Abstract
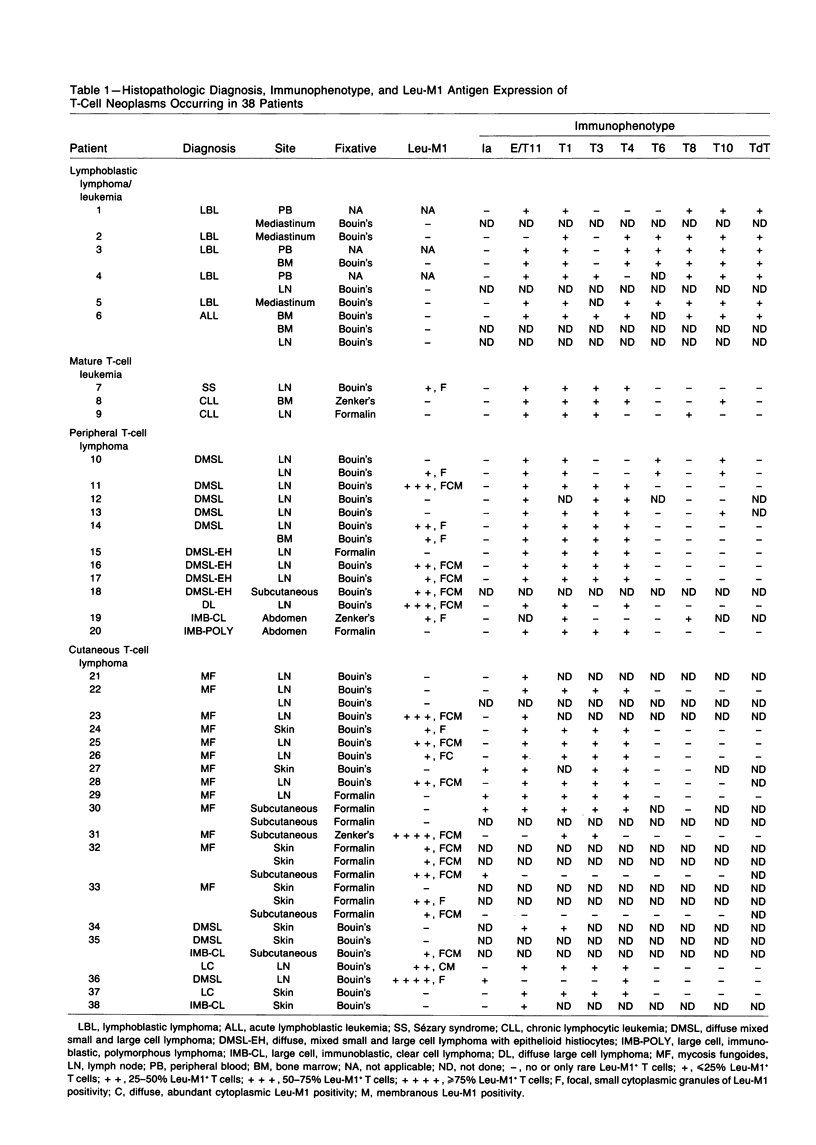
The Leu-M1 antigen has been recently proposed as a valuable immunodiagnostic marker of the Reed-Sternberg cells of Hodgkin's disease and to be particularly helpful is distinguishing Hodgkin's disease from other lymphoproliferative disorders such as peripheral T-cell lymphomas. In this study, the authors examined paraffin-embedded tissue sections obtained from 38 patients with previously well-characterized T-cell neoplasms for the presence of the Leu-M1 antigen. The cases comprised a spectrum of T-cell malignancies and were divided into four broad clinicopathologic groups: lymphoblastic lymphoma/ leukemias (6), mature T-cell leukemias (3), peripheral T-cell lymphomas (11), and cutaneous T-cell lymphomas (18), which included both mycosis fungoides and nonmycosis fungoides types. The neoplastic T cells in 19 patients (50%) expressed the Leu-M1 antigen. The proportion of Leu-M1-positive cells and the immunostaining pattern varied greatly among these cases but correlated with mature, postthymic stages of T-cell differentiation and activation. Of particular significance was the observation that the more pleomorphic neoplastic T cells, including Reed-Sternberg-like cells, exhibited an intense cytoplasmic and membranous staining pattern which was often indistinguishable from the immunostaining pattern observed in Hodgkin's disease. The authors conclude that Leu-M1 is not a specific immunodiagnostic marker of Hodgkin's disease and has limited value in distinguishing Hodgkin's disease from T-cell neoplasms which stimulate Hodgkin's disease morphologically.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abdalla S., Helmy N., el Essaily M., Nasser S., Hirschhorn N. Sodium balance in low birthweight babies after oral rehydration. Lancet. 1985 Mar 30;1(8431):757–757. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)91297-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aisenberg A. C., Wilkes B. M. Lymph node T cells in Hodgkin's disease: analysis of suspensions with monoclonal antibody and rosetting techniques. Blood. 1982 Mar;59(3):522–527. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brisbane J. U., Berman L. D., Neiman R. S. Peripheral T-cell lymphoma: a clinicopathologic study of nine cases. Am J Clin Pathol. 1983 Mar;79(3):285–293. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/79.3.285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanjan S. N., Kearney J. F., Cooper M. D. A monoclonal antibody (MMA) that identifies a differentiation antigen on human myelomonocytic cells. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1982 May;23(2):172–188. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(82)90106-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofman F. M., Lopez D., Husmann L., Meyer P. R., Taylor C. R. Heterogeneity of macrophage populations in human lymphoid tissue and peripheral blood. Cell Immunol. 1984 Oct 1;88(1):61–74. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(84)90052-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu S. M., Jaffe E. S. Leu M1 and peanut agglutinin stain the neoplastic cells of Hodgkin's disease. Am J Clin Pathol. 1984 Jul;82(1):29–32. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/82.1.29. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu S. M., Yang K., Jaffe E. S. Phenotypic expression of Hodgkin's and Reed-Sternberg cells in Hodgkin's disease. Am J Pathol. 1985 Feb;118(2):209–217. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu S. M., Zhang H. Z., Jaffe E. S. Utility of monoclonal antibodies directed against B and T lymphocytes and monocytes in paraffin-embedded sections. Am J Clin Pathol. 1983 Oct;80(4):415–420. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/80.4.415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaffe E. S. Pathologic and clinical spectrum of post-thymic T-cell malignancies. Cancer Invest. 1984;2(5):413–426. doi: 10.3109/07357908409040316. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadin M., Nasu K., Sako D., Said J., Vonderheid E. Lymphomatoid papulosis. A cutaneous proliferation of activated helper T cells expressing Hodgkin's disease-associated antigens. Am J Pathol. 