Abstract
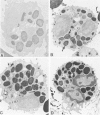
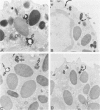
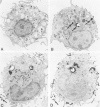
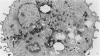
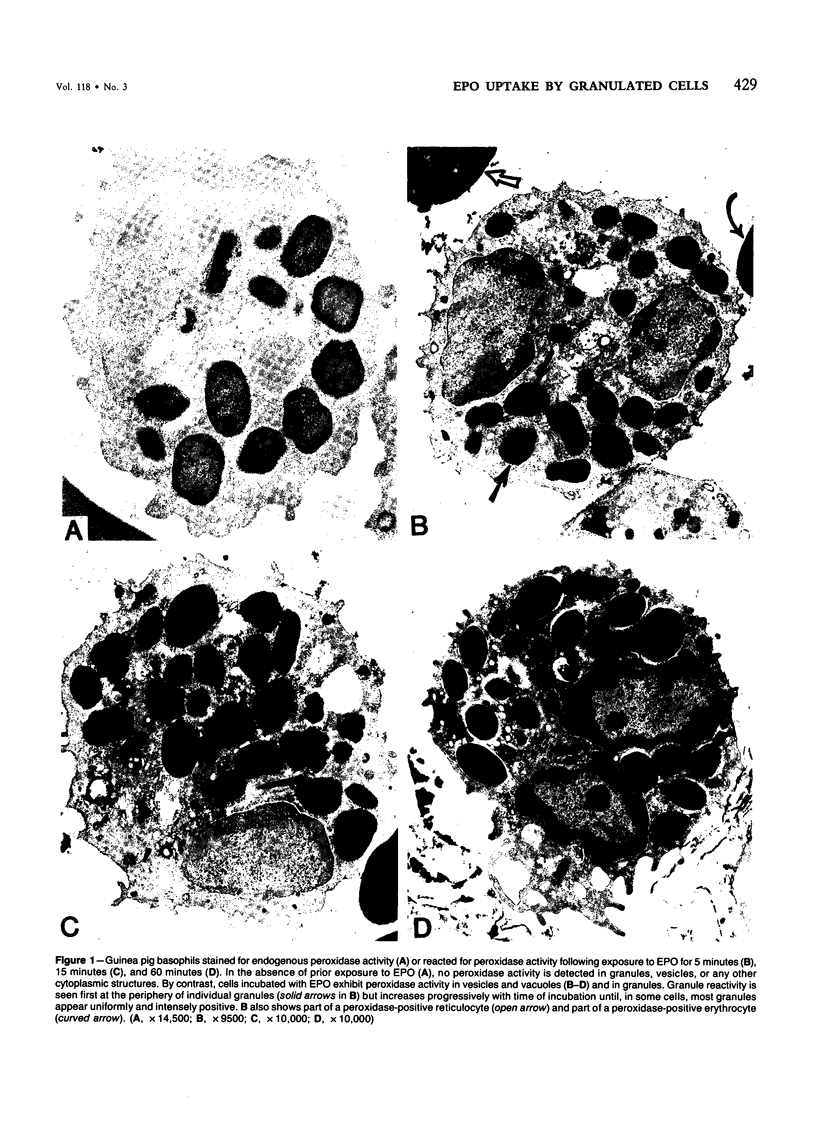
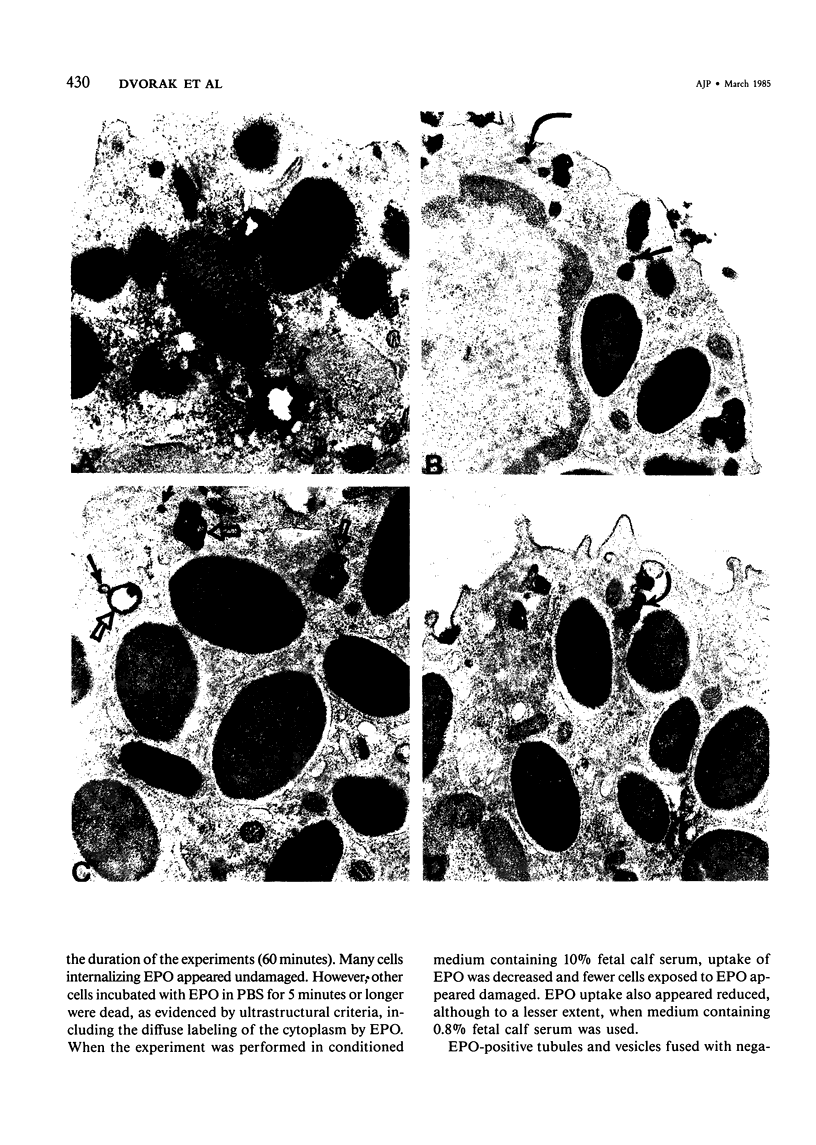
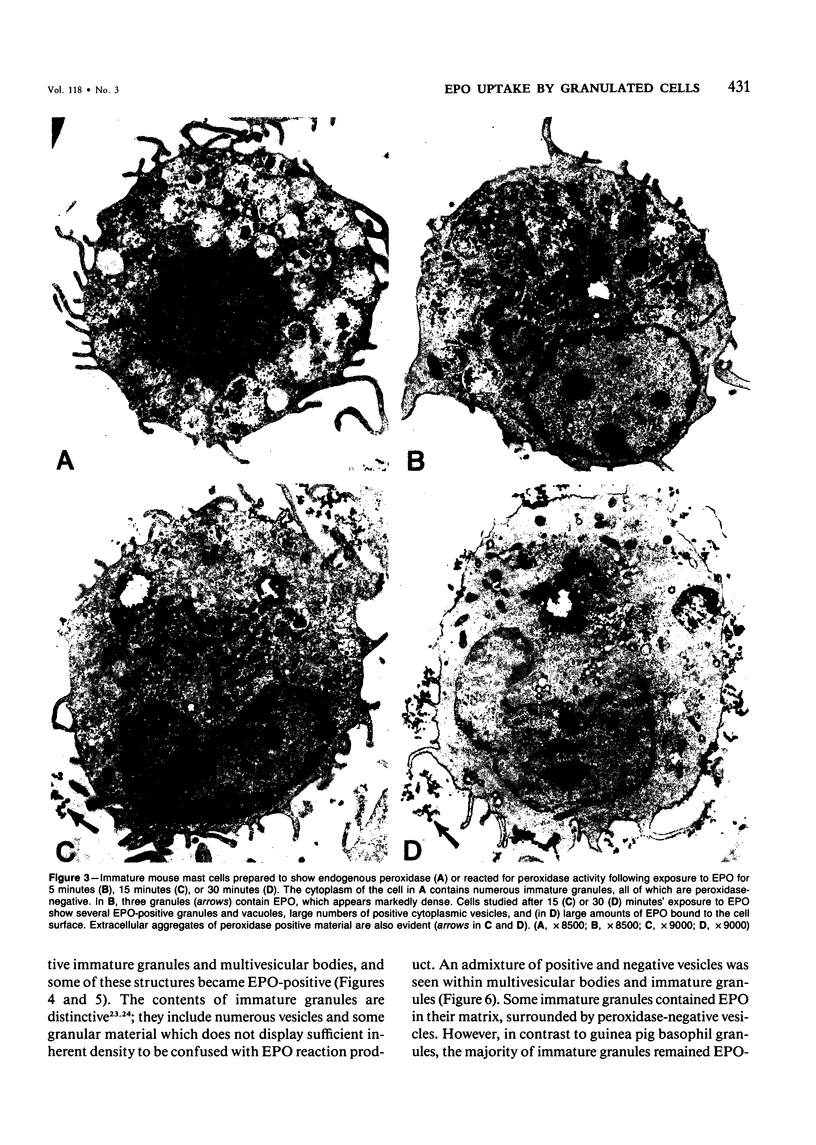
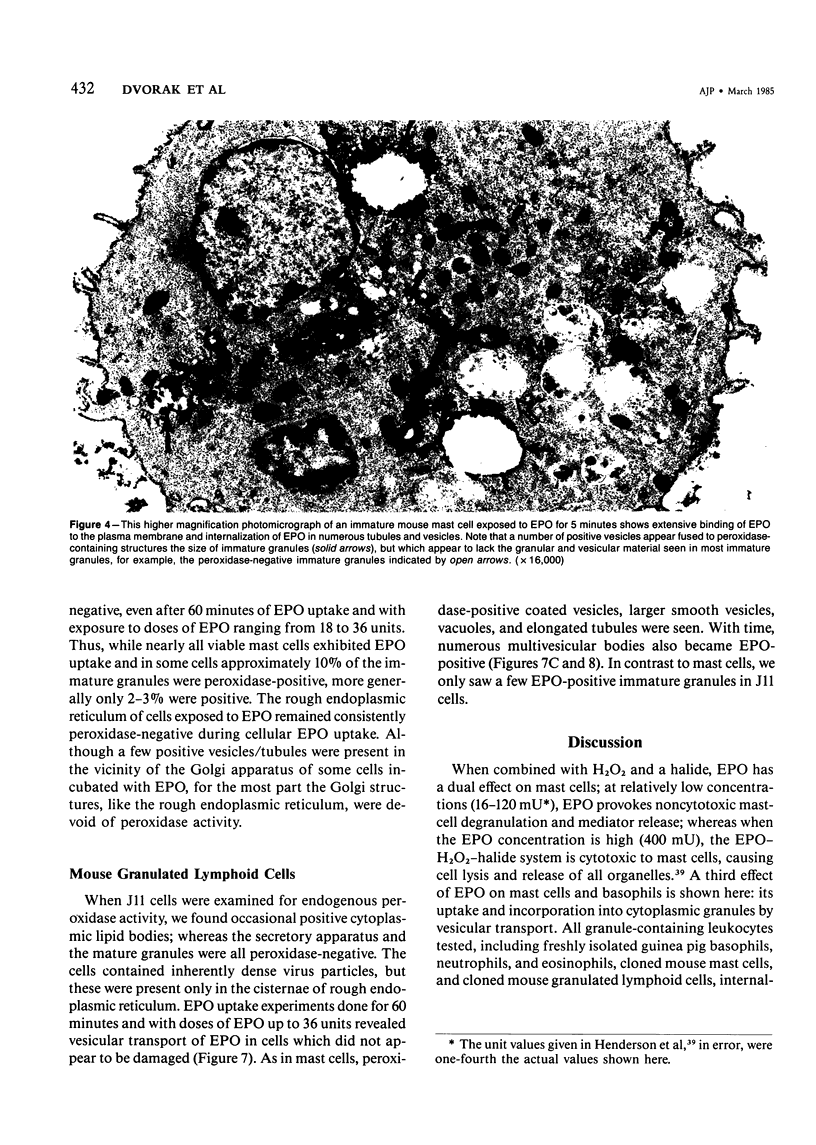
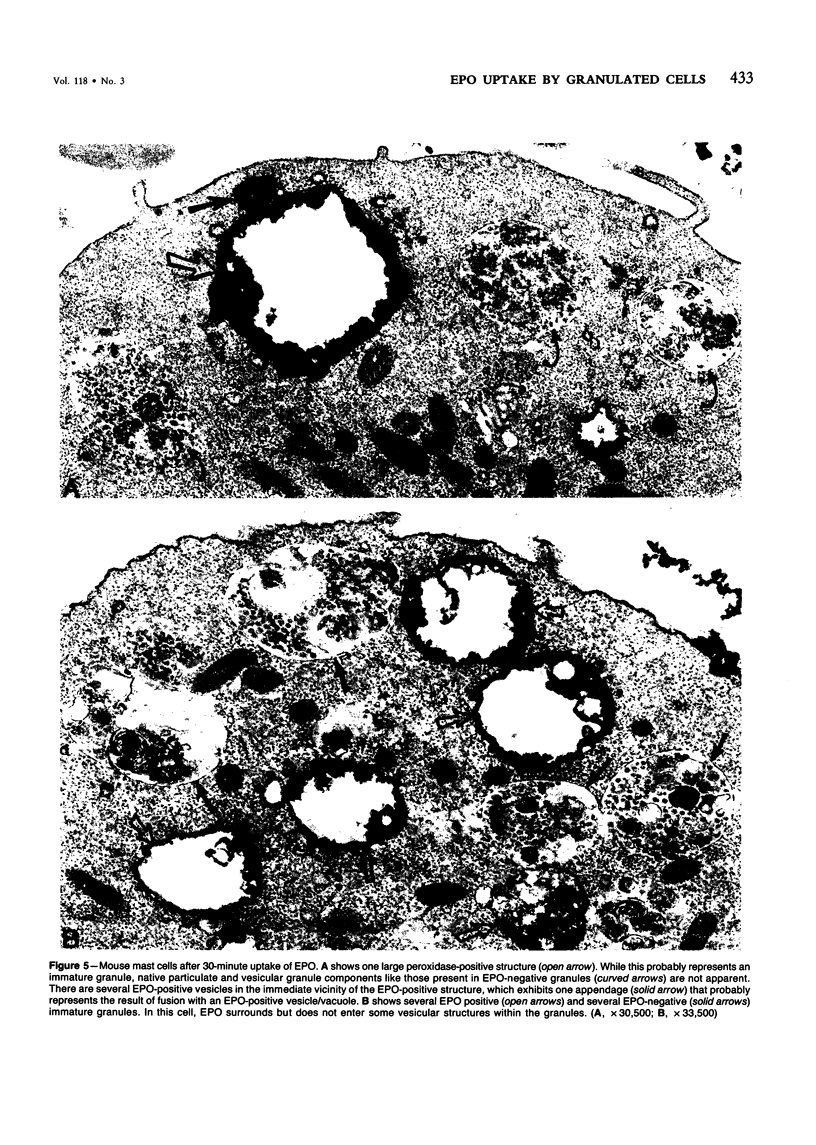
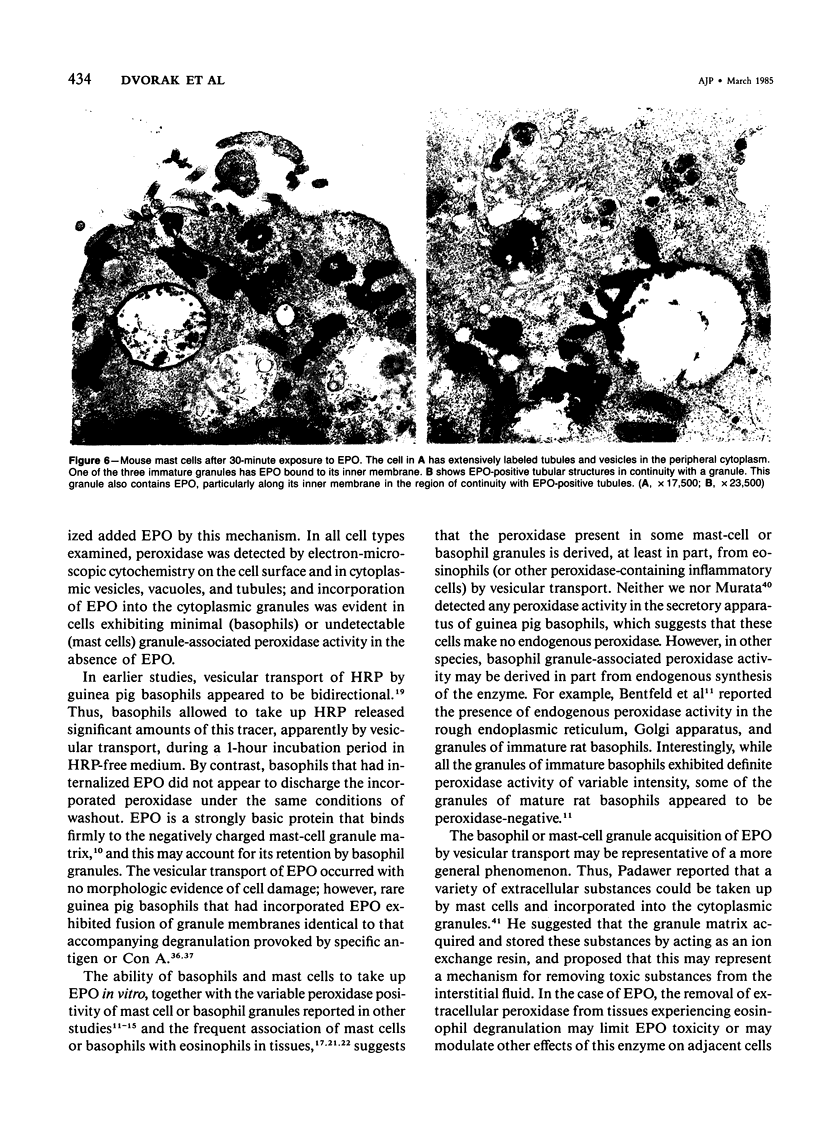
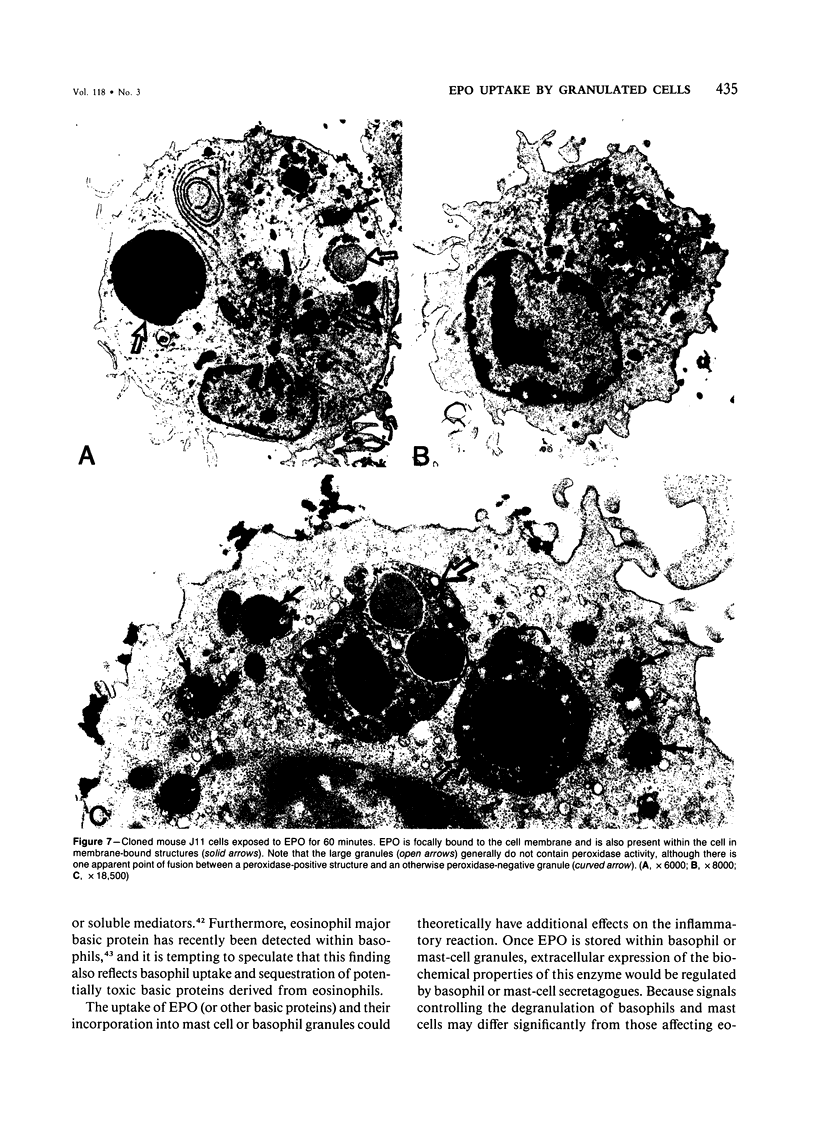
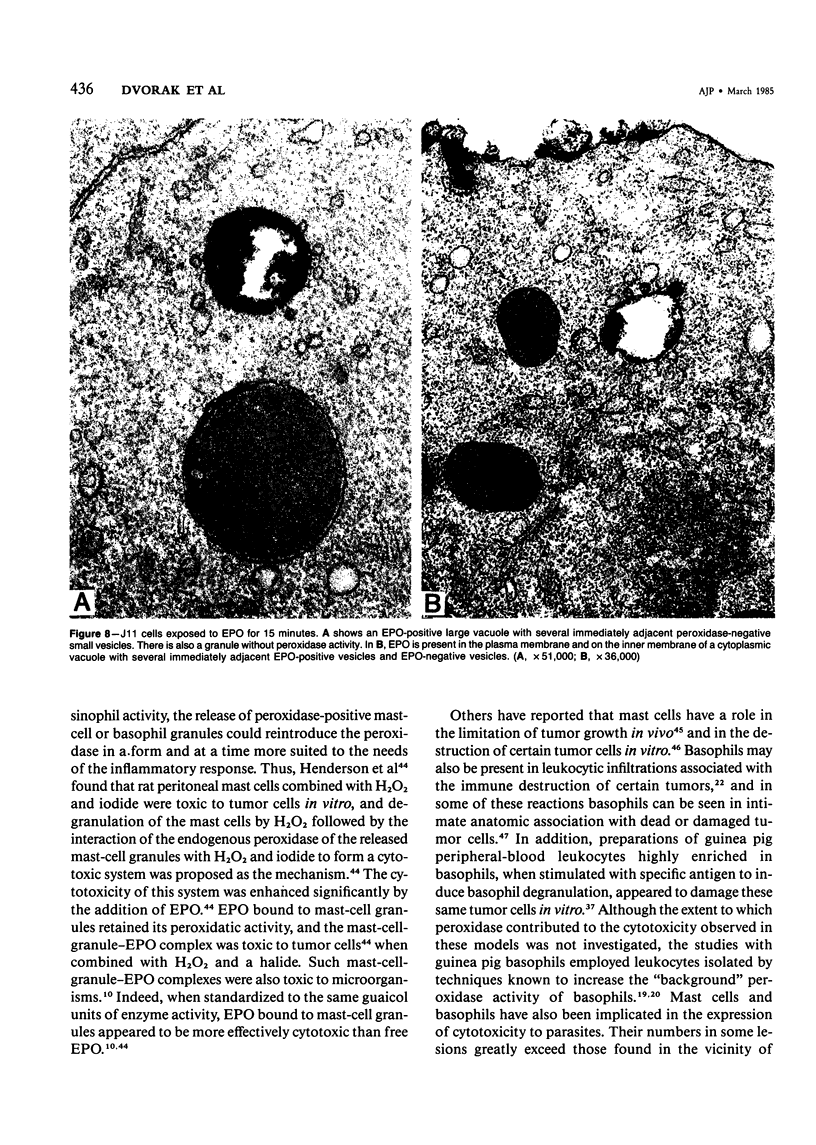
Guinea pig basophils, cloned mouse mast cells, and cloned mouse granule-containing lymphoid cells were found to utilize a vesicular transport system to internalize eosinophil peroxidase (EPO) added in vitro. Kinetic analysis indicated that EPO internalization involved the binding of EPO to the plasma membrane, the formation of complex surface invaginations, and the movement of EPO-laden vesicles, tubules, and vacuoles toward the center of the cells. EPO became associated with multivesicular bodies in granule-containing lymphoid cells and mast cells, with immature granules in mast cells, and with mature granules in basophils. In other cells, the endogenous production of granule peroxidases (neutrophils and eosinophils) or the prior uptake of exogenous peroxidatic substances (some basophils) precluded cytochemical analysis of granules for EPO. Vesicular transport of EPO provides a possible explanation for the variable detection of peroxidase activity in mast cells or basophils. It also provides a mechanism for sequestration of this potentially toxic material or for its storage for possible future use.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ackerman G. A., Clark M. A. Ultrastructural localization of peroxidase activity in human basophil leukocytes. Acta Haematol. 1971;45(5):280–284. doi: 10.1159/000208637. