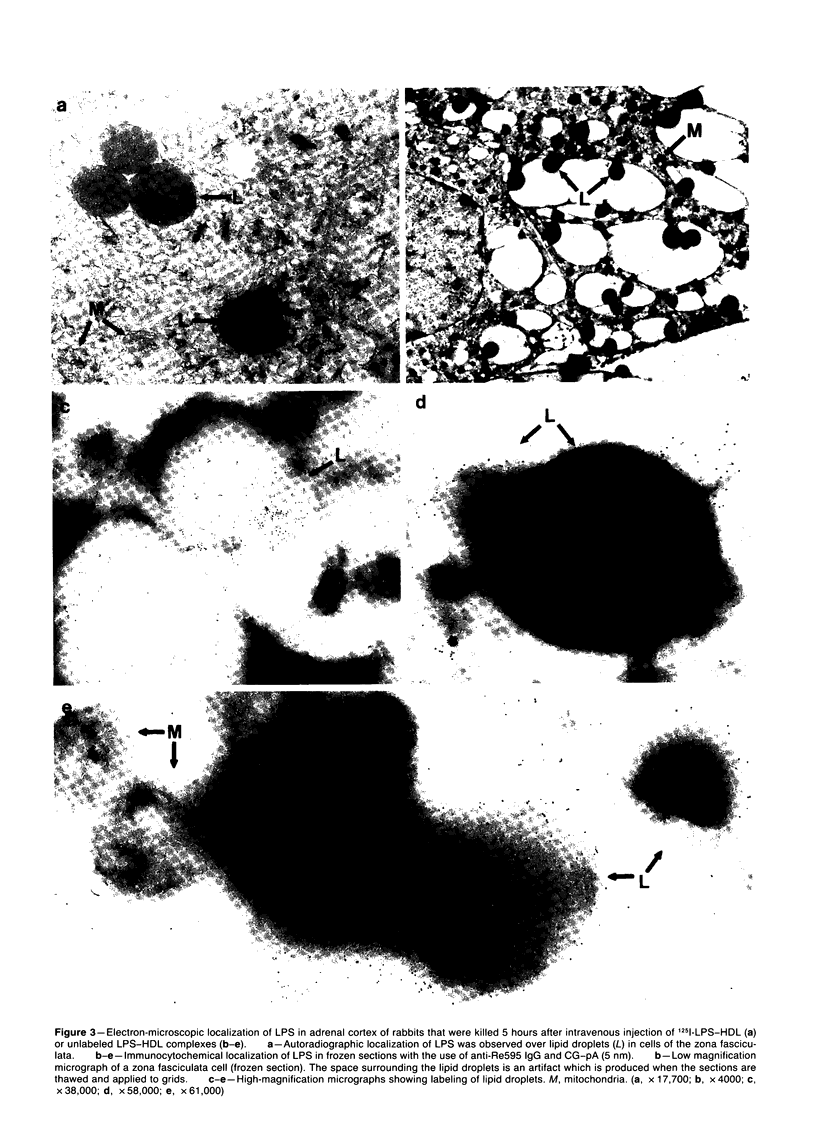
Abstract
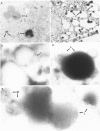
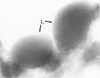
For determination of the kinetics of uptake and subcellular localization of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) from LPS-high density lipoprotein (LPS-HDL) complexes in the adrenal gland, LPS-HDL complexes were isolated by immunoaffinity chromatography of 125I-Salmonella minnesota Re595 LPS that had been incubated with 20 mM EDTA-rabbit plasma. After intravenous injection of LPS-HDL complexes in rabbits, preferential uptake of the LPS was observed in the adrenal, so that by 5 hours, adrenal-tissue-bound LPS concentrations (determined by use of 131I-BSA blood marker) exceeded all other tissues examined, including liver and spleen, by at least three-fold. For determination of the subcellular localization of LPS, cholesterol-rich (lipid droplet) fractions and cholesterol-depleted fractions were obtained by ultracentrifugation of homogenates of adrenal tissue from rabbits killed at various times after injection of LPS-HDL complexes. As much as 40% of the adrenal-tissue-bound LPS was recovered in the cholesterol-rich fraction 2.5-24 hours after injection of LPS-HDL complexes. Electron-microscopic autoradiographic and immunocytochemical analysis of adrenal cortex of animals killed 5 hours after injection of LPS-HDL complexes demonstrated specific localization of LPS in lipid droplets. These data thus provide direct evidence for the uptake of LPS into the adrenal cortex of animals with intravascular LPS-HDL complexes and indicate that further study of the effect of LPS on adrenocortical function is warranted.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersen J. M., Dietschy J. M. Kinetic parameters of the lipoprotein transport systems in the adrenal gland of the rat determined in vivo. Comparison of low and high density lipoproteins of human and rat origin. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jul 25;256(14):7362–7370. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BERRY L. J., SMYTHE D. S., YOUNG L. G. Effects of bacterial endotoxin on metabolism. I. Carbohydrate depletion and the protective role of cortisone. J Exp Med. 1959 Sep 1;110:389–405. doi: 10.1084/jem.110.3.389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L. Receptor-mediated endocytosis: insights from the lipoprotein receptor system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jul;76(7):3330–3337. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.7.3330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CARO L. G., VAN TUBERGEN R. P., KOLB J. A. High-resolution autoradiography. I. Methods. J Cell Biol. 1962 Nov;15:173–188. doi: 10.1083/jcb.15.2.173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHEDID L., PARANT M. [Study of the tolerance of adrenalectomized mice using an endotoxin labeled with Cr-51]. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1961 Aug;101:170–177. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catalano R. D., Parameswaran V., Ramachandran J., Trunkey D. D. Mechanisms of adrenocortical depression during Escherichia coli shock. Arch Surg. 1984 Feb;119(2):145–150. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1984.01390140011002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncan R. L., Jr, Morrison D. C. The fate of E. coli lipopolysaccharide after the uptake of E. coli by murine macrophages in vitro. J Immunol. 1984 Mar;132(3):1416–1424. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOLCH J., LEES M., SLOANE STANLEY G. H. A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipides from animal tissues. J Biol Chem. 1957 May;226(1):497–509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faulk W. P., Taylor G. M. An immunocolloid method for the electron microscope. Immunochemistry. 1971 Nov;8(11):1081–1083. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(71)90496-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galanos C., Lüderitz O., Westphal O. A new method for the extraction of R lipopolysaccharides. Eur J Biochem. 1969 Jun;9(2):245–249. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1969.tb00601.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman D. S. Cholesterol ester metabolism. Physiol Rev. 1965 Oct;45(4):747–839. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1965.45.4.747. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gwynne J. T., Hess B. The role of high density lipoproteins in rat adrenal cholesterol metabolism and steroidogenesis. J Biol Chem. 1980 Nov 25;255(22):10875–10883. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall C. L., Munford R. S. Enzymatic deacylation of the lipid A moiety of Salmonella typhimurium lipopolysaccharides by human neutrophils. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Nov;80(21):6671–6675. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.21.6671. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keri G., Parameswaran V., Trunkey D. D., Ramachandran J. Effects of septic shock plasma on adrenocortical cell function. Life Sci. 1981 Apr 27;28(17):1917–1923. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(81)90299-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kita T., Beisiegel U., Goldstein J. L., Schneider W. J., Brown M. S. Antibody against low density lipoprotein receptor blocks uptake of low density lipoprotein (but not high density lipoprotein) by the adrenal gland of the mouse in vivo. J Biol Chem. 1981 May 25;256(10):4701–4703. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovanen P. T., Schneider W. J., Hillman G. M., Goldstein J. L., Brown M. S. Separate mechanisms for the uptake of high and low density lipoproteins by mouse adrenal gland in vivo. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jun 25;254(12):5498–5505. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maitra S. K., Rachmilewitz D., Eberle D., Kaplowitz N. The hepatocellular uptake and biliary excretion of endotoxin in the rat. Hepatology. 1981 Sep-Oct;1(5):401–407. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840010506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathison J. C., La Forest A. C., Ulevitch R. J. Properties and requirements for production of a macrophage product which suppresses steroid production by adrenocortical cells. Infect Immun. 1984 Aug;45(2):360–366. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.2.360-366.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathison J. C., Schreiber R. D., La Forest A. C., Ulevitch R. J. Suppression of ACTH-induced steroidogenesis by supernatants from LPS-treated peritoneal exudate macrophages. J Immunol. 1983 Jun;130(6):2757–2762. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathison J. C., Ulevitch R. J. In vivo interaction of bacterial lipopolysaccharide (LPS) with rabbit platelets: modulation by C3 and high density lipoproteins. J Immunol. 1981 Apr;126(4):1575–1580. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathison J. C., Ulevitch R. J. The clearance, tissue distribution, and cellular localization of intravenously injected lipopolysaccharide in rabbits. J Immunol. 