Abstract
The regulation of cell growth in the kidney glomerulus plays a key role in many physiologic and pathologic processes. In this communication, the authors examine the possible role of heparin-like species as inhibitors of mesangial-cell proliferation. Heparin profoundly inhibited the growth of cultured mesangial cells in a dose-dependent manner, with an ED50 = 5-10 micrograms/ml. The antiproliferative activity of heparin was reversible and specific for mesangial cells as the target cell in the glomerulus. Heparin was much more effective than other glycosaminoglycans. Cultured glomerular epithelial cells were found to secrete both stimulators and inhibitors of mesangial-cell growth. Approximately half of the inhibitory activity was destroyed by a highly purified heparinase; the other half was sensitive to trypsin. Approximately 80% of the mitogenic activity was protease-sensitive. These results suggest that heparin and glomerular epithelial cells may participate in mesangial-cell growth regulation.
Full text
PDF


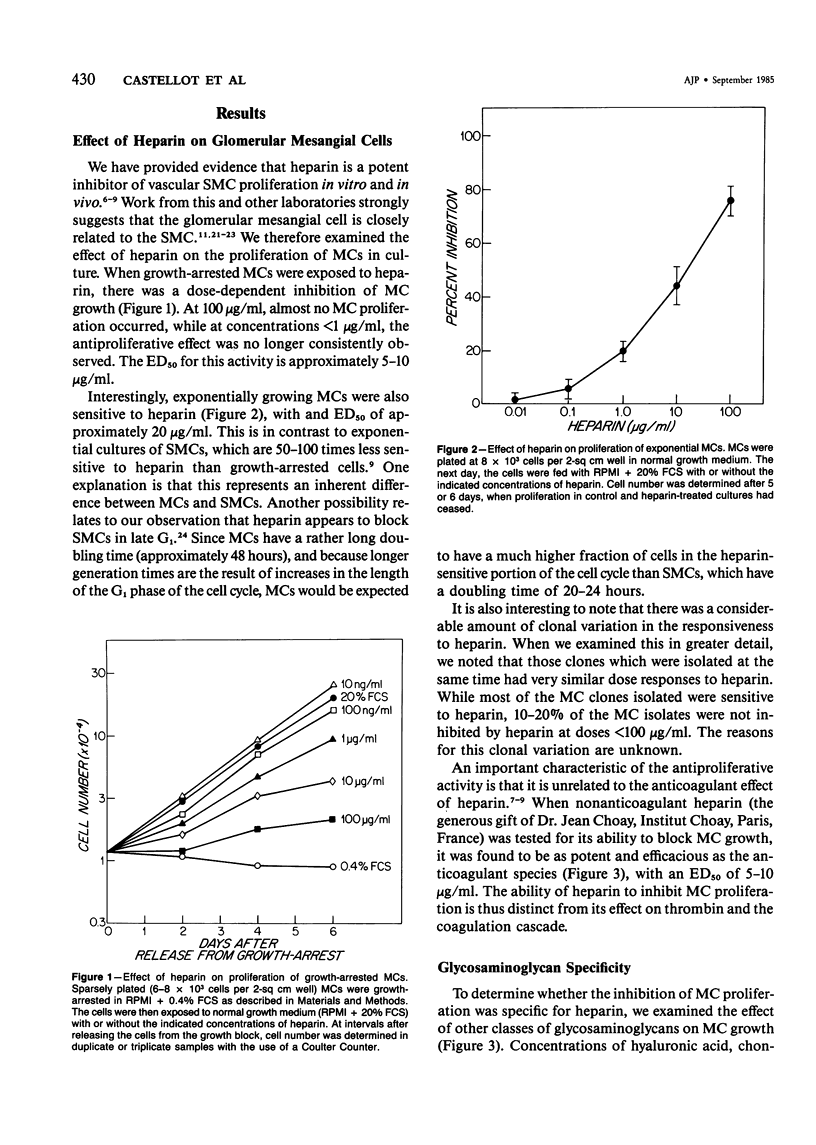
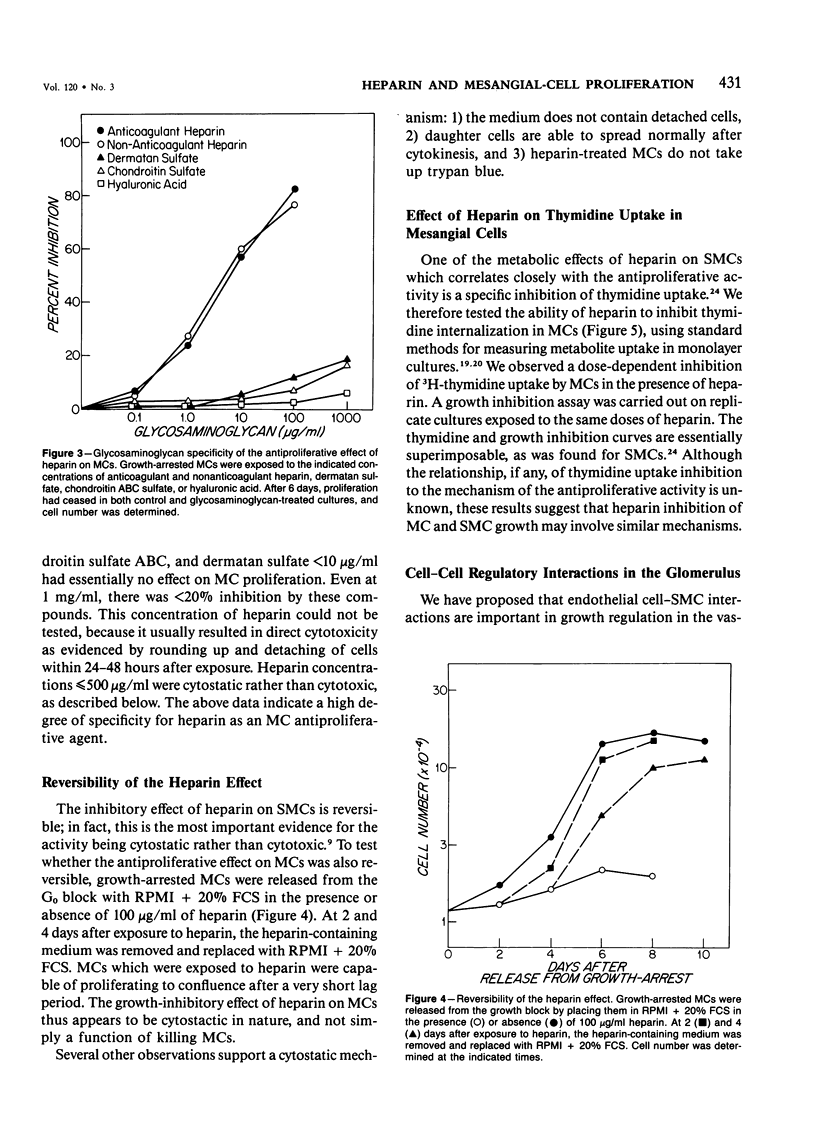
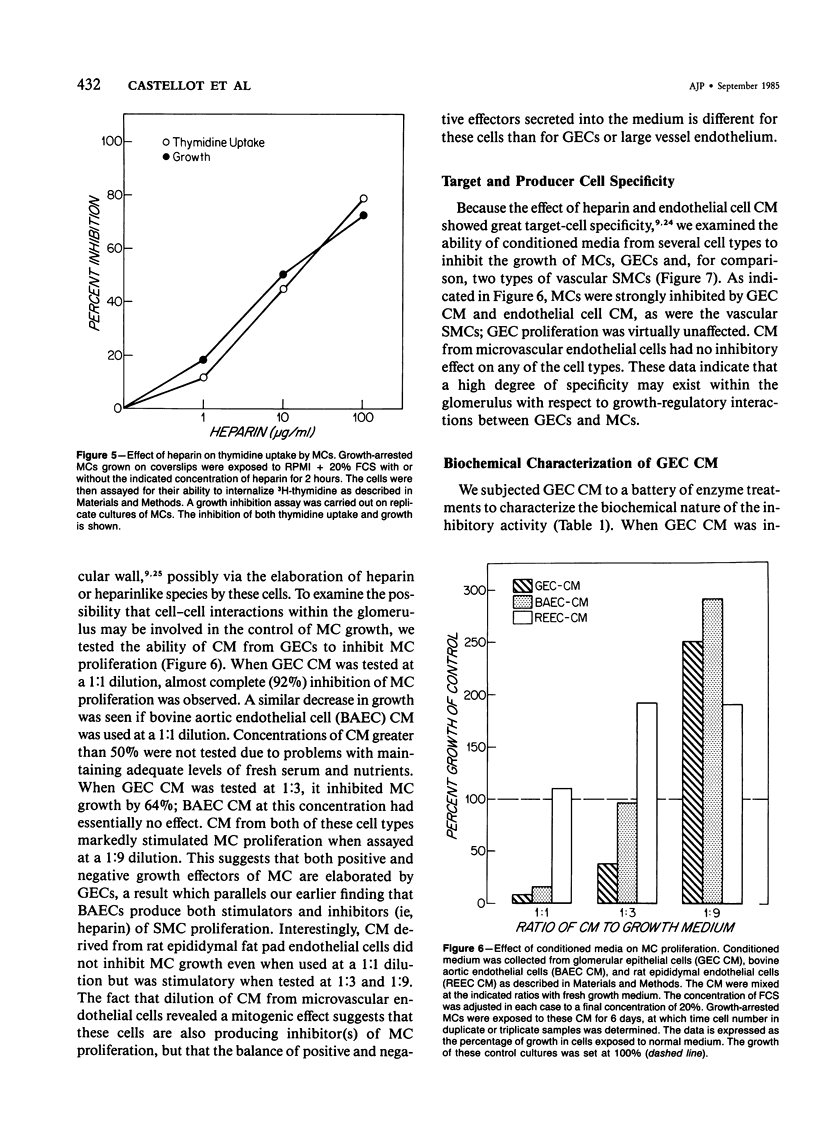
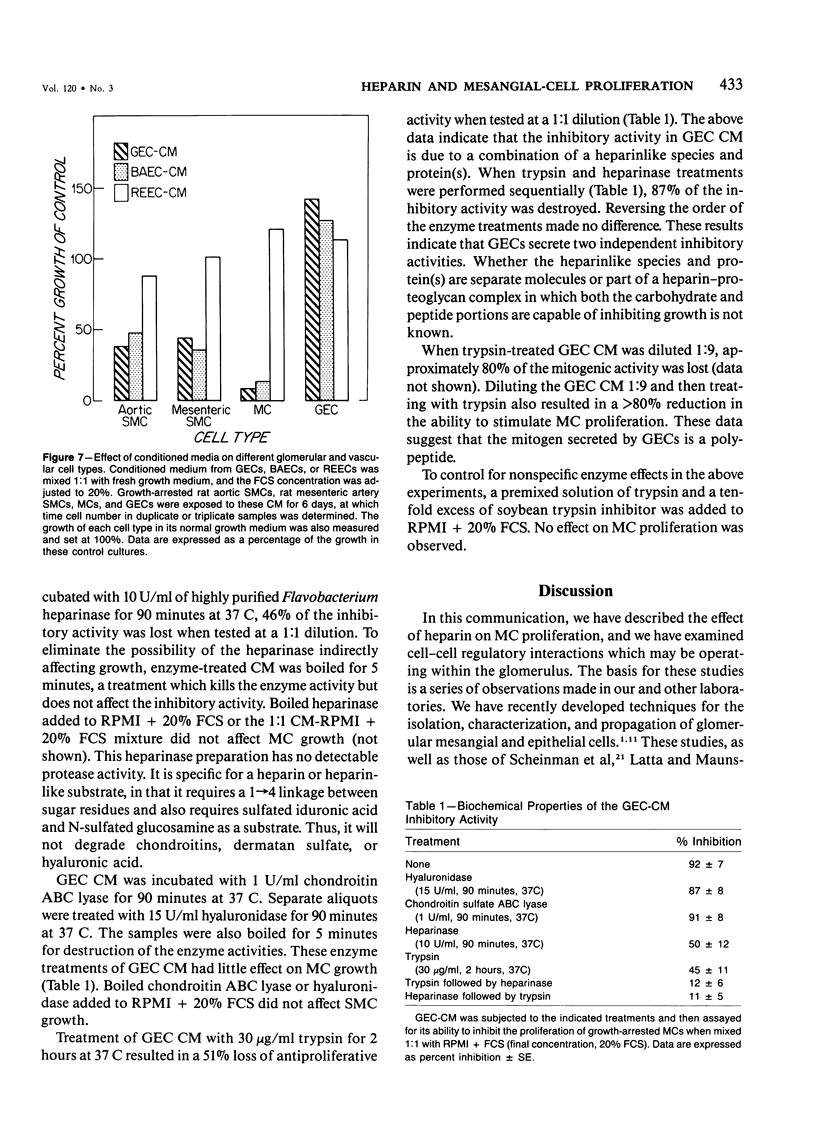


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ausiello D. A., Kreisberg J. I., Roy C., Karnovsky M. J. Contraction of cultured rat glomerular cells of apparent mesangial origin after stimulation with angiotensin II and arginine vasopressin. J Clin Invest. 1980 Mar;65(3):754–760. doi: 10.1172/JCI109723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burlington H., Cronkite E. P. Characteristics of cell cultures derived from renal glomeruli. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1973 Jan;142(1):143–149. doi: 10.3181/00379727-142-36977. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castellot J. J., Jr, Addonizio M. L., Rosenberg R., Karnovsky M. J. Cultured endothelial cells produce a heparinlike inhibitor of smooth muscle cell growth. J Cell Biol. 1981 Aug;90(2):372–379. doi: 10.1083/jcb.90.2.372. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castellot J. J., Jr, Cochran D. L., Karnovsky M. J. Effect of heparin on vascular smooth muscle cells. I. Cell metabolism. J Cell Physiol. 1985 Jul;124(1):21–28. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041240105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castellot J. J., Jr, Favreau L. V., Karnovsky M. J., Rosenberg R. D. Inhibition of vascular smooth muscle cell growth by endothelial cell-derived heparin. Possible role of a platelet endoglycosidase. J Biol Chem. 1982 Oct 10;257(19):11256–11260. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Churg J., Grishman E. Ultrastructure of glomerular disease: a review. Kidney Int. 1975 Apr;7(4):254–261. doi: 10.1038/ki.1975.37. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clowes A. W., Karnowsky M. J. Suppression by heparin of smooth muscle cell proliferation in injured arteries. Nature. 1977 Feb 17;265(5595):625–626. doi: 10.1038/265625a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guyton J. R., Rosenberg R. D., Clowes A. W., Karnovsky M. J. Inhibition of rat arterial smooth muscle cell proliferation by heparin. In vivo studies with anticoagulant and nonanticoagulant heparin. Circ Res. 1980 May;46(5):625–634. doi: 10.1161/01.res.46.5.625. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoover R. L., Rosenberg R., Haering W., Karnovsky M. J. Inhibition of rat arterial smooth muscle cell proliferation by heparin. II. In vitro studies. Circ Res. 1980 Oct;47(4):578–583. doi: 10.1161/01.res.47.4.578. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaffe E. A., Nachman R. L., Becker C. G., Minick C. R. Culture of human endothelial cells derived from umbilical veins. Identification by morphologic and immunologic criteria. J Clin Invest. 1973 Nov;52(11):2745–2756. doi: 10.1172/JCI107470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanwar Y. S., Farquhar M. G. Anionic sites in the glomerular basement membrane. In vivo and in vitro localization to the laminae rarae by cationic probes. J Cell Biol. 1979 Apr;81(1):137–153. doi: 10.1083/jcb.81.1.137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreisberg J. I., Hoover R. L., Karnovsky M. J. Isolation and characterization of rat glomerular epithelial cells in vitro. Kidney Int. 1978 Jul;14(1):21–30. doi: 10.1038/ki.1978.86. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LATTA H., MAUNSBACH A. B. Relations of the centrolobular region of the glomerulus to the juxtaglomerular apparatus. J Ultrastruct Res. 1962 Jun;6:562–578. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(62)80010-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larson D. M., Fujiwara K., Alexander R. W., Gimbrone M. A., Jr Heterogeneity of myosin antigenic expression in vascular smooth muscle in vivo. Lab Invest. 1984 Apr;50(4):401–407. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCully K. S., Rinehimer L. A., Gillies C. G., Hopfer S. M., Sunderman F. W., Jr Erythrocytosis, glomerulomegaly, mesangial hyperplasia, sialyl hyperplasia, and arteriosclerosis induced in rats by nickel subsulfide. Virchows Arch A Pathol Anat Histol. 