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ackerman S. J., Kephart G. M., Habermann T. M., Greipp P. R., Gleich G. J. Localization of eosinophil granule major basic protein in human basophils. J Exp Med. 1983 Sep 1;158(3):946–961. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.3.946. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anwar A. R., McKean J. R., Smithers S. R., Kay A. B. Human eosinophil- and neutrophil-mediated killing of schistosomula of Schistosoma mansoni in vitro. I. Enhancement of complement-dependent damage by mast cell-derived mediators and formyl methionyl peptides. J Immunol. 1980 Mar;124(3):1122–1129. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bainton D. F., Farquhar M. G. Segregation and packaging of granule enzymes in eosinophilic leukocytes. J Cell Biol. 1970 Apr;45(1):54–73. doi: 10.1083/jcb.45.1.54. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bainton D. F., Ullyot J. L., Farquhar M. G. The development of neutrophilic polymorphonuclear leukocytes in human bone marrow. J Exp Med. 1971 Oct 1;134(4):907–934. doi: 10.1084/jem.134.4.907. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bentfeld M. E., Nichols B. A., Bainton D. F. Ultrastructural localization of peroxidase in leukocytes of rat bone marrow and blood. Anat Rec. 1977 Feb;187(2):219–240. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091870208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown S. J., Galli S. J., Gleich G. J., Askenase P. W. Ablation of immunity to Amblyomma americanum by anti-basophil serum: cooperation between basophils and eosinophils in expression of immunity to ectoparasites (ticks) in guinea pigs. J Immunol. 1982 Aug;129(2):790–796. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capron M., Capron A., Goetzl E. J., Austen K. F. Tetrapeptides of the eosinophil chemotactic factor of anaphylaxis (ECF-A) enhance eosinophil Fc receptor. Nature. 