1985 May;119(2):315–325. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knowles D. M., 2nd, Dodson L., Burke J. S., Wang J. M., Bonetti F., Pelicci P. G., Flug F., Dalla-Favera R., Wang C. Y. SIg-E- ("null-cell") non-Hodgkin's lymphomas. Multiparametric determination of their B- or T-cell lineage. Am J Pathol. 1985 Sep;120(3):356–370. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knowles D. M., 2nd, Halper J. P. Human T-cell malignancies: Correlative clinical, histopathologic, immunologic, and cytochemical analysis of 23 cases. Am J Pathol. 1982 Feb;106(2):187–203. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knowles D. M., 2nd, Halper J. P., Jakobiec F. A. T-lymphocyte subpopulations in B-cell-derived non-Hodgkin's lymphomas and Hodgkin's disease. Cancer. 1984 Aug 15;54(4):644–651. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(1984)54:4<644::aid-cncr2820540410>3.0.co;2-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knowles D. M., 2nd, Halper J. P., Machin G. A., Byeff P., Mertelsman R., Chess L. Phenotypic heterogeneity of human T-cell malignancies: demonstration by monoclonal antibodies and cytochemical markers. Am J Hematol. 1982 May;12(3):233–245. doi: 10.1002/ajh.2830120305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knowles D. M., 2nd, Tolidjian B., Marboe C. C., Halper J. P., Azzo W., Wang C. Y. A new human B-lymphocyte surface antigen (BL 2) detectable by a hybridoma monoclonal antibody: distribution on benign and malignant lymphoid cells. Blood. 1983 Jul;62(1):191–199. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller T. P., Byrne G. E., Jones S. E. Mistaken clinical and pathologic diagnoses of Hodgkin's disease: a Southwest oncology group study. Cancer Treat Rep. 1982 Apr;66(4):645–651. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinkus G. S., Said J. W. Hodgkin's disease, lymphocyte predominance type, nodular--a distinct entity? Unique staining profile for L&H variants of Reed-Sternberg cells defined by monoclonal antibodies to leukocyte common antigen, granulocyte-specific antigen, and B-cell-specific antigen. Am J Pathol. 1985 Jan;118(1):1–6. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinkus G. S., Thomas P., Said J. W. Leu-M1--a marker for Reed-Sternberg cells in Hodgkin's disease. An immunoperoxidase study of paraffin-embedded tissues. Am J Pathol. 1985 May;119(2):244–252. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poppema S., Bhan A. K., Reinherz E. L., Posner M. R., Schlossman S. F. In situ immunologic characterization of cellular constituents in lymph nodes and spleens involved by Hodgkin's disease. Blood. 1982 Feb;59(2):226–232. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubenfeld M. R., Silverstone A. E., Knowles D. M., Halper J. P., De Sostoa A., Fenoglio C. M., Edelson R. L. Induction of lymphocyte differentiation by epidermal cultures. J Invest Dermatol. 1981 Aug;77(2):221–224. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12480029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talle M. A., Allegar N., Makowski M., Golstein G. Distinct classes of human T-cell activation antigens. Cell Immunol. 1984 Apr 1;84(2):285–298. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(84)90100-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tindle B. H. Malignant lymphomas. Am J Pathol. 1984 Jul;116(1):119–174. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner R. R., Wood G. S., Beckstead J. H., Colby T. V., Horning S. J., Warnke R. A. Histiocytic malignancies. Morphologic, immunologic, and enzymatic heterogeneity. Am J Surg Pathol. 1984 Jul;8(7):485–500. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uchiyama T., Broder S., Waldmann T. A. A monoclonal antibody (anti-Tac) reactive with activated and functionally mature human T cells. I. Production of anti-Tac monoclonal antibody and distribution of Tac (+) cells. J Immunol. 1981 Apr;126(4):1393–1397. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