1982;394(3):207–220. doi: 10.1007/BF00430666. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCully K. S., Sunderman F. W., Jr, Hopfer S. M., Kevorkian C. B., Reid M. C. Effects of unilateral nephrectomy on erythrocytosis and arteriosclerosis induced in rats by intrarenal injection of nickel subsulfide. Virchows Arch A Pathol Anat Histol. 1982;397(3):251–259. doi: 10.1007/BF00496568. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melcion C., Lachman L., Killen P. D., Morel-Maroger L., Striker G. E. Mesangial cells, effect of monocyte products on proliferation and matrix synthesis. Transplant Proc. 1982 Sep;14(3):559–564. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakashima Y., Hirose S., Hamashima Y. Proliferation of cultured rabbit renal glomerular cells stimulated by platelet factor. Acta Pathol Jpn. 1980 Jan;30(1):1–7. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1827.1980.tb01300.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ooi Y. M., Weiss M. A., Hsu A., Ooi B. S. Mechanisms of suppression of mouse mesangial cell proliferation by macrophage supernatants. J Immunol. 1983 Apr;130(4):1790–1795. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plagemann P. G., Richey D. P., Zylka J. M., Erbe J. Thymidine transport by Novikoff rat hepatoma cells synchronized by double hydroxyurea treatment. Exp Cell Res. 1974 Feb;83(2):303–310. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(74)90343-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purkerson M. L., Hoffsten P. E., Klahr S. Pathogenesis of the glomerulopathy associated with renal infarction in rats. Kidney Int. 1976 May;9(5):407–417. doi: 10.1038/ki.1976.50. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purkerson M. L., Joist J. H., Greenberg J. M., Kay D., Hoffsten P. E., Klahr S. Inhibition by anticoagulant drugs of the progressive hypertension and uremia associated with renal infarction in rats. Thromb Res. 1982 May 15;26(4):227–240. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(82)90287-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheinman J. I., Fish A. J., Brown D. M., Michael A. J. Human glomerular smooth muscle (mesangial) cells in culture. Lab Invest. 1976 Feb;34(2):150–158. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taub M., Sato G. Growth of functional primary cultures of kidney epithelial cells in defined medium. J Cell Physiol. 1980 Nov;105(2):369–378. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041050220. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner C. M., Lucas D. O., Nagle R. B. The effect of macrophages on the metabolism of glomerular cells: preliminary studies. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1983 Feb;33(2):93–107. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner R. C., Matthews M. A. The isolation and culture of capillary endothelium from epididymal fat. Microvasc Res. 1975 Nov;10(3):286–297. doi: 10.1016/0026-2862(75)90033-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson S. K., Solez K., Boitnott J. K., Heptinstall R. H. The effects of heparin treatment on hypertension and vascular lesions in stroke-prone spontaneously hypertensive rats. Am J Pathol. 1981 Jan;102(1):62–71. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