1981 Jan 1;289(5793):71–73. doi: 10.1038/289071a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capron M., Capron A., Torpier G., Bazin H., Bout D., Joseph M. Eosinophil-dependent cytotoxicity in rat schistosomiasis. Involvement of IgG2a antibody and role of mast cells. Eur J Immunol. 1978 Feb;8(2):127–133. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830080211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capron M., Rousseaux J., Mazingue C., Bazin H., Capron A. Rat mast cell-eosinophil interaction in antibody-dependent eosinophil cytotoxicity to Schistosoma mansoni schistosomula. J Immunol. 1978 Dec;121(6):2518–2525. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chi E. Y., Henderson W. R. Ultrastructure of mast cell degranulation induced by eosinophil peroxidase: Use of diaminobenzidine cytochemistry by scanning electron microscopy. J Histochem Cytochem. 1984 Mar;32(3):337–341. doi: 10.1177/32.3.6420461. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christie K. N., Stoward P. J. Endogenous peroxidase in mast cells localized with a semipermeable membrane technique. Histochem J. 1978 Jul;10(4):425–433. doi: 10.1007/BF01003006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dvorak A. M., Dvorak H. F., Karnovsky M. J. Uptake of horseradish peroxidase by guinea pig basophilic leukocytes. Lab Invest. 1972 Jan;26(1):27–39. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dvorak A. M., Galli S. J., Galli A. S., Hammond M. E., Churchill W. H., Jr, Dvorak H. F. Tumor-basophil interactions in vitro--a scanning and transmission electron microscopic study. J Immunol. 1979 Jun;122(6):2447–2457. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dvorak A. M., Galli S. J., Marcum J. A., Nabel G., der Simonian H., Goldin J., Monahan R. A., Pyne K., Cantor H., Rosenberg R. D. Cloned mouse cells with natural killer function and cloned suppressor T cells express ultrastructural and biochemical features not shared by cloned inducer T cells. J Exp Med. 1983 Mar 1;157(3):843–861. doi: 10.1084/jem.157.3.843. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dvorak A. M., Galli S. J., Morgan E., Galli A. S., Hammond M. E., Dvorak H. F. Anaphylactic degranulation of guinea pig basophilic leukocytes. I. Fusion of granule membranes and cytoplasmic vesicles formation and resolution of degranulation sacs. Lab Invest. 1981 Feb;44(2):174–191. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dvorak A. M., Hammond M. E., Morgan E., Orenstein N. S., Galli S. J., Dvorak H. F. Evidence for a vesicular transport mechanism in guinea pig basophilic leukocytes. Lab Invest. 1980 Feb;42(2):263–276. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dvorak A. M., Mihm M. C., Jr, Osage J. E., Kwan T. H., Austen K. F., Wintroub B. U. Bullous pemphigoid, an ultrastructural study of the inflammatory response: eosinophil, basophil and mast cell granule changes in multiple biopsies from one patient. J Invest Dermatol. 1982 Feb;78(2):91–101. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12505711. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dvorak A. M., Monahan R. A., Dickersin G. R. Diagnostic electron microscopy. I. Hematology: differential diagnosis of acute lymphoblastic and acute myeloblastic leukemia. Use of ultrastructural peroxidase cytochemistry and routine electron microscopic technology. Pathol Annu. 1981;16(Pt 1):101–137. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dvorak A. M., Monahan R. A., Osage J. E., Dickersin G. R. Crohn's disease: transmission electron microscopic studies. II. Immunologic inflammatory response. Alterations of mast cells, basophils, eosinophils, and the microvasculature. Hum Pathol. 1980 Nov;11(6):606–619. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(80)80072-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dvorak A. M., Nabel G., Pyne K., Cantor H., Dvorak H. F., Galli S. J. Ultrastructural identification of the mouse basophil. Blood. 