1979 Nov;123(5):2133–2143. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moses H. L., Davis W. W., Rosenthal A. S., Garren L. D. Adrenal cholesterol: localization by electron-microscope autoradiography. Science. 1969 Mar 14;163(3872):1203–1205. doi: 10.1126/science.163.3872.1203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munford R. S., Andersen J. M., Dietschy J. M. Sites of tissue binding and uptake in vivo of bacterial lipopolysaccharide-high density lipoprotein complexes: studies in the rat and squirrel monkey. J Clin Invest. 1981 Dec;68(6):1503–1513. doi: 10.1172/JCI110404. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REYNOLDS E. S. The use of lead citrate at high pH as an electron-opaque stain in electron microscopy. J Cell Biol. 1963 Apr;17:208–212. doi: 10.1083/jcb.17.1.208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth J., Bendayan M., Orci L. Ultrastructural localization of intracellular antigens by the use of protein A-gold complex. J Histochem Cytochem. 1978 Dec;26(12):1074–1081. doi: 10.1177/26.12.366014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schumer W. Steroids in the treatment of clinical septic shock. Ann Surg. 1976 Sep;184(3):333–341. doi: 10.1097/00000658-197609000-00011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sibbald W. J., Short A., Cohen M. P., Wilson R. F. Variations in adrenocortical responsiveness during severe bacterial infections. Unrecognized adrenocortical insufficiency in severe bacterial infections. Ann Surg. 1977 Jul;186(1):29–33. doi: 10.1097/00000658-197707000-00005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tokuyasu K. T. A study of positive staining of ultrathin frozen sections. J Ultrastruct Res. 1978 Jun;63(3):287–307. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(78)80053-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tokuyasu K. T., Singer S. J. Improved procedures for immunoferritin labeling of ultrathin frozen sections. J Cell Biol. 1976 Dec;71(3):894–906. doi: 10.1083/jcb.71.3.894. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulevitch R. J., Cochrane C. G., Henson P. M., Morrison D. C., Doe W. F. Mediation systems in bacterial lipopolysaccharide-induced hypotension and disseminated intravascular coagulation. I. The role of complement. J Exp Med. 1975 Dec 1;142(6):1570–1590. doi: 10.1084/jem.142.6.1570. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulevitch R. J., Johnston A. R. The modification of biophysical and endotoxic properties of bacterial lipopolysaccharides by serum. J Clin Invest. 1978 Dec;62(6):1313–1324. doi: 10.1172/JCI109252. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulevitch R. J., Johnston A. R., Weinstein D. B. New function for high density lipoproteins. Isolation and characterization of a bacterial lipopolysaccharide-high density lipoprotein complex formed in rabbit plasma. J Clin Invest. 1981 Mar;67(3):827–837. doi: 10.1172/JCI110100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulevitch R. J., Johnston A. R., Weinstein D. B. New function for high density lipoproteins. Their participation in intravascular reactions of bacterial lipopolysaccharides. J Clin Invest. 1979 Nov;64(5):1516–1524. doi: 10.1172/JCI109610. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulevitch R. J. The preparation and characterization of a radioiodinated bacterial lipopolysaccharide. Immunochemistry. 1978 Mar;15(3):157–164. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(78)90144-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]