1976 May;83(2):396–418. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unanue E. R. The macrophage as a regulator of lymphocyte function. Hosp Pract. 1979 Nov;14(11):61-4, 69-74. doi: 10.1080/21548331.1979.11707644. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VAN ROBERTSON W. B., SCHWARTZ B. Ascorbic acid and the formation of collagen. J Biol Chem. 1953 Apr;201(2):689–696. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yam L. T., Li C. Y., Crosby W. H. Cytochemical identification of monocytes and granulocytes. Am J Clin Pathol. 1971 Mar;55(3):283–290. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/55.3.283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Furth R. Origin and kinetics of monocytes and macrophages. Semin Hematol. 1970 Apr;7(2):125–141. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]