1982 Jun;59(6):1279–1285. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dvorak A. M. Ultrastructural evidence for release of major basic protein-containing crystalline cores of eosinophil granules in vivo: cytotoxic potential in Crohn's disease. J Immunol. 1980 Jul;125(1):460–462. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dvorak H. F., Dvorak A. M., Churchill W. H. Immunologic rejection of diethylnitrosamine-induced hepatomas in strain 2 guinea pigs: participation of basophilic leukocytes and macrophage aggregates. J Exp Med. 1973 Mar 1;137(3):751–775. doi: 10.1084/jem.137.3.751. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dvorak H. F., Selvaggio S. S., Dvorak A. M., Colvin R. B., Lean D. B., Rypysc J. Purification of basophilic leukocytes from guinea pig blood and bone marrow. J Immunol. 1974 Dec;113(6):1694–1702. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farram E., Nelson D. S. Mouse mast cells as anti-tumor effector cells. Cell Immunol. 1980 Oct;55(2):294–301. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(80)90162-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fung M. C., Hapel A. J., Ymer S., Cohen D. R., Johnson R. M., Campbell H. D., Young I. G. Molecular cloning of cDNA for murine interleukin-3. Nature. 1984 Jan 19;307(5948):233–237. doi: 10.1038/307233a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galli S. J., Dvorak A. M., Dvorak H. F. Basophils and mast cells: morphologic insights into their biology, secretory patterns, and function. Prog Allergy. 1984;34:1–141. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galli S. J., Dvorak A. M., Ishizaka T., Nabel G., Der Simonian H., Cantor H., Dvorak H. F. A cloned cell with NK function resembles basophils by ultrastructure and expresses IgE receptors. Nature. 