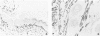Abstract
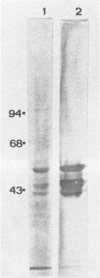
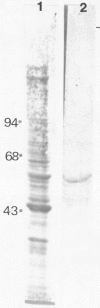
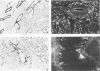
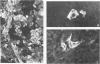
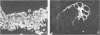
Normal testicular tissue and 76 testicular germ-cell tumors of various types were immunohistochemically evaluated for the expression of intermediate filament proteins of different types. In normal testes, the rete testis epithelium was positive to cytokeratin, and the Sertoli cells, stromal cells, and Leydig cells were positive for vimentin. Cytokeratin-positive cells were also found lining atrophic seminiferous tubules and were occasionally seen within nonatrophic seminiferous tubules. The classical seminomas showed vimentin positivity, but this was usually observed in a small number of tumor cells. In addition, nearly half the seminomas contained single cytokeratin-positive cells, some of which were multinucleated and appeared to represent syncytiotrophoblastic giant cells. The tumor cells in embryonal carcinomas, endodermal sinus tumors, and choriocarcinomas displayed cytokeratin positivity. In some embryonal carcinomas vimentin-positive tumor cells were also found, probably representing attempts at further differentiation of the tumor cells. In immature teratomas, both the immature and the mature epithelial structures showed cytokeratin positivity. The stromal components, including cartilage, contained vimentin, and the smooth-muscle elements, desmin. Neural tissue positive for neurofilaments and glial tissue positive for glial fibrillary acidic protein, were observed in 5 and 3 of 15 cases, respectively. It is considered that antibodies to intermediate filaments are suitable tools to characterize the differentiation patterns of testicular germ-cell tumors and have the potential to aid in the differential diagnosis especially between seminoma and embryonal carcinoma.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altmannsberger M., Osborn M., Schauer A., Weber K. Antibodies to different intermediate filament proteins. Cell type-specific markers on paraffin-embedded human tissues. Lab Invest. 1981 Nov;45(5):427–434. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderton B. H. Intermediate filaments: a family of homologous structures. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 1981 Jun;2(2):141–166. doi: 10.1007/BF00711866. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Badley R. A., Woods A., Carruthers L., Rees D. A. Cytoskeleton changes in fibroblast adhesion and detachment. J Cell Sci. 1980 Jun;43:379–390. doi: 10.1242/jcs.43.1.379. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Battifora H., Sheibani K., Tubbs R. R., Kopinski M. I., Sun T. T. Antikeratin antibodies in tumor diagnosis. Distinction between seminoma and embryonal carcinoma. Cancer. 1984 Sep 1;54(5):843–848. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19840901)54:5<843::aid-cncr2820540514>3.0.co;2-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blobel G. A., Gould V. E., Moll R., Lee I., Huszar M., Geiger B., Franke W. W. Coexpression of neuroendocrine markers and epithelial cytoskeletal proteins in bronchopulmonary neuroendocrine neoplasms. Lab Invest. 1985 Jan;52(1):39–51. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brozman M. Immunohistochemical analysis of formaldehyde- and trypsin- or pepsin-treated material. Acta Histochem. 1978;63(2):251–260. doi: 10.1016/S0065-1281(78)80032-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crook J. C. Morphogenesis of testicular tumours. J Clin Pathol. 1968 Jan;21(1):71–74. doi: 10.1136/jcp.21.1.71. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Damjanov I., Andrews P. W. Ultrastructural differentiation of a clonal human embryonal carcinoma cell line in vitro. Cancer Res. 1983 May;43(5):2190–2198. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franke W. W., Grund C., Kuhn C., Jackson B. W., Illmensee K. Formation of cytoskeletal elements during mouse embryogenesis. III. Primary mesenchymal cells and the first appearance of vimentin filaments. Differentiation. 1982;23(1):43–59. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.1982.tb01266.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franke W. W., Grund C., Schmid E. Intermediate-sized filaments present in Sertoli cells are of the vimentin type. Eur J Cell Biol. 1979 Aug;19(3):269–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franke W. W., Schmid E., Schiller D. L., Winter S., Jarasch E. D., Moll R., Denk H., Jackson B. W., Illmensee K. Differentiation-related patterns of expression of proteins of intermediate-size filaments in tissues and cultured cells. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1982;46(Pt 1):431–453. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1982.046.01.041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOBSON B. M. THE EXCRETION OF CHORIONIC GONADOTROPHIN BY MEN WITH TESTICULAR TUMOURS. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1965 Jul;49:337–348. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.0490337. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haugen O. A., Taylor C. R. Immunohistochemical studies of ovarian and testicular teratomas with antiserum to glial fibrillary acidic protein. Acta Pathol Microbiol Immunol Scand A. 1984 Jan;92(1):9–14. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1984.tb04371.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holthöfer H., Miettinen A., Lehto V. P., Lehtonen E., Virtanen I. Expression of vimentin and cytokeratin types of intermediate filament proteins in developing and adult human kidneys. Lab Invest. 1984 May;50(5):552–559. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holthöfer H., Miettinen A., Paasivuo R., Lehto V. P., Linder E., Alfthan O., Virtanen I. Cellular origin and differentiation of renal carcinomas. A fluorescence microscopic study with kidney-specific antibodies, antiintermediate filament antibodies, and lectins. Lab Invest. 1983 Sep;49(3):317–326. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson B. W., Grund C., Schmid E., Bürki K., Franke W. W., Illmensee K. Formation of cytoskeletal elements during mouse embryogenesis. Intermediate filaments of the cytokeratin type and desmosomes in preimplantation embryos. Differentiation. 1980;17(3):161–179. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.1980.tb01093.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kariniemi A. L., Holthöfer H., Vartio T., Virtanen I. Cellular differentiation of basal cell carcinoma studied with fluorescent lectins and cytokeratin antibodies. J Cutan Pathol. 1984 Dec;11(6):541–548. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0560.1984.tb00416.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazarides E. Intermediate filaments: a chemically heterogeneous, developmentally regulated class of proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1982;51:219–250. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.51.070182.001251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehto V. P., Virtanen I. Immunolocalization of a novel, cytoskeleton-associated polypeptide of Mr 230,000 daltons (p230). J Cell Biol. 1983 Mar;96(3):703–716. doi: 10.1083/jcb.96.3.703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehtonen E., Lehto V. P., Paasivuo R., Virtanen I. Parietal and visceral endoderm differ in their expression of intermediate filaments. EMBO J. 1983;2(7):1023–1028. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01540.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miettinen M., Franssila K., Lehto V. P., Paasivuo R., Virtanen I. Expression of intermediate filament proteins in thyroid gland and thyroid tumors. Lab Invest. 1984 Mar;50(3):262–270. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miettinen M., Lehto V. P., Badley R. A., Virtanen I. Alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma. Demonstration of the muscle type of intermediate filament protein, desmin, as a diagnostic aid. Am J Pathol. 1982 Aug;108(2):246–251. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miettinen M., Lehto V. P., Badley R. A., Virtanen I. Expression of intermediate filaments in soft-tissue sarcomas. Int J Cancer. 1982 Nov 15;30(5):541–546. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910300502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miettinen M., Lehto V. P., Virtanen I. Antibodies to intermediate filament proteins in the diagnosis and classification of human tumors. Ultrastruct Pathol. 1984;7(2-3):83–107. doi: 10.3109/01913128409141467. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miettinen M., Lehto V. P., Virtanen I. Expression of intermediate filaments in normal ovaries and ovarian epithelial, sex cord-stromal, and germinal tumors. Int J Gynecol Pathol. 1983;2(1):64–71. doi: 10.1097/00004347-198301000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moll R., Franke W. W., Schiller D. L., Geiger B., Krepler R. The catalog of human cytokeratins: patterns of expression in normal epithelia, tumors and cultured cells. Cell. 1982 Nov;31(1):11–24. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90400-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn M., Altmannsberger M., Shaw G., Schauer A., Weber K. Various sympathetic derived human tumors differ in neurofilament expression. Use in diagnosis of neuroblastoma, ganglioneuroblastoma and pheochromocytoma. Virchows Arch B Cell Pathol Incl Mol Pathol. 1982 Aug;40(2):141–156. doi: 10.1007/BF02932859. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn M., Weber K. Tumor diagnosis by intermediate filament typing: a novel tool for surgical pathology. Lab Invest. 1983 Apr;48(4):372–394. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramaekers F. C., Puts J. J., Moesker O., Kant A., Huysmans A., Haag D., Jap P. H., Herman C. J., Vooijs G. P. Antibodies to intermediate filament proteins in the immunohistochemical identification of human tumours: an overview. Histochem J. 1983 Jul;15(7):691–713. doi: 10.1007/BF01002988. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trojanowski J. Q., Hickey W. F. Human teratomas express differentiated neural antigens. An immunohistochemical study with anti-neurofilament, anti-glial filament, and anti-myelin basic protein monoclonal antibodies. Am J Pathol. 1984 Jun;115(3):383–389. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Virtanen I., Badley R. A., Paasivuo R., Lehto V. P. Distinct cytoskeletal domains revealed in sperm cells. J Cell Biol. 1984 Sep;99(3):1083–1091. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.3.1083. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Virtanen I., Lehto V. P., Lehtonen E., Vartio T., Stenman S., Kurki P., Wager O., Small J. V., Dahl D., Badley R. A. Expression of intermediate filaments in cultured cells. J Cell Sci. 1981 Aug;50:45–63. doi: 10.1242/jcs.50.1.45. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Virtanen I., von Koskull H., Lehto V. P., Vartio T., Aula P. Cultured human amniotic fluid cells characterized with antibodies against intermediate filaments in indirect immunofluorescence microscopy. J Clin Invest. 1981 Nov;68(5):1348–1355. doi: 10.1172/JCI110382. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. Cytoskeleton: definition, structure and gene regulation. Pathol Res Pract. 1982;175(2-3):128–145. doi: 10.1016/S0344-0338(82)80104-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]