1982 Jul 15;298(5871):288–290. doi: 10.1038/298288a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galli S. J., Dvorak A. M., Marcum J. A., Ishizaka T., Nabel G., Der Simonian H., Pyne K., Goldin J. M., Rosenberg R. D., Cantor H. Mast cell clones: a model for the analysis of cellular maturation. J Cell Biol. 1982 Nov;95(2 Pt 1):435–444. doi: 10.1083/jcb.95.2.435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galli S. J., Dvorak A. M., Marcum J. A., Nabel G., Goldin J. M., Rosenberg R. D., Cantor H., Dvorak H. F. Mouse mast cell clones: modulation of functional maturity in vitro. Monogr Allergy. 1983;18:166–170. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ha T. Y., Reed N. D., Crowle P. K. Delayed expulsion of adult Trichinella spiralis by mast cell-deficient W/Wv mice. Infect Immun. 1983 Jul;41(1):445–447. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.1.445-447.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson W. R., Chi E. Y., Jong E. C., Klebanoff S. J. Mast cell-mediated tumor-cell cytotoxicity. Role of the peroxidase system. J Exp Med. 1981 Mar 1;153(3):520–533. doi: 10.1084/jem.153.3.520. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson W. R., Chi E. Y., Klebanoff S. J. Eosinophil peroxidase-induced mast cell secretion. J Exp Med. 1980 Aug 1;152(2):265–279. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.2.265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson W. R., Jong E. C., Klebanoff S. J. Binding of eosinophil peroxidase to mast cell granules with retention of peroxidatic activity. J Immunol. 1980 Mar;124(3):1383–1388. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson W. R., Jörg A., Klebanoff S. J. Eosinophil peroxidase-mediated inactivation of leukotrienes B4, C4, and D4. J Immunol. 1982 Jun;128(6):2609–2613. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson W. R., Kaliner M. Mast cell granule peroxidase: location, secretion, and SRS-A inactivation. J Immunol. 1979 Apr;122(4):1322–1328. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jong E. C., Chi E. Y., Klebanoff S. J. Human neutrophil-mediated killing of schistosomula of Schistosoma mansoni: augmentation by schistosomal binding of eosinophil peroxidase. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1984 Jan;33(1):104–115. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1984.33.104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jörg A., Pasquier J. M., Klebanoff S. J. Purification of horse eosinophil peroxidase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Feb 18;701(2):185–191. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(82)90112-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karnovsky M. J. The ultrastructural basis of capillary permeability studied with peroxidase as a tracer. J Cell Biol. 1967 Oct;35(1):213–236. doi: 10.1083/jcb.35.1.213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitamura Y., Go S., Hatanaka K. Decrease of mast cells in W/Wv mice and their increase by bone marrow transplantation. Blood. 1978 Aug;52(2):447–452. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Locksley R. M., Wilson C. B., Klebanoff S. J. Role for endogenous and acquired peroxidase in the toxoplasmacidal activity of murine and human mononuclear phagocytes. J Clin Invest. 1982 May;69(5):1099–1111. doi: 10.1172/JCI110545. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MONTAGNA W., NOBACK C. R. Localization of lipids and other chemical substances in the mast cells of man and laboratory mammals. Anat Rec. 1948 Apr;100(4):535–545. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091000404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nabel G., Allard W. J., Cantor H. A cloned cell line mediating natural killer cell function inhibits immunoglobulin secretion. J Exp Med. 1982 Aug 1;156(2):658–663. doi: 10.1084/jem.156.2.658. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nabel G., Allard W. J., Cantor H. A cloned cell line mediating natural killer cell function inhibits immunoglobulin secretion. J Exp Med. 1982 Aug 1;156(2):658–663. doi: 10.1084/jem.156.2.658. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nabel G., Galli S. J., Dvorak A. M., Dvorak H. F., Cantor H. Inducer T lymphocytes synthesize a factor that stimulates proliferation of cloned mast cells. Nature. 1981 May 28;291(5813):332–334. doi: 10.1038/291332a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan C. F., Klebanoff S. J. Augmentation of spontaneous macrophage-mediated cytolysis by eosinophil peroxidase. J Exp Med. 1982 May 1;155(5):1291–1308. doi: 10.1084/jem.155.5.1291. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nogueira N. M., Klebanoff S. J., Cohn Z. A. T. cruzi: sensitization to macrophage killing by eosinophil peroxidase. J Immunol. 1982 Apr;128(4):1705–1708. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramsey P. G., Martin T., Chi E., Klebanoff S. J. Arming of mononuclear phagocytes by eosinophil peroxidase bound to Staphylococcus aureus. J Immunol. 1982 Jan;128(1):415–420. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanooka H., Kitamura Y., Sado T., Tanaka K., Nagase M., Kondo S. Evidence for involvement of mast cells in tumor suppression in mice. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1982 Dec;69(6):1305–1309. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokota T., Lee F., Rennick D., Hall C., Arai N., Mosmann T., Nabel G., Cantor H., Arai K. Isolation and characterization of a mouse cDNA clone that expresses mast-cell growth-factor activity in monkey cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Feb;81(4):1070–1074. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.4.